Lina Wang
Wuhan University
PATFinger: Prompt-Adapted Transferable Fingerprinting against Unauthorized Multimodal Dataset Usage
Apr 15, 2025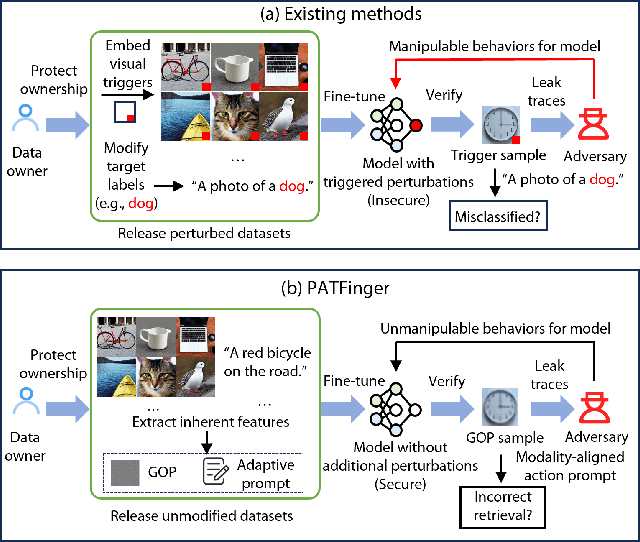
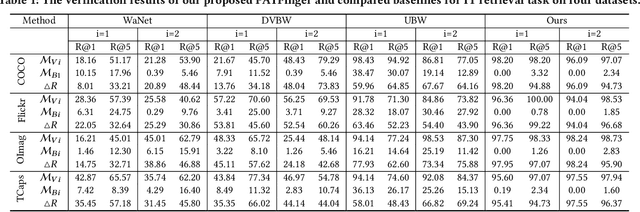
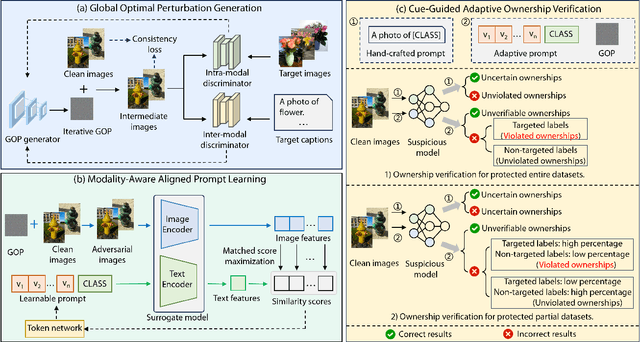
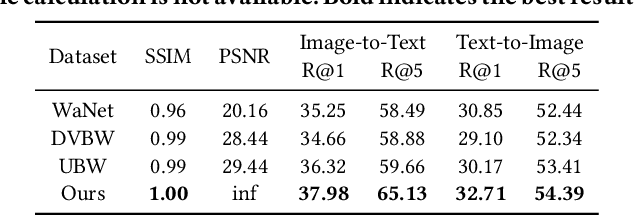
Abstract:The multimodal datasets can be leveraged to pre-train large-scale vision-language models by providing cross-modal semantics. Current endeavors for determining the usage of datasets mainly focus on single-modal dataset ownership verification through intrusive methods and non-intrusive techniques, while cross-modal approaches remain under-explored. Intrusive methods can adapt to multimodal datasets but degrade model accuracy, while non-intrusive methods rely on label-driven decision boundaries that fail to guarantee stable behaviors for verification. To address these issues, we propose a novel prompt-adapted transferable fingerprinting scheme from a training-free perspective, called PATFinger, which incorporates the global optimal perturbation (GOP) and the adaptive prompts to capture dataset-specific distribution characteristics. Our scheme utilizes inherent dataset attributes as fingerprints instead of compelling the model to learn triggers. The GOP is derived from the sample distribution to maximize embedding drifts between different modalities. Subsequently, our PATFinger re-aligns the adaptive prompt with GOP samples to capture the cross-modal interactions on the carefully crafted surrogate model. This allows the dataset owner to check the usage of datasets by observing specific prediction behaviors linked to the PATFinger during retrieval queries. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our scheme against unauthorized multimodal dataset usage on various cross-modal retrieval architectures by 30% over state-of-the-art baselines.
PDSL: Privacy-Preserved Decentralized Stochastic Learning with Heterogeneous Data Distribution
Mar 31, 2025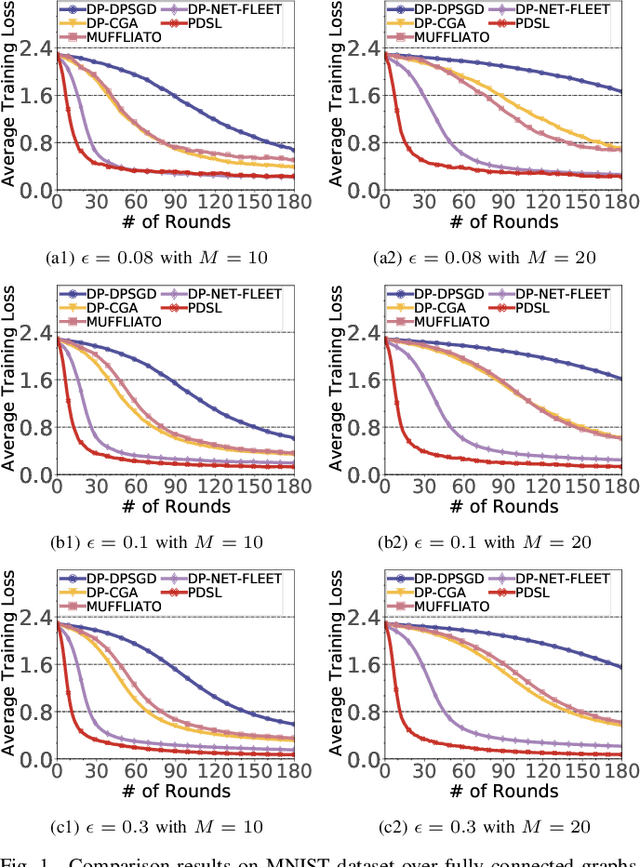
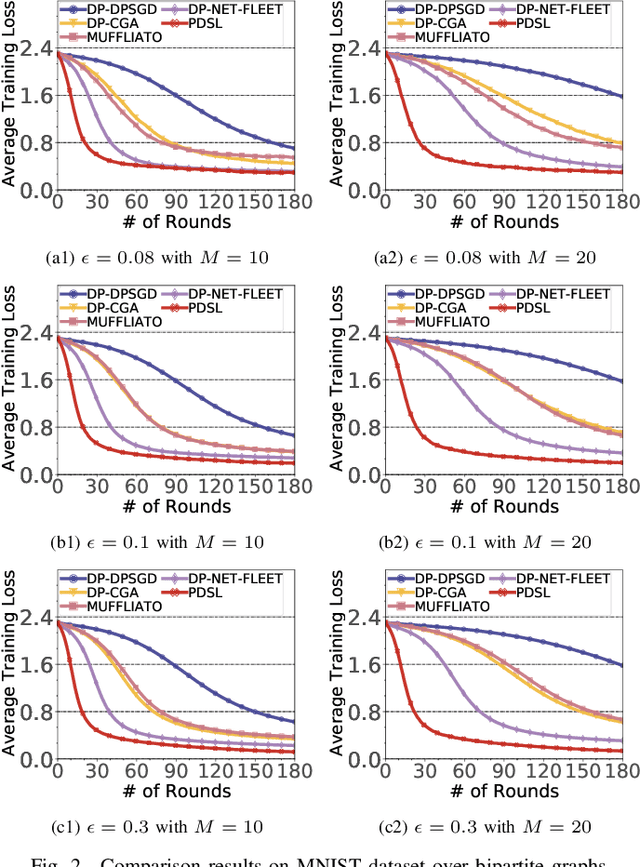
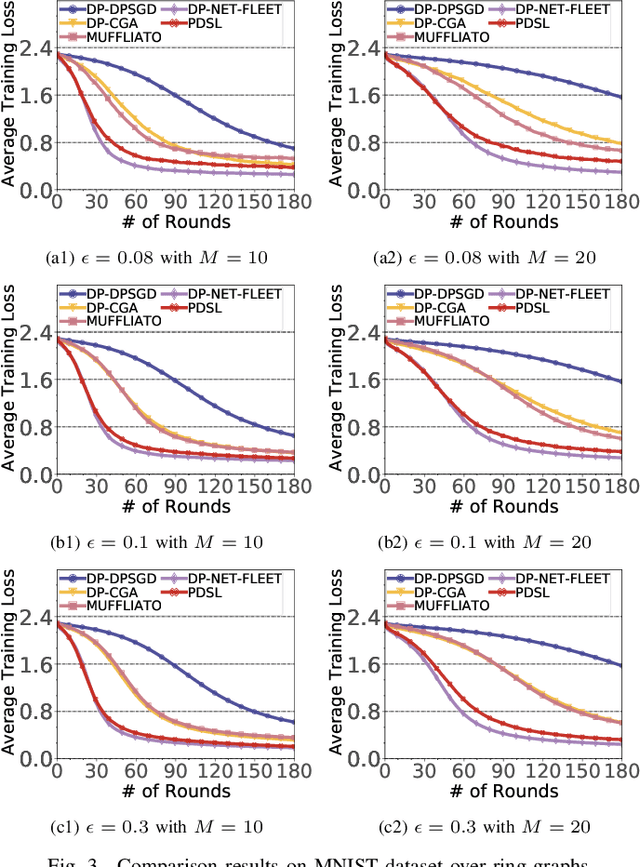
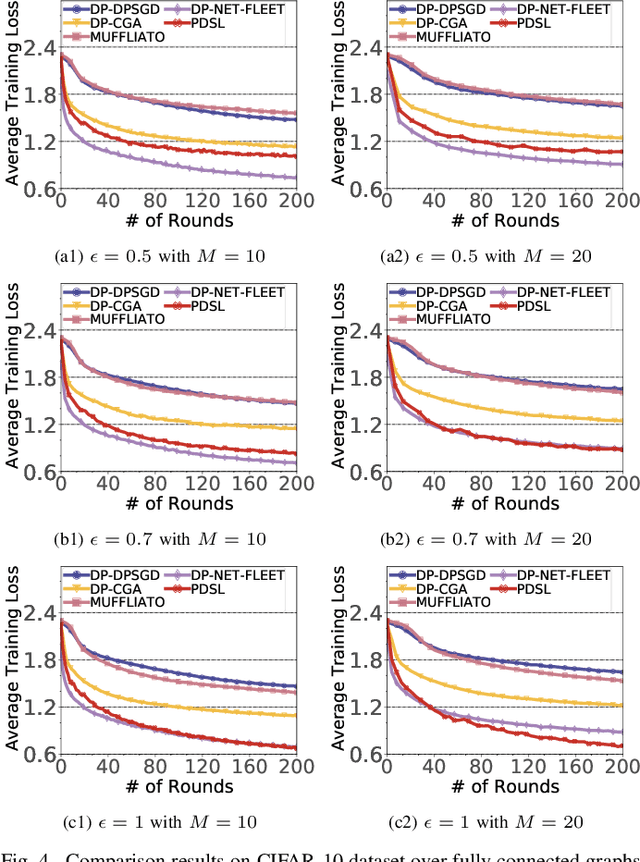
Abstract:In the paradigm of decentralized learning, a group of agents collaborates to learn a global model using distributed datasets without a central server. However, due to the heterogeneity of the local data across the different agents, learning a robust global model is rather challenging. Moreover, the collaboration of the agents relies on their gradient information exchange, which poses a risk of privacy leakage. In this paper, to address these issues, we propose PDSL, a novel privacy-preserved decentralized stochastic learning algorithm with heterogeneous data distribution. On one hand, we innovate in utilizing the notion of Shapley values such that each agent can precisely measure the contributions of its heterogeneous neighbors to the global learning goal; on the other hand, we leverage the notion of differential privacy to prevent each agent from suffering privacy leakage when it contributes gradient information to its neighbors. We conduct both solid theoretical analysis and extensive experiments to demonstrate the efficacy of our PDSL algorithm in terms of privacy preservation and convergence.
ROSS:RObust decentralized Stochastic learning based on Shapley values
Nov 01, 2024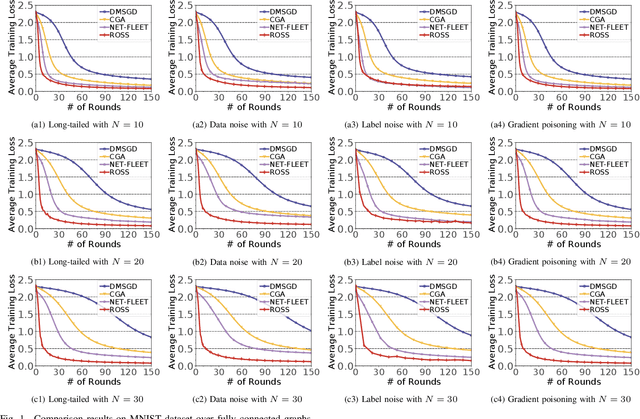
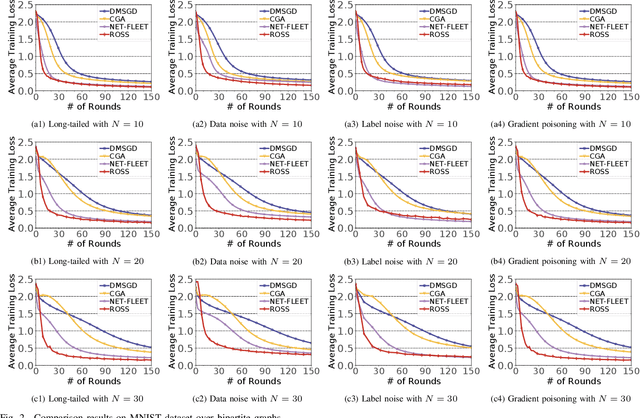
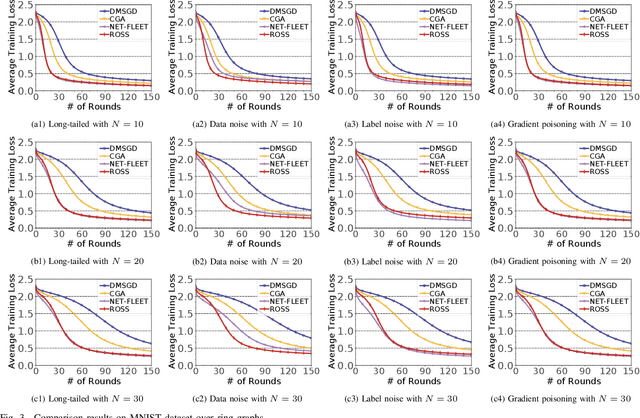
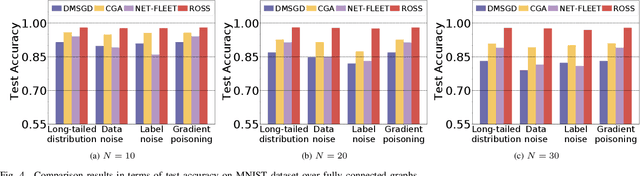
Abstract:In the paradigm of decentralized learning, a group of agents collaborate to learn a global model using a distributed dataset without a central server; nevertheless, it is severely challenged by the heterogeneity of the data distribution across the agents. For example, the data may be distributed non-independently and identically, and even be noised or poisoned. To address these data challenges, we propose ROSS, a novel robust decentralized stochastic learning algorithm based on Shapley values, in this paper. Specifically, in each round, each agent aggregates the cross-gradient information from its neighbors, i.e., the derivatives of its local model with respect to the datasets of its neighbors, to update its local model in a momentum like manner, while we innovate in weighting the derivatives according to their contributions measured by Shapley values. We perform solid theoretical analysis to reveal the linear convergence speedup of our ROSS algorithm. We also verify the efficacy of our algorithm through extensive experiments on public datasets. Our results demonstrate that, in face of the above variety of data challenges, our ROSS algorithm have oblivious advantages over existing state-of-the-art proposals in terms of both convergence and prediction accuracy.
PDSR: A Privacy-Preserving Diversified Service Recommendation Method on Distributed Data
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:The last decade has witnessed a tremendous growth of service computing, while efficient service recommendation methods are desired to recommend high-quality services to users. It is well known that collaborative filtering is one of the most popular methods for service recommendation based on QoS, and many existing proposals focus on improving recommendation accuracy, i.e., recommending high-quality redundant services. Nevertheless, users may have different requirements on QoS, and hence diversified recommendation has been attracting increasing attention in recent years to fulfill users' diverse demands and to explore potential services. Unfortunately, the recommendation performances relies on a large volume of data (e.g., QoS data), whereas the data may be distributed across multiple platforms. Therefore, to enable data sharing across the different platforms for diversified service recommendation, we propose a Privacy-preserving Diversified Service Recommendation (PDSR) method. Specifically, we innovate in leveraging the Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH) mechanism such that privacy-preserved data sharing across different platforms is enabled to construct a service similarity graph. Based on the similarity graph, we propose a novel accuracy-diversity metric and design a $2$-approximation algorithm to select $K$ services to recommend by maximizing the accuracy-diversity measure. Extensive experiments on real datasets are conducted to verify the efficacy of our PDSR method.
KGPA: Robustness Evaluation for Large Language Models via Cross-Domain Knowledge Graphs
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Existing frameworks for assessing robustness of large language models (LLMs) overly depend on specific benchmarks, increasing costs and failing to evaluate performance of LLMs in professional domains due to dataset limitations. This paper proposes a framework that systematically evaluates the robustness of LLMs under adversarial attack scenarios by leveraging knowledge graphs (KGs). Our framework generates original prompts from the triplets of knowledge graphs and creates adversarial prompts by poisoning, assessing the robustness of LLMs through the results of these adversarial attacks. We systematically evaluate the effectiveness of this framework and its modules. Experiments show that adversarial robustness of the ChatGPT family ranks as GPT-4-turbo > GPT-4o > GPT-3.5-turbo, and the robustness of large language models is influenced by the professional domains in which they operate.
Let Real Images be as a Judger, Spotting Fake Images Synthesized with Generative Models
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:In the last few years, generative models have shown their powerful capabilities in synthesizing realistic images in both quality and diversity (i.e., facial images, and natural subjects). Unfortunately, the artifact patterns in fake images synthesized by different generative models are inconsistent, leading to the failure of previous research that relied on spotting subtle differences between real and fake. In our preliminary experiments, we find that the artifacts in fake images always change with the development of the generative model, while natural images exhibit stable statistical properties. In this paper, we employ natural traces shared only by real images as an additional predictive target in the detector. Specifically, the natural traces are learned from the wild real images and we introduce extended supervised contrastive learning to bring them closer to real images and further away from fake ones. This motivates the detector to make decisions based on the proximity of images to the natural traces. To conduct a comprehensive experiment, we built a high-quality and diverse dataset that includes generative models comprising 6 GAN and 6 diffusion models, to evaluate the effectiveness in generalizing unknown forgery techniques and robustness in surviving different transformations. Experimental results show that our proposed method gives 96.1% mAP significantly outperforms the baselines. Extensive experiments conducted on the widely recognized platform Midjourney reveal that our proposed method achieves an accuracy exceeding 78.4%, underscoring its practicality for real-world application deployment. The source code and partial self-built dataset are available in supplementary material.
What can Discriminator do? Towards Box-free Ownership Verification of Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 29, 2023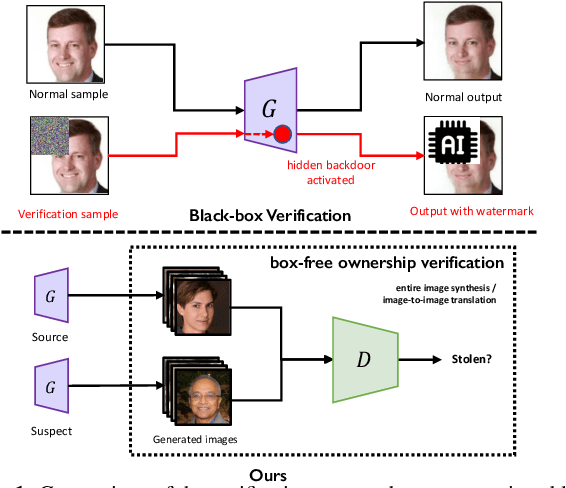
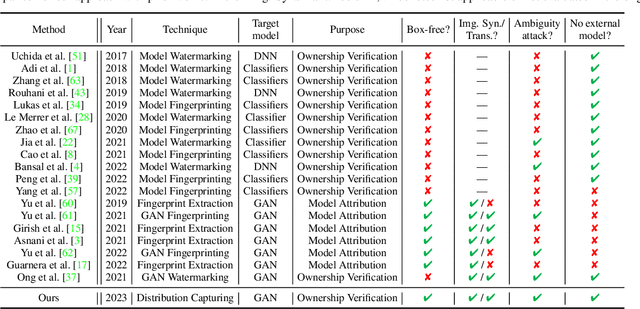
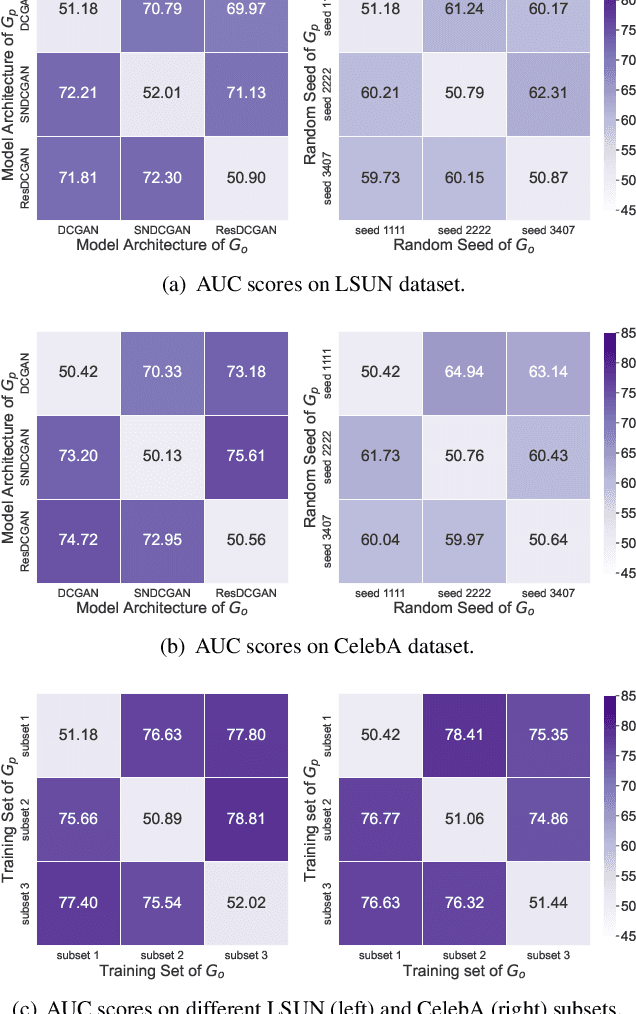
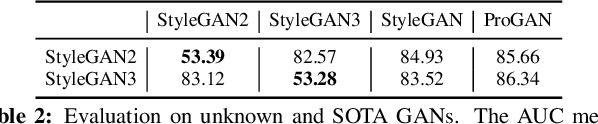
Abstract:In recent decades, Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and its variants have achieved unprecedented success in image synthesis. However, well-trained GANs are under the threat of illegal steal or leakage. The prior studies on remote ownership verification assume a black-box setting where the defender can query the suspicious model with specific inputs, which we identify is not enough for generation tasks. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel IP protection scheme for GANs where ownership verification can be done by checking outputs only, without choosing the inputs (i.e., box-free setting). Specifically, we make use of the unexploited potential of the discriminator to learn a hypersphere that captures the unique distribution learned by the paired generator. Extensive evaluations on two popular GAN tasks and more than 10 GAN architectures demonstrate our proposed scheme to effectively verify the ownership. Our proposed scheme shown to be immune to popular input-based removal attacks and robust against other existing attacks. The source code and models are available at https://github.com/AbstractTeen/gan_ownership_verification
Dual-level Interaction for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Jul 16, 2023



Abstract:To circumvent the costly pixel-wise annotations of real-world images in the semantic segmentation task, the Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is explored to firstly train a model with the labeled source data (synthetic images) and then adapt it to the unlabeled target data (real images). Among all the techniques being studied, the self-training approach recently secures its position in domain adaptive semantic segmentation, where a model is trained with target domain pseudo-labels. Current advances have mitigated noisy pseudo-labels resulting from the domain gap. However, they still struggle with erroneous pseudo-labels near the decision boundaries of the semantic classifier. In this paper, we tackle this issue by proposing a dual-level interaction for domain adaptation (DIDA) in semantic segmentation. Explicitly, we encourage the different augmented views of the same pixel to have not only similar class prediction (semantic-level) but also akin similarity relationship respected to other pixels (instance-level). As it is impossible to keep features of all pixel instances for a dataset, we novelly design and maintain a labeled instance bank with dynamic updating strategies to selectively store the informative features of instances. Further, DIDA performs cross-level interaction with scattering and gathering techniques to regenerate more reliable pseudolabels. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art by a notable margin, especially on confusing and long-tailed classes. Code is available at https://github.com/RainJamesY/DIDA.
Who is Speaking Actually? Robust and Versatile Speaker Traceability for Voice Conversion
May 09, 2023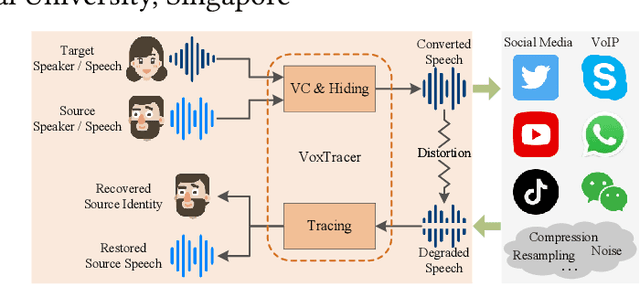
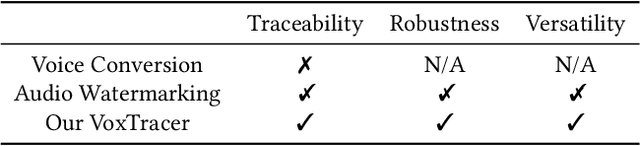
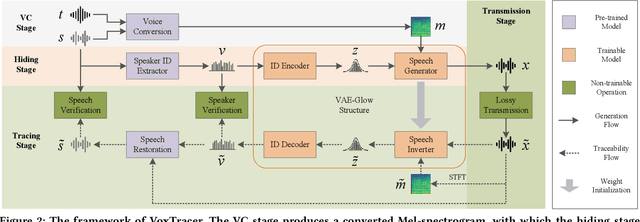
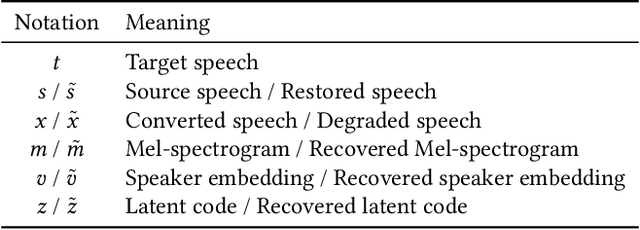
Abstract:Voice conversion (VC), as a voice style transfer technology, is becoming increasingly prevalent while raising serious concerns about its illegal use. Proactively tracing the origins of VC-generated speeches, i.e., speaker traceability, can prevent the misuse of VC, but unfortunately has not been extensively studied. In this paper, we are the first to investigate the speaker traceability for VC and propose a traceable VC framework named VoxTracer. Our VoxTracer is similar to but beyond the paradigm of audio watermarking. We first use unique speaker embedding to represent speaker identity. Then we design a VAE-Glow structure, in which the hiding process imperceptibly integrates the source speaker identity into the VC, and the tracing process accurately recovers the source speaker identity and even the source speech in spite of severe speech quality degradation. To address the speech mismatch between the hiding and tracing processes affected by different distortions, we also adopt an asynchronous training strategy to optimize the VAE-Glow models. The VoxTracer is versatile enough to be applied to arbitrary VC methods and popular audio coding standards. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the VoxTracer achieves not only high imperceptibility in hiding, but also nearly 100% tracing accuracy against various types of audio lossy compressions (AAC, MP3, Opus and SILK) with a broad range of bitrates (16 kbps - 128 kbps) even in a very short time duration (0.74s). Our speech demo is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/w/DEMOofVoxTracer.
Collaborative Learning in General Graphs with Limited Memorization: Learnability, Complexity and Reliability
Jan 29, 2022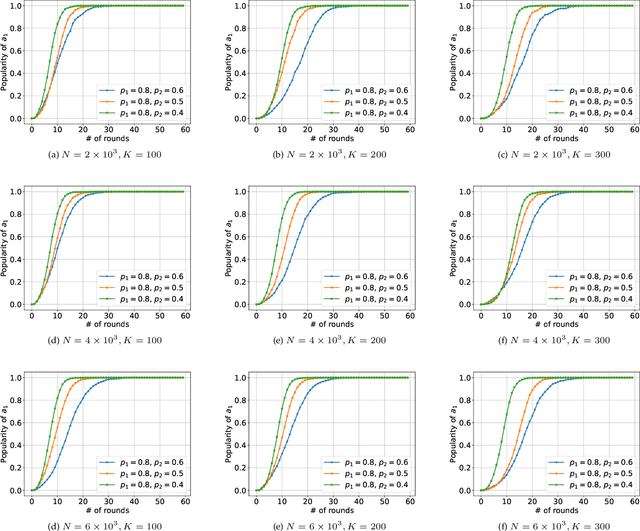
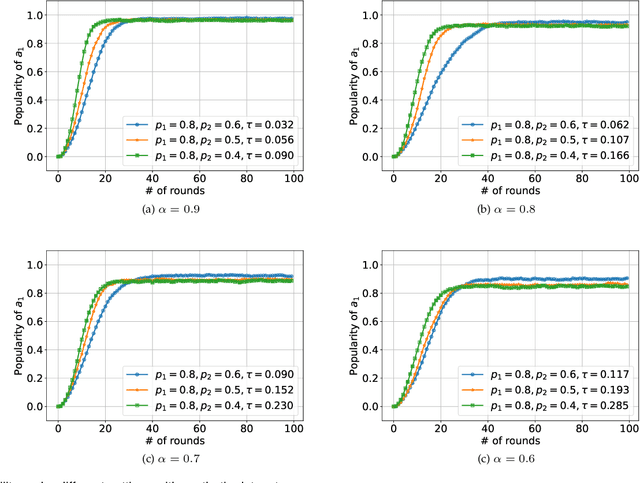
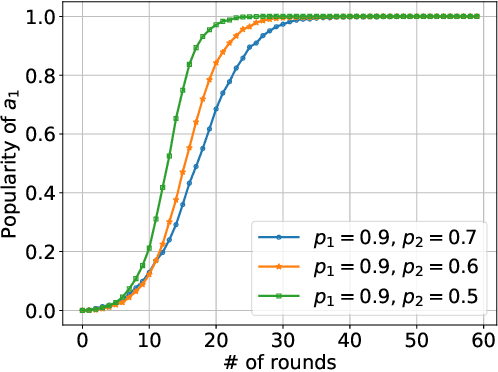
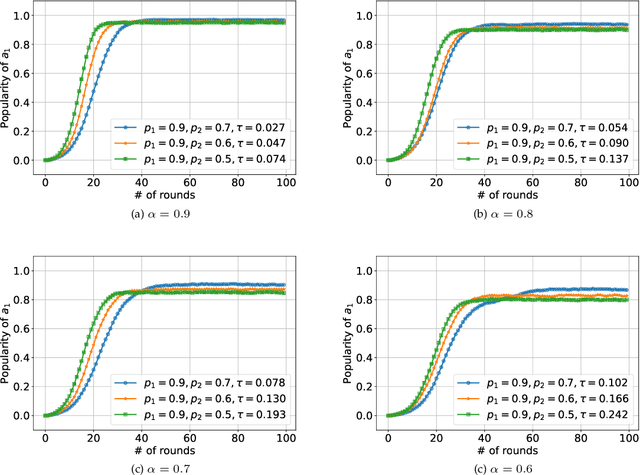
Abstract:We consider K-armed bandit problem in general graphs where agents are arbitrarily connected and each of them has limited memorization and communication bandwidth. The goal is to let each of the agents learn the best arm. Although recent studies show the power of collaboration among the agents in improving the efficacy of learning, it is assumed in these studies that the communication graphs should be complete or well-structured, whereas such an assumption is not always valid in practice. Furthermore, limited memorization and communication bandwidth also restrict the collaborations of the agents, since very few knowledge can be drawn by each agent from its experiences or the ones shared by its peers in this case. Additionally, the agents may be corrupted to share falsified experience, while the resource limit may considerably restrict the reliability of the learning process. To address the above issues, we propose a three-staged collaborative learning algorithm. In each step, the agents share their experience with each other through light-weight random walks in the general graphs, and then make decisions on which arms to pull according to the randomly memorized suggestions. The agents finally update their adoptions (i.e., preferences to the arms) based on the reward feedback of the arm pulling. Our theoretical analysis shows that, by exploiting the limited memorization and communication resources, all the agents eventually learn the best arm with high probability. We also reveal in our theoretical analysis the upper-bound on the number of corrupted agents our algorithm can tolerate. The efficacy of our proposed three-staged collaborative learning algorithm is finally verified by extensive experiments on both synthetic and real datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge