Ju Jia
Southeast University
Cross-Modal Unlearning via Influential Neuron Path Editing in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) extend foundation models to real-world applications by integrating inputs such as text and vision. However, their broad knowledge capacity raises growing concerns about privacy leakage, toxicity mitigation, and intellectual property violations. Machine Unlearning (MU) offers a practical solution by selectively forgetting targeted knowledge while preserving overall model utility. When applied to MLLMs, existing neuron-editing-based MU approaches face two fundamental challenges: (1) forgetting becomes inconsistent across modalities because existing point-wise attribution methods fail to capture the structured, layer-by-layer information flow that connects different modalities; and (2) general knowledge performance declines when sensitive neurons that also support important reasoning paths are pruned, as this disrupts the model's ability to generalize. To alleviate these limitations, we propose a multimodal influential neuron path editor (MIP-Editor) for MU. Our approach introduces modality-specific attribution scores to identify influential neuron paths responsible for encoding forget-set knowledge and applies influential-path-aware neuron-editing via representation misdirection. This strategy also enables effective and coordinated forgetting across modalities while preserving the model's general capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that MIP-Editor achieves a superior unlearning performance on multimodal tasks, with a maximum forgetting rate of 87.75% and up to 54.26% improvement in general knowledge retention. On textual tasks, MIP-Editor achieves up to 80.65% forgetting and preserves 77.9% of general performance. Codes are available at https://github.com/PreckLi/MIP-Editor.
PhysPatch: A Physically Realizable and Transferable Adversarial Patch Attack for Multimodal Large Language Models-based Autonomous Driving Systems
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are becoming integral to autonomous driving (AD) systems due to their strong vision-language reasoning capabilities. However, MLLMs are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, particularly adversarial patch attacks, which can pose serious threats in real-world scenarios. Existing patch-based attack methods are primarily designed for object detection models and perform poorly when transferred to MLLM-based systems due to the latter's complex architectures and reasoning abilities. To address these limitations, we propose PhysPatch, a physically realizable and transferable adversarial patch framework tailored for MLLM-based AD systems. PhysPatch jointly optimizes patch location, shape, and content to enhance attack effectiveness and real-world applicability. It introduces a semantic-based mask initialization strategy for realistic placement, an SVD-based local alignment loss with patch-guided crop-resize to improve transferability, and a potential field-based mask refinement method. Extensive experiments across open-source, commercial, and reasoning-capable MLLMs demonstrate that PhysPatch significantly outperforms prior methods in steering MLLM-based AD systems toward target-aligned perception and planning outputs. Moreover, PhysPatch consistently places adversarial patches in physically feasible regions of AD scenes, ensuring strong real-world applicability and deployability.
PATFinger: Prompt-Adapted Transferable Fingerprinting against Unauthorized Multimodal Dataset Usage
Apr 15, 2025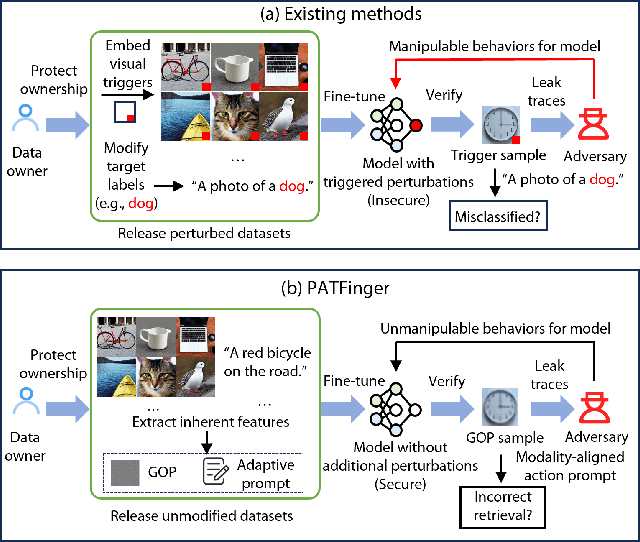
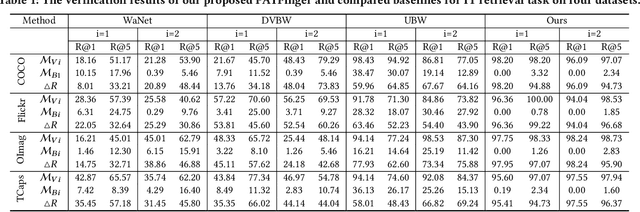
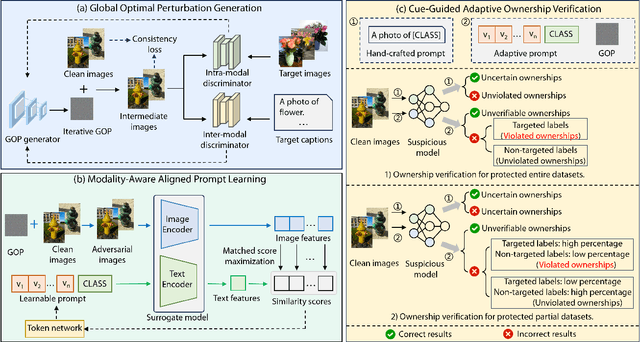
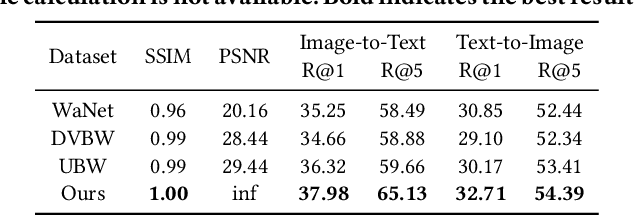
Abstract:The multimodal datasets can be leveraged to pre-train large-scale vision-language models by providing cross-modal semantics. Current endeavors for determining the usage of datasets mainly focus on single-modal dataset ownership verification through intrusive methods and non-intrusive techniques, while cross-modal approaches remain under-explored. Intrusive methods can adapt to multimodal datasets but degrade model accuracy, while non-intrusive methods rely on label-driven decision boundaries that fail to guarantee stable behaviors for verification. To address these issues, we propose a novel prompt-adapted transferable fingerprinting scheme from a training-free perspective, called PATFinger, which incorporates the global optimal perturbation (GOP) and the adaptive prompts to capture dataset-specific distribution characteristics. Our scheme utilizes inherent dataset attributes as fingerprints instead of compelling the model to learn triggers. The GOP is derived from the sample distribution to maximize embedding drifts between different modalities. Subsequently, our PATFinger re-aligns the adaptive prompt with GOP samples to capture the cross-modal interactions on the carefully crafted surrogate model. This allows the dataset owner to check the usage of datasets by observing specific prediction behaviors linked to the PATFinger during retrieval queries. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our scheme against unauthorized multimodal dataset usage on various cross-modal retrieval architectures by 30% over state-of-the-art baselines.
SelfPrompt: Autonomously Evaluating LLM Robustness via Domain-Constrained Knowledge Guidelines and Refined Adversarial Prompts
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Traditional methods for evaluating the robustness of large language models (LLMs) often rely on standardized benchmarks, which can escalate costs and limit evaluations across varied domains. This paper introduces a novel framework designed to autonomously evaluate the robustness of LLMs by incorporating refined adversarial prompts and domain-constrained knowledge guidelines in the form of knowledge graphs. Our method systematically generates descriptive sentences from domain-constrained knowledge graph triplets to formulate adversarial prompts, enhancing the relevance and challenge of the evaluation. These prompts, generated by the LLM itself and tailored to evaluate its own robustness, undergo a rigorous filtering and refinement process, ensuring that only those with high textual fluency and semantic fidelity are used. This self-evaluation mechanism allows the LLM to evaluate its robustness without the need for external benchmarks. We assess the effectiveness of our framework through extensive testing on both proprietary models like ChatGPT and open-source models such as Llama-3.1, Phi-3, and Mistral. Results confirm that our approach not only reduces dependency on conventional data but also provides a targeted and efficient means of evaluating LLM robustness in constrained domains.
KGPA: Robustness Evaluation for Large Language Models via Cross-Domain Knowledge Graphs
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Existing frameworks for assessing robustness of large language models (LLMs) overly depend on specific benchmarks, increasing costs and failing to evaluate performance of LLMs in professional domains due to dataset limitations. This paper proposes a framework that systematically evaluates the robustness of LLMs under adversarial attack scenarios by leveraging knowledge graphs (KGs). Our framework generates original prompts from the triplets of knowledge graphs and creates adversarial prompts by poisoning, assessing the robustness of LLMs through the results of these adversarial attacks. We systematically evaluate the effectiveness of this framework and its modules. Experiments show that adversarial robustness of the ChatGPT family ranks as GPT-4-turbo > GPT-4o > GPT-3.5-turbo, and the robustness of large language models is influenced by the professional domains in which they operate.
Reliable Model Watermarking: Defending Against Theft without Compromising on Evasion
Apr 21, 2024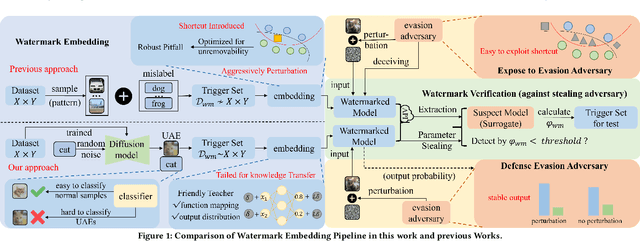
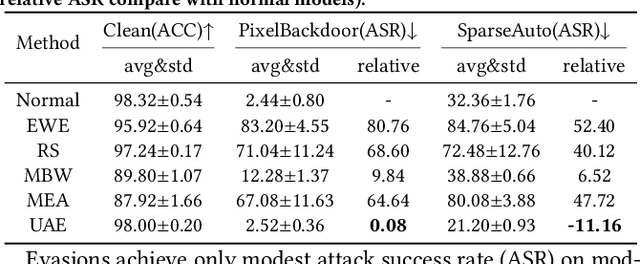
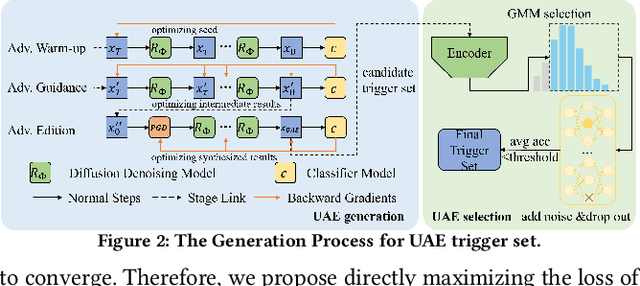

Abstract:With the rise of Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) platforms,safeguarding the intellectual property of deep learning models is becoming paramount. Among various protective measures, trigger set watermarking has emerged as a flexible and effective strategy for preventing unauthorized model distribution. However, this paper identifies an inherent flaw in the current paradigm of trigger set watermarking: evasion adversaries can readily exploit the shortcuts created by models memorizing watermark samples that deviate from the main task distribution, significantly impairing their generalization in adversarial settings. To counteract this, we leverage diffusion models to synthesize unrestricted adversarial examples as trigger sets. By learning the model to accurately recognize them, unique watermark behaviors are promoted through knowledge injection rather than error memorization, thus avoiding exploitable shortcuts. Furthermore, we uncover that the resistance of current trigger set watermarking against removal attacks primarily relies on significantly damaging the decision boundaries during embedding, intertwining unremovability with adverse impacts. By optimizing the knowledge transfer properties of protected models, our approach conveys watermark behaviors to extraction surrogates without aggressively decision boundary perturbation. Experimental results on CIFAR-10/100 and Imagenette datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, showing not only improved robustness against evasion adversaries but also superior resistance to watermark removal attacks compared to state-of-the-art solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge