Feifei Zhao
Light Alignment Improves LLM Safety via Model Self-Reflection with a Single Neuron
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The safety of large language models (LLMs) has increasingly emerged as a fundamental aspect of their development. Existing safety alignment for LLMs is predominantly achieved through post-training methods, which are computationally expensive and often fail to generalize well across different models. A small number of lightweight alignment approaches either rely heavily on prior-computed safety injections or depend excessively on the model's own capabilities, resulting in limited generalization and degraded efficiency and usability during generation. In this work, we propose a safety-aware decoding method that requires only low-cost training of an expert model and employs a single neuron as a gating mechanism. By effectively balancing the model's intrinsic capabilities with external guidance, our approach simultaneously preserves utility and enhances output safety. It demonstrates clear advantages in training overhead and generalization across model scales, offering a new perspective on lightweight alignment for the safe and practical deployment of large language models. Code: https://github.com/Beijing-AISI/NGSD.
TEFormer: Structured Bidirectional Temporal Enhancement Modeling in Spiking Transformers
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:In recent years, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have achieved remarkable progress, with Spiking Transformers emerging as a promising architecture for energy-efficient sequence modeling. However, existing Spiking Transformers still lack a principled mechanism for effective temporal fusion, limiting their ability to fully exploit spatiotemporal dependencies. Inspired by feedforward-feedback modulation in the human visual pathway, we propose TEFormer, the first Spiking Transformer framework that achieves bidirectional temporal fusion by decoupling temporal modeling across its core components. Specifically, TEFormer employs a lightweight and hyperparameter-free forward temporal fusion mechanism in the attention module, enabling fully parallel computation, while incorporating a backward gated recurrent structure in the MLP to aggregate temporal information in reverse order and reinforce temporal consistency. Extensive experiments across a wide range of benchmarks demonstrate that TEFormer consistently and significantly outperforms strong SNN and Spiking Transformer baselines under diverse datasets. Moreover, through the first systematic evaluation of Spiking Transformers under different neural encoding schemes, we show that the performance gains of TEFormer remain stable across encoding choices, indicating that the improved temporal modeling directly translates into reliable accuracy improvements across varied spiking representations. These results collectively establish TEFormer as an effective and general framework for temporal modeling in Spiking Transformers.
CogToM: A Comprehensive Theory of Mind Benchmark inspired by Human Cognition for Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Whether Large Language Models (LLMs) truly possess human-like Theory of Mind (ToM) capabilities has garnered increasing attention. However, existing benchmarks remain largely restricted to narrow paradigms like false belief tasks, failing to capture the full spectrum of human cognitive mechanisms. We introduce CogToM, a comprehensive, theoretically grounded benchmark comprising over 8000 bilingual instances across 46 paradigms, validated by 49 human annotator.A systematic evaluation of 22 representative models, including frontier models like GPT-5.1 and Qwen3-Max, reveals significant performance heterogeneities and highlights persistent bottlenecks in specific dimensions. Further analysis based on human cognitive patterns suggests potential divergences between LLM and human cognitive structures. CogToM offers a robust instrument and perspective for investigating the evolving cognitive boundaries of LLMs.
MVPBench: A Benchmark and Fine-Tuning Framework for Aligning Large Language Models with Diverse Human Values
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:The alignment of large language models (LLMs) with human values is critical for their safe and effective deployment across diverse user populations. However, existing benchmarks often neglect cultural and demographic diversity, leading to limited understanding of how value alignment generalizes globally. In this work, we introduce MVPBench, a novel benchmark that systematically evaluates LLMs' alignment with multi-dimensional human value preferences across 75 countries. MVPBench contains 24,020 high-quality instances annotated with fine-grained value labels, personalized questions, and rich demographic metadata, making it the most comprehensive resource of its kind to date. Using MVPBench, we conduct an in-depth analysis of several state-of-the-art LLMs, revealing substantial disparities in alignment performance across geographic and demographic lines. We further demonstrate that lightweight fine-tuning methods, such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), can significantly enhance value alignment in both in-domain and out-of-domain settings. Our findings underscore the necessity for population-aware alignment evaluation and provide actionable insights for building culturally adaptive and value-sensitive LLMs. MVPBench serves as a practical foundation for future research on global alignment, personalized value modeling, and equitable AI development.
Redefining Superalignment: From Weak-to-Strong Alignment to Human-AI Co-Alignment to Sustainable Symbiotic Society
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems are becoming increasingly powerful and autonomous, and may progress to surpass human intelligence levels, namely Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). During the progression from AI to ASI, it may exceed human control, violate human values, and even lead to irreversible catastrophic consequences in extreme cases. This gives rise to a pressing issue that needs to be addressed: superalignment, ensuring that AI systems much smarter than humans, remain aligned with human (compatible) intentions and values. Existing scalable oversight and weak-to-strong generalization methods may prove substantially infeasible and inadequate when facing ASI. We must explore safer and more pluralistic frameworks and approaches for superalignment. In this paper, we redefine superalignment as the human-AI co-alignment towards a sustainable symbiotic society, and highlight a framework that integrates external oversight and intrinsic proactive alignment. External oversight superalignment should be grounded in human-centered ultimate decision, supplemented by interpretable automated evaluation and correction, to achieve continuous alignment with humanity's evolving values. Intrinsic proactive superalignment is rooted in a profound understanding of the self, others, and society, integrating self-awareness, self-reflection, and empathy to spontaneously infer human intentions, distinguishing good from evil and proactively considering human well-being, ultimately attaining human-AI co-alignment through iterative interaction. The integration of externally-driven oversight with intrinsically-driven proactive alignment empowers sustainable symbiotic societies through human-AI co-alignment, paving the way for achieving safe and beneficial AGI and ASI for good, for human, and for a symbiotic ecology.
Continual Learning of Multiple Cognitive Functions with Brain-inspired Temporal Development Mechanism
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Cognitive functions in current artificial intelligence networks are tied to the exponential increase in network scale, whereas the human brain can continuously learn hundreds of cognitive functions with remarkably low energy consumption. This advantage is in part due to the brain cross-regional temporal development mechanisms, where the progressive formation, reorganization, and pruning of connections from basic to advanced regions, facilitate knowledge transfer and prevent network redundancy. Inspired by these, we propose the Continual Learning of Multiple Cognitive Functions with Brain-inspired Temporal Development Mechanism(TD-MCL), enabling cognitive enhancement from simple to complex in Perception-Motor-Interaction(PMI) multiple cognitive task scenarios. The TD-MCL model proposes the sequential evolution of long-range connections between different cognitive modules to promote positive knowledge transfer, while using feedback-guided local connection inhibition and pruning to effectively eliminate redundancies in previous tasks, reducing energy consumption while preserving acquired knowledge. Experiments show that the proposed method can achieve continual learning capabilities while reducing network scale, without introducing regularization, replay, or freezing strategies, and achieving superior accuracy on new tasks compared to direct learning. The proposed method shows that the brain's developmental mechanisms offer a valuable reference for exploring biologically plausible, low-energy enhancements of general cognitive abilities.
Autonomous Alignment with Human Value on Altruism through Considerate Self-imagination and Theory of Mind
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:With the widespread application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in human society, enabling AI to autonomously align with human values has become a pressing issue to ensure its sustainable development and benefit to humanity. One of the most important aspects of aligning with human values is the necessity for agents to autonomously make altruistic, safe, and ethical decisions, considering and caring for human well-being. Current AI extremely pursues absolute superiority in certain tasks, remaining indifferent to the surrounding environment and other agents, which has led to numerous safety risks. Altruistic behavior in human society originates from humans' capacity for empathizing others, known as Theory of Mind (ToM), combined with predictive imaginative interactions before taking action to produce thoughtful and altruistic behaviors. Inspired by this, we are committed to endow agents with considerate self-imagination and ToM capabilities, driving them through implicit intrinsic motivations to autonomously align with human altruistic values. By integrating ToM within the imaginative space, agents keep an eye on the well-being of other agents in real time, proactively anticipate potential risks to themselves and others, and make thoughtful altruistic decisions that balance negative effects on the environment. The ancient Chinese story of Sima Guang Smashes the Vat illustrates the moral behavior of the young Sima Guang smashed a vat to save a child who had accidentally fallen into it, which is an excellent reference scenario for this paper. We design an experimental scenario similar to Sima Guang Smashes the Vat and its variants with different complexities, which reflects the trade-offs and comprehensive considerations between self-goals, altruistic rescue, and avoiding negative side effects.
Evolving Efficient Genetic Encoding for Deep Spiking Neural Networks
Nov 11, 2024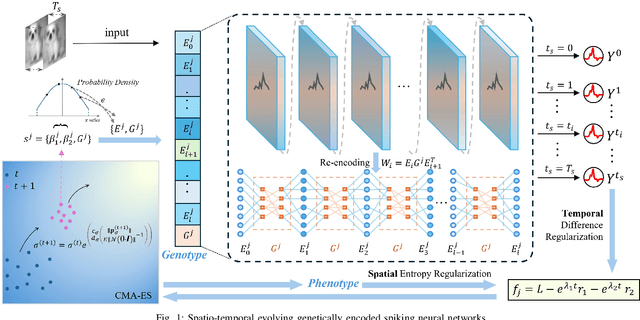
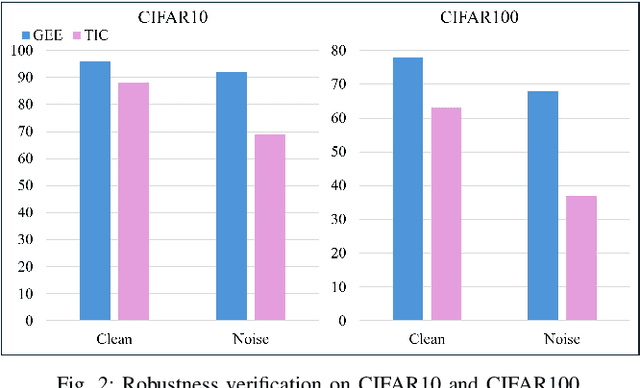
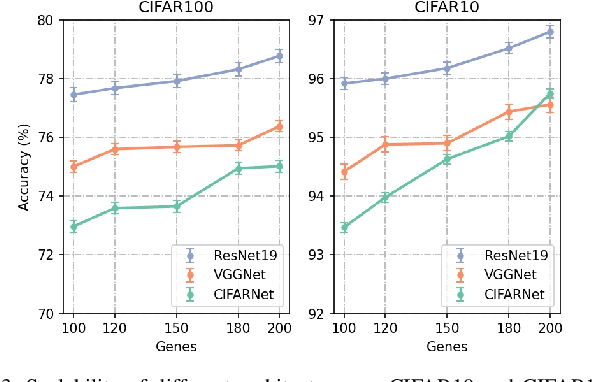
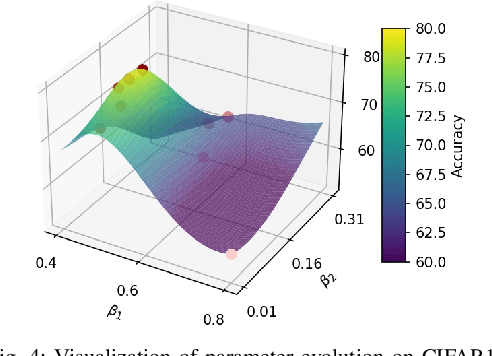
Abstract:By exploiting discrete signal processing and simulating brain neuron communication, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer a low-energy alternative to Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs). However, existing SNN models, still face high computational costs due to the numerous time steps as well as network depth and scale. The tens of billions of neurons and trillions of synapses in the human brain are developed from only 20,000 genes, which inspires us to design an efficient genetic encoding strategy that dynamic evolves to regulate large-scale deep SNNs at low cost. Therefore, we first propose a genetically scaled SNN encoding scheme that incorporates globally shared genetic interactions to indirectly optimize neuronal encoding instead of weight, which obviously brings about reductions in parameters and energy consumption. Then, a spatio-temporal evolutionary framework is designed to optimize the inherently initial wiring rules. Two dynamic regularization operators in the fitness function evolve the neuronal encoding to a suitable distribution and enhance information quality of the genetic interaction respectively, substantially accelerating evolutionary speed and improving efficiency. Experiments show that our approach compresses parameters by approximately 50\% to 80\%, while outperforming models on the same architectures by 0.21\% to 4.38\% on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100 and ImageNet. In summary, the consistent trends of the proposed genetically encoded spatio-temporal evolution across different datasets and architectures highlight its significant enhancements in terms of efficiency, broad scalability and robustness, demonstrating the advantages of the brain-inspired evolutionary genetic coding for SNN optimization.
Building Altruistic and Moral AI Agent with Brain-inspired Affective Empathy Mechanisms
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:As AI closely interacts with human society, it is crucial to ensure that its decision-making is safe, altruistic, and aligned with human ethical and moral values. However, existing research on embedding ethical and moral considerations into AI remains insufficient, and previous external constraints based on principles and rules are inadequate to provide AI with long-term stability and generalization capabilities. In contrast, the intrinsic altruistic motivation based on empathy is more willing, spontaneous, and robust. Therefore, this paper is dedicated to autonomously driving intelligent agents to acquire morally behaviors through human-like affective empathy mechanisms. We draw inspiration from the neural mechanism of human brain's moral intuitive decision-making, and simulate the mirror neuron system to construct a brain-inspired affective empathy-driven altruistic decision-making model. Here, empathy directly impacts dopamine release to form intrinsic altruistic motivation. Based on the principle of moral utilitarianism, we design the moral reward function that integrates intrinsic empathy and extrinsic self-task goals. A comprehensive experimental scenario incorporating empathetic processes, personal objectives, and altruistic goals is developed. The proposed model enables the agent to make consistent moral decisions (prioritizing altruism) by balancing self-interest with the well-being of others. We further introduce inhibitory neurons to regulate different levels of empathy and verify the positive correlation between empathy levels and altruistic preferences, yielding conclusions consistent with findings from psychological behavioral experiments. This work provides a feasible solution for the development of ethical AI by leveraging the intrinsic human-like empathy mechanisms, and contributes to the harmonious coexistence between humans and AI.
Directly Training Temporal Spiking Neural Network with Sparse Surrogate Gradient
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Brain-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have attracted much attention due to their event-based computing and energy-efficient features. However, the spiking all-or-none nature has prevented direct training of SNNs for various applications. The surrogate gradient (SG) algorithm has recently enabled spiking neural networks to shine in neuromorphic hardware. However, introducing surrogate gradients has caused SNNs to lose their original sparsity, thus leading to the potential performance loss. In this paper, we first analyze the current problem of direct training using SGs and then propose Masked Surrogate Gradients (MSGs) to balance the effectiveness of training and the sparseness of the gradient, thereby improving the generalization ability of SNNs. Moreover, we introduce a temporally weighted output (TWO) method to decode the network output, reinforcing the importance of correct timesteps. Extensive experiments on diverse network structures and datasets show that training with MSG and TWO surpasses the SOTA technique.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge