Yan Cai
Conditional Diffusion Model-Driven Generative Channels for Double RIS-Aided Wireless Systems
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:With the development of the upcoming sixth-generation networks (6G), reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have gained significant attention due to its ability of reconfiguring wireless channels via smart reflections. However, traditional channel state information (CSI) acquisition techniques for double-RIS systems face challenges (e.g., high pilot overhead or multipath interference). This paper proposes a new channel generation method in double-RIS communication systems based on the tool of conditional diffusion model (CDM). The CDM is trained on synthetic channel data to capture channel characteristics. It addresses the limitations of traditional CSI generation methods, such as insufficient model understanding capability and poor environmental adaptability. We provide a detailed analysis of the diffusion process for channel generation, and it is validated through simulations. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed CDM based method outperforms traditional channel acquisition methods in terms of normalized mean squared error (NMSE). This method offers a new paradigm for channel acquisition in double-RIS systems, which is expected to improve the quality of channel acquisition with low pilot overhead.
Step1X-Edit: A Practical Framework for General Image Editing
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:In recent years, image editing models have witnessed remarkable and rapid development. The recent unveiling of cutting-edge multimodal models such as GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash has introduced highly promising image editing capabilities. These models demonstrate an impressive aptitude for fulfilling a vast majority of user-driven editing requirements, marking a significant advancement in the field of image manipulation. However, there is still a large gap between the open-source algorithm with these closed-source models. Thus, in this paper, we aim to release a state-of-the-art image editing model, called Step1X-Edit, which can provide comparable performance against the closed-source models like GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash. More specifically, we adopt the Multimodal LLM to process the reference image and the user's editing instruction. A latent embedding has been extracted and integrated with a diffusion image decoder to obtain the target image. To train the model, we build a data generation pipeline to produce a high-quality dataset. For evaluation, we develop the GEdit-Bench, a novel benchmark rooted in real-world user instructions. Experimental results on GEdit-Bench demonstrate that Step1X-Edit outperforms existing open-source baselines by a substantial margin and approaches the performance of leading proprietary models, thereby making significant contributions to the field of image editing.
SITA: Structurally Imperceptible and Transferable Adversarial Attacks for Stylized Image Generation
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Image generation technology has brought significant advancements across various fields but has also raised concerns about data misuse and potential rights infringements, particularly with respect to creating visual artworks. Current methods aimed at safeguarding artworks often employ adversarial attacks. However, these methods face challenges such as poor transferability, high computational costs, and the introduction of noticeable noise, which compromises the aesthetic quality of the original artwork. To address these limitations, we propose a Structurally Imperceptible and Transferable Adversarial (SITA) attacks. SITA leverages a CLIP-based destylization loss, which decouples and disrupts the robust style representation of the image. This disruption hinders style extraction during stylized image generation, thereby impairing the overall stylization process. Importantly, SITA eliminates the need for a surrogate diffusion model, leading to significantly reduced computational overhead. The method's robust style feature disruption ensures high transferability across diverse models. Moreover, SITA introduces perturbations by embedding noise within the imperceptible structural details of the image. This approach effectively protects against style extraction without compromising the visual quality of the artwork. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SITA offers superior protection for artworks against unauthorized use in stylized generation. It significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of transferability, computational efficiency, and noise imperceptibility. Code is available at https://github.com/A-raniy-day/SITA.
MedBench: A Large-Scale Chinese Benchmark for Evaluating Medical Large Language Models
Dec 20, 2023Abstract:The emergence of various medical large language models (LLMs) in the medical domain has highlighted the need for unified evaluation standards, as manual evaluation of LLMs proves to be time-consuming and labor-intensive. To address this issue, we introduce MedBench, a comprehensive benchmark for the Chinese medical domain, comprising 40,041 questions sourced from authentic examination exercises and medical reports of diverse branches of medicine. In particular, this benchmark is composed of four key components: the Chinese Medical Licensing Examination, the Resident Standardization Training Examination, the Doctor In-Charge Qualification Examination, and real-world clinic cases encompassing examinations, diagnoses, and treatments. MedBench replicates the educational progression and clinical practice experiences of doctors in Mainland China, thereby establishing itself as a credible benchmark for assessing the mastery of knowledge and reasoning abilities in medical language learning models. We perform extensive experiments and conduct an in-depth analysis from diverse perspectives, which culminate in the following findings: (1) Chinese medical LLMs underperform on this benchmark, highlighting the need for significant advances in clinical knowledge and diagnostic precision. (2) Several general-domain LLMs surprisingly possess considerable medical knowledge. These findings elucidate both the capabilities and limitations of LLMs within the context of MedBench, with the ultimate goal of aiding the medical research community.
What can Discriminator do? Towards Box-free Ownership Verification of Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 29, 2023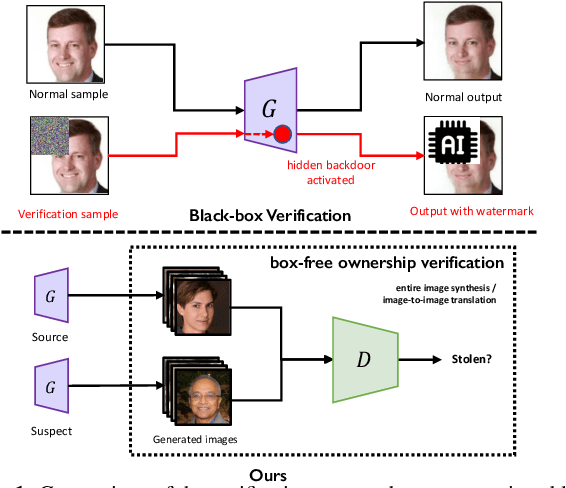
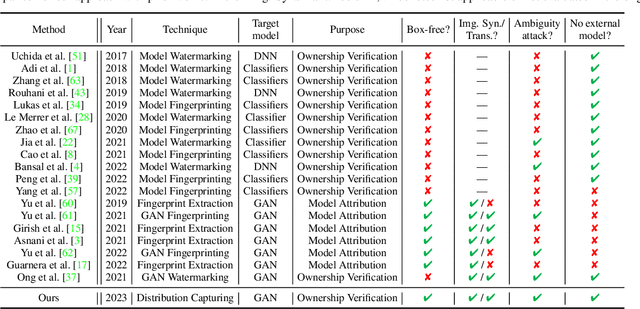
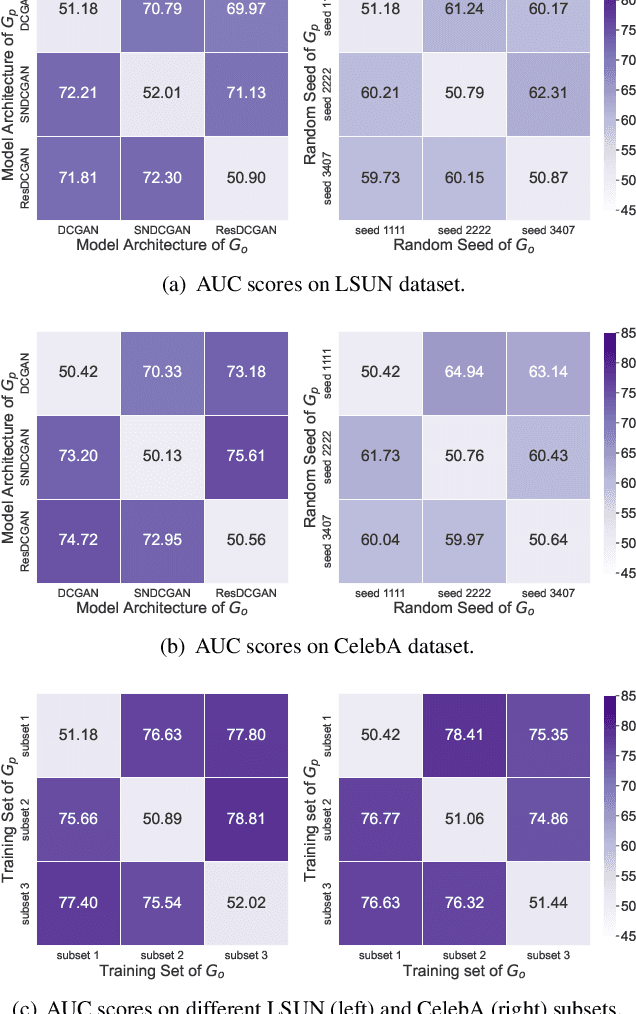
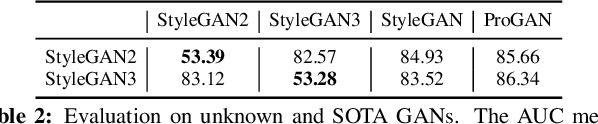
Abstract:In recent decades, Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and its variants have achieved unprecedented success in image synthesis. However, well-trained GANs are under the threat of illegal steal or leakage. The prior studies on remote ownership verification assume a black-box setting where the defender can query the suspicious model with specific inputs, which we identify is not enough for generation tasks. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel IP protection scheme for GANs where ownership verification can be done by checking outputs only, without choosing the inputs (i.e., box-free setting). Specifically, we make use of the unexploited potential of the discriminator to learn a hypersphere that captures the unique distribution learned by the paired generator. Extensive evaluations on two popular GAN tasks and more than 10 GAN architectures demonstrate our proposed scheme to effectively verify the ownership. Our proposed scheme shown to be immune to popular input-based removal attacks and robust against other existing attacks. The source code and models are available at https://github.com/AbstractTeen/gan_ownership_verification
A detail-enhanced sampling strategy in Hadamard single-pixel imaging
Sep 09, 2022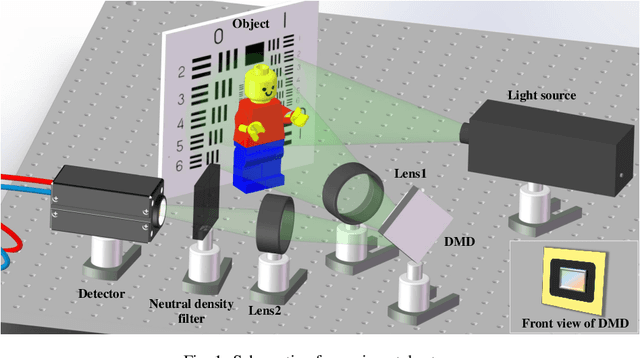
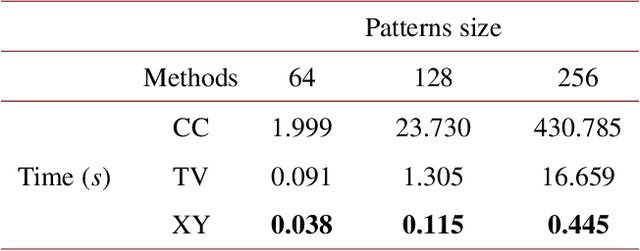
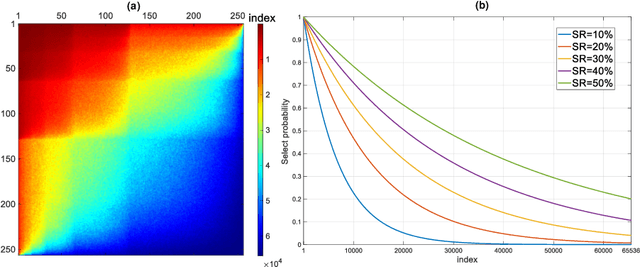
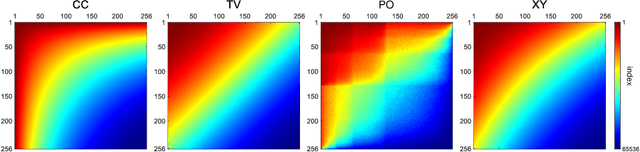
Abstract:Hadamard single-pixel imaging (HSI) is an appealing imaging technique due to its features of low hardware complexity and industrial cost. To improve imaging efficiency, many studies have focused on sorting Hadamard patterns to obtain reliable reconstructed images with very few samples. In this study, we present an efficient HSI imaging method that employs an exponential probability function to sample Hadamard spectra along a direction with better energy concentration for obtaining Hadamard patterns. We also propose an XY order to further optimize the pattern-selection method with extremely fast Hadamard order generation while retaining the original performance. We used the compressed sensing algorithm for image reconstruction. The simulation and experimental results show that these pattern-selection method reliably reconstructs objects and preserves the edge and details of images.
Single-pixel tracking and imaging of a high-speed moving object
Sep 04, 2022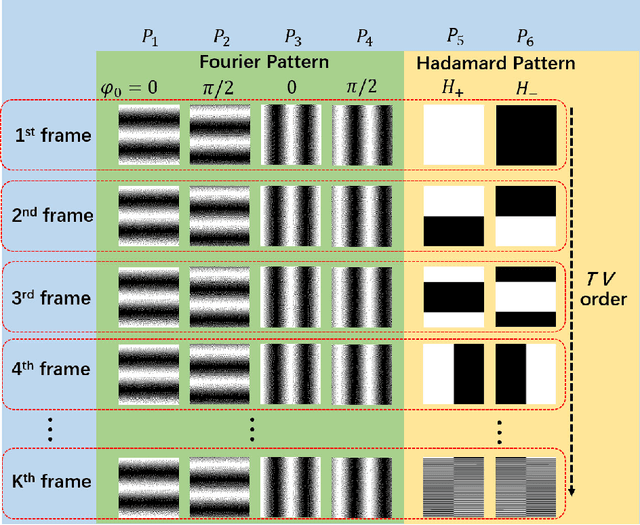
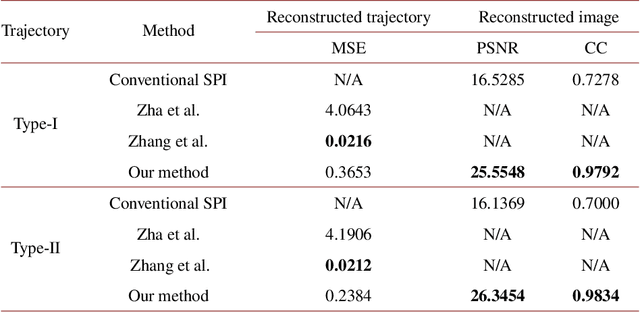
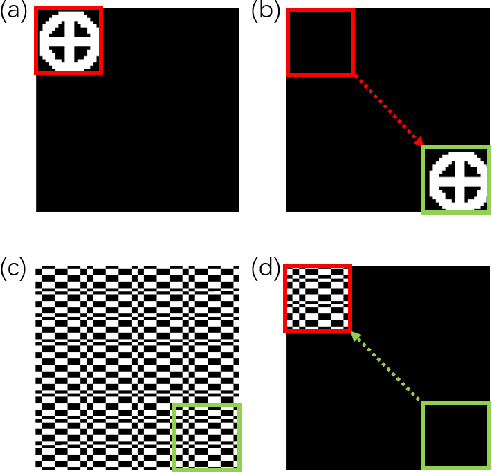
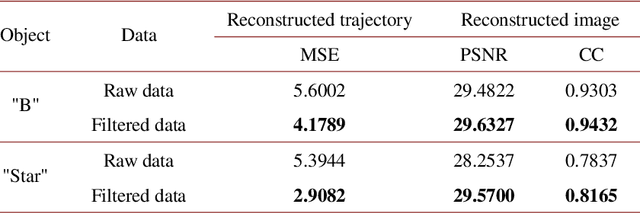
Abstract:Image-free tracking methods based on single-pixel detection have been able to track a moving object at a very high frame rate, but these tracking methods can not achieve simultaneous imaging of the object. Here we report a method for simultaneously tracking and imaging a high-speed moving object. Four binary Fourier patterns and two differential Hadamard patterns are used to modulate one frame of the object, then the modulated light signals are obtained by single-pixel detection. The trajectory and the image of the moving object can be gradually obtained along with the detection. The proposed method does not need any prior knowledge of the object and its motion. It has been verified by simulations and experiments which achieves a frame rate of 3332$~\mathrm{Hz}$ at a spatial resolution of $128 \times 128$ pixels by using a 20000$~\mathrm{Hz}$ digital micromirror device. This proposed method can broaden the application of image-free tracking methods and realize the detection of spatial information of the moving object.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge