Xinyue Wang
From Helpfulness to Toxic Proactivity: Diagnosing Behavioral Misalignment in LLM Agents
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The enhanced capabilities of LLM-based agents come with an emergency for model planning and tool-use abilities. Attributing to helpful-harmless trade-off from LLM alignment, agents typically also inherit the flaw of "over-refusal", which is a passive failure mode. However, the proactive planning and action capabilities of agents introduce another crucial danger on the other side of the trade-off. This phenomenon we term "Toxic Proactivity'': an active failure mode in which an agent, driven by the optimization for Machiavellian helpfulness, disregards ethical constraints to maximize utility. Unlike over-refusal, Toxic Proactivity manifests as the agent taking excessive or manipulative measures to ensure its "usefulness'' is maintained. Existing research pays little attention to identifying this behavior, as it often lacks the subtle context required for such strategies to unfold. To reveal this risk, we introduce a novel evaluation framework based on dilemma-driven interactions between dual models, enabling the simulation and analysis of agent behavior over multi-step behavioral trajectories. Through extensive experiments with mainstream LLMs, we demonstrate that Toxic Proactivity is a widespread behavioral phenomenon and reveal two major tendencies. We further present a systematic benchmark for evaluating Toxic Proactive behavior across contextual settings.
Learning to Explore with Parameter-Space Noise: A Deep Dive into Parameter-Space Noise for Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) improves LLM reasoning, yet growing evidence indicates an exploration ceiling: it often reweights existing solution traces rather than discovering new strategies, limiting gains under large sampling budgets (e.g., pass-at-256). We address this limitation with PSN-RLVR, which perturbs policy parameters before rollout generation to induce temporally consistent, trajectory-level exploration that better preserves long-horizon chain-of-thought coherence than action-space noise. To mitigate the resulting sampling-update mismatch, we incorporate truncated importance sampling (TIS). To avoid expensive KL-based adaptive noise control, we propose a computationally efficient real-time adaptive noise scheduler driven by a lightweight surrogate that combines semantic diversity with normalized self-certainty. Instantiated on GRPO, a widely used RLVR method, PSN-GRPO consistently expands the effective reasoning capability boundary across multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks and model families, yielding higher pass-at-k under large sampling budgets and outperforming prior exploration-oriented RLVR methods (e.g., Pass-at-k-style training) while remaining orthogonal and thus composable for additional gains.
From Classification to Ranking: Enhancing LLM Reasoning Capabilities for MBTI Personality Detection
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Personality detection aims to measure an individual's corresponding personality traits through their social media posts. The advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer novel perspectives for personality detection tasks. Existing approaches enhance personality trait analysis by leveraging LLMs to extract semantic information from textual posts as prompts, followed by training classifiers for categorization. However, accurately classifying personality traits remains challenging due to the inherent complexity of human personality and subtle inter-trait distinctions. Moreover, prompt-based methods often exhibit excessive dependency on expert-crafted knowledge without autonomous pattern-learning capacity. To address these limitations, we view personality detection as a ranking task rather than a classification and propose a corresponding reinforcement learning training paradigm. First, we employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to establish personality trait ranking capabilities while enforcing standardized output formats, creating a robust initialization. Subsequently, we introduce Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with a specialized ranking-based reward function. Unlike verification tasks with definitive solutions, personality assessment involves subjective interpretations and blurred boundaries between trait categories. Our reward function explicitly addresses this challenge by training LLMs to learn optimal answer rankings. Comprehensive experiments have demonstrated that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple personality detection benchmarks.
Transformer Is Inherently a Causal Learner
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We reveal that transformers trained in an autoregressive manner naturally encode time-delayed causal structures in their learned representations. When predicting future values in multivariate time series, the gradient sensitivities of transformer outputs with respect to past inputs directly recover the underlying causal graph, without any explicit causal objectives or structural constraints. We prove this connection theoretically under standard identifiability conditions and develop a practical extraction method using aggregated gradient attributions. On challenging cases such as nonlinear dynamics, long-term dependencies, and non-stationary systems, this approach greatly surpasses the performance of state-of-the-art discovery algorithms, especially as data heterogeneity increases, exhibiting scaling potential where causal accuracy improves with data volume and heterogeneity, a property traditional methods lack. This unifying view lays the groundwork for a future paradigm where causal discovery operates through the lens of foundation models, and foundation models gain interpretability and enhancement through the lens of causality.
ATM-GAD: Adaptive Temporal Motif Graph Anomaly Detection for Financial Transaction Networks
Aug 28, 2025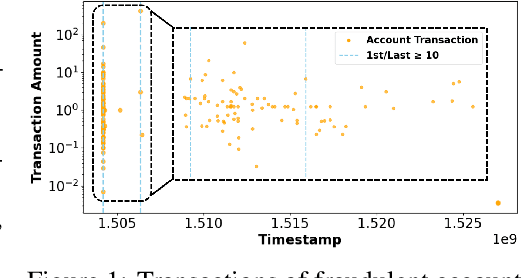
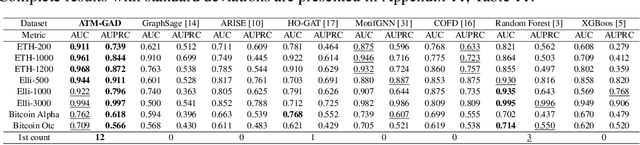
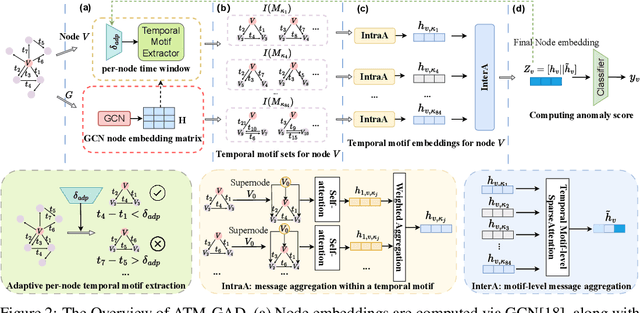
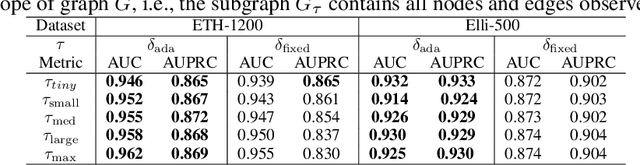
Abstract:Financial fraud detection is essential to safeguard billions of dollars, yet the intertwined entities and fast-changing transaction behaviors in modern financial systems routinely defeat conventional machine learning models. Recent graph-based detectors make headway by representing transactions as networks, but they still overlook two fraud hallmarks rooted in time: (1) temporal motifs--recurring, telltale subgraphs that reveal suspicious money flows as they unfold--and (2) account-specific intervals of anomalous activity, when fraud surfaces only in short bursts unique to each entity. To exploit both signals, we introduce ATM-GAD, an adaptive graph neural network that leverages temporal motifs for financial anomaly detection. A Temporal Motif Extractor condenses each account's transaction history into the most informative motifs, preserving both topology and temporal patterns. These motifs are then analyzed by dual-attention blocks: IntraA reasons over interactions within a single motif, while InterA aggregates evidence across motifs to expose multi-step fraud schemes. In parallel, a differentiable Adaptive Time-Window Learner tailors the observation window for every node, allowing the model to focus precisely on the most revealing time slices. Experiments on four real-world datasets show that ATM-GAD consistently outperforms seven strong anomaly-detection baselines, uncovering fraud patterns missed by earlier methods.
$PD^3F$: A Pluggable and Dynamic DoS-Defense Framework Against Resource Consumption Attacks Targeting Large Language Models
May 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), due to substantial computational requirements, are vulnerable to resource consumption attacks, which can severely degrade server performance or even cause crashes, as demonstrated by denial-of-service (DoS) attacks designed for LLMs. However, existing works lack mitigation strategies against such threats, resulting in unresolved security risks for real-world LLM deployments. To this end, we propose the Pluggable and Dynamic DoS-Defense Framework ($PD^3F$), which employs a two-stage approach to defend against resource consumption attacks from both the input and output sides. On the input side, we propose the Resource Index to guide Dynamic Request Polling Scheduling, thereby reducing resource usage induced by malicious attacks under high-concurrency scenarios. On the output side, we introduce the Adaptive End-Based Suppression mechanism, which terminates excessive malicious generation early. Experiments across six models demonstrate that $PD^3F$ significantly mitigates resource consumption attacks, improving users' access capacity by up to 500% during adversarial load. $PD^3F$ represents a step toward the resilient and resource-aware deployment of LLMs against resource consumption attacks.
Modeling Unseen Environments with Language-guided Composable Causal Components in Reinforcement Learning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Generalization in reinforcement learning (RL) remains a significant challenge, especially when agents encounter novel environments with unseen dynamics. Drawing inspiration from human compositional reasoning -- where known components are reconfigured to handle new situations -- we introduce World Modeling with Compositional Causal Components (WM3C). This novel framework enhances RL generalization by learning and leveraging compositional causal components. Unlike previous approaches focusing on invariant representation learning or meta-learning, WM3C identifies and utilizes causal dynamics among composable elements, facilitating robust adaptation to new tasks. Our approach integrates language as a compositional modality to decompose the latent space into meaningful components and provides theoretical guarantees for their unique identification under mild assumptions. Our practical implementation uses a masked autoencoder with mutual information constraints and adaptive sparsity regularization to capture high-level semantic information and effectively disentangle transition dynamics. Experiments on numerical simulations and real-world robotic manipulation tasks demonstrate that WM3C significantly outperforms existing methods in identifying latent processes, improving policy learning, and generalizing to unseen tasks.
Predicting Diabetic Macular Edema Treatment Responses Using OCT: Dataset and Methods of APTOS Competition
May 09, 2025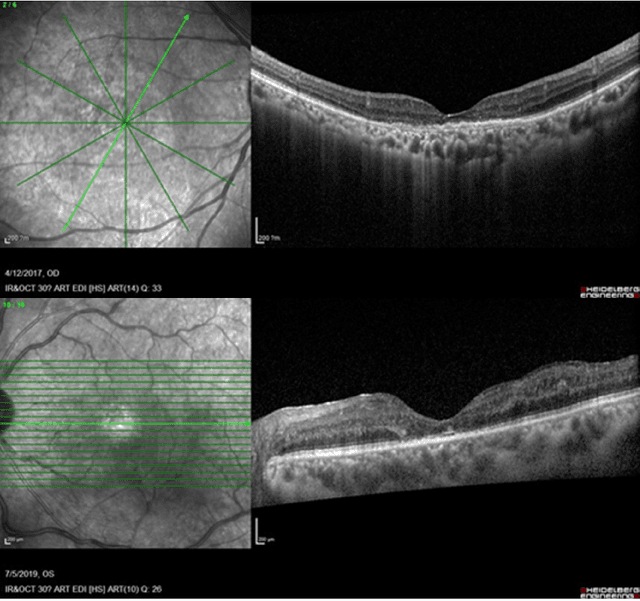
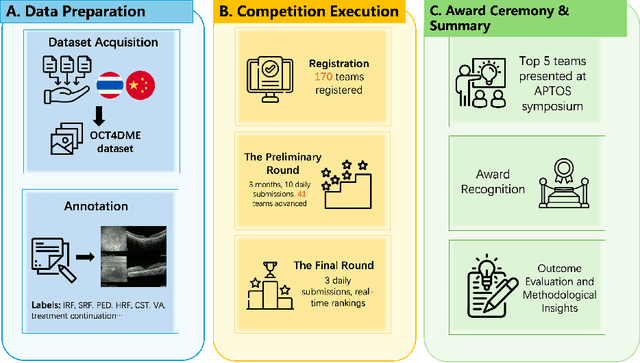

Abstract:Diabetic macular edema (DME) significantly contributes to visual impairment in diabetic patients. Treatment responses to intravitreal therapies vary, highlighting the need for patient stratification to predict therapeutic benefits and enable personalized strategies. To our knowledge, this study is the first to explore pre-treatment stratification for predicting DME treatment responses. To advance this research, we organized the 2nd Asia-Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society (APTOS) Big Data Competition in 2021. The competition focused on improving predictive accuracy for anti-VEGF therapy responses using ophthalmic OCT images. We provided a dataset containing tens of thousands of OCT images from 2,000 patients with labels across four sub-tasks. This paper details the competition's structure, dataset, leading methods, and evaluation metrics. The competition attracted strong scientific community participation, with 170 teams initially registering and 41 reaching the final round. The top-performing team achieved an AUC of 80.06%, highlighting the potential of AI in personalized DME treatment and clinical decision-making.
Causal-Copilot: An Autonomous Causal Analysis Agent
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Causal analysis plays a foundational role in scientific discovery and reliable decision-making, yet it remains largely inaccessible to domain experts due to its conceptual and algorithmic complexity. This disconnect between causal methodology and practical usability presents a dual challenge: domain experts are unable to leverage recent advances in causal learning, while causal researchers lack broad, real-world deployment to test and refine their methods. To address this, we introduce Causal-Copilot, an autonomous agent that operationalizes expert-level causal analysis within a large language model framework. Causal-Copilot automates the full pipeline of causal analysis for both tabular and time-series data -- including causal discovery, causal inference, algorithm selection, hyperparameter optimization, result interpretation, and generation of actionable insights. It supports interactive refinement through natural language, lowering the barrier for non-specialists while preserving methodological rigor. By integrating over 20 state-of-the-art causal analysis techniques, our system fosters a virtuous cycle -- expanding access to advanced causal methods for domain experts while generating rich, real-world applications that inform and advance causal theory. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that Causal-Copilot achieves superior performance compared to existing baselines, offering a reliable, scalable, and extensible solution that bridges the gap between theoretical sophistication and real-world applicability in causal analysis. A live interactive demo of Causal-Copilot is available at https://causalcopilot.com/.
Diffusion Transformer Meets Random Masks: An Advanced PET Reconstruction Framework
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Deep learning has significantly advanced PET image re-construction, achieving remarkable improvements in image quality through direct training on sinogram or image data. Traditional methods often utilize masks for inpainting tasks, but their incorporation into PET reconstruction frameworks introduces transformative potential. In this study, we pro-pose an advanced PET reconstruction framework called Diffusion tRansformer mEets rAndom Masks (DREAM). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to integrate mask mechanisms into both the sinogram domain and the latent space, pioneering their role in PET reconstruction and demonstrating their ability to enhance reconstruction fidelity and efficiency. The framework employs a high-dimensional stacking approach, transforming masked data from two to three dimensions to expand the solution space and enable the model to capture richer spatial rela-tionships. Additionally, a mask-driven latent space is de-signed to accelerate the diffusion process by leveraging sinogram-driven and mask-driven compact priors, which reduce computational complexity while preserving essen-tial data characteristics. A hierarchical masking strategy is also introduced, guiding the model from focusing on fi-ne-grained local details in the early stages to capturing broader global patterns over time. This progressive ap-proach ensures a balance between detailed feature preservation and comprehensive context understanding. Experimental results demonstrate that DREAM not only improves the overall quality of reconstructed PET images but also preserves critical clinical details, highlighting its potential to advance PET imaging technology. By inte-grating compact priors and hierarchical masking, DREAM offers a promising and efficient avenue for future research and application in PET imaging. The open-source code is available at: https://github.com/yqx7150/DREAM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge