Ziqi Zhang
Peking University
Connect the Dots: Knowledge Graph-Guided Crawler Attack on Retrieval-Augmented Generation Systems
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems integrate document retrieval with large language models and have been widely adopted. However, in privacy-related scenarios, RAG introduces a new privacy risk: adversaries can issue carefully crafted queries to exfiltrate sensitive content from the underlying corpus gradually. Although recent studies have demonstrated multi-turn extraction attacks, they rely on heuristics and fail to perform long-term extraction planning. To address these limitations, we formulate the RAG extraction attack as an adaptive stochastic coverage problem (ASCP). In ASCP, each query is treated as a probabilistic action that aims to maximize conditional marginal gain (CMG), enabling principled long-term planning under uncertainty. However, integrating ASCP with practical RAG attack faces three key challenges: unobservable CMG, intractability in the action space, and feasibility constraints. To overcome these challenges, we maintain a global attacker-side state to guide the attack. Building on this idea, we introduce RAGCRAWLER, which builds a knowledge graph to represent revealed information, uses this global state to estimate CMG, and plans queries in semantic space that target unretrieved regions. In comprehensive experiments across diverse RAG architectures and datasets, our proposed method, RAGCRAWLER, consistently outperforms all baselines. It achieves up to 84.4% corpus coverage within a fixed query budget and deliver an average improvement of 20.7% over the top-performing baseline. It also maintains high semantic fidelity and strong content reconstruction accuracy with low attack cost. Crucially, RAGCRAWLER proves its robustness by maintaining effectiveness against advanced RAG systems employing query rewriting and multi-query retrieval strategies. Our work reveals significant security gaps and highlights the pressing need for stronger safeguards for RAG.
CCAD: Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection holds considerable industrial significance, especially in scenarios with limited anomalous data. Currently, reconstruction-based and unsupervised representation-based approaches are the primary focus. However, unsupervised representation-based methods struggle to extract robust features under domain shift, whereas reconstruction-based methods often suffer from low training efficiency and performance degradation due to insufficient constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method named Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection (CCAD). CCAD synergizes the strengths of both paradigms by adapting global features as a new modality condition for the reconstruction model. Furthermore, we design an adaptive compression mechanism to enhance both generalization and training efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CCAD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of AUC while achieving faster convergence. In addition, we contribute a reorganized and re-annotated version of the DAGM 2007 dataset with new annotations to further validate our method's effectiveness. The code for reproducing main results is available at https://github.com/chloeqxq/CCAD.
UrbanV2X: A Multisensory Vehicle-Infrastructure Dataset for Cooperative Navigation in Urban Areas
Dec 23, 2025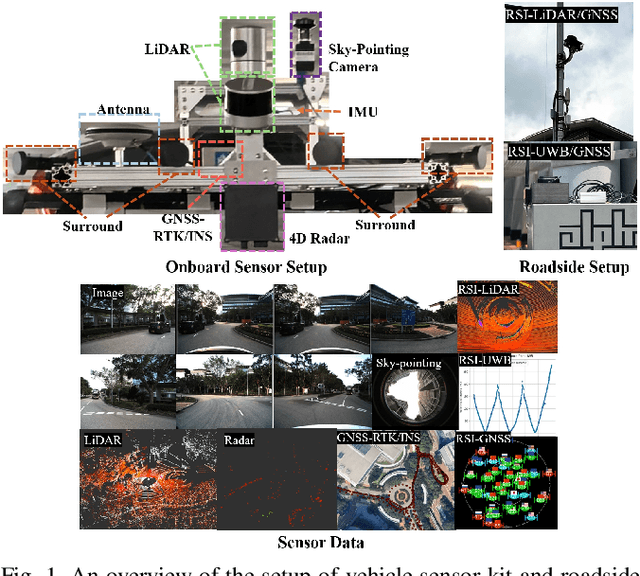
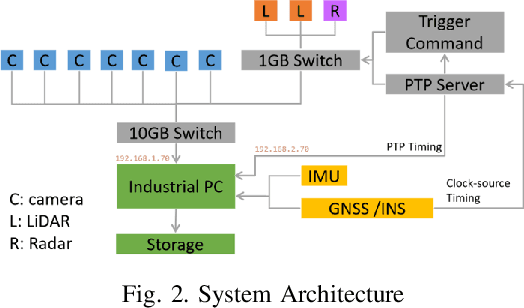

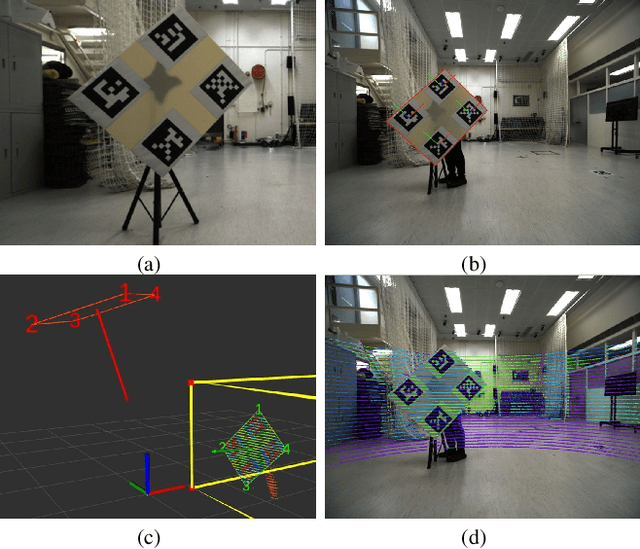
Abstract:Due to the limitations of a single autonomous vehicle, Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X) technology opens a new window for achieving fully autonomous driving through sensor information sharing. However, real-world datasets supporting vehicle-infrastructure cooperative navigation in complex urban environments remain rare. To address this gap, we present UrbanV2X, a comprehensive multisensory dataset collected from vehicles and roadside infrastructure in the Hong Kong C-V2X testbed, designed to support research on smart mobility applications in dense urban areas. Our onboard platform provides synchronized data from multiple industrial cameras, LiDARs, 4D radar, ultra-wideband (UWB), IMU, and high-precision GNSS-RTK/INS navigation systems. Meanwhile, our roadside infrastructure provides LiDAR, GNSS, and UWB measurements. The entire vehicle-infrastructure platform is synchronized using the Precision Time Protocol (PTP), with sensor calibration data provided. We also benchmark various navigation algorithms to evaluate the collected cooperative data. The dataset is publicly available at https://polyu-taslab.github.io/UrbanV2X/.
MMhops-R1: Multimodal Multi-hop Reasoning
Dec 16, 2025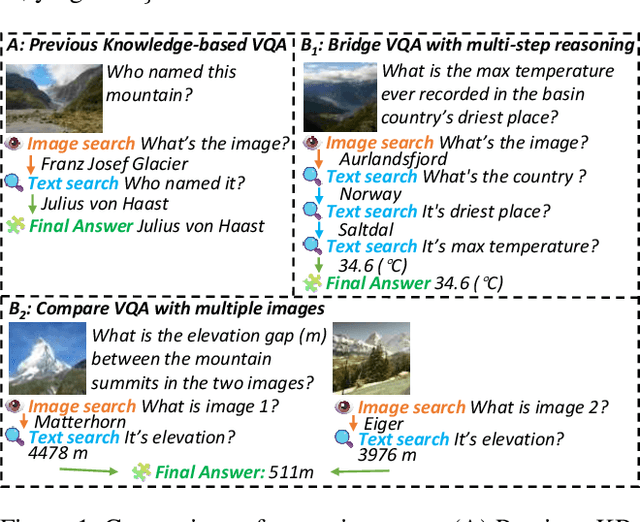

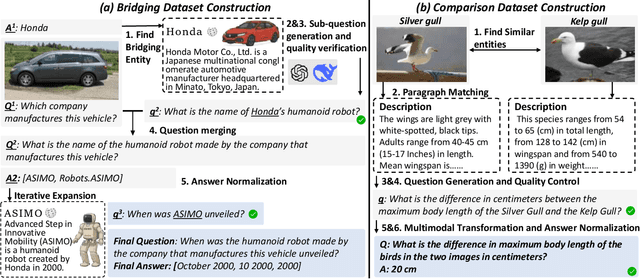
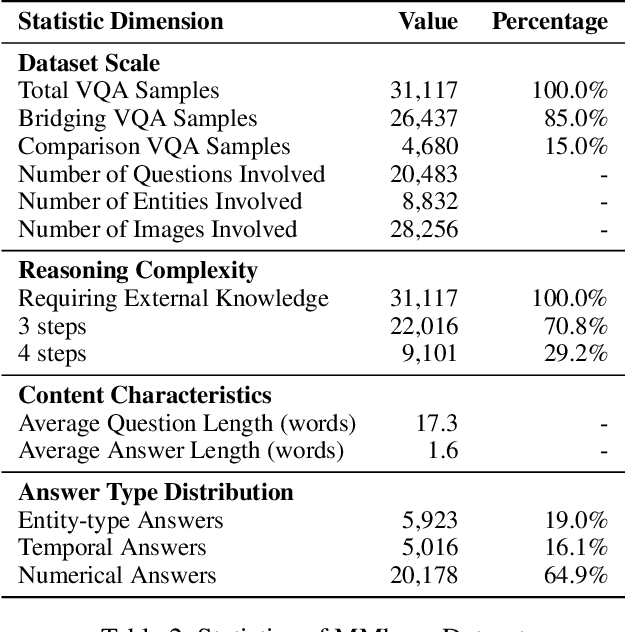
Abstract:The ability to perform multi-modal multi-hop reasoning by iteratively integrating information across various modalities and external knowledge is critical for addressing complex real-world challenges. However, existing Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are predominantly limited to single-step reasoning, as existing benchmarks lack the complexity needed to evaluate and drive multi-hop abilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce MMhops, a novel, large-scale benchmark designed to systematically evaluate and foster multi-modal multi-hop reasoning. MMhops dataset comprises two challenging task formats, Bridging and Comparison, which necessitate that models dynamically construct complex reasoning chains by integrating external knowledge. To tackle the challenges posed by MMhops, we propose MMhops-R1, a novel multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (mRAG) framework for dynamic reasoning. Our framework utilizes reinforcement learning to optimize the model for autonomously planning reasoning paths, formulating targeted queries, and synthesizing multi-level information. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MMhops-R1 significantly outperforms strong baselines on MMhops, highlighting that dynamic planning and multi-modal knowledge integration are crucial for complex reasoning. Moreover, MMhops-R1 demonstrates strong generalization to tasks requiring fixed-hop reasoning, underscoring the robustness of our dynamic planning approach. In conclusion, our work contributes a challenging new benchmark and a powerful baseline model, and we will release the associated code, data, and weights to catalyze future research in this critical area.
Taming Transformer for Emotion-Controllable Talking Face Generation
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Talking face generation is a novel and challenging generation task, aiming at synthesizing a vivid speaking-face video given a specific audio. To fulfill emotion-controllable talking face generation, current methods need to overcome two challenges: One is how to effectively model the multimodal relationship related to the specific emotion, and the other is how to leverage this relationship to synthesize identity preserving emotional videos. In this paper, we propose a novel method to tackle the emotion-controllable talking face generation task discretely. Specifically, we employ two pre-training strategies to disentangle audio into independent components and quantize videos into combinations of visual tokens. Subsequently, we propose the emotion-anchor (EA) representation that integrates the emotional information into visual tokens. Finally, we introduce an autoregressive transformer to model the global distribution of the visual tokens under the given conditions and further predict the index sequence for synthesizing the manipulated videos. We conduct experiments on the MEAD dataset that controls the emotion of videos conditioned on multiple emotional audios. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiorities of our method both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Membership and Memorization in LLM Knowledge Distillation
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Knowledge Distillation (KD) aim to mitigate the high computational demands of Large Language Models (LLMs) by transferring knowledge from a large ''teacher'' to a smaller ''student'' model. However, students may inherit the teacher's privacy when the teacher is trained on private data. In this work, we systematically characterize and investigate membership and memorization privacy risks inherent in six LLM KD techniques. Using instruction-tuning settings that span seven NLP tasks, together with three teacher model families (GPT-2, LLAMA-2, and OPT), and various size student models, we demonstrate that all existing LLM KD approaches carry membership and memorization privacy risks from the teacher to its students. However, the extent of privacy risks varies across different KD techniques. We systematically analyse how key LLM KD components (KD objective functions, student training data and NLP tasks) impact such privacy risks. We also demonstrate a significant disagreement between memorization and membership privacy risks of LLM KD techniques. Finally, we characterize per-block privacy risk and demonstrate that the privacy risk varies across different blocks by a large margin.
VeFIA: An Efficient Inference Auditing Framework for Vertical Federated Collaborative Software
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Vertical Federated Learning (VFL) is a distributed AI software deployment mechanism for cross-silo collaboration without accessing participants' data. However, existing VFL work lacks a mechanism to audit the execution correctness of the inference software of the data party. To address this problem, we design a Vertical Federated Inference Auditing (VeFIA) framework. VeFIA helps the task party to audit whether the data party's inference software is executed as expected during large-scale inference without leaking the data privacy of the data party or introducing additional latency to the inference system. The core of VeFIA is that the task party can use the inference results from a framework with Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) and the coordinator to validate the correctness of the data party's computation results. VeFIA guarantees that, as long as the abnormal inference exceeds 5.4%, the task party can detect execution anomalies in the inference software with a probability of 99.99%, without incurring any additional online inference latency. VeFIA's random sampling validation achieves 100% positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and true positive rate in detecting abnormal inference. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first paper to discuss the correctness of inference software execution in VFL.
SEC-bench: Automated Benchmarking of LLM Agents on Real-World Software Security Tasks
Jun 13, 2025



Abstract:Rigorous security-focused evaluation of large language model (LLM) agents is imperative for establishing trust in their safe deployment throughout the software development lifecycle. However, existing benchmarks largely rely on synthetic challenges or simplified vulnerability datasets that fail to capture the complexity and ambiguity encountered by security engineers in practice. We introduce SEC-bench, the first fully automated benchmarking framework for evaluating LLM agents on authentic security engineering tasks. SEC-bench employs a novel multi-agent scaffold that automatically constructs code repositories with harnesses, reproduces vulnerabilities in isolated environments, and generates gold patches for reliable evaluation. Our framework automatically creates high-quality software vulnerability datasets with reproducible artifacts at a cost of only $0.87 per instance. Using SEC-bench, we implement two critical software security tasks to rigorously evaluate LLM agents' capabilities: proof-of-concept (PoC) generation and vulnerability patching. A comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art LLM code agents reveals significant performance gaps, achieving at most 18.0% success in PoC generation and 34.0% in vulnerability patching on our complete dataset. These results highlight the crucial steps needed toward developing LLM agents that are more practical, intelligent, and autonomous for security engineering.
STAR-R1: Spatial TrAnsformation Reasoning by Reinforcing Multimodal LLMs
May 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, yet they lag significantly behind humans in spatial reasoning. We investigate this gap through Transformation-Driven Visual Reasoning (TVR), a challenging task requiring identification of object transformations across images under varying viewpoints. While traditional Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) fails to generate coherent reasoning paths in cross-view settings, sparse-reward Reinforcement Learning (RL) suffers from inefficient exploration and slow convergence. To address these limitations, we propose STAR-R1, a novel framework that integrates a single-stage RL paradigm with a fine-grained reward mechanism tailored for TVR. Specifically, STAR-R1 rewards partial correctness while penalizing excessive enumeration and passive inaction, enabling efficient exploration and precise reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that STAR-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance across all 11 metrics, outperforming SFT by 23% in cross-view scenarios. Further analysis reveals STAR-R1's anthropomorphic behavior and highlights its unique ability to compare all objects for improving spatial reasoning. Our work provides critical insights in advancing the research of MLLMs and reasoning models. The codes, model weights, and data will be publicly available at https://github.com/zongzhao23/STAR-R1.
DetailFusion: A Dual-branch Framework with Detail Enhancement for Composed Image Retrieval
May 23, 2025Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) aims to retrieve target images from a gallery based on a reference image and modification text as a combined query. Recent approaches focus on balancing global information from two modalities and encode the query into a unified feature for retrieval. However, due to insufficient attention to fine-grained details, these coarse fusion methods often struggle with handling subtle visual alterations or intricate textual instructions. In this work, we propose DetailFusion, a novel dual-branch framework that effectively coordinates information across global and detailed granularities, thereby enabling detail-enhanced CIR. Our approach leverages atomic detail variation priors derived from an image editing dataset, supplemented by a detail-oriented optimization strategy to develop a Detail-oriented Inference Branch. Furthermore, we design an Adaptive Feature Compositor that dynamically fuses global and detailed features based on fine-grained information of each unique multimodal query. Extensive experiments and ablation analyses not only demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on both CIRR and FashionIQ datasets but also validate the effectiveness and cross-domain adaptability of detail enhancement for CIR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge