Xiaofeng Wu
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Information Gain-based Policy Optimization: A Simple and Effective Approach for Multi-Turn LLM Agents
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents are increasingly trained with reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance their ability to interact with external environments through tool use, particularly in search-based settings that require multi-turn reasoning and knowledge acquisition. However, existing approaches typically rely on outcome-based rewards that are only provided at the final answer. This reward sparsity becomes particularly problematic in multi-turn settings, where long trajectories exacerbate two critical issues: (i) advantage collapse, where all rollouts receive identical rewards and provide no useful learning signals, and (ii) lack of fine-grained credit assignment, where dependencies between turns are obscured, especially in long-horizon tasks. In this paper, we propose Information Gain-based Policy Optimization (IGPO), a simple yet effective RL framework that provides dense and intrinsic supervision for multi-turn agent training. IGPO models each interaction turn as an incremental process of acquiring information about the ground truth, and defines turn-level rewards as the marginal increase in the policy's probability of producing the correct answer. Unlike prior process-level reward approaches that depend on external reward models or costly Monte Carlo estimation, IGPO derives intrinsic rewards directly from the model's own belief updates. These intrinsic turn-level rewards are combined with outcome-level supervision to form dense reward trajectories. Extensive experiments on both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks demonstrate that IGPO consistently outperforms strong baselines in multi-turn scenarios, achieving higher accuracy and improved sample efficiency.
Evaluating LLMs on Chinese Idiom Translation
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Idioms, whose figurative meanings usually differ from their literal interpretations, are common in everyday language, especially in Chinese, where they often contain historical references and follow specific structural patterns. Despite recent progress in machine translation with large language models, little is known about Chinese idiom translation. In this work, we introduce IdiomEval, a framework with a comprehensive error taxonomy for Chinese idiom translation. We annotate 900 translation pairs from nine modern systems, including GPT-4o and Google Translate, across four domains: web, news, Wikipedia, and social media. We find these systems fail at idiom translation, producing incorrect, literal, partial, or even missing translations. The best-performing system, GPT-4, makes errors in 28% of cases. We also find that existing evaluation metrics measure idiom quality poorly with Pearson correlation below 0.48 with human ratings. We thus develop improved models that achieve F$_1$ scores of 0.68 for detecting idiom translation errors.
Tabular Data Understanding with LLMs: A Survey of Recent Advances and Challenges
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Tables have gained significant attention in large language models (LLMs) and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) due to their complex and flexible structure. Unlike linear text inputs, tables are two-dimensional, encompassing formats that range from well-structured database tables to complex, multi-layered spreadsheets, each with different purposes. This diversity in format and purpose has led to the development of specialized methods and tasks, instead of universal approaches, making navigation of table understanding tasks challenging. To address these challenges, this paper introduces key concepts through a taxonomy of tabular input representations and an introduction of table understanding tasks. We highlight several critical gaps in the field that indicate the need for further research: (1) the predominance of retrieval-focused tasks that require minimal reasoning beyond mathematical and logical operations; (2) significant challenges faced by models when processing complex table structures, large-scale tables, length context, or multi-table scenarios; and (3) the limited generalization of models across different tabular representations and formats.
Discrete Codebook Design for Self-interference Suppression in mmWave ISAC
Apr 22, 2025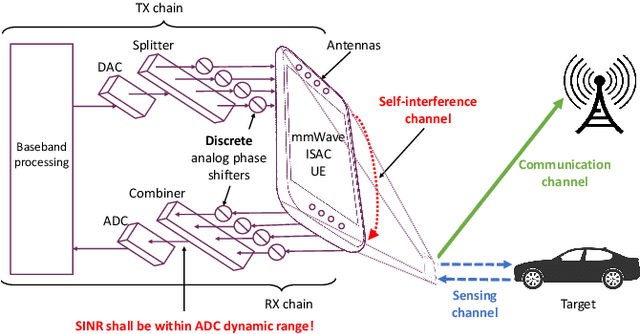
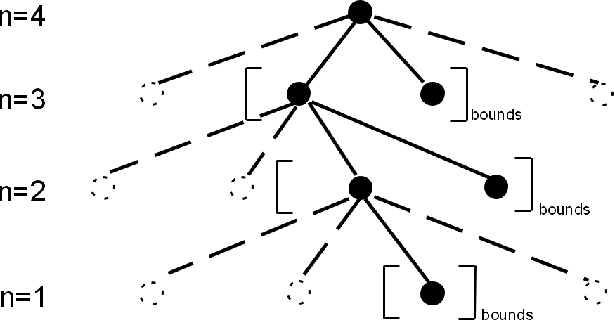
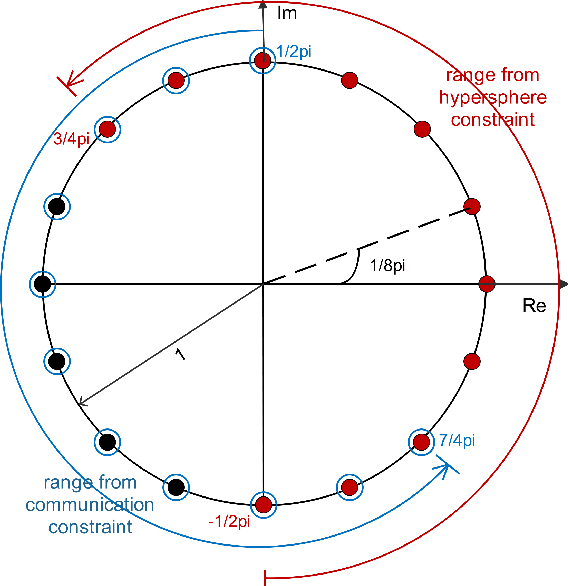
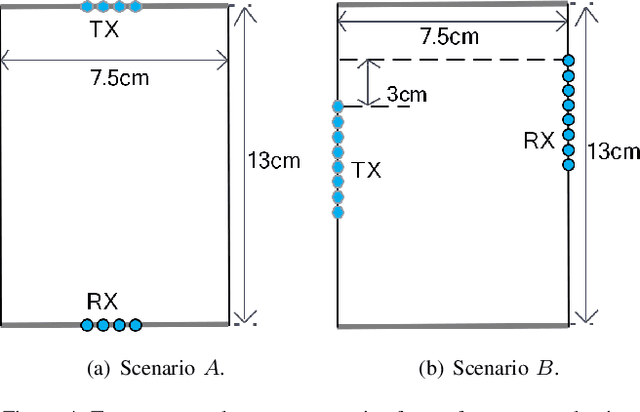
Abstract:This paper presents discrete codebook synthesis methods for self-interference (SI) suppression in a mmWave device, designed to support FD ISAC. We formulate a SINR maximization problem that optimizes the RX and TX codewords, aimed at suppressing the near-field SI signal while maintaining the beamforming gain in the far-field sensing directions. The formulation considers the practical constraints of discrete RX and TX codebooks with quantized phase settings, as well as a TX beamforming gain requirement in the specified communication direction. Under an alternating optimization framework, the RX and TX codewords are iteratively optimized, with one fixed while the other is optimized. When the TX codeword is fixed, we show that the RX codeword optimization problem can be formulated as an integer quadratic fractional programming (IQFP) problem. Using Dinkelbach's algorithm, we transform the problem into a sequence of subproblems in which the numerator and the denominator of the objective function are decoupled. These subproblems, subject to discrete constraints, are then efficiently solved by the spherical search (SS) method. This overall approach is referred to as FP-SS. When the RX codeword is fixed, the TX codeword optimization problem can similarly be formulated as an IQFP problem, whereas an additional TX beamforming constraint for communication needs to be considered. The problem is solved through Dinkelbach's transformation followed by the constrained spherical search (CSS), and we refer to this approach as FP-CSS. Finally, we integrate the FP-SS and FP-CSS methods into a joint RX-TX codebook design approach. Simulations show that, the proposed FP-SS and FP-CSS achieve the same SI suppression performance as the corresponding exhaustive search method, but with much lower complexity. Furthermore, the alternating optimization framework achieved even better SI suppression performance.
Efficient UAV Swarm-Based Multi-Task Federated Learning with Dynamic Task Knowledge Sharing
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:UAV swarms are widely used in emergency communications, area monitoring, and disaster relief. Coordinated by control centers, they are ideal for federated learning (FL) frameworks. However, current UAV-assisted FL methods primarily focus on single tasks, overlooking the need for multi-task training. In disaster relief scenarios, UAVs perform tasks such as crowd detection, road feasibility analysis, and disaster assessment, which exhibit time-varying demands and potential correlations. In order to meet the time-varying requirements of tasks and complete multiple tasks efficiently under resource constraints, in this paper, we propose a UAV swarm based multi-task FL framework, where ground emergency vehicles (EVs) collaborate with UAVs to accomplish multiple tasks efficiently under constrained energy and bandwidth resources. Through theoretical analysis, we identify key factors affecting task performance and introduce a task attention mechanism to dynamically evaluate task importance, thereby achieving efficient resource allocation. Additionally, we propose a task affinity (TA) metric to capture the dynamic correlation among tasks, thereby promoting task knowledge sharing to accelerate training and improve the generalization ability of the model in different scenarios. To optimize resource allocation, we formulate a two-layer optimization problem to jointly optimize UAV transmission power, computation frequency, bandwidth allocation, and UAV-EV associations. For the inner problem, we derive closed-form solutions for transmission power, computation frequency, and bandwidth allocation and apply a block coordinate descent method for optimization. For the outer problem, a two-stage algorithm is designed to determine optimal UAV-EV associations. Furthermore, theoretical analysis reveals a trade-off between UAV energy consumption and multi-task performance.
Drift-Aware Federated Learning: A Causal Perspective
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) facilitates collaborative model training among multiple clients while preserving data privacy, often resulting in enhanced performance compared to models trained by individual clients. However, factors such as communication frequency and data distribution can contribute to feature drift, hindering the attainment of optimal training performance. This paper examine the relationship between model update drift and global as well as local optimizer from causal perspective. The influence of the global optimizer on feature drift primarily arises from the participation frequency of certain clients in server updates, whereas the effect of the local optimizer is typically associated with imbalanced data distributions.To mitigate this drift, we propose a novel framework termed Causal drift-Aware Federated lEarning (CAFE). CAFE exploits the causal relationship between feature-invariant components and classification outcomes to independently calibrate local client sample features and classifiers during the training phase. In the inference phase, it eliminated the drifts in the global model that favor frequently communicating clients.Experimental results demonstrate that CAFE's integration of feature calibration, parameter calibration, and historical information effectively reduces both drift towards majority classes and tendencies toward frequently communicating nodes.
Invariant Federated Learning: A Novel Approach to Addressing Challenges in Federated Learning for Edge Intelligence
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has become a crucial solution for distributed learning in edge intelligence, addressing communication constraints and privacy protection. However, challenges such as heterogeneous and asynchronous clients significantly impact model performance. This paper analyzes the harm of abnormal clients through parameter orthogonal decomposition innovatively and shows that the exit of abnormal clients can guarantee the effect of the model in most clients. To ensure the models' performance on exited abnormal clients and those who lack training resources, we also introduce a Federated Learning with Invariant Penalty for Generalization (FedIPG). With the assistance of the invariant penalty term, the model can achieve robust generalization capability. This approach indirectly mitigates the effects of data heterogeneity and asynchrony without additional communication overhead, making it ideal for edge intelligence systems. Our theoretical and empirical results demonstrate that FedIPG, combined with an exit strategy, enhances both in-distribution performance and out-of-distribution generalization capabilities while maintaining model convergence. This approach provides a robust framework for federated learning in resource-constrained environments while offering preliminary causal insights.
The Impact Analysis of Delays in Asynchronous Federated Learning with Data Heterogeneity for Edge Intelligence
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has provided a new methodology for coordinating a group of clients to train a machine learning model collaboratively, bringing an efficient paradigm in edge intelligence. Despite its promise, FL faces several critical challenges in practical applications involving edge devices, such as data heterogeneity and delays stemming from communication and computation constraints. This paper examines the impact of unknown causes of delay on training performance in an Asynchronous Federated Learning (AFL) system with data heterogeneity. Initially, an asynchronous error definition is proposed, based on which the solely adverse impact of data heterogeneity is theoretically analyzed within the traditional Synchronous Federated Learning (SFL) framework. Furthermore, Asynchronous Updates with Delayed Gradients (AUDG), a conventional AFL scheme, is discussed. Investigation into AUDG reveals that the negative influence of data heterogeneity is correlated with delays, while a shorter average delay from a specific client does not consistently enhance training performance. In order to compensate for the scenarios where AUDG are not adapted, Pseudo-synchronous Updates by Reusing Delayed Gradients (PSURDG) is proposed, and its theoretical convergence is analyzed. In both AUDG and PSURDG, only a random set of clients successfully transmits their updated results to the central server in each iteration. The critical difference between them lies in whether the delayed information is reused. Finally, both schemes are validated and compared through theoretical analysis and simulations, demonstrating more intuitively that discarding outdated information due to time delays is not always the best approach.
MAB-Based Channel Scheduling for Asynchronous Federated Learning in Non-Stationary Environments
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Federated learning enables distributed model training across clients under central coordination without raw data exchange. However, in wireless implementations, frequent parameter updates between the server and clients create significant communication overhead. While existing research assumes known channel state information (CSI) or stationary distributions, practical wireless channels exhibit non-stationary characteristics due to channel fading, user mobility, and hostile attacks. The unavailability of CSI and time-varying statistics can cause unpredictable transmission failures, exacerbating client staleness and affecting model convergence. To address these challenges, we propose an asynchronous federated learning scheduling framework for non-stationary channel environments to reduce staleness while promoting fair and efficient communication and aggregation.We focus on two channel scenarios: extremely non-stationary and piecewise stationary. Age of Information (AoI) quantifies client staleness under non-stationary conditions. Through a rigorous convergence analysis, we explore how AoI and per-round client participation affect learning performance. The scheduling problem is modeled within a multi-armed bandit (MAB) framework, and we derive the theoretical lower bounds on AoI regret. Based on these findings, we develop scheduling strategies for both scenarios using the GLR-CUCB and M-exp3 algorithms, also deriving their respective upper bounds on AoI regret. To address imbalanced client updates, we introduce an adaptive allocation strategy that incorporates marginal utility and fairness. Simulations demonstrate that our algorithm reduces AoI regret growth, accelerates federated learning convergence, and promotes fairer aggregation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge