Mingze Li
DMFlow: Disordered Materials Generation by Flow Matching
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The design of materials with tailored properties is crucial for technological progress. However, most deep generative models focus exclusively on perfectly ordered crystals, neglecting the important class of disordered materials. To address this gap, we introduce DMFlow, a generative framework specifically designed for disordered crystals. Our approach introduces a unified representation for ordered, Substitutionally Disordered (SD), and Positionally Disordered (PD) crystals, and employs a flow matching model to jointly generate all structural components. A key innovation is a Riemannian flow matching framework with spherical reparameterization, which ensures physically valid disorder weights on the probability simplex. The vector field is learned by a novel Graph Neural Network (GNN) that incorporates physical symmetries and a specialized message-passing scheme. Finally, a two-stage discretization procedure converts the continuous weights into multi-hot atomic assignments. To support research in this area, we release a benchmark containing SD, PD, and mixed structures curated from the Crystallography Open Database. Experiments on Crystal Structure Prediction (CSP) and De Novo Generation (DNG) tasks demonstrate that DMFlow significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines adapted from ordered crystal generation. We hope our work provides a foundation for the AI-driven discovery of disordered materials.
InfMem: Learning System-2 Memory Control for Long-Context Agent
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Reasoning over ultra-long documents requires synthesizing sparse evidence scattered across distant segments under strict memory constraints. While streaming agents enable scalable processing, their passive memory update strategy often fails to preserve low-salience bridging evidence required for multi-hop reasoning. We propose InfMem, a control-centric agent that instantiates System-2-style control via a PreThink-Retrieve-Write protocol. InfMem actively monitors evidence sufficiency, performs targeted in-document retrieval, and applies evidence-aware joint compression to update a bounded memory. To ensure reliable control, we introduce a practical SFT-to-RL training recipe that aligns retrieval, writing, and stopping decisions with end-task correctness. On ultra-long QA benchmarks from 32k to 1M tokens, InfMem consistently outperforms MemAgent across backbones. Specifically, InfMem improves average absolute accuracy by +10.17, +11.84, and +8.23 points on Qwen3-1.7B, Qwen3-4B, and Qwen2.5-7B, respectively, while reducing inference time by $3.9\times$ on average (up to $5.1\times$) via adaptive early stopping.
SWE-Universe: Scale Real-World Verifiable Environments to Millions
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We propose SWE-Universe, a scalable and efficient framework for automatically constructing real-world software engineering (SWE) verifiable environments from GitHub pull requests (PRs). To overcome the prevalent challenges of automatic building, such as low production yield, weak verifiers, and prohibitive cost, our framework utilizes a building agent powered by an efficient custom-trained model. This agent employs iterative self-verification and in-loop hacking detection to ensure the reliable generation of high-fidelity, verifiable tasks. Using this method, we scale the number of real-world multilingual SWE environments to a million scale (807,693). We demonstrate the profound value of our environments through large-scale agentic mid-training and reinforcement learning. Finally, we applied this technique to Qwen3-Max-Thinking and achieved a score of 75.3% on SWE-Bench Verified. Our work provides both a critical resource and a robust methodology to advance the next generation of coding agents.
From Macro to Micro: Benchmarking Microscopic Spatial Intelligence on Molecules via Vision-Language Models
Dec 12, 2025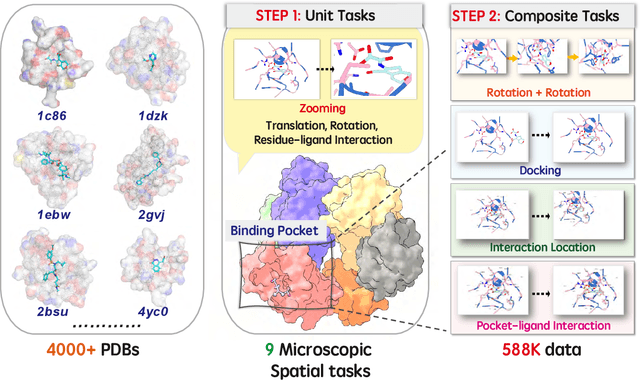
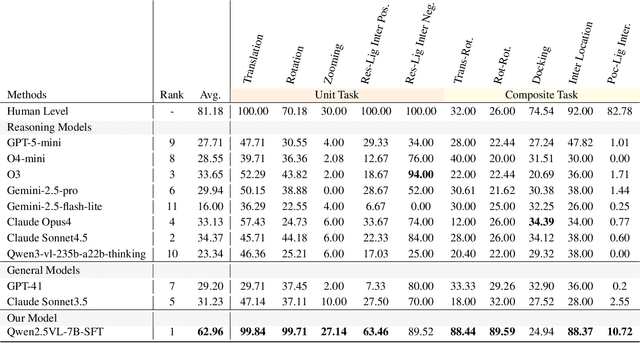
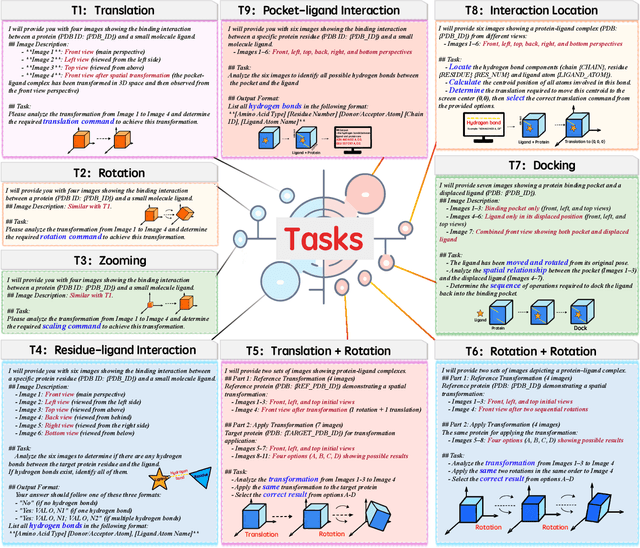
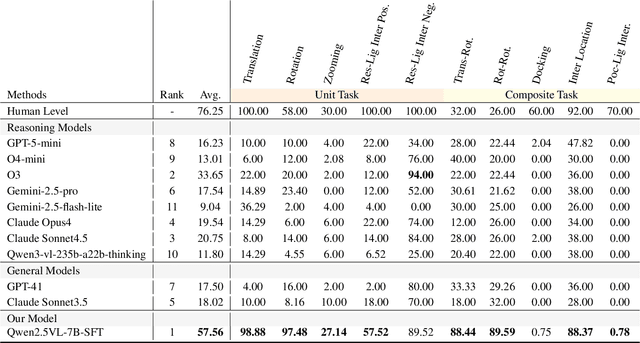
Abstract:This paper introduces the concept of Microscopic Spatial Intelligence (MiSI), the capability to perceive and reason about the spatial relationships of invisible microscopic entities, which is fundamental to scientific discovery. To assess the potential of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in this domain, we propose a systematic benchmark framework MiSI-Bench. This framework features over 163,000 question-answer pairs and 587,000 images derived from approximately 4,000 molecular structures, covering nine complementary tasks that evaluate abilities ranging from elementary spatial transformations to complex relational identifications. Experimental results reveal that current state-of-the-art VLMs perform significantly below human level on this benchmark. However, a fine-tuned 7B model demonstrates substantial potential, even surpassing humans in spatial transformation tasks, while its poor performance in scientifically-grounded tasks like hydrogen bond recognition underscores the necessity of integrating explicit domain knowledge for progress toward scientific AGI. The datasets are available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/zongzhao/MiSI-bench.
Group Sequence Policy Optimization
Jul 24, 2025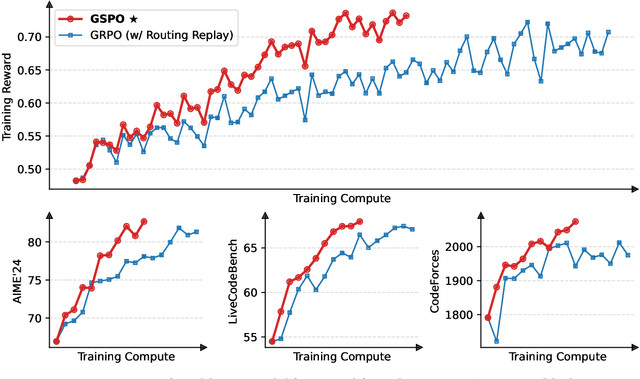
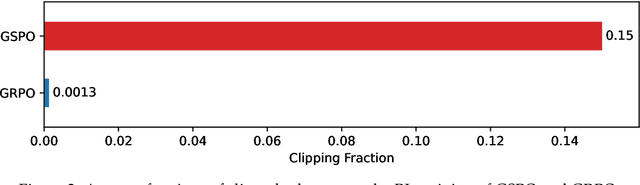
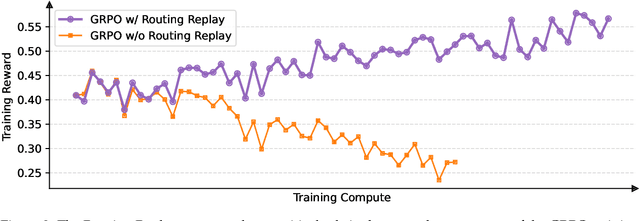
Abstract:This paper introduces Group Sequence Policy Optimization (GSPO), our stable, efficient, and performant reinforcement learning algorithm for training large language models. Unlike previous algorithms that adopt token-level importance ratios, GSPO defines the importance ratio based on sequence likelihood and performs sequence-level clipping, rewarding, and optimization. We demonstrate that GSPO achieves superior training efficiency and performance compared to the GRPO algorithm, notably stabilizes Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) RL training, and has the potential for simplifying the design of RL infrastructure. These merits of GSPO have contributed to the remarkable improvements in the latest Qwen3 models.
STAR-R1: Spatial TrAnsformation Reasoning by Reinforcing Multimodal LLMs
May 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, yet they lag significantly behind humans in spatial reasoning. We investigate this gap through Transformation-Driven Visual Reasoning (TVR), a challenging task requiring identification of object transformations across images under varying viewpoints. While traditional Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) fails to generate coherent reasoning paths in cross-view settings, sparse-reward Reinforcement Learning (RL) suffers from inefficient exploration and slow convergence. To address these limitations, we propose STAR-R1, a novel framework that integrates a single-stage RL paradigm with a fine-grained reward mechanism tailored for TVR. Specifically, STAR-R1 rewards partial correctness while penalizing excessive enumeration and passive inaction, enabling efficient exploration and precise reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that STAR-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance across all 11 metrics, outperforming SFT by 23% in cross-view scenarios. Further analysis reveals STAR-R1's anthropomorphic behavior and highlights its unique ability to compare all objects for improving spatial reasoning. Our work provides critical insights in advancing the research of MLLMs and reasoning models. The codes, model weights, and data will be publicly available at https://github.com/zongzhao23/STAR-R1.
STAR-R1: Spacial TrAnsformation Reasoning by Reinforcing Multimodal LLMs
May 21, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, yet they lag significantly behind humans in spatial reasoning. We investigate this gap through Transformation-Driven Visual Reasoning (TVR), a challenging task requiring identification of object transformations across images under varying viewpoints. While traditional Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) fails to generate coherent reasoning paths in cross-view settings, sparse-reward Reinforcement Learning (RL) suffers from inefficient exploration and slow convergence. To address these limitations, we propose STAR-R1, a novel framework that integrates a single-stage RL paradigm with a fine-grained reward mechanism tailored for TVR. Specifically, STAR-R1 rewards partial correctness while penalizing excessive enumeration and passive inaction, enabling efficient exploration and precise reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that STAR-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance across all 11 metrics, outperforming SFT by 23% in cross-view scenarios. Further analysis reveals STAR-R1's anthropomorphic behavior and highlights its unique ability to compare all objects for improving spatial reasoning. Our work provides critical insights in advancing the research of MLLMs and reasoning models. The codes, model weights, and data will be publicly available at https://github.com/zongzhao23/STAR-R1.
Qwen3 Technical Report
May 14, 2025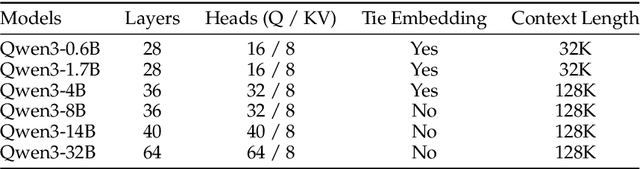
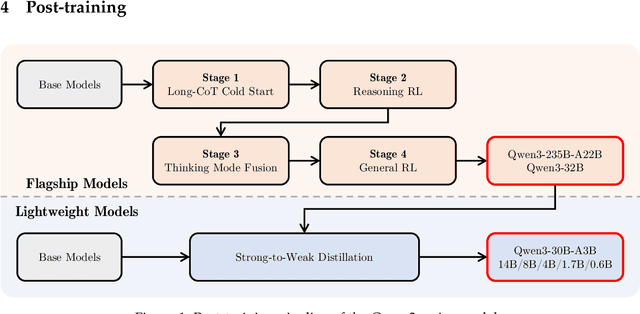
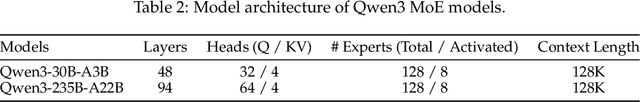
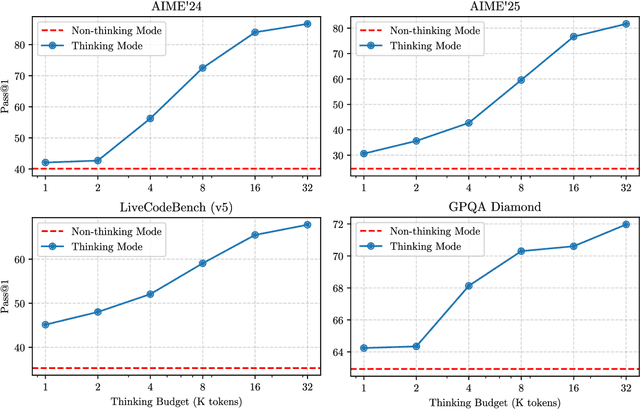
Abstract:In this work, we present Qwen3, the latest version of the Qwen model family. Qwen3 comprises a series of large language models (LLMs) designed to advance performance, efficiency, and multilingual capabilities. The Qwen3 series includes models of both dense and Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) architectures, with parameter scales ranging from 0.6 to 235 billion. A key innovation in Qwen3 is the integration of thinking mode (for complex, multi-step reasoning) and non-thinking mode (for rapid, context-driven responses) into a unified framework. This eliminates the need to switch between different models--such as chat-optimized models (e.g., GPT-4o) and dedicated reasoning models (e.g., QwQ-32B)--and enables dynamic mode switching based on user queries or chat templates. Meanwhile, Qwen3 introduces a thinking budget mechanism, allowing users to allocate computational resources adaptively during inference, thereby balancing latency and performance based on task complexity. Moreover, by leveraging the knowledge from the flagship models, we significantly reduce the computational resources required to build smaller-scale models, while ensuring their highly competitive performance. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that Qwen3 achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse benchmarks, including tasks in code generation, mathematical reasoning, agent tasks, etc., competitive against larger MoE models and proprietary models. Compared to its predecessor Qwen2.5, Qwen3 expands multilingual support from 29 to 119 languages and dialects, enhancing global accessibility through improved cross-lingual understanding and generation capabilities. To facilitate reproducibility and community-driven research and development, all Qwen3 models are publicly accessible under Apache 2.0.
A MEMS-based terahertz broadband beam steering technique
Sep 06, 2024Abstract:A multi-level tunable reflection array wide-angle beam scanning method is proposed to address the limited bandwidth and small scanning angle issues of current terahertz beam scanning technology. In this method, a focusing lens and its array are used to achieve terahertz wave spatial beam control, and MEMS mirrors and their arrays are used to achieve wide-angle beam scanning. The 1~3 order terahertz MEMS beam scanning system designed based on this method can extend the mechanical scanning angle of MEMS mirrors by 2~6 times, when tested and verified using an electromagnetic MEMS mirror with a 7mm optical aperture and a scanning angle of 15{\deg} and a D-band terahertz signal source. The experiment shows that the operating bandwidth of the first-order terahertz MEMS beam scanning system is better than 40GHz, the continuous beam scanning angle is about 30{\deg}, the continuous beam scanning cycle response time is about 1.1ms, and the antenna gain is better than 15dBi at 160GHz. This method has been validated for its large bandwidth and scalable scanning angle, and has potential application prospects in terahertz dynamic communication, detection radar, scanning imaging, and other fields.
MSceneSpeech: A Multi-Scene Speech Dataset For Expressive Speech Synthesis
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:We introduce an open source high-quality Mandarin TTS dataset MSceneSpeech (Multiple Scene Speech Dataset), which is intended to provide resources for expressive speech synthesis. MSceneSpeech comprises numerous audio recordings and texts performed and recorded according to daily life scenarios. Each scenario includes multiple speakers and a diverse range of prosodic styles, making it suitable for speech synthesis that entails multi-speaker style and prosody modeling. We have established a robust baseline, through the prompting mechanism, that can effectively synthesize speech characterized by both user-specific timbre and scene-specific prosody with arbitrary text input. The open source MSceneSpeech Dataset and audio samples of our baseline are available at https://speechai-demo.github.io/MSceneSpeech/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge