Chao Liu
Tencent Inc.
Transition Matching Distillation for Fast Video Generation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Large video diffusion and flow models have achieved remarkable success in high-quality video generation, but their use in real-time interactive applications remains limited due to their inefficient multi-step sampling process. In this work, we present Transition Matching Distillation (TMD), a novel framework for distilling video diffusion models into efficient few-step generators. The central idea of TMD is to match the multi-step denoising trajectory of a diffusion model with a few-step probability transition process, where each transition is modeled as a lightweight conditional flow. To enable efficient distillation, we decompose the original diffusion backbone into two components: (1) a main backbone, comprising the majority of early layers, that extracts semantic representations at each outer transition step; and (2) a flow head, consisting of the last few layers, that leverages these representations to perform multiple inner flow updates. Given a pretrained video diffusion model, we first introduce a flow head to the model, and adapt it into a conditional flow map. We then apply distribution matching distillation to the student model with flow head rollout in each transition step. Extensive experiments on distilling Wan2.1 1.3B and 14B text-to-video models demonstrate that TMD provides a flexible and strong trade-off between generation speed and visual quality. In particular, TMD outperforms existing distilled models under comparable inference costs in terms of visual fidelity and prompt adherence. Project page: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/genair/tmd
On the Adversarial Robustness of 3D Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:3D Vision-Language Models (VLMs), such as PointLLM and GPT4Point, have shown strong reasoning and generalization abilities in 3D understanding tasks. However, their adversarial robustness remains largely unexplored. Prior work in 2D VLMs has shown that the integration of visual inputs significantly increases vulnerability to adversarial attacks, making these models easier to manipulate into generating toxic or misleading outputs. In this paper, we investigate whether incorporating 3D vision similarly compromises the robustness of 3D VLMs. To this end, we present the first systematic study of adversarial robustness in point-based 3D VLMs. We propose two complementary attack strategies: \textit{Vision Attack}, which perturbs the visual token features produced by the 3D encoder and projector to assess the robustness of vision-language alignment; and \textit{Caption Attack}, which directly manipulates output token sequences to evaluate end-to-end system robustness. Each attack includes both untargeted and targeted variants to measure general vulnerability and susceptibility to controlled manipulation. Our experiments reveal that 3D VLMs exhibit significant adversarial vulnerabilities under untargeted attacks, while demonstrating greater resilience against targeted attacks aimed at forcing specific harmful outputs, compared to their 2D counterparts. These findings highlight the importance of improving the adversarial robustness of 3D VLMs, especially as they are deployed in safety-critical applications.
DynaFix: Iterative Automated Program Repair Driven by Execution-Level Dynamic Information
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Automated Program Repair (APR) aims to automatically generate correct patches for buggy programs. Recent approaches leveraging large language models (LLMs) have shown promise but face limitations. Most rely solely on static analysis, ignoring runtime behaviors. Some attempt to incorporate dynamic signals, but these are often restricted to training or fine-tuning, or injected only once into the repair prompt, without iterative use. This fails to fully capture program execution. Current iterative repair frameworks typically rely on coarse-grained feedback, such as pass/fail results or exception types, and do not leverage fine-grained execution-level information effectively. As a result, models struggle to simulate human stepwise debugging, limiting their effectiveness in multi-step reasoning and complex bug repair. To address these challenges, we propose DynaFix, an execution-level dynamic information-driven APR method that iteratively leverages runtime information to refine the repair process. In each repair round, DynaFix captures execution-level dynamic information such as variable states, control-flow paths, and call stacks, transforming them into structured prompts to guide LLMs in generating candidate patches. If a patch fails validation, DynaFix re-executes the modified program to collect new execution information for the next attempt. This iterative loop incrementally improves patches based on updated feedback, similar to the stepwise debugging practices of human developers. We evaluate DynaFix on the Defects4J v1.2 and v2.0 benchmarks. DynaFix repairs 186 single-function bugs, a 10% improvement over state-of-the-art baselines, including 38 bugs previously unrepaired. It achieves correct patches within at most 35 attempts, reducing the patch search space by 70% compared with existing methods, thereby demonstrating both effectiveness and efficiency in repairing complex bugs.
AKG kernel Agent: A Multi-Agent Framework for Cross-Platform Kernel Synthesis
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Modern AI models demand high-performance computation kernels. The growing complexity of LLMs, multimodal architectures, and recommendation systems, combined with techniques like sparsity and quantization, creates significant computational challenges. Moreover, frequent hardware updates and diverse chip architectures further complicate this landscape, requiring tailored kernel implementations for each platform. However, manual optimization cannot keep pace with these demands, creating a critical bottleneck in AI system development. Recent advances in LLM code generation capabilities have opened new possibilities for automating kernel development. In this work, we propose AKG kernel agent (AI-driven Kernel Generator), a multi-agent system that automates kernel generation, migration, and performance tuning. AKG kernel agent is designed to support multiple domain-specific languages (DSLs), including Triton, TileLang, CPP, and CUDA-C, enabling it to target different hardware backends while maintaining correctness and portability. The system's modular design allows rapid integration of new DSLs and hardware targets. When evaluated on KernelBench using Triton DSL across GPU and NPU backends, AKG kernel agent achieves an average speedup of 1.46$\times$ over PyTorch Eager baselines implementations, demonstrating its effectiveness in accelerating kernel development for modern AI workloads.
FocusMed: A Large Language Model-based Framework for Enhancing Medical Question Summarization with Focus Identification
Oct 06, 2025
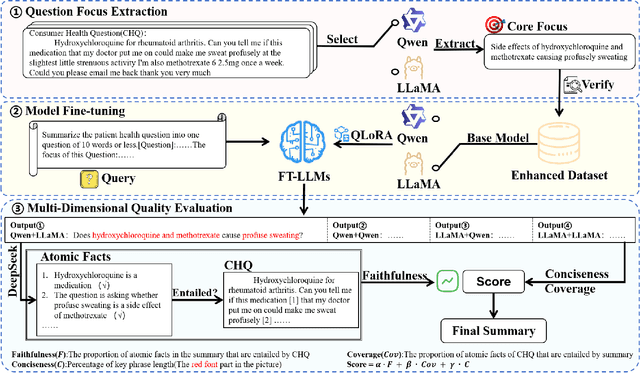

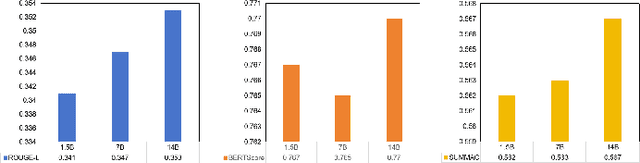
Abstract:With the rapid development of online medical platforms, consumer health questions (CHQs) are inefficient in diagnosis due to redundant information and frequent non-professional terms. The medical question summary (MQS) task aims to transform CHQs into streamlined doctors' frequently asked questions (FAQs), but existing methods still face challenges such as poor identification of question focus and model hallucination. This paper explores the potential of large language models (LLMs) in the MQS task and finds that direct fine-tuning is prone to focus identification bias and generates unfaithful content. To this end, we propose an optimization framework based on core focus guidance. First, a prompt template is designed to drive the LLMs to extract the core focus from the CHQs that is faithful to the original text. Then, a fine-tuning dataset is constructed in combination with the original CHQ-FAQ pairs to improve the ability to identify the focus of the question. Finally, a multi-dimensional quality evaluation and selection mechanism is proposed to comprehensively improve the quality of the summary from multiple dimensions. We conduct comprehensive experiments on two widely-adopted MQS datasets using three established evaluation metrics. The proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance across all measures, demonstrating a significant boost in the model's ability to identify critical focus of questions and a notable mitigation of hallucinations. The source codes are freely available at https://github.com/DUT-LiuChao/FocusMed.
Balancing Utility and Privacy: Dynamically Private SGD with Random Projection
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Stochastic optimization is a pivotal enabler in modern machine learning, producing effective models for various tasks. However, several existing works have shown that model parameters and gradient information are susceptible to privacy leakage. Although Differentially Private SGD (DPSGD) addresses privacy concerns, its static noise mechanism impacts the error bounds for model performance. Additionally, with the exponential increase in model parameters, efficient learning of these models using stochastic optimizers has become more challenging. To address these concerns, we introduce the Dynamically Differentially Private Projected SGD (D2P2-SGD) optimizer. In D2P2-SGD, we combine two important ideas: (i) dynamic differential privacy (DDP) with automatic gradient clipping and (ii) random projection with SGD, allowing dynamic adjustment of the tradeoff between utility and privacy of the model. It exhibits provably sub-linear convergence rates across different objective functions, matching the best available rate. The theoretical analysis further suggests that DDP leads to better utility at the cost of privacy, while random projection enables more efficient model learning. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets show that D2P2-SGD remarkably enhances accuracy while maintaining privacy. Our code is available here.
BrowseComp-ZH: Benchmarking Web Browsing Ability of Large Language Models in Chinese
May 01, 2025
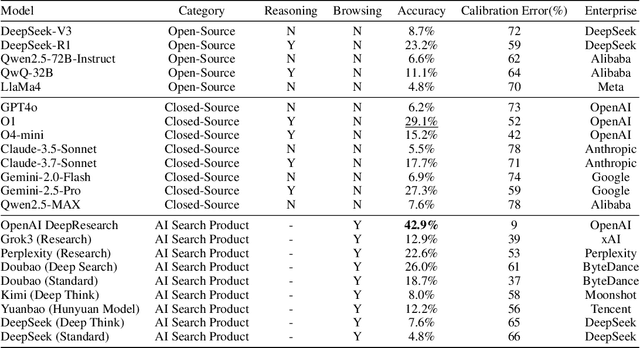
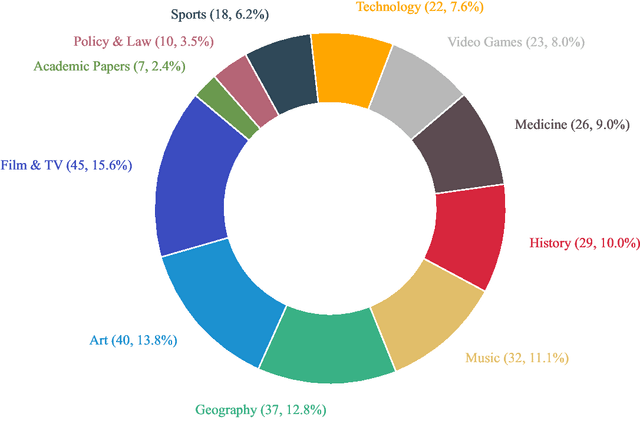
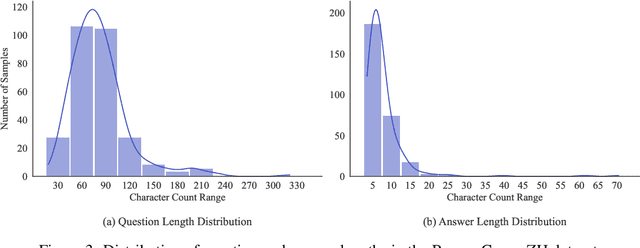
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) evolve into tool-using agents, the ability to browse the web in real-time has become a critical yardstick for measuring their reasoning and retrieval competence. Existing benchmarks such as BrowseComp concentrate on English and overlook the linguistic, infrastructural, and censorship-related complexities of other major information ecosystems -- most notably Chinese. To address this gap, we introduce BrowseComp-ZH, a high-difficulty benchmark purpose-built to comprehensively evaluate LLM agents on the Chinese web. BrowseComp-ZH consists of 289 multi-hop questions spanning 11 diverse domains. Each question is reverse-engineered from a short, objective, and easily verifiable answer (e.g., a date, number, or proper noun). A two-stage quality control protocol is applied to strive for high question difficulty and answer uniqueness. We benchmark over 20 state-of-the-art language models and agentic search systems on our proposed BrowseComp-ZH. Despite their strong conversational and retrieval capabilities, most models struggle severely: a large number achieve accuracy rates below 10%, and only a handful exceed 20%. Even the best-performing system, OpenAI's DeepResearch, reaches just 42.9%. These results demonstrate the considerable difficulty of BrowseComp-ZH, where success demands not only effective retrieval strategies, but also sophisticated reasoning and information reconciliation -- capabilities that current models still struggle to master. Our dataset, construction guidelines, and benchmark results have been publicly released at https://github.com/PALIN2018/BrowseComp-ZH.
Redefining Superalignment: From Weak-to-Strong Alignment to Human-AI Co-Alignment to Sustainable Symbiotic Society
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems are becoming increasingly powerful and autonomous, and may progress to surpass human intelligence levels, namely Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). During the progression from AI to ASI, it may exceed human control, violate human values, and even lead to irreversible catastrophic consequences in extreme cases. This gives rise to a pressing issue that needs to be addressed: superalignment, ensuring that AI systems much smarter than humans, remain aligned with human (compatible) intentions and values. Existing scalable oversight and weak-to-strong generalization methods may prove substantially infeasible and inadequate when facing ASI. We must explore safer and more pluralistic frameworks and approaches for superalignment. In this paper, we redefine superalignment as the human-AI co-alignment towards a sustainable symbiotic society, and highlight a framework that integrates external oversight and intrinsic proactive alignment. External oversight superalignment should be grounded in human-centered ultimate decision, supplemented by interpretable automated evaluation and correction, to achieve continuous alignment with humanity's evolving values. Intrinsic proactive superalignment is rooted in a profound understanding of the self, others, and society, integrating self-awareness, self-reflection, and empathy to spontaneously infer human intentions, distinguishing good from evil and proactively considering human well-being, ultimately attaining human-AI co-alignment through iterative interaction. The integration of externally-driven oversight with intrinsically-driven proactive alignment empowers sustainable symbiotic societies through human-AI co-alignment, paving the way for achieving safe and beneficial AGI and ASI for good, for human, and for a symbiotic ecology.
EquiVDM: Equivariant Video Diffusion Models with Temporally Consistent Noise
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Temporally consistent video-to-video generation is essential for applications of video diffusion models in areas such as sim-to-real, style-transfer, video upsampling, etc. In this paper, we propose a video diffusion framework that leverages temporally consistent noise to generate coherent video frames without specialized modules or additional constraints. We show that the standard training objective of diffusion models, when applied with temporally consistent noise, encourages the model to be equivariant to spatial transformations in input video and noise. This enables our model to better follow motion patterns from the input video, producing aligned motion and high-fidelity frames. Furthermore, we extend our approach to 3D-consistent video generation by attaching noise as textures on 3D meshes, ensuring 3D consistency in sim-to-real applications. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses state-of-the-art baselines in motion alignment, 3D consistency, and video quality while requiring only a few sampling steps in practice.
Bidirectional Linear Recurrent Models for Sequence-Level Multisource Fusion
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Sequence modeling is a critical yet challenging task with wide-ranging applications, especially in time series forecasting for domains like weather prediction, temperature monitoring, and energy load forecasting. Transformers, with their attention mechanism, have emerged as state-of-the-art due to their efficient parallel training, but they suffer from quadratic time complexity, limiting their scalability for long sequences. In contrast, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) offer linear time complexity, spurring renewed interest in linear RNNs for more computationally efficient sequence modeling. In this work, we introduce BLUR (Bidirectional Linear Unit for Recurrent network), which uses forward and backward linear recurrent units (LRUs) to capture both past and future dependencies with high computational efficiency. BLUR maintains the linear time complexity of traditional RNNs, while enabling fast parallel training through LRUs. Furthermore, it offers provably stable training and strong approximation capabilities, making it highly effective for modeling long-term dependencies. Extensive experiments on sequential image and time series datasets reveal that BLUR not only surpasses transformers and traditional RNNs in accuracy but also significantly reduces computational costs, making it particularly suitable for real-world forecasting tasks. Our code is available here.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge