PATFinger: Prompt-Adapted Transferable Fingerprinting against Unauthorized Multimodal Dataset Usage
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2025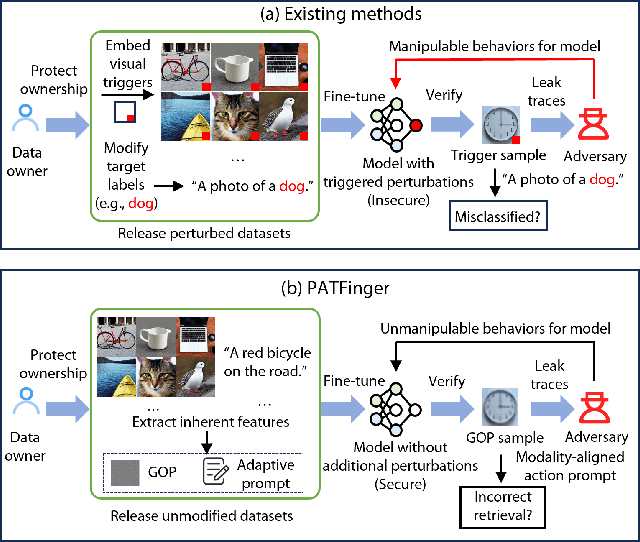
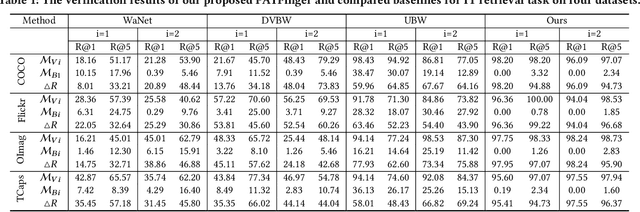
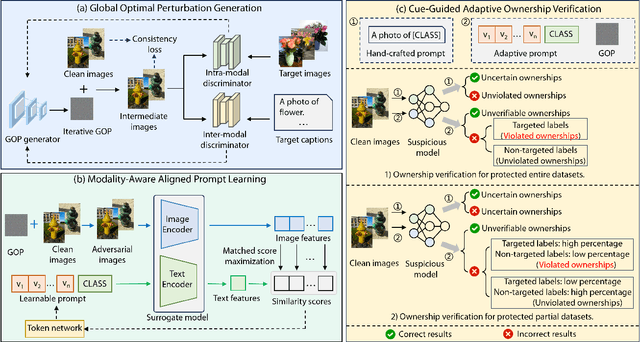
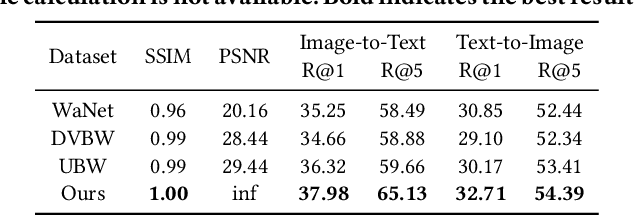
The multimodal datasets can be leveraged to pre-train large-scale vision-language models by providing cross-modal semantics. Current endeavors for determining the usage of datasets mainly focus on single-modal dataset ownership verification through intrusive methods and non-intrusive techniques, while cross-modal approaches remain under-explored. Intrusive methods can adapt to multimodal datasets but degrade model accuracy, while non-intrusive methods rely on label-driven decision boundaries that fail to guarantee stable behaviors for verification. To address these issues, we propose a novel prompt-adapted transferable fingerprinting scheme from a training-free perspective, called PATFinger, which incorporates the global optimal perturbation (GOP) and the adaptive prompts to capture dataset-specific distribution characteristics. Our scheme utilizes inherent dataset attributes as fingerprints instead of compelling the model to learn triggers. The GOP is derived from the sample distribution to maximize embedding drifts between different modalities. Subsequently, our PATFinger re-aligns the adaptive prompt with GOP samples to capture the cross-modal interactions on the carefully crafted surrogate model. This allows the dataset owner to check the usage of datasets by observing specific prediction behaviors linked to the PATFinger during retrieval queries. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our scheme against unauthorized multimodal dataset usage on various cross-modal retrieval architectures by 30% over state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge