Shengfeng He
OmniVTON++: Training-Free Universal Virtual Try-On with Principal Pose Guidance
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Image-based Virtual Try-On (VTON) concerns the synthesis of realistic person imagery through garment re-rendering under human pose and body constraints. In practice, however, existing approaches are typically optimized for specific data conditions, making their deployment reliant on retraining and limiting their generalization as a unified solution. We present OmniVTON++, a training-free VTON framework designed for universal applicability. It addresses the intertwined challenges of garment alignment, human structural coherence, and boundary continuity by coordinating Structured Garment Morphing for correspondence-driven garment adaptation, Principal Pose Guidance for step-wise structural regulation during diffusion sampling, and Continuous Boundary Stitching for boundary-aware refinement, forming a cohesive pipeline without task-specific retraining. Experimental results demonstrate that OmniVTON++ achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse generalization settings, including cross-dataset and cross-garment-type evaluations, while reliably operating across scenarios and diffusion backbones within a single formulation. In addition to single-garment, single-human cases, the framework supports multi-garment, multi-human, and anime character virtual try-on, expanding the scope of virtual try-on applications. The source code will be released to the public.
Cross-modal Proxy Evolving for OOD Detection with Vision-Language Models
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Reliable zero-shot detection of out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs is critical for deploying vision-language models in open-world settings. However, the lack of labeled negatives in zero-shot OOD detection necessitates proxy signals that remain effective under distribution shift. Existing negative-label methods rely on a fixed set of textual proxies, which (i) sparsely sample the semantic space beyond in-distribution (ID) classes and (ii) remain static while only visual features drift, leading to cross-modal misalignment and unstable predictions. In this paper, we propose CoEvo, a training- and annotation-free test-time framework that performs bidirectional, sample-conditioned adaptation of both textual and visual proxies. Specifically, CoEvo introduces a proxy-aligned co-evolution mechanism to maintain two evolving proxy caches, which dynamically mines contextual textual negatives guided by test images and iteratively refines visual proxies, progressively realigning cross-modal similarities and enlarging local OOD margins. Finally, we dynamically re-weight the contributions of dual-modal proxies to obtain a calibrated OOD score that is robust to distribution shift. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that CoEvo achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving AUROC by 1.33% and reducing FPR95 by 45.98% on ImageNet-1K compared to strong negative-label baselines.
MotionAdapter: Video Motion Transfer via Content-Aware Attention Customization
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion-based text-to-video models, particularly those built on the diffusion transformer architecture, have achieved remarkable progress in generating high-quality and temporally coherent videos. However, transferring complex motions between videos remains challenging. In this work, we present MotionAdapter, a content-aware motion transfer framework that enables robust and semantically aligned motion transfer within DiT-based T2V models. Our key insight is that effective motion transfer requires \romannumeral1) explicit disentanglement of motion from appearance and \romannumeral 2) adaptive customization of motion to target content. MotionAdapter first isolates motion by analyzing cross-frame attention within 3D full-attention modules to extract attention-derived motion fields. To bridge the semantic gap between reference and target videos, we further introduce a DINO-guided motion customization module that rearranges and refines motion fields based on content correspondences. The customized motion field is then used to guide the DiT denoising process, ensuring that the synthesized video inherits the reference motion while preserving target appearance and semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MotionAdapter outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Moreover, MotionAdapter naturally supports complex motion transfer and motion editing tasks such as zooming.
FlashMesh: Faster and Better Autoregressive Mesh Synthesis via Structured Speculation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive models can generate high-quality 3D meshes by sequentially producing vertices and faces, but their token-by-token decoding results in slow inference, limiting practical use in interactive and large-scale applications. We present FlashMesh, a fast and high-fidelity mesh generation framework that rethinks autoregressive decoding through a predict-correct-verify paradigm. The key insight is that mesh tokens exhibit strong structural and geometric correlations that enable confident multi-token speculation. FlashMesh leverages this by introducing a speculative decoding scheme tailored to the commonly used hourglass transformer architecture, enabling parallel prediction across face, point, and coordinate levels. Extensive experiments show that FlashMesh achieves up to a 2 x speedup over standard autoregressive models while also improving generation fidelity. Our results demonstrate that structural priors in mesh data can be systematically harnessed to accelerate and enhance autoregressive generation.
AvatarVTON: 4D Virtual Try-On for Animatable Avatars
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:We propose AvatarVTON, the first 4D virtual try-on framework that generates realistic try-on results from a single in-shop garment image, enabling free pose control, novel-view rendering, and diverse garment choices. Unlike existing methods, AvatarVTON supports dynamic garment interactions under single-view supervision, without relying on multi-view garment captures or physics priors. The framework consists of two key modules: (1) a Reciprocal Flow Rectifier, a prior-free optical-flow correction strategy that stabilizes avatar fitting and ensures temporal coherence; and (2) a Non-Linear Deformer, which decomposes Gaussian maps into view-pose-invariant and view-pose-specific components, enabling adaptive, non-linear garment deformations. To establish a benchmark for 4D virtual try-on, we extend existing baselines with unified modules for fair qualitative and quantitative comparisons. Extensive experiments show that AvatarVTON achieves high fidelity, diversity, and dynamic garment realism, making it well-suited for AR/VR, gaming, and digital-human applications.
HarmonPaint: Harmonized Training-Free Diffusion Inpainting
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Existing inpainting methods often require extensive retraining or fine-tuning to integrate new content seamlessly, yet they struggle to maintain coherence in both structure and style between inpainted regions and the surrounding background. Motivated by these limitations, we introduce HarmonPaint, a training-free inpainting framework that seamlessly integrates with the attention mechanisms of diffusion models to achieve high-quality, harmonized image inpainting without any form of training. By leveraging masking strategies within self-attention, HarmonPaint ensures structural fidelity without model retraining or fine-tuning. Additionally, we exploit intrinsic diffusion model properties to transfer style information from unmasked to masked regions, achieving a harmonious integration of styles. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of HarmonPaint across diverse scenes and styles, validating its versatility and performance.
Action Dubber: Timing Audible Actions via Inflectional Flow
Jun 16, 2025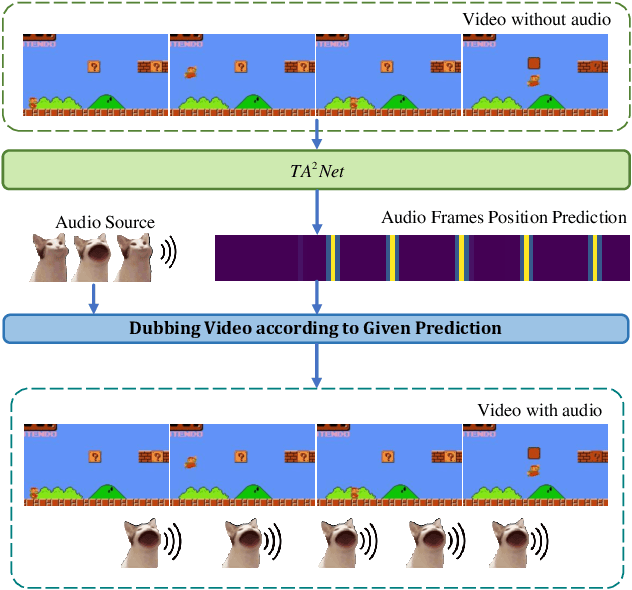
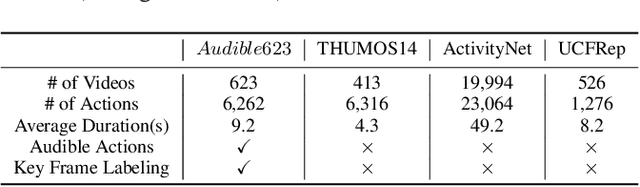

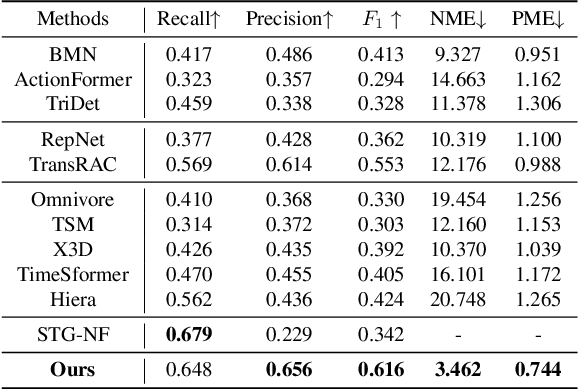
Abstract:We introduce the task of Audible Action Temporal Localization, which aims to identify the spatio-temporal coordinates of audible movements. Unlike conventional tasks such as action recognition and temporal action localization, which broadly analyze video content, our task focuses on the distinct kinematic dynamics of audible actions. It is based on the premise that key actions are driven by inflectional movements; for example, collisions that produce sound often involve abrupt changes in motion. To capture this, we propose $TA^{2}Net$, a novel architecture that estimates inflectional flow using the second derivative of motion to determine collision timings without relying on audio input. $TA^{2}Net$ also integrates a self-supervised spatial localization strategy during training, combining contrastive learning with spatial analysis. This dual design improves temporal localization accuracy and simultaneously identifies sound sources within video frames. To support this task, we introduce a new benchmark dataset, $Audible623$, derived from Kinetics and UCF101 by removing non-essential vocalization subsets. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of our approach on $Audible623$ and show strong generalizability to other domains, such as repetitive counting and sound source localization. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/WenlongWan/Audible623.
Instruct2See: Learning to Remove Any Obstructions Across Distributions
May 23, 2025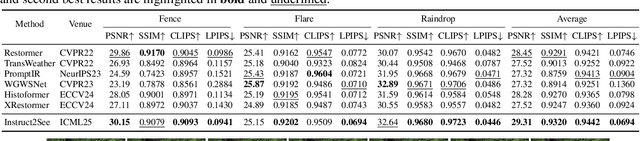
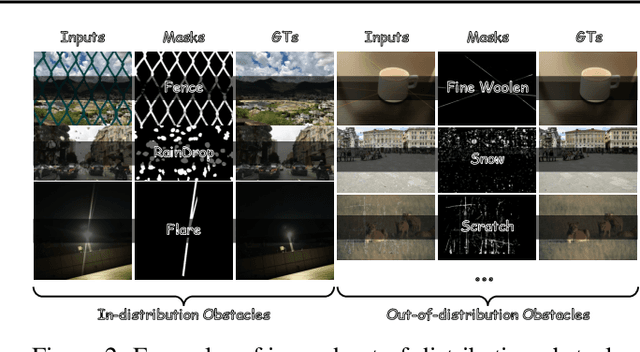
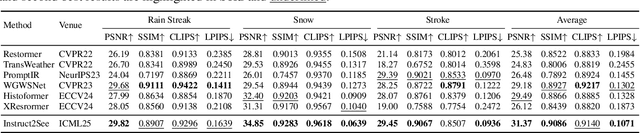
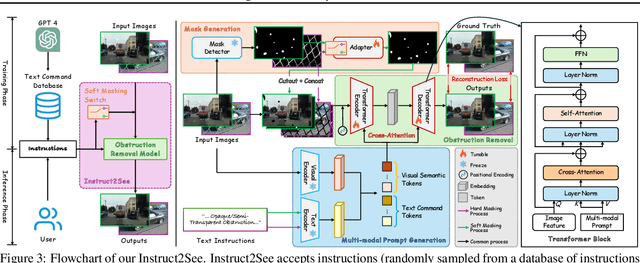
Abstract:Images are often obstructed by various obstacles due to capture limitations, hindering the observation of objects of interest. Most existing methods address occlusions from specific elements like fences or raindrops, but are constrained by the wide range of real-world obstructions, making comprehensive data collection impractical. To overcome these challenges, we propose Instruct2See, a novel zero-shot framework capable of handling both seen and unseen obstacles. The core idea of our approach is to unify obstruction removal by treating it as a soft-hard mask restoration problem, where any obstruction can be represented using multi-modal prompts, such as visual semantics and textual instructions, processed through a cross-attention unit to enhance contextual understanding and improve mode control. Additionally, a tunable mask adapter allows for dynamic soft masking, enabling real-time adjustment of inaccurate masks. Extensive experiments on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution obstacles show that Instruct2See consistently achieves strong performance and generalization in obstruction removal, regardless of whether the obstacles were present during the training phase. Code and dataset are available at https://jhscut.github.io/Instruct2See.
Expanding Zero-Shot Object Counting with Rich Prompts
May 21, 2025Abstract:Expanding pre-trained zero-shot counting models to handle unseen categories requires more than simply adding new prompts, as this approach does not achieve the necessary alignment between text and visual features for accurate counting. We introduce RichCount, the first framework to address these limitations, employing a two-stage training strategy that enhances text encoding and strengthens the model's association with objects in images. RichCount improves zero-shot counting for unseen categories through two key objectives: (1) enriching text features with a feed-forward network and adapter trained on text-image similarity, thereby creating robust, aligned representations; and (2) applying this refined encoder to counting tasks, enabling effective generalization across diverse prompts and complex images. In this manner, RichCount goes beyond simple prompt expansion to establish meaningful feature alignment that supports accurate counting across novel categories. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of RichCount, achieving state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot counting and significantly enhancing generalization to unseen categories in open-world scenarios.
Safe-Sora: Safe Text-to-Video Generation via Graphical Watermarking
May 19, 2025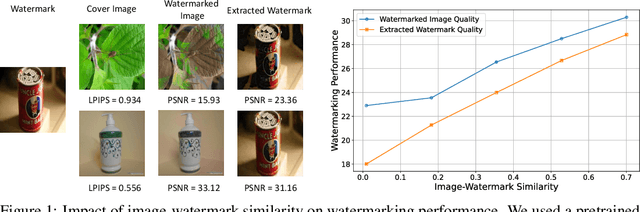
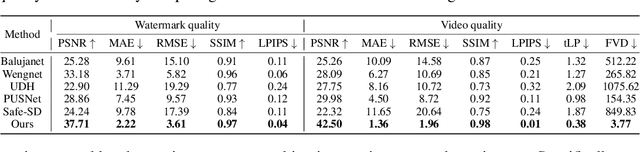
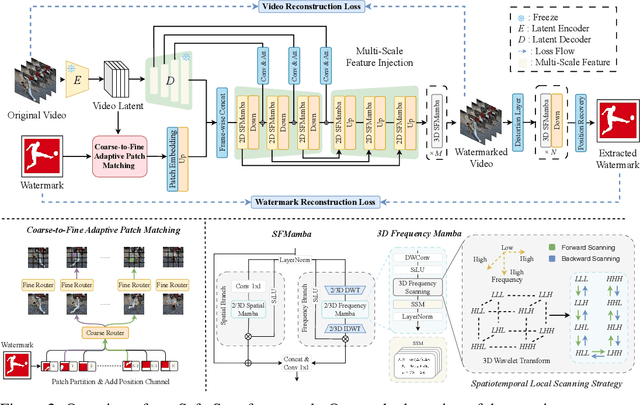

Abstract:The explosive growth of generative video models has amplified the demand for reliable copyright preservation of AI-generated content. Despite its popularity in image synthesis, invisible generative watermarking remains largely underexplored in video generation. To address this gap, we propose Safe-Sora, the first framework to embed graphical watermarks directly into the video generation process. Motivated by the observation that watermarking performance is closely tied to the visual similarity between the watermark and cover content, we introduce a hierarchical coarse-to-fine adaptive matching mechanism. Specifically, the watermark image is divided into patches, each assigned to the most visually similar video frame, and further localized to the optimal spatial region for seamless embedding. To enable spatiotemporal fusion of watermark patches across video frames, we develop a 3D wavelet transform-enhanced Mamba architecture with a novel spatiotemporal local scanning strategy, effectively modeling long-range dependencies during watermark embedding and retrieval. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to apply state space models to watermarking, opening new avenues for efficient and robust watermark protection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Safe-Sora achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of video quality, watermark fidelity, and robustness, which is largely attributed to our proposals. We will release our code upon publication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge