Kelu Yao
PhysRVG: Physics-Aware Unified Reinforcement Learning for Video Generative Models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Physical principles are fundamental to realistic visual simulation, but remain a significant oversight in transformer-based video generation. This gap highlights a critical limitation in rendering rigid body motion, a core tenet of classical mechanics. While computer graphics and physics-based simulators can easily model such collisions using Newton formulas, modern pretrain-finetune paradigms discard the concept of object rigidity during pixel-level global denoising. Even perfectly correct mathematical constraints are treated as suboptimal solutions (i.e., conditions) during model optimization in post-training, fundamentally limiting the physical realism of generated videos. Motivated by these considerations, we introduce, for the first time, a physics-aware reinforcement learning paradigm for video generation models that enforces physical collision rules directly in high-dimensional spaces, ensuring the physics knowledge is strictly applied rather than treated as conditions. Subsequently, we extend this paradigm to a unified framework, termed Mimicry-Discovery Cycle (MDcycle), which allows substantial fine-tuning while fully preserving the model's ability to leverage physics-grounded feedback. To validate our approach, we construct new benchmark PhysRVGBench and perform extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments to thoroughly assess its effectiveness.
Asymmetric Cross-Modal Knowledge Distillation: Bridging Modalities with Weak Semantic Consistency
Nov 12, 2025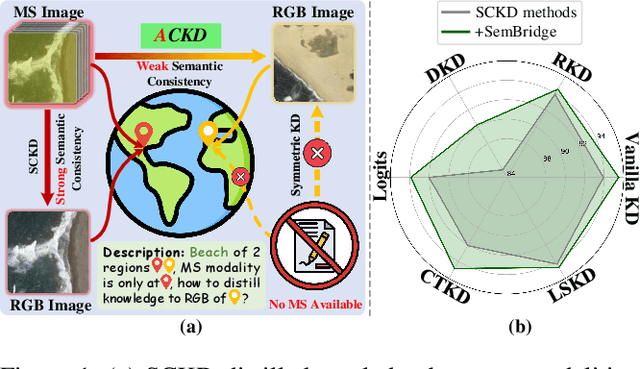



Abstract:Cross-modal Knowledge Distillation has demonstrated promising performance on paired modalities with strong semantic connections, referred to as Symmetric Cross-modal Knowledge Distillation (SCKD). However, implementing SCKD becomes exceedingly constrained in real-world scenarios due to the limited availability of paired modalities. To this end, we investigate a general and effective knowledge learning concept under weak semantic consistency, dubbed Asymmetric Cross-modal Knowledge Distillation (ACKD), aiming to bridge modalities with limited semantic overlap. Nevertheless, the shift from strong to weak semantic consistency improves flexibility but exacerbates challenges in knowledge transmission costs, which we rigorously verified based on optimal transport theory. To mitigate the issue, we further propose a framework, namely SemBridge, integrating a Student-Friendly Matching module and a Semantic-aware Knowledge Alignment module. The former leverages self-supervised learning to acquire semantic-based knowledge and provide personalized instruction for each student sample by dynamically selecting the relevant teacher samples. The latter seeks the optimal transport path by employing Lagrangian optimization. To facilitate the research, we curate a benchmark dataset derived from two modalities, namely Multi-Spectral (MS) and asymmetric RGB images, tailored for remote sensing scene classification. Comprehensive experiments exhibit that our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with 7 existing approaches on 6 different model architectures across various datasets.
Falcon: A Remote Sensing Vision-Language Foundation Model
Mar 14, 2025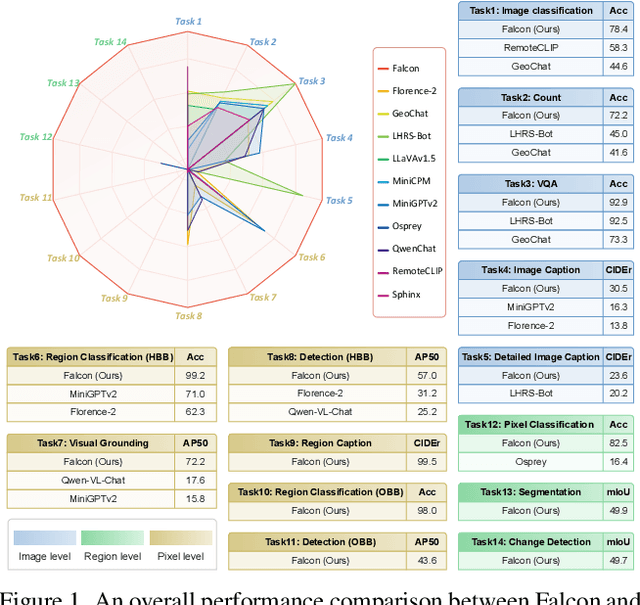
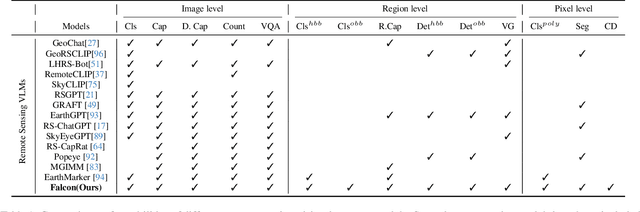
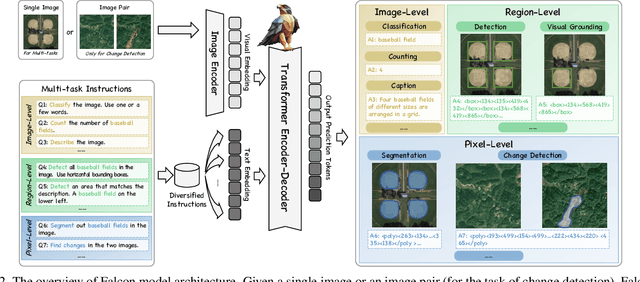
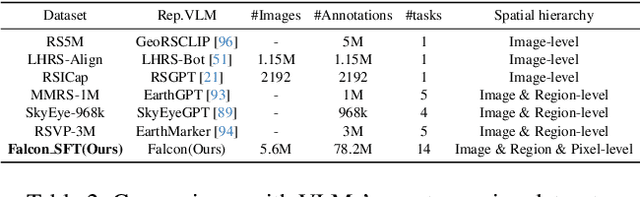
Abstract:This paper introduces a holistic vision-language foundation model tailored for remote sensing, named Falcon. Falcon offers a unified, prompt-based paradigm that effectively executes comprehensive and complex remote sensing tasks. Falcon demonstrates powerful understanding and reasoning abilities at the image, region, and pixel levels. Specifically, given simple natural language instructions and remote sensing images, Falcon can produce impressive results in text form across 14 distinct tasks, i.e., image classification, object detection, segmentation, image captioning, and etc. To facilitate Falcon's training and empower its representation capacity to encode rich spatial and semantic information, we developed Falcon_SFT, a large-scale, multi-task, instruction-tuning dataset in the field of remote sensing. The Falcon_SFT dataset consists of approximately 78 million high-quality data samples, covering 5.6 million multi-spatial resolution and multi-view remote sensing images with diverse instructions. It features hierarchical annotations and undergoes manual sampling verification to ensure high data quality and reliability. Extensive comparative experiments are conducted, which verify that Falcon achieves remarkable performance over 67 datasets and 14 tasks, despite having only 0.7B parameters. We release the complete dataset, code, and model weights at https://github.com/TianHuiLab/Falcon, hoping to help further develop the open-source community.
ECG-guided individual identification via PPG
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Photoplethsmography (PPG)-based individual identification aiming at recognizing humans via intrinsic cardiovascular activities has raised extensive attention due to its high security and resistance to mimicry. However, this kind of technology witnesses unpromising results due to the limitation of low information density. To this end, electrocardiogram (ECG) signals have been introduced as a novel modality to enhance the density of input information. Specifically, a novel cross-modal knowledge distillation framework is implemented to propagate discriminate knowledge from ECG modality to PPG modality without incurring additional computational demands at the inference phase. Furthermore, to ensure efficient knowledge propagation, Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP)-based knowledge alignment and cross-knowledge assessment modules are proposed respectively. Comprehensive experiments are conducted and results show our framework outperforms the baseline model with the improvement of 2.8% and 3.0% in terms of overall accuracy on seen- and unseen individual recognitions.
Advancements in Visual Language Models for Remote Sensing: Datasets, Capabilities, and Enhancement Techniques
Oct 15, 2024
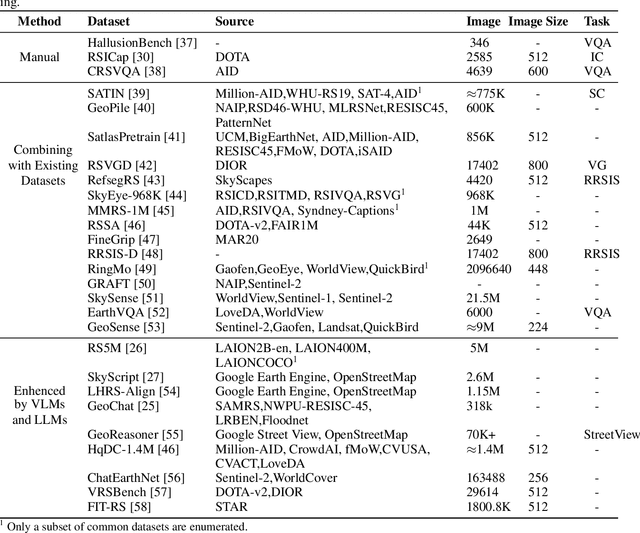
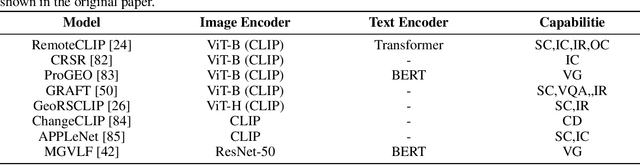
Abstract:Recently, the remarkable success of ChatGPT has sparked a renewed wave of interest in artificial intelligence (AI), and the advancements in visual language models (VLMs) have pushed this enthusiasm to new heights. Differring from previous AI approaches that generally formulated different tasks as discriminative models, VLMs frame tasks as generative models and align language with visual information, enabling the handling of more challenging problems. The remote sensing (RS) field, a highly practical domain, has also embraced this new trend and introduced several VLM-based RS methods that have demonstrated promising performance and enormous potential. In this paper, we first review the fundamental theories related to VLM, then summarize the datasets constructed for VLMs in remote sensing and the various tasks they addressed. Finally, we categorize the improvement methods into three main parts according to the core components of VLMs and provide a detailed introduction and comparison of these methods.
OVA-DETR: Open Vocabulary Aerial Object Detection Using Image-Text Alignment and Fusion
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:Aerial object detection has been a hot topic for many years due to its wide application requirements. However, most existing approaches can only handle predefined categories, which limits their applicability for the open scenarios in real-world. In this paper, we extend aerial object detection to open scenarios by exploiting the relationship between image and text, and propose OVA-DETR, a high-efficiency open-vocabulary detector for aerial images. Specifically, based on the idea of image-text alignment, we propose region-text contrastive loss to replace the category regression loss in the traditional detection framework, which breaks the category limitation. Then, we propose Bidirectional Vision-Language Fusion (Bi-VLF), which includes a dual-attention fusion encoder and a multi-level text-guided Fusion Decoder. The dual-attention fusion encoder enhances the feature extraction process in the encoder part. The multi-level text-guided Fusion Decoder is designed to improve the detection ability for small objects, which frequently appear in aerial object detection scenarios. Experimental results on three widely used benchmark datasets show that our proposed method significantly improves the mAP and recall, while enjoying faster inference speed. For instance, in zero shot detection experiments on DIOR, the proposed OVA-DETR outperforms DescReg and YOLO-World by 37.4% and 33.1%, respectively, while achieving 87 FPS inference speed, which is 7.9x faster than DescReg and 3x faster than YOLO-world. The code is available at https://github.com/GT-Wei/OVA-DETR.
Diagnosing the Compositional Knowledge of Vision Language Models from a Game-Theoretic View
May 27, 2024



Abstract:Compositional reasoning capabilities are usually considered as fundamental skills to characterize human perception. Recent studies show that current Vision Language Models (VLMs) surprisingly lack sufficient knowledge with respect to such capabilities. To this end, we propose to thoroughly diagnose the composition representations encoded by VLMs, systematically revealing the potential cause for this weakness. Specifically, we propose evaluation methods from a novel game-theoretic view to assess the vulnerability of VLMs on different aspects of compositional understanding, e.g., relations and attributes. Extensive experimental results demonstrate and validate several insights to understand the incapabilities of VLMs on compositional reasoning, which provide useful and reliable guidance for future studies. The deliverables will be updated at https://vlms-compositionality-gametheory.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge