Yuxuan Zhao
Early and Prediagnostic Detection of Pancreatic Cancer from Computed Tomography
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), one of the deadliest solid malignancies, is often detected at a late and inoperable stage. Retrospective reviews of prediagnostic CT scans, when conducted by expert radiologists aware that the patient later developed PDAC, frequently reveal lesions that were previously overlooked. To help detecting these lesions earlier, we developed an automated system named ePAI (early Pancreatic cancer detection with Artificial Intelligence). It was trained on data from 1,598 patients from a single medical center. In the internal test involving 1,009 patients, ePAI achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.939-0.999, a sensitivity of 95.3%, and a specificity of 98.7% for detecting small PDAC less than 2 cm in diameter, precisely localizing PDAC as small as 2 mm. In an external test involving 7,158 patients across 6 centers, ePAI achieved an AUC of 0.918-0.945, a sensitivity of 91.5%, and a specificity of 88.0%, precisely localizing PDAC as small as 5 mm. Importantly, ePAI detected PDACs on prediagnostic CT scans obtained 3 to 36 months before clinical diagnosis that had originally been overlooked by radiologists. It successfully detected and localized PDACs in 75 of 159 patients, with a median lead time of 347 days before clinical diagnosis. Our multi-reader study showed that ePAI significantly outperformed 30 board-certified radiologists by 50.3% (P < 0.05) in sensitivity while maintaining a comparable specificity of 95.4% in detecting PDACs early and prediagnostic. These findings suggest its potential of ePAI as an assistive tool to improve early detection of pancreatic cancer.
PyFi: Toward Pyramid-like Financial Image Understanding for VLMs via Adversarial Agents
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes PyFi, a novel framework for pyramid-like financial image understanding that enables vision language models (VLMs) to reason through question chains in a progressive, simple-to-complex manner. At the core of PyFi is PyFi-600K, a dataset comprising 600K financial question-answer pairs organized into a reasoning pyramid: questions at the base require only basic perception, while those toward the apex demand increasing levels of capability in financial visual understanding and expertise. This data is scalable because it is synthesized without human annotations, using PyFi-adv, a multi-agent adversarial mechanism under the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) paradigm, in which, for each image, a challenger agent competes with a solver agent by generating question chains that progressively probe deeper capability levels in financial visual reasoning. Leveraging this dataset, we present fine-grained, hierarchical, and comprehensive evaluations of advanced VLMs in the financial domain. Moreover, fine-tuning Qwen2.5-VL-3B and Qwen2.5-VL-7B on the pyramid-structured question chains enables these models to answer complex financial questions by decomposing them into sub-questions with gradually increasing reasoning demands, yielding average accuracy improvements of 19.52% and 8.06%, respectively, on the dataset. All resources of code, dataset and models are available at: https://github.com/AgenticFinLab/PyFi .
A QP Framework for Improving Data Collection: Quantifying Device-Controller Performance in Robot Teleoperation
Nov 11, 2025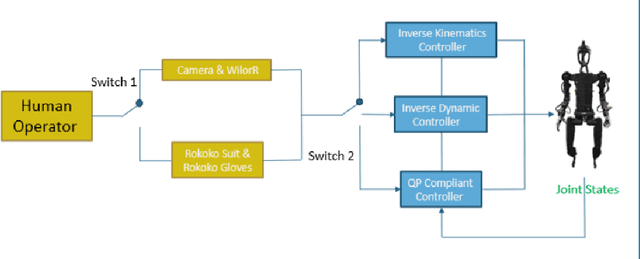


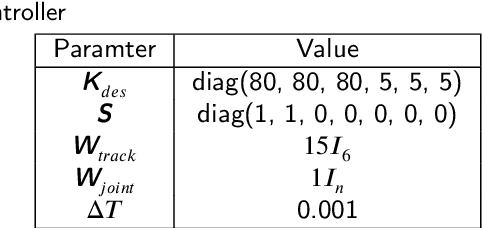
Abstract:Robot learning empowers the robot system with human brain-like intelligence to autonomously acquire and adapt skills through experience, enhancing flexibility and adaptability in various environments. Aimed at achieving a similar level of capability in large language models (LLMs) for embodied intelligence, data quality plays a crucial role in training a foundational model with diverse robot skills. In this study, we investigate the collection of data for manipulation tasks using teleoperation devices. Different devices yield varying effects when paired with corresponding controller strategies, including position-based inverse kinematics (IK) control, torque-based inverse dynamics (ID) control, and optimization-based compliance control. In this paper, we develop a teleoperation pipeline that is compatible with different teleoperation devices and manipulator controllers. Within the pipeline, we construct the optimal QP formulation with the dynamic nullspace and the impedance tracking as the novel optimal controller to achieve compliant pose tracking and singularity avoidance. Regarding the optimal controller, it adaptively adjusts the weights assignment depending on the robot joint manipulability that reflects the state of joint configuration for the pose tracking in the form of impedance control and singularity avoidance with nullspace tracking. Analysis of quantitative experimental results suggests the quality of the teleoperated trajectory data, including tracking error, occurrence of singularity, and the smoothness of the joints' trajectory, with different combinations of teleoperation interface and the motion controller.
Evolution of Optimization Algorithms for Global Placement via Large Language Models
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Optimization algorithms are widely employed to tackle complex problems, but designing them manually is often labor-intensive and requires significant expertise. Global placement is a fundamental step in electronic design automation (EDA). While analytical approaches represent the state-of-the-art (SOTA) in global placement, their core optimization algorithms remain heavily dependent on heuristics and customized components, such as initialization strategies, preconditioning methods, and line search techniques. This paper presents an automated framework that leverages large language models (LLM) to evolve optimization algorithms for global placement. We first generate diverse candidate algorithms using LLM through carefully crafted prompts. Then we introduce an LLM-based genetic flow to evolve selected candidate algorithms. The discovered optimization algorithms exhibit substantial performance improvements across many benchmarks. Specifically, Our design-case-specific discovered algorithms achieve average HPWL improvements of \textbf{5.05\%}, \text{5.29\%} and \textbf{8.30\%} on MMS, ISPD2005 and ISPD2019 benchmarks, and up to \textbf{17\%} improvements on individual cases. Additionally, the discovered algorithms demonstrate good generalization ability and are complementary to existing parameter-tuning methods.
In-Context Learning of Linear Dynamical Systems with Transformers: Error Bounds and Depth-Separation
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates approximation-theoretic aspects of the in-context learning capability of the transformers in representing a family of noisy linear dynamical systems. Our first theoretical result establishes an upper bound on the approximation error of multi-layer transformers with respect to an $L^2$-testing loss uniformly defined across tasks. This result demonstrates that transformers with logarithmic depth can achieve error bounds comparable with those of the least-squares estimator. In contrast, our second result establishes a non-diminishing lower bound on the approximation error for a class of single-layer linear transformers, which suggests a depth-separation phenomenon for transformers in the in-context learning of dynamical systems. Moreover, this second result uncovers a critical distinction in the approximation power of single-layer linear transformers when learning from IID versus non-IID data.
ScaleMAI: Accelerating the Development of Trusted Datasets and AI Models
Jan 06, 2025

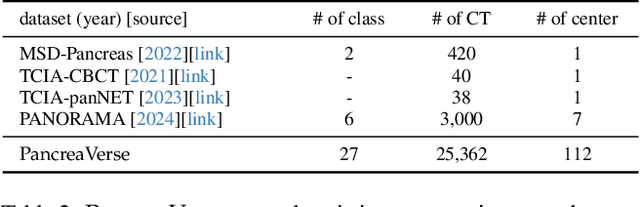

Abstract:Building trusted datasets is critical for transparent and responsible Medical AI (MAI) research, but creating even small, high-quality datasets can take years of effort from multidisciplinary teams. This process often delays AI benefits, as human-centric data creation and AI-centric model development are treated as separate, sequential steps. To overcome this, we propose ScaleMAI, an agent of AI-integrated data curation and annotation, allowing data quality and AI performance to improve in a self-reinforcing cycle and reducing development time from years to months. We adopt pancreatic tumor detection as an example. First, ScaleMAI progressively creates a dataset of 25,362 CT scans, including per-voxel annotations for benign/malignant tumors and 24 anatomical structures. Second, through progressive human-in-the-loop iterations, ScaleMAI provides Flagship AI Model that can approach the proficiency of expert annotators (30-year experience) in detecting pancreatic tumors. Flagship Model significantly outperforms models developed from smaller, fixed-quality datasets, with substantial gains in tumor detection (+14%), segmentation (+5%), and classification (72%) on three prestigious benchmarks. In summary, ScaleMAI transforms the speed, scale, and reliability of medical dataset creation, paving the way for a variety of impactful, data-driven applications.
mR$^2$AG: Multimodal Retrieval-Reflection-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Based VQA
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Advanced Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) struggle with recent Knowledge-based VQA tasks, such as INFOSEEK and Encyclopedic-VQA, due to their limited and frozen knowledge scope, often leading to ambiguous and inaccurate responses. Thus, multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (mRAG) is naturally introduced to provide MLLMs with comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge, effectively expanding the knowledge scope. However, current mRAG methods have inherent drawbacks, including: 1) Performing retrieval even when external knowledge is not needed. 2) Lacking of identification of evidence that supports the query. 3) Increasing model complexity due to additional information filtering modules or rules. To address these shortcomings, we propose a novel generalized framework called \textbf{m}ultimodal \textbf{R}etrieval-\textbf{R}eflection-\textbf{A}ugmented \textbf{G}eneration (mR$^2$AG), which achieves adaptive retrieval and useful information localization to enable answers through two easy-to-implement reflection operations, preventing high model complexity. In mR$^2$AG, Retrieval-Reflection is designed to distinguish different user queries and avoids redundant retrieval calls, and Relevance-Reflection is introduced to guide the MLLM in locating beneficial evidence of the retrieved content and generating answers accordingly. In addition, mR$^2$AG can be integrated into any well-trained MLLM with efficient fine-tuning on the proposed mR$^2$AG Instruction-Tuning dataset (mR$^2$AG-IT). mR$^2$AG significantly outperforms state-of-the-art MLLMs (e.g., GPT-4v/o) and RAG-based MLLMs on INFOSEEK and Encyclopedic-VQA, while maintaining the exceptional capabilities of base MLLMs across a wide range of Visual-dependent tasks.
StraightTrack: Towards Mixed Reality Navigation System for Percutaneous K-wire Insertion
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:In percutaneous pelvic trauma surgery, accurate placement of Kirschner wires (K-wires) is crucial to ensure effective fracture fixation and avoid complications due to breaching the cortical bone along an unsuitable trajectory. Surgical navigation via mixed reality (MR) can help achieve precise wire placement in a low-profile form factor. Current approaches in this domain are as yet unsuitable for real-world deployment because they fall short of guaranteeing accurate visual feedback due to uncontrolled bending of the wire. To ensure accurate feedback, we introduce StraightTrack, an MR navigation system designed for percutaneous wire placement in complex anatomy. StraightTrack features a marker body equipped with a rigid access cannula that mitigates wire bending due to interactions with soft tissue and a covered bony surface. Integrated with an Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Display (OST HMD) capable of tracking the cannula body, StraightTrack offers real-time 3D visualization and guidance without external trackers, which are prone to losing line-of-sight. In phantom experiments with two experienced orthopedic surgeons, StraightTrack improves wire placement accuracy, achieving the ideal trajectory within $5.26 \pm 2.29$ mm and $2.88 \pm 1.49$ degree, compared to over 12.08 mm and 4.07 degree for comparable methods. As MR navigation systems continue to mature, StraightTrack realizes their potential for internal fracture fixation and other percutaneous orthopedic procedures.
Brain-inspired and Self-based Artificial Intelligence
Feb 29, 2024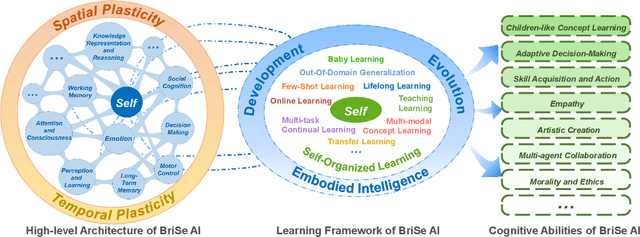
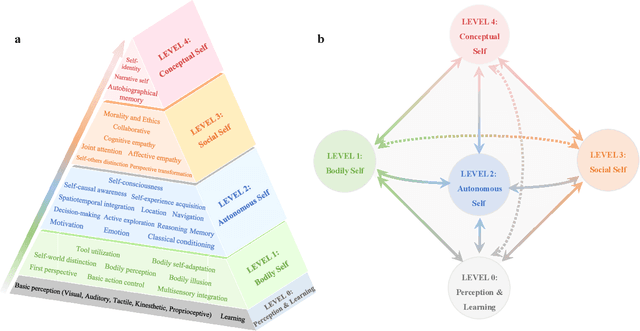
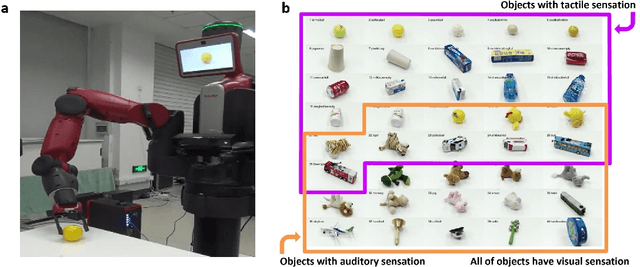
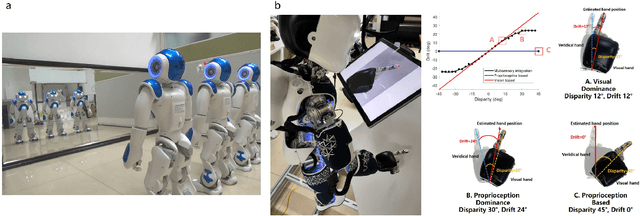
Abstract:The question "Can machines think?" and the Turing Test to assess whether machines could achieve human-level intelligence is one of the roots of AI. With the philosophical argument "I think, therefore I am", this paper challenge the idea of a "thinking machine" supported by current AIs since there is no sense of self in them. Current artificial intelligence is only seemingly intelligent information processing and does not truly understand or be subjectively aware of oneself and perceive the world with the self as human intelligence does. In this paper, we introduce a Brain-inspired and Self-based Artificial Intelligence (BriSe AI) paradigm. This BriSe AI paradigm is dedicated to coordinating various cognitive functions and learning strategies in a self-organized manner to build human-level AI models and robotic applications. Specifically, BriSe AI emphasizes the crucial role of the Self in shaping the future AI, rooted with a practical hierarchical Self framework, including Perception and Learning, Bodily Self, Autonomous Self, Social Self, and Conceptual Self. The hierarchical framework of the Self highlights self-based environment perception, self-bodily modeling, autonomous interaction with the environment, social interaction and collaboration with others, and even more abstract understanding of the Self. Furthermore, the positive mutual promotion and support among multiple levels of Self, as well as between Self and learning, enhance the BriSe AI's conscious understanding of information and flexible adaptation to complex environments, serving as a driving force propelling BriSe AI towards real Artificial General Intelligence.
Challenges and Contributing Factors in the Utilization of Large Language Models (LLMs)
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:With the development of large language models (LLMs) like the GPT series, their widespread use across various application scenarios presents a myriad of challenges. This review initially explores the issue of domain specificity, where LLMs may struggle to provide precise answers to specialized questions within niche fields. The problem of knowledge forgetting arises as these LLMs might find it hard to balance old and new information. The knowledge repetition phenomenon reveals that sometimes LLMs might deliver overly mechanized responses, lacking depth and originality. Furthermore, knowledge illusion describes situations where LLMs might provide answers that seem insightful but are actually superficial, while knowledge toxicity focuses on harmful or biased information outputs. These challenges underscore problems in the training data and algorithmic design of LLMs. To address these issues, it's suggested to diversify training data, fine-tune models, enhance transparency and interpretability, and incorporate ethics and fairness training. Future technological trends might lean towards iterative methodologies, multimodal learning, model personalization and customization, and real-time learning and feedback mechanisms. In conclusion, future LLMs should prioritize fairness, transparency, and ethics, ensuring they uphold high moral and ethical standards when serving humanity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge