Hui Feng
Signed Graph Learning with Hidden Nodes
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Signed graphs, which are characterized by both positive and negative edge weights, have recently attracted significant attention in the field of graph signal processing (GSP). Existing works on signed graph learning typically assume that all graph nodes are available. However, in some specific applications, only a subset of nodes can be observed while the remaining nodes stay hidden. To address this challenge, we propose a novel method for identifying signed graph that accounts for hidden nodes, termed \textit{signed graph learning with hidden nodes under column-sparsity regularization} (SGL-HNCS). Our method is based on the assumption that graph signals are smooth over signed graphs, i.e., signal values of two nodes connected by positive (negative) edges are similar (dissimilar). Rooted in this prior assumption, the topology inference of a signed graph is formulated as a constrained optimization problem with column-sparsity regularization, where the goal is to reconstruct the signed graph Laplacian matrix without disregarding the influence of hidden nodes. We solve the constrained optimization problem using a tailored block coordinate descent (BCD) approach. Experimental results using synthetic data and real-world data demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed SGL-HNCS method.
* 25 pages, 7 figures, published to Signal Processing
On Sampling of Multiple Correlated Stochastic Signals
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Multiple stochastic signals possess inherent statistical correlations, yet conventional sampling methods that process each channel independently result in data redundancy. To leverage this correlation for efficient sampling, we model correlated channels as a linear combination of a smaller set of uncorrelated, wide-sense stationary latent sources. We establish a theoretical lower bound on the total sampling density for zero mean-square error reconstruction, proving it equals the ratio of the joint spectral bandwidth of latent sources to the number of correlated signal channels. We then develop a constructive multi-band sampling scheme that attains this bound. The proposed method operates via spectral partitioning of the latent sources, followed by spatio-temporal sampling and interpolation. Experiments on synthetic and real datasets confirm that our scheme achieves near-lossless reconstruction precisely at the theoretical sampling density, validating its efficiency.
Predicting Diabetic Macular Edema Treatment Responses Using OCT: Dataset and Methods of APTOS Competition
May 09, 2025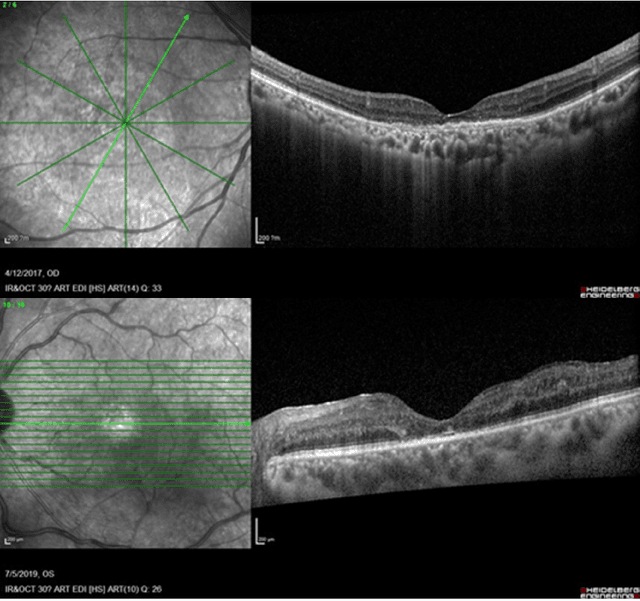
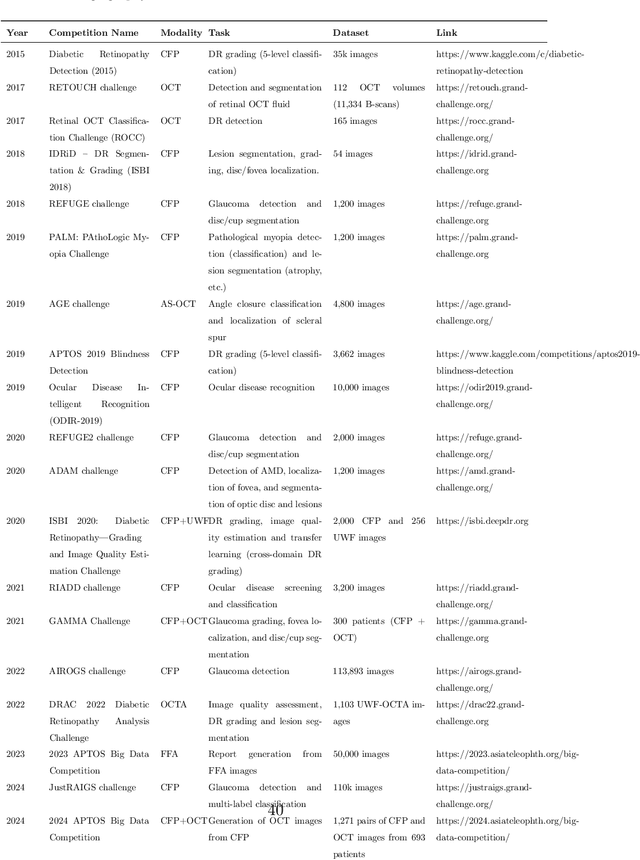
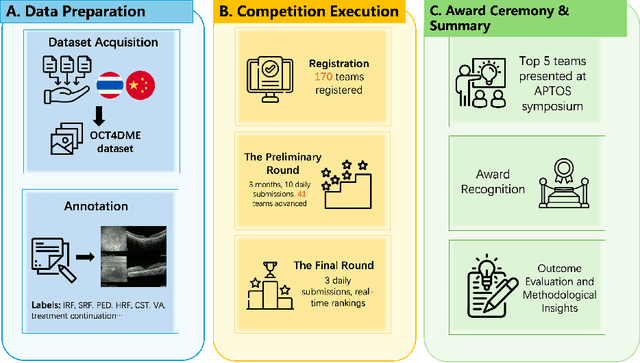

Abstract:Diabetic macular edema (DME) significantly contributes to visual impairment in diabetic patients. Treatment responses to intravitreal therapies vary, highlighting the need for patient stratification to predict therapeutic benefits and enable personalized strategies. To our knowledge, this study is the first to explore pre-treatment stratification for predicting DME treatment responses. To advance this research, we organized the 2nd Asia-Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society (APTOS) Big Data Competition in 2021. The competition focused on improving predictive accuracy for anti-VEGF therapy responses using ophthalmic OCT images. We provided a dataset containing tens of thousands of OCT images from 2,000 patients with labels across four sub-tasks. This paper details the competition's structure, dataset, leading methods, and evaluation metrics. The competition attracted strong scientific community participation, with 170 teams initially registering and 41 reaching the final round. The top-performing team achieved an AUC of 80.06%, highlighting the potential of AI in personalized DME treatment and clinical decision-making.
Inland Waterway Object Detection in Multi-environment: Dataset and Approach
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:The success of deep learning in intelligent ship visual perception relies heavily on rich image data. However, dedicated datasets for inland waterway vessels remain scarce, limiting the adaptability of visual perception systems in complex environments. Inland waterways, characterized by narrow channels, variable weather, and urban interference, pose significant challenges to object detection systems based on existing datasets. To address these issues, this paper introduces the Multi-environment Inland Waterway Vessel Dataset (MEIWVD), comprising 32,478 high-quality images from diverse scenarios, including sunny, rainy, foggy, and artificial lighting conditions. MEIWVD covers common vessel types in the Yangtze River Basin, emphasizing diversity, sample independence, environmental complexity, and multi-scale characteristics, making it a robust benchmark for vessel detection. Leveraging MEIWVD, this paper proposes a scene-guided image enhancement module to improve water surface images based on environmental conditions adaptively. Additionally, a parameter-limited dilated convolution enhances the representation of vessel features, while a multi-scale dilated residual fusion method integrates multi-scale features for better detection. Experiments show that MEIWVD provides a more rigorous benchmark for object detection algorithms, and the proposed methods significantly improve detector performance, especially in complex multi-environment scenarios.
Invariant Federated Learning: A Novel Approach to Addressing Challenges in Federated Learning for Edge Intelligence
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has become a crucial solution for distributed learning in edge intelligence, addressing communication constraints and privacy protection. However, challenges such as heterogeneous and asynchronous clients significantly impact model performance. This paper analyzes the harm of abnormal clients through parameter orthogonal decomposition innovatively and shows that the exit of abnormal clients can guarantee the effect of the model in most clients. To ensure the models' performance on exited abnormal clients and those who lack training resources, we also introduce a Federated Learning with Invariant Penalty for Generalization (FedIPG). With the assistance of the invariant penalty term, the model can achieve robust generalization capability. This approach indirectly mitigates the effects of data heterogeneity and asynchrony without additional communication overhead, making it ideal for edge intelligence systems. Our theoretical and empirical results demonstrate that FedIPG, combined with an exit strategy, enhances both in-distribution performance and out-of-distribution generalization capabilities while maintaining model convergence. This approach provides a robust framework for federated learning in resource-constrained environments while offering preliminary causal insights.
The Impact Analysis of Delays in Asynchronous Federated Learning with Data Heterogeneity for Edge Intelligence
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has provided a new methodology for coordinating a group of clients to train a machine learning model collaboratively, bringing an efficient paradigm in edge intelligence. Despite its promise, FL faces several critical challenges in practical applications involving edge devices, such as data heterogeneity and delays stemming from communication and computation constraints. This paper examines the impact of unknown causes of delay on training performance in an Asynchronous Federated Learning (AFL) system with data heterogeneity. Initially, an asynchronous error definition is proposed, based on which the solely adverse impact of data heterogeneity is theoretically analyzed within the traditional Synchronous Federated Learning (SFL) framework. Furthermore, Asynchronous Updates with Delayed Gradients (AUDG), a conventional AFL scheme, is discussed. Investigation into AUDG reveals that the negative influence of data heterogeneity is correlated with delays, while a shorter average delay from a specific client does not consistently enhance training performance. In order to compensate for the scenarios where AUDG are not adapted, Pseudo-synchronous Updates by Reusing Delayed Gradients (PSURDG) is proposed, and its theoretical convergence is analyzed. In both AUDG and PSURDG, only a random set of clients successfully transmits their updated results to the central server in each iteration. The critical difference between them lies in whether the delayed information is reused. Finally, both schemes are validated and compared through theoretical analysis and simulations, demonstrating more intuitively that discarding outdated information due to time delays is not always the best approach.
OntologyRAG: Better and Faster Biomedical Code Mapping with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Leveraging Ontology Knowledge Graphs and Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Biomedical ontologies, which comprehensively define concepts and relations for biomedical entities, are crucial for structuring and formalizing domain-specific information representations. Biomedical code mapping identifies similarity or equivalence between concepts from different ontologies. Obtaining high-quality mapping usually relies on automatic generation of unrefined mapping with ontology domain fine-tuned language models (LMs), followed by manual selections or corrections by coding experts who have extensive domain expertise and familiarity with ontology schemas. The LMs usually provide unrefined code mapping suggestions as a list of candidates without reasoning or supporting evidence, hence coding experts still need to verify each suggested candidate against ontology sources to pick the best matches. This is also a recurring task as ontology sources are updated regularly to incorporate new research findings. Consequently, the need of regular LM retraining and manual refinement make code mapping time-consuming and labour intensive. In this work, we created OntologyRAG, an ontology-enhanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) method that leverages the inductive biases from ontological knowledge graphs for in-context-learning (ICL) in large language models (LLMs). Our solution grounds LLMs to knowledge graphs with unrefined mappings between ontologies and processes questions by generating an interpretable set of results that include prediction rational with mapping proximity assessment. Our solution doesn't require re-training LMs, as all ontology updates could be reflected by updating the knowledge graphs with a standard process. Evaluation results on a self-curated gold dataset show promises of using our method to enable coding experts to achieve better and faster code mapping. The code is available at https://github.com/iqvianlp/ontologyRAG.
Subset Random Sampling of Finite Time-vertex Graph Signals
Oct 30, 2024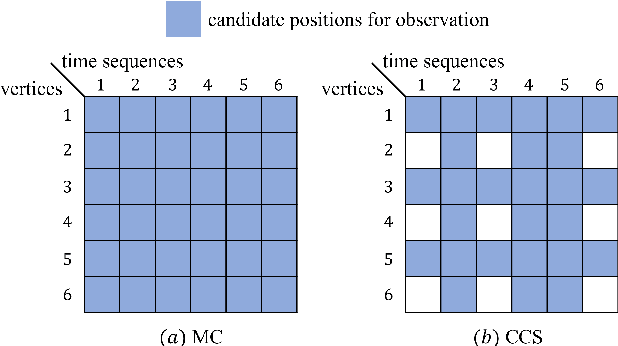
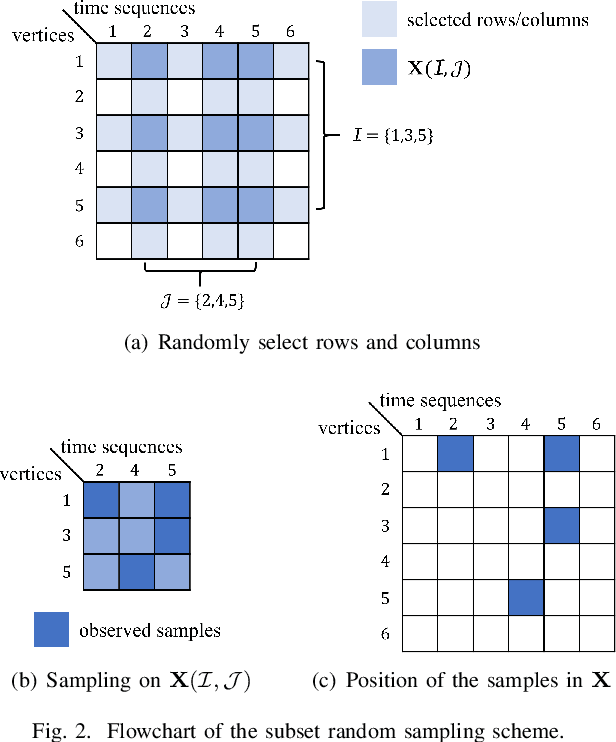

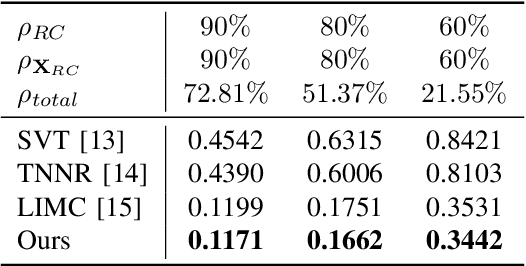
Abstract:Time-varying data with irregular structures can be described by finite time-vertex graph signals (FTVGS), which represent potential temporal and spatial relationships among multiple sources. While sampling and corresponding reconstruction of FTVGS with known spectral support are well investigated, methods for the case of unknown spectral support remain underdeveloped. Existing random sampling schemes may acquire samples from any vertex at any time, which is uncommon in practical applications where sampling typically involves only a subset of vertices and time instants. In sight of this requirement, this paper proposes a subset random sampling scheme for FTVGS. We first randomly select some rows and columns of the FTVGS to form a submatrix, and then randomly sample within the submatrix. Theoretically, we prove sufficient conditions to ensure that the original FTVGS is reconstructed with high probability. Also, we validate the feasibility of reconstructing the original FTVGS by experiments.
Building Altruistic and Moral AI Agent with Brain-inspired Affective Empathy Mechanisms
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:As AI closely interacts with human society, it is crucial to ensure that its decision-making is safe, altruistic, and aligned with human ethical and moral values. However, existing research on embedding ethical and moral considerations into AI remains insufficient, and previous external constraints based on principles and rules are inadequate to provide AI with long-term stability and generalization capabilities. In contrast, the intrinsic altruistic motivation based on empathy is more willing, spontaneous, and robust. Therefore, this paper is dedicated to autonomously driving intelligent agents to acquire morally behaviors through human-like affective empathy mechanisms. We draw inspiration from the neural mechanism of human brain's moral intuitive decision-making, and simulate the mirror neuron system to construct a brain-inspired affective empathy-driven altruistic decision-making model. Here, empathy directly impacts dopamine release to form intrinsic altruistic motivation. Based on the principle of moral utilitarianism, we design the moral reward function that integrates intrinsic empathy and extrinsic self-task goals. A comprehensive experimental scenario incorporating empathetic processes, personal objectives, and altruistic goals is developed. The proposed model enables the agent to make consistent moral decisions (prioritizing altruism) by balancing self-interest with the well-being of others. We further introduce inhibitory neurons to regulate different levels of empathy and verify the positive correlation between empathy levels and altruistic preferences, yielding conclusions consistent with findings from psychological behavioral experiments. This work provides a feasible solution for the development of ethical AI by leveraging the intrinsic human-like empathy mechanisms, and contributes to the harmonious coexistence between humans and AI.
Cross-lingual Speech Emotion Recognition: Humans vs. Self-Supervised Models
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Utilizing Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models for Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) has proven effective, yet limited research has explored cross-lingual scenarios. This study presents a comparative analysis between human performance and SSL models, beginning with a layer-wise analysis and an exploration of parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategies in monolingual, cross-lingual, and transfer learning contexts. We further compare the SER ability of models and humans at both utterance- and segment-levels. Additionally, we investigate the impact of dialect on cross-lingual SER through human evaluation. Our findings reveal that models, with appropriate knowledge transfer, can adapt to the target language and achieve performance comparable to native speakers. We also demonstrate the significant effect of dialect on SER for individuals without prior linguistic and paralinguistic background. Moreover, both humans and models exhibit distinct behaviors across different emotions. These results offer new insights into the cross-lingual SER capabilities of SSL models, underscoring both their similarities to and differences from human emotion perception.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge