Chang Gao
Outcome Accuracy is Not Enough: Aligning the Reasoning Process of Reward Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Generative Reward Models (GenRMs) and LLM-as-a-Judge exhibit deceptive alignment by producing correct judgments for incorrect reasons, as they are trained and evaluated to prioritize Outcome Accuracy, which undermines their ability to generalize during RLHF. We introduce Rationale Consistency, a fine-grained metric that quantifies the alignment between the model's reasoning process and human judgment. Our evaluation of frontier models reveals that rationale consistency effectively discriminates among state-of-the-art models and detects deceptive alignment, while outcome accuracy falls short in both respects. To mitigate this gap, we introduce a hybrid signal that combines rationale consistency with outcome accuracy for GenRM training. Our training method achieves state-of-the-art performance on RM-Bench (87.1%) and JudgeBench (82%), surpassing outcome-only baselines by an average of 5%. Using RM during RLHF, our method effectively improves performance as demonstrated on Arena Hard v2, notably yielding a 7% improvement in creative writing tasks. Further analysis confirms that our method escapes the deceptive alignment trap, effectively reversing the decline in rationale consistency observed in outcome-only training.
Learning Neural Operators from Partial Observations via Latent Autoregressive Modeling
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Real-world scientific applications frequently encounter incomplete observational data due to sensor limitations, geographic constraints, or measurement costs. Although neural operators significantly advanced PDE solving in terms of computational efficiency and accuracy, their underlying assumption of fully-observed spatial inputs severely restricts applicability in real-world applications. We introduce the first systematic framework for learning neural operators from partial observation. We identify and formalize two fundamental obstacles: (i) the supervision gap in unobserved regions that prevents effective learning of physical correlations, and (ii) the dynamic spatial mismatch between incomplete inputs and complete solution fields. Specifically, our proposed Latent Autoregressive Neural Operator(LANO) introduces two novel components designed explicitly to address the core difficulties of partial observations: (i) a mask-to-predict training strategy that creates artificial supervision by strategically masking observed regions, and (ii) a Physics-Aware Latent Propagator that reconstructs solutions through boundary-first autoregressive generation in latent space. Additionally, we develop POBench-PDE, a dedicated and comprehensive benchmark designed specifically for evaluating neural operators under partial observation conditions across three PDE-governed tasks. LANO achieves state-of-the-art performance with 18--69$\%$ relative L2 error reduction across all benchmarks under patch-wise missingness with less than 50$\%$ missing rate, including real-world climate prediction. Our approach effectively addresses practical scenarios involving up to 75$\%$ missing rate, to some extent bridging the existing gap between idealized research settings and the complexities of real-world scientific computing.
Neural-HAR: A Dimension-Gated CNN Accelerator for Real-Time Radar Human Activity Recognition
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Radar-based human activity recognition (HAR) is attractive for unobtrusive and privacy-preserving monitoring, yet many CNN/RNN solutions remain too heavy for edge deployment, and even lightweight ViT/SSM variants often exceed practical compute and memory budgets. We introduce Neural-HAR, a dimension-gated CNN accelerator tailored for real-time radar HAR on resource-constrained platforms. At its core is GateCNN, a parameter-efficient Doppler-temporal network that (i) embeds Doppler vectors to emphasize frequency evolution over time and (ii) applies dual-path gated convolutions that modulate Doppler-aware content features with temporal gates, complemented by a residual path for stable training. On the University of Glasgow UoG2020 continuous radar dataset, GateCNN attains 86.4% accuracy with only 2.7k parameters and 0.28M FLOPs per inference, comparable to CNN-BiGRU at a fraction of the complexity. Our FPGA prototype on Xilinx Zynq-7000 Z-7007S reaches 107.5 $\mu$s latency and 15 mW dynamic power using LUT-based ROM and distributed RAM only (zero DSP/BRAM), demonstrating real-time, energy-efficient edge inference. Code and HLS conversion scripts are available at https://github.com/lab-emi/AIRHAR.
MANZANO: A Simple and Scalable Unified Multimodal Model with a Hybrid Vision Tokenizer
Sep 19, 2025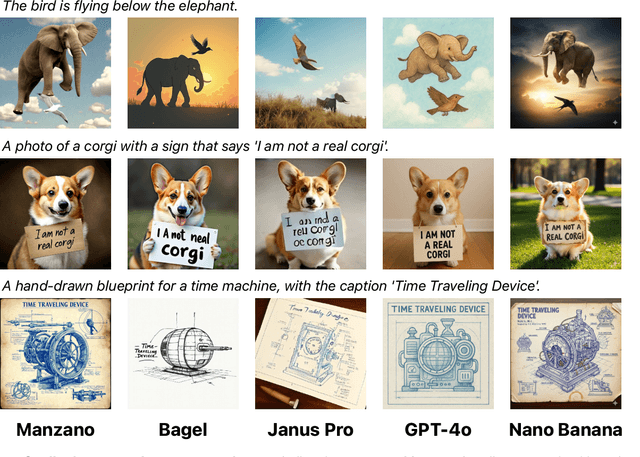
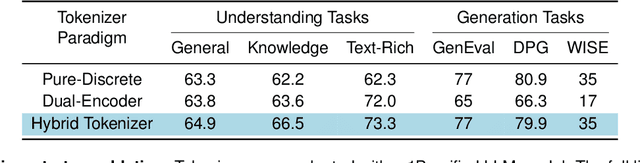
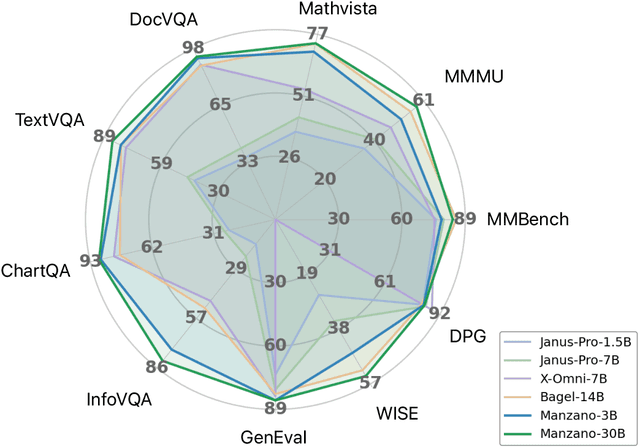
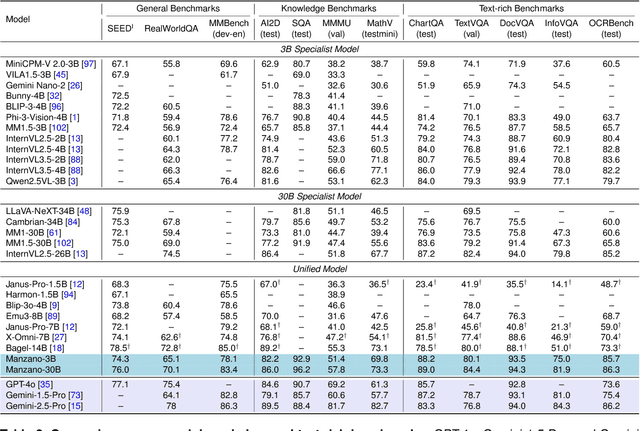
Abstract:Unified multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) that can both understand and generate visual content hold immense potential. However, existing open-source models often suffer from a performance trade-off between these capabilities. We present Manzano, a simple and scalable unified framework that substantially reduces this tension by coupling a hybrid image tokenizer with a well-curated training recipe. A single shared vision encoder feeds two lightweight adapters that produce continuous embeddings for image-to-text understanding and discrete tokens for text-to-image generation within a common semantic space. A unified autoregressive LLM predicts high-level semantics in the form of text and image tokens, with an auxiliary diffusion decoder subsequently translating the image tokens into pixels. The architecture, together with a unified training recipe over understanding and generation data, enables scalable joint learning of both capabilities. Manzano achieves state-of-the-art results among unified models, and is competitive with specialist models, particularly on text-rich evaluation. Our studies show minimal task conflicts and consistent gains from scaling model size, validating our design choice of a hybrid tokenizer.
EvHand-FPV: Efficient Event-Based 3D Hand Tracking from First-Person View
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Hand tracking holds great promise for intuitive interaction paradigms, but frame-based methods often struggle to meet the requirements of accuracy, low latency, and energy efficiency, especially in resource-constrained settings such as Extended Reality (XR) devices. Event cameras provide $\mu$s-level temporal resolution at mW-level power by asynchronously sensing brightness changes. In this work, we present EvHand-FPV, a lightweight framework for egocentric First-Person-View 3D hand tracking from a single event camera. We construct an event-based FPV dataset that couples synthetic training data with 3D labels and real event data with 2D labels for evaluation to address the scarcity of egocentric benchmarks. EvHand-FPV also introduces a wrist-based region of interest (ROI) that localizes the hand region via geometric cues, combined with an end-to-end mapping strategy that embeds ROI offsets into the network to reduce computation without explicit reconstruction, and a multi-task learning strategy with an auxiliary geometric feature head that improves representations without test-time overhead. On our real FPV test set, EvHand-FPV improves 2D-AUCp from 0.77 to 0.85 while reducing parameters from 11.2M to 1.2M by 89% and FLOPs per inference from 1.648G to 0.185G by 89%. It also maintains a competitive 3D-AUCp of 0.84 on synthetic data. These results demonstrate accurate and efficient egocentric event-based hand tracking suitable for on-device XR applications. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/zen5x5/EvHand-FPV.
Group Sequence Policy Optimization
Jul 24, 2025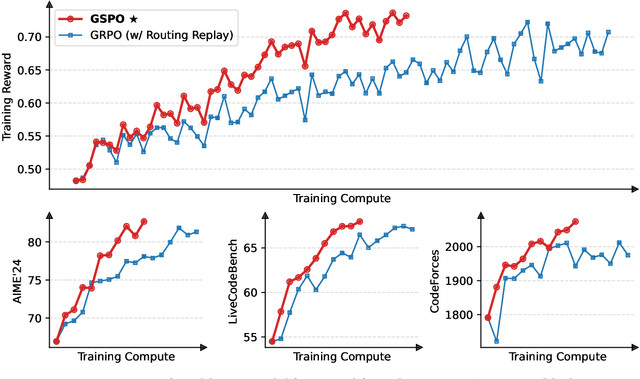
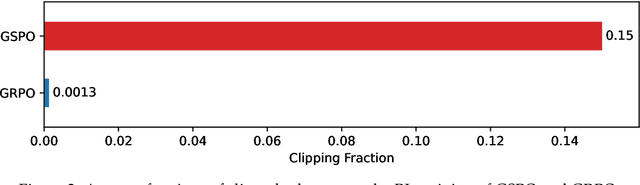
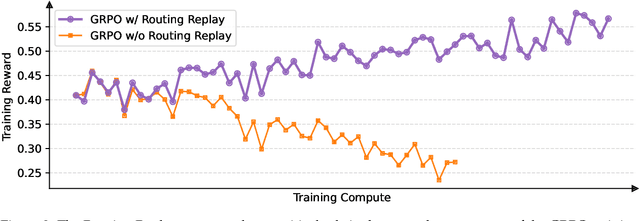
Abstract:This paper introduces Group Sequence Policy Optimization (GSPO), our stable, efficient, and performant reinforcement learning algorithm for training large language models. Unlike previous algorithms that adopt token-level importance ratios, GSPO defines the importance ratio based on sequence likelihood and performs sequence-level clipping, rewarding, and optimization. We demonstrate that GSPO achieves superior training efficiency and performance compared to the GRPO algorithm, notably stabilizes Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) RL training, and has the potential for simplifying the design of RL infrastructure. These merits of GSPO have contributed to the remarkable improvements in the latest Qwen3 models.
A Policy-Improved Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Framework for the Discount Order Acceptance Strategy of Ride-hailing Drivers
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:The rapid expansion of platform integration has emerged as an effective solution to mitigate market fragmentation by consolidating multiple ride-hailing platforms into a single application. To address heterogeneous passenger preferences, third-party integrators provide Discount Express service delivered by express drivers at lower trip fares. For the individual platform, encouraging broader participation of drivers in Discount Express services has the potential to expand the accessible demand pool and improve matching efficiency, but often at the cost of reduced profit margins. This study aims to dynamically manage drivers' acceptance of Discount Express from the perspective of individual platforms. The lack of historical data under the new business model necessitates online learning. However, early-stage exploration through trial and error can be costly in practice, highlighting the need for reliable early-stage performance in real-world deployment. To address these challenges, this study formulates the decision regarding the proportion of drivers' acceptance behavior as a continuous control task. In response to the high stochasticity, the opaque matching mechanisms employed by third-party integrator, and the limited availability of historical data, we propose a policy-improved deep deterministic policy gradient (pi-DDPG) framework. The proposed framework incorporates a refiner module to boost policy performance during the early training phase, leverages a convolutional long short-term memory network to effectively capture complex spatiotemporal patterns, and adopts a prioritized experience replay mechanism to enhance learning efficiency. A simulator based on a real-world dataset is developed to validate the effectiveness of the proposed pi-DDPG. Numerical experiments demonstrate that pi-DDPG achieves superior learning efficiency and significantly reduces early-stage training losses.
OpenDPDv2: A Unified Learning and Optimization Framework for Neural Network Digital Predistortion
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Neural network (NN)-based Digital Predistortion (DPD) stands out in improving signal quality in wideband radio frequency (RF) power amplifiers (PAs) employing complex modulation. However, NN DPDs usually rely on a large number of parameters for effective linearization and can significantly contribute to the energy consumption of the digital back-end in RF systems. This paper presents OpenDPDv2, a unified framework for PA modeling, DPD learning, and model optimization to reduce power consumption while maintaining high linearization performance. The optimization techniques feature a novel DPD algorithm, TRes-DeltaGRU, alongside two energy-efficient methods. The top-performing 32-bit floating-point (FP32) TRes-DeltaGRU-DPD model achieves an Adjacent Channel Power Ratio (ACPR) of -59.4 dBc and Error Vector Magnitude (EVM) of -42.1 dBc. By exploiting fixed-point quantization and dynamic temporal sparsity of input signals and hidden neurons, the inference energy of our model can be reduced by 4.5X while still maintaining -50.3 dBc ACPR and -35.2 dB EVM with 56% temporal sparsity. This was evaluated using a TM3.1a 200 MHz bandwidth 256-QAM OFDM signal applied to a 3.5 GHz GaN Doherty RF PA. OpenDPDv2 code, datasets, and documentation are publicly accessible at: https://github.com/lab-emi/OpenDPD.
TCN-DPD: Parameter-Efficient Temporal Convolutional Networks for Wideband Digital Predistortion
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Digital predistortion (DPD) is essential for mitigating nonlinearity in RF power amplifiers, particularly for wideband applications. This paper presents TCN-DPD, a parameter-efficient architecture based on temporal convolutional networks, integrating noncausal dilated convolutions with optimized activation functions. Evaluated on the OpenDPD framework with the DPA_200MHz dataset, TCN-DPD achieves simulated ACPRs of -51.58/-49.26 dBc (L/R), EVM of -47.52 dB, and NMSE of -44.61 dB with 500 parameters and maintains superior linearization than prior models down to 200 parameters, making it promising for efficient wideband PA linearization.
AS-ASR: A Lightweight Framework for Aphasia-Specific Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes AS-ASR, a lightweight aphasia-specific speech recognition framework based on Whisper-tiny, tailored for low-resource deployment on edge devices. Our approach introduces a hybrid training strategy that systematically combines standard and aphasic speech at varying ratios, enabling robust generalization, and a GPT-4-based reference enhancement method that refines noisy aphasic transcripts, improving supervision quality. We conduct extensive experiments across multiple data mixing configurations and evaluation settings. Results show that our fine-tuned model significantly outperforms the zero-shot baseline, reducing WER on aphasic speech by over 30% while preserving performance on standard speech. The proposed framework offers a scalable, efficient solution for real-world disordered speech recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge