Yi Ren
Arizona State University
Hierarchical Vision-Language Interaction for Facial Action Unit Detection
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Facial Action Unit (AU) detection seeks to recognize subtle facial muscle activations as defined by the Facial Action Coding System (FACS). A primary challenge w.r.t AU detection is the effective learning of discriminative and generalizable AU representations under conditions of limited annotated data. To address this, we propose a Hierarchical Vision-language Interaction for AU Understanding (HiVA) method, which leverages textual AU descriptions as semantic priors to guide and enhance AU detection. Specifically, HiVA employs a large language model to generate diverse and contextually rich AU descriptions to strengthen language-based representation learning. To capture both fine-grained and holistic vision-language associations, HiVA introduces an AU-aware dynamic graph module that facilitates the learning of AU-specific visual representations. These features are further integrated within a hierarchical cross-modal attention architecture comprising two complementary mechanisms: Disentangled Dual Cross-Attention (DDCA), which establishes fine-grained, AU-specific interactions between visual and textual features, and Contextual Dual Cross-Attention (CDCA), which models global inter-AU dependencies. This collaborative, cross-modal learning paradigm enables HiVA to leverage multi-grained vision-based AU features in conjunction with refined language-based AU details, culminating in robust and semantically enriched AU detection capabilities. Extensive experiments show that HiVA consistently surpasses state-of-the-art approaches. Besides, qualitative analyses reveal that HiVA produces semantically meaningful activation patterns, highlighting its efficacy in learning robust and interpretable cross-modal correspondences for comprehensive facial behavior analysis.
* Accepted to IEEE Transaction on Affective Computing 2026
BiKC+: Bimanual Hierarchical Imitation with Keypose-Conditioned Coordination-Aware Consistency Policies
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Robots are essential in industrial manufacturing due to their reliability and efficiency. They excel in performing simple and repetitive unimanual tasks but still face challenges with bimanual manipulation. This difficulty arises from the complexities of coordinating dual arms and handling multi-stage processes. Recent integration of generative models into imitation learning (IL) has made progress in tackling specific challenges. However, few approaches explicitly consider the multi-stage nature of bimanual tasks while also emphasizing the importance of inference speed. In multi-stage tasks, failures or delays at any stage can cascade over time, impacting the success and efficiency of subsequent sub-stages and ultimately hindering overall task performance. In this paper, we propose a novel keypose-conditioned coordination-aware consistency policy tailored for bimanual manipulation. Our framework instantiates hierarchical imitation learning with a high-level keypose predictor and a low-level trajectory generator. The predicted keyposes serve as sub-goals for trajectory generation, indicating targets for individual sub-stages. The trajectory generator is formulated as a consistency model, generating action sequences based on historical observations and predicted keyposes in a single inference step. In particular, we devise an innovative approach for identifying bimanual keyposes, considering both robot-centric action features and task-centric operation styles. Simulation and real-world experiments illustrate that our approach significantly outperforms baseline methods in terms of success rates and operational efficiency. Implementation codes can be found at https://github.com/JoanaHXU/BiKC-plus.
Neural Contrast Expansion for Explainable Structure-Property Prediction and Random Microstructure Design
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Effective properties of composite materials are defined as the ensemble average of property-specific PDE solutions over the underlying microstructure distributions. Traditionally, predicting such properties can be done by solving PDEs derived from microstructure samples or building data-driven models that directly map microstructure samples to properties. The former has a higher running cost, but provides explainable sensitivity information that may guide material design; the latter could be more cost-effective if the data overhead is amortized, but its learned sensitivities are often less explainable. With a focus on properties governed by linear self-adjoint PDEs (e.g., Laplace, Helmholtz, and Maxwell curl-curl) defined on bi-phase microstructures, we propose a structure-property model that is both cost-effective and explainable. Our method is built on top of the strong contrast expansion (SCE) formalism, which analytically maps $N$-point correlations of an unbounded random field to its effective properties. Since real-world material samples have finite sizes and analytical PDE kernels are not always available, we propose Neural Contrast Expansion (NCE), an SCE-inspired architecture to learn surrogate PDE kernels from structure-property data. For static conduction and electromagnetic wave propagation cases, we show that NCE models reveal accurate and insightful sensitivity information useful for material design. Compared with other PDE kernel learning methods, our method does not require measurements about the PDE solution fields, but rather only requires macroscopic property measurements that are more accessible in material development contexts.
UniTalker: Conversational Speech-Visual Synthesis
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS) is a key task in the user-agent interaction area, aiming to generate more expressive and empathetic speech for users. However, it is well-known that "listening" and "eye contact" play crucial roles in conveying emotions during real-world interpersonal communication. Existing CSS research is limited to perceiving only text and speech within the dialogue context, which restricts its effectiveness. Moreover, speech-only responses further constrain the interactive experience. To address these limitations, we introduce a Conversational Speech-Visual Synthesis (CSVS) task as an extension of traditional CSS. By leveraging multimodal dialogue context, it provides users with coherent audiovisual responses. To this end, we develop a CSVS system named UniTalker, which is a unified model that seamlessly integrates multimodal perception and multimodal rendering capabilities. Specifically, it leverages a large-scale language model to comprehensively understand multimodal cues in the dialogue context, including speaker, text, speech, and the talking-face animations. After that, it employs multi-task sequence prediction to first infer the target utterance's emotion and then generate empathetic speech and natural talking-face animations. To ensure that the generated speech-visual content remains consistent in terms of emotion, content, and duration, we introduce three key optimizations: 1) Designing a specialized neural landmark codec to tokenize and reconstruct facial expression sequences. 2) Proposing a bimodal speech-visual hard alignment decoding strategy. 3) Applying emotion-guided rendering during the generation stage. Comprehensive objective and subjective experiments demonstrate that our model synthesizes more empathetic speech and provides users with more natural and emotionally consistent talking-face animations.
AC-Refiner: Efficient Arithmetic Circuit Optimization Using Conditional Diffusion Models
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Arithmetic circuits, such as adders and multipliers, are fundamental components of digital systems, directly impacting the performance, power efficiency, and area footprint. However, optimizing these circuits remains challenging due to the vast design space and complex physical constraints. While recent deep learning-based approaches have shown promise, they struggle to consistently explore high-potential design variants, limiting their optimization efficiency. To address this challenge, we propose AC-Refiner, a novel arithmetic circuit optimization framework leveraging conditional diffusion models. Our key insight is to reframe arithmetic circuit synthesis as a conditional image generation task. By carefully conditioning the denoising diffusion process on target quality-of-results (QoRs), AC-Refiner consistently produces high-quality circuit designs. Furthermore, the explored designs are used to fine-tune the diffusion model, which focuses the exploration near the Pareto frontier. Experimental results demonstrate that AC-Refiner generates designs with superior Pareto optimality, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. The performance gain is further validated by integrating AC-Refiner into practical applications.
SViP: Sequencing Bimanual Visuomotor Policies with Object-Centric Motion Primitives
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning (IL), particularly when leveraging high-dimensional visual inputs for policy training, has proven intuitive and effective in complex bimanual manipulation tasks. Nonetheless, the generalization capability of visuomotor policies remains limited, especially when small demonstration datasets are available. Accumulated errors in visuomotor policies significantly hinder their ability to complete long-horizon tasks. To address these limitations, we propose SViP, a framework that seamlessly integrates visuomotor policies into task and motion planning (TAMP). SViP partitions human demonstrations into bimanual and unimanual operations using a semantic scene graph monitor. Continuous decision variables from the key scene graph are employed to train a switching condition generator. This generator produces parameterized scripted primitives that ensure reliable performance even when encountering out-of-the-distribution observations. Using only 20 real-world demonstrations, we show that SViP enables visuomotor policies to generalize across out-of-distribution initial conditions without requiring object pose estimators. For previously unseen tasks, SViP automatically discovers effective solutions to achieve the goal, leveraging constraint modeling in TAMP formulism. In real-world experiments, SViP outperforms state-of-the-art generative IL methods, indicating wider applicability for more complex tasks. Project website: https://sites.google.com/view/svip-bimanual
On the Effect of Negative Gradient in Group Relative Deep Reinforcement Optimization
May 24, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become popular in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) emerging as a widely used algorithm in recent systems. Despite GRPO's widespread adoption, we identify a previously unrecognized phenomenon we term Lazy Likelihood Displacement (LLD), wherein the likelihood of correct responses marginally increases or even decreases during training. This behavior mirrors a recently discovered misalignment issue in Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), attributed to the influence of negative gradients. We provide a theoretical analysis of GRPO's learning dynamic, identifying the source of LLD as the naive penalization of all tokens in incorrect responses with the same strength. To address this, we develop a method called NTHR, which downweights penalties on tokens contributing to the LLD. Unlike prior DPO-based approaches, NTHR takes advantage of GRPO's group-based structure, using correct responses as anchors to identify influential tokens. Experiments on math reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that NTHR effectively mitigates LLD, yielding consistent performance gains across models ranging from 0.5B to 3B parameters.
Chain-Talker: Chain Understanding and Rendering for Empathetic Conversational Speech Synthesis
May 19, 2025Abstract:Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS) aims to align synthesized speech with the emotional and stylistic context of user-agent interactions to achieve empathy. Current generative CSS models face interpretability limitations due to insufficient emotional perception and redundant discrete speech coding. To address the above issues, we present Chain-Talker, a three-stage framework mimicking human cognition: Emotion Understanding derives context-aware emotion descriptors from dialogue history; Semantic Understanding generates compact semantic codes via serialized prediction; and Empathetic Rendering synthesizes expressive speech by integrating both components. To support emotion modeling, we develop CSS-EmCap, an LLM-driven automated pipeline for generating precise conversational speech emotion captions. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that Chain-Talker produces more expressive and empathetic speech than existing methods, with CSS-EmCap contributing to reliable emotion modeling. The code and demos are available at: https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/Chain-Talker.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images: Methods and Results
Apr 19, 2025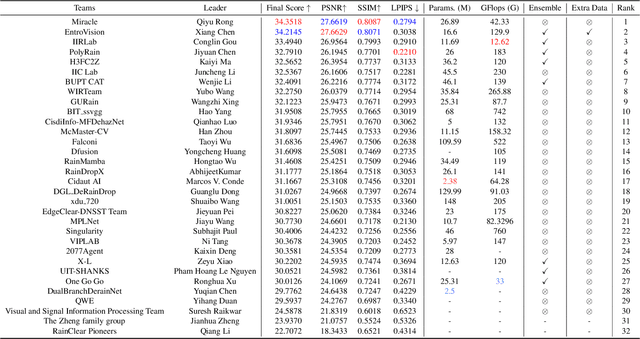
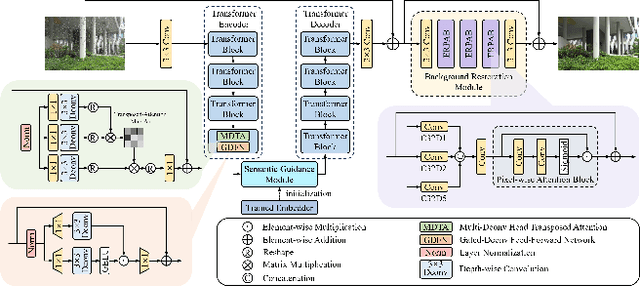
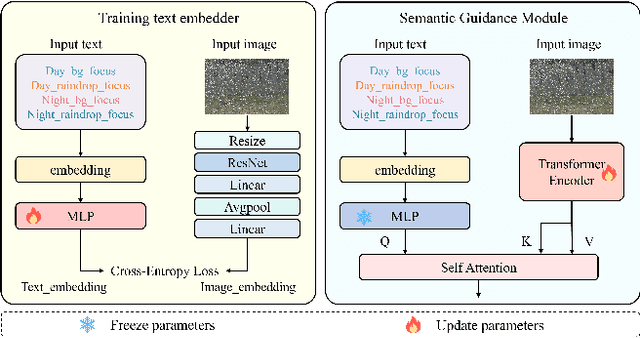
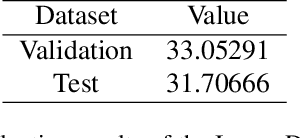
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Day and Night Raindrop Removal for Dual-Focused Images. This challenge received a wide range of impressive solutions, which are developed and evaluated using our collected real-world Raindrop Clarity dataset. Unlike existing deraining datasets, our Raindrop Clarity dataset is more diverse and challenging in degradation types and contents, which includes day raindrop-focused, day background-focused, night raindrop-focused, and night background-focused degradations. This dataset is divided into three subsets for competition: 14,139 images for training, 240 images for validation, and 731 images for testing. The primary objective of this challenge is to establish a new and powerful benchmark for the task of removing raindrops under varying lighting and focus conditions. There are a total of 361 participants in the competition, and 32 teams submitting valid solutions and fact sheets for the final testing phase. These submissions achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the Raindrop Clarity dataset. The project can be found at https://lixinustc.github.io/CVPR-NTIRE2025-RainDrop-Competition.github.io/.
Falcon: A Remote Sensing Vision-Language Foundation Model
Mar 14, 2025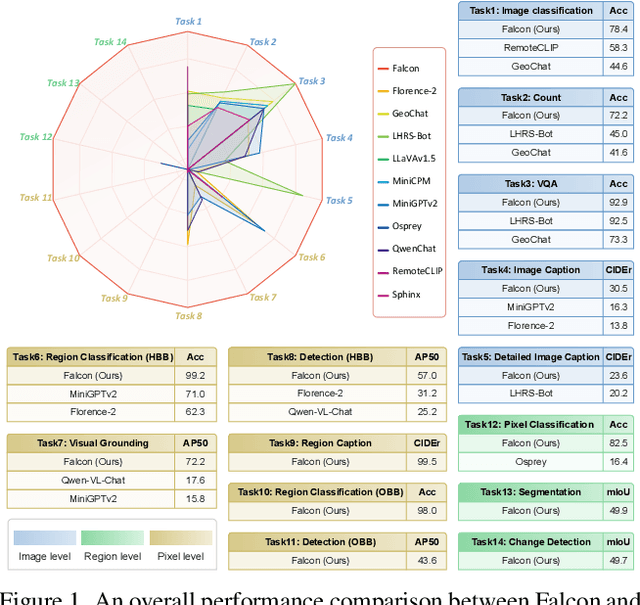
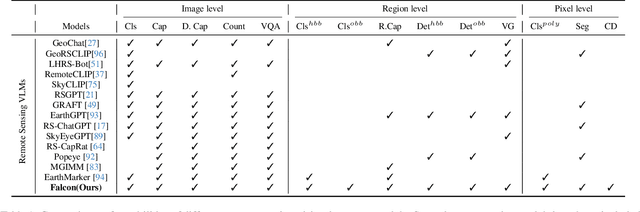
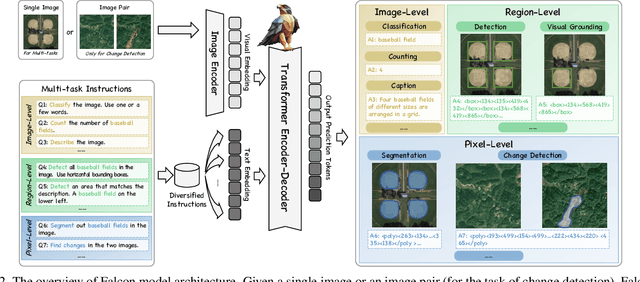
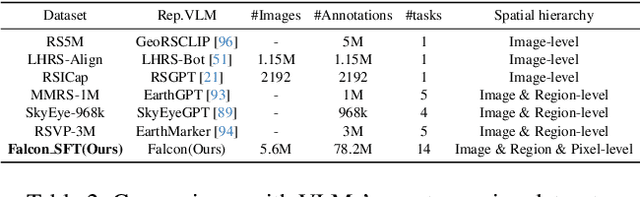
Abstract:This paper introduces a holistic vision-language foundation model tailored for remote sensing, named Falcon. Falcon offers a unified, prompt-based paradigm that effectively executes comprehensive and complex remote sensing tasks. Falcon demonstrates powerful understanding and reasoning abilities at the image, region, and pixel levels. Specifically, given simple natural language instructions and remote sensing images, Falcon can produce impressive results in text form across 14 distinct tasks, i.e., image classification, object detection, segmentation, image captioning, and etc. To facilitate Falcon's training and empower its representation capacity to encode rich spatial and semantic information, we developed Falcon_SFT, a large-scale, multi-task, instruction-tuning dataset in the field of remote sensing. The Falcon_SFT dataset consists of approximately 78 million high-quality data samples, covering 5.6 million multi-spatial resolution and multi-view remote sensing images with diverse instructions. It features hierarchical annotations and undergoes manual sampling verification to ensure high data quality and reliability. Extensive comparative experiments are conducted, which verify that Falcon achieves remarkable performance over 67 datasets and 14 tasks, despite having only 0.7B parameters. We release the complete dataset, code, and model weights at https://github.com/TianHuiLab/Falcon, hoping to help further develop the open-source community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge