Beyond Overfitting: Doubly Adaptive Dropout for Generalizable AU Detection
Paper and Code
Mar 12, 2025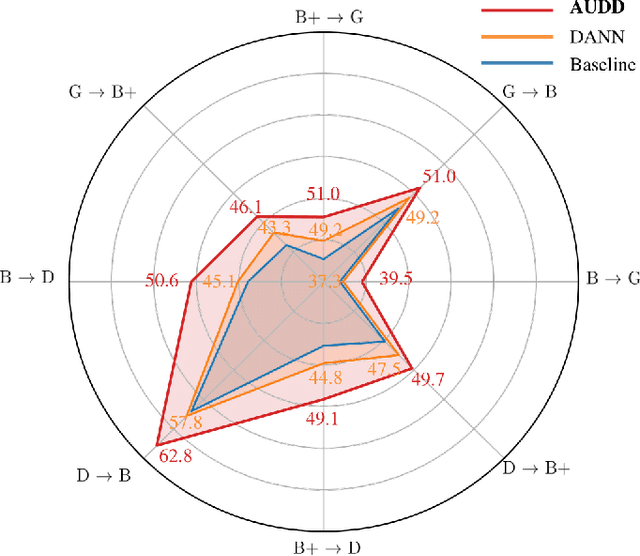
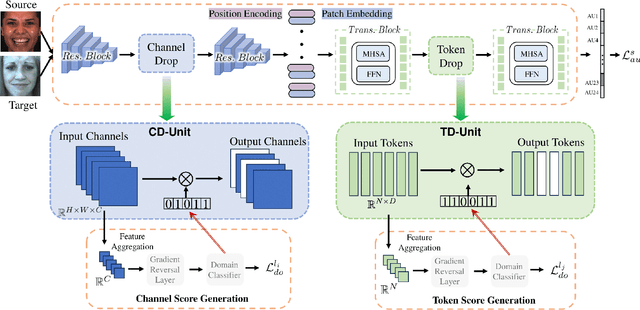
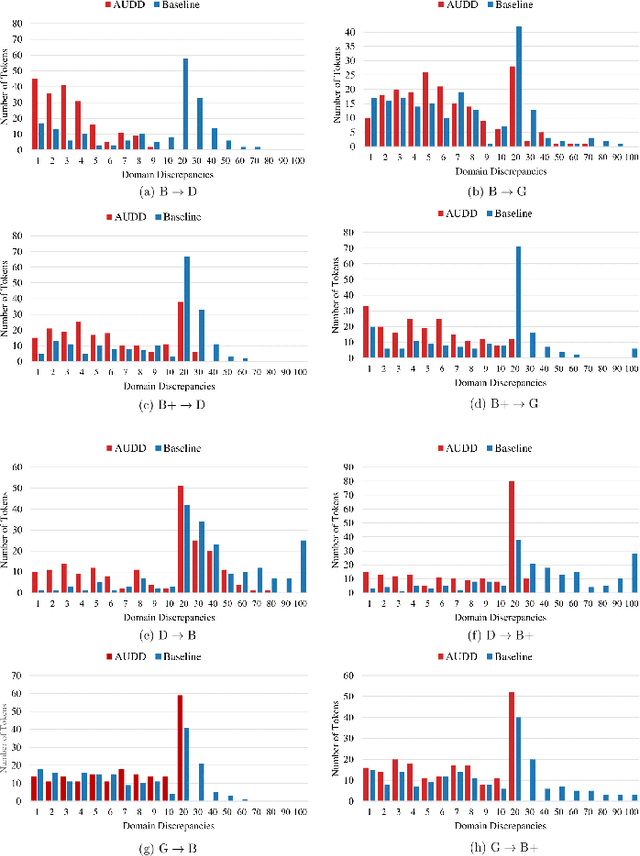
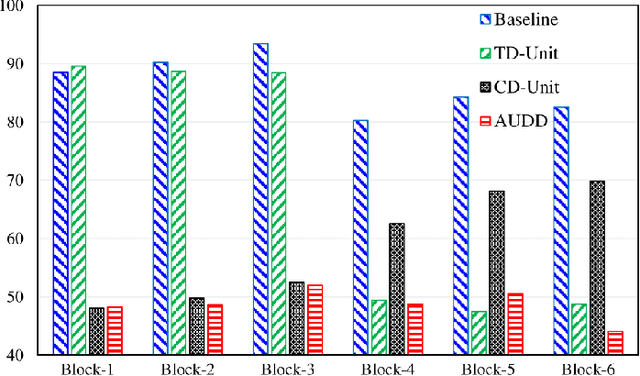
Facial Action Units (AUs) are essential for conveying psychological states and emotional expressions. While automatic AU detection systems leveraging deep learning have progressed, they often overfit to specific datasets and individual features, limiting their cross-domain applicability. To overcome these limitations, we propose a doubly adaptive dropout approach for cross-domain AU detection, which enhances the robustness of convolutional feature maps and spatial tokens against domain shifts. This approach includes a Channel Drop Unit (CD-Unit) and a Token Drop Unit (TD-Unit), which work together to reduce domain-specific noise at both the channel and token levels. The CD-Unit preserves domain-agnostic local patterns in feature maps, while the TD-Unit helps the model identify AU relationships generalizable across domains. An auxiliary domain classifier, integrated at each layer, guides the selective omission of domain-sensitive features. To prevent excessive feature dropout, a progressive training strategy is used, allowing for selective exclusion of sensitive features at any model layer. Our method consistently outperforms existing techniques in cross-domain AU detection, as demonstrated by extensive experimental evaluations. Visualizations of attention maps also highlight clear and meaningful patterns related to both individual and combined AUs, further validating the approach's effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge