Haizhao Jing
Language Embedding Meets Dynamic Graph: A New Exploration for Neural Architecture Representation Learning
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Neural Architecture Representation Learning aims to transform network models into feature representations for predicting network attributes, playing a crucial role in deploying and designing networks for real-world applications. Recently, inspired by the success of transformers, transformer-based models integrated with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved significant progress in representation learning. However, current methods still have some limitations. First, existing methods overlook hardware attribute information, which conflicts with the current trend of diversified deep learning hardware and limits the practical applicability of models. Second, current encoding approaches rely on static adjacency matrices to represent topological structures, failing to capture the structural differences between computational nodes, which ultimately compromises encoding effectiveness. In this paper, we introduce LeDG-Former, an innovative framework that addresses these limitations through the synergistic integration of language-based semantic embedding and dynamic graph representation learning. Specifically, inspired by large language models (LLMs), we propose a language embedding framework where both neural architectures and hardware platform specifications are projected into a unified semantic space through tokenization and LLM processing, enabling zero-shot prediction across different hardware platforms for the first time. Then, we propose a dynamic graph-based transformer for modeling neural architectures, resulting in improved neural architecture modeling performance. On the NNLQP benchmark, LeDG-Former surpasses previous methods, establishing a new SOTA while demonstrating the first successful cross-hardware latency prediction capability. Furthermore, our framework achieves superior performance on the cell-structured NAS-Bench-101 and NAS-Bench-201 datasets.
Advancements in Visual Language Models for Remote Sensing: Datasets, Capabilities, and Enhancement Techniques
Oct 15, 2024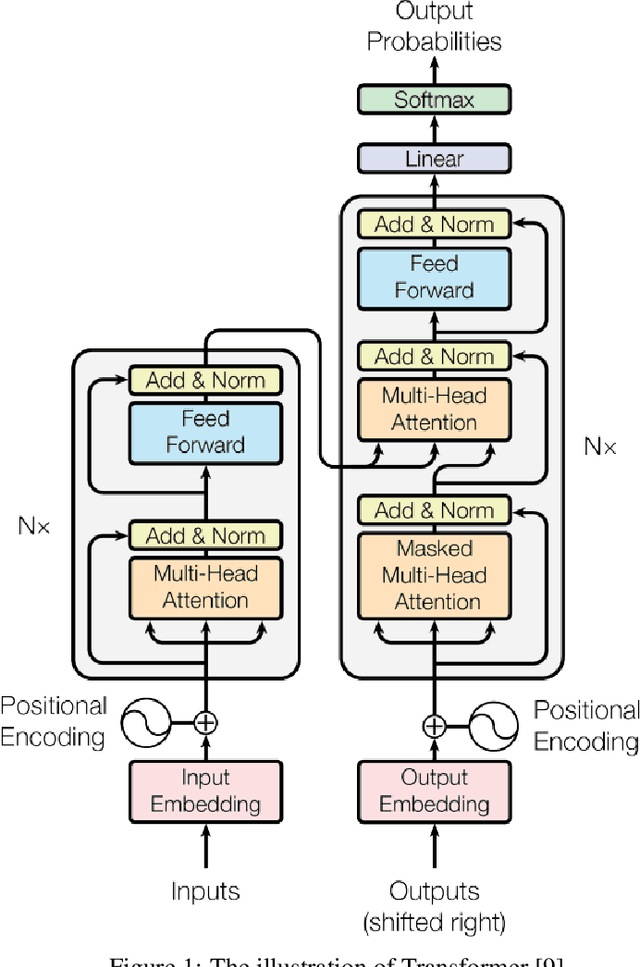
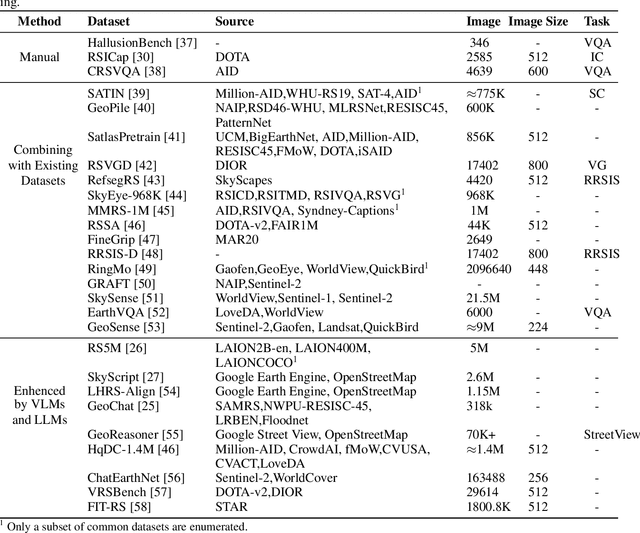
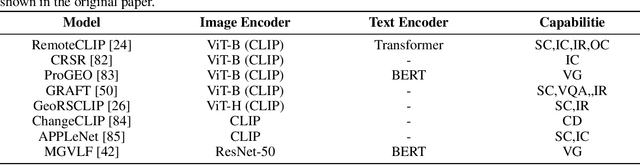
Abstract:Recently, the remarkable success of ChatGPT has sparked a renewed wave of interest in artificial intelligence (AI), and the advancements in visual language models (VLMs) have pushed this enthusiasm to new heights. Differring from previous AI approaches that generally formulated different tasks as discriminative models, VLMs frame tasks as generative models and align language with visual information, enabling the handling of more challenging problems. The remote sensing (RS) field, a highly practical domain, has also embraced this new trend and introduced several VLM-based RS methods that have demonstrated promising performance and enormous potential. In this paper, we first review the fundamental theories related to VLM, then summarize the datasets constructed for VLMs in remote sensing and the various tasks they addressed. Finally, we categorize the improvement methods into three main parts according to the core components of VLMs and provide a detailed introduction and comparison of these methods.
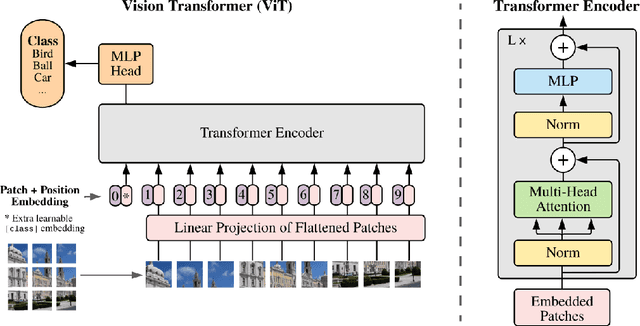
3D-RCNet: Learning from Transformer to Build a 3D Relational ConvNet for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Aug 25, 2024Abstract:Recently, the Vision Transformer (ViT) model has replaced the classical Convolutional Neural Network (ConvNet) in various computer vision tasks due to its superior performance. Even in hyperspectral image (HSI) classification field, ViT-based methods also show promising potential. Nevertheless, ViT encounters notable difficulties in processing HSI data. Its self-attention mechanism, which exhibits quadratic complexity, escalates computational costs. Additionally, ViT's substantial demand for training samples does not align with the practical constraints posed by the expensive labeling of HSI data. To overcome these challenges, we propose a 3D relational ConvNet named 3D-RCNet, which inherits both strengths of ConvNet and ViT, resulting in high performance in HSI classification. We embed the self-attention mechanism of Transformer into the convolutional operation of ConvNet to design 3D relational convolutional operation and use it to build the final 3D-RCNet. The proposed 3D-RCNet maintains the high computational efficiency of ConvNet while enjoying the flexibility of ViT. Additionally, the proposed 3D relational convolutional operation is a plug-and-play operation, which can be inserted into previous ConvNet-based HSI classification methods seamlessly. Empirical evaluations on three representative benchmark HSI datasets show that the proposed model outperforms previous ConvNet-based and ViT-based HSI approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge