Zhiqing Hong
GeoGen: A Two-stage Coarse-to-Fine Framework for Fine-grained Synthetic Location-based Social Network Trajectory Generation
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Location-Based Social Network (LBSN) check-in trajectory data are important for many practical applications, like POI recommendation, advertising, and pandemic intervention. However, the high collection costs and ever-increasing privacy concerns prevent us from accessing large-scale LBSN trajectory data. The recent advances in synthetic data generation provide us with a new opportunity to achieve this, which utilizes generative AI to generate synthetic data that preserves the characteristics of real data while ensuring privacy protection. However, generating synthetic LBSN check-in trajectories remains challenging due to their spatially discrete, temporally irregular nature and the complex spatio-temporal patterns caused by sparse activities and uncertain human mobility. To address this challenge, we propose GeoGen, a two-stage coarse-to-fine framework for large-scale LBSN check-in trajectory generation. In the first stage, we reconstruct spatially continuous, temporally regular latent movement sequences from the original LBSN check-in trajectories and then design a Sparsity-aware Spatio-temporal Diffusion model (S$^2$TDiff) with an efficient denosing network to learn their underlying behavioral patterns. In the second stage, we design Coarse2FineNet, a Transformer-based Seq2Seq architecture equipped with a dynamic context fusion mechanism in the encoder and a multi-task hybrid-head decoder, which generates fine-grained LBSN trajectories based on coarse-grained latent movement sequences by modeling semantic relevance and behavioral uncertainty. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets show that GeoGen excels state-of-the-art models for both fidelity and utility evaluation, e.g., it increases over 69% and 55% in distance and radius metrics on the FS-TKY dataset.
Towards Generalizable Human Activity Recognition: A Survey
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:As a critical component of Wearable AI, IMU-based Human Activity Recognition (HAR) has attracted increasing attention from both academia and industry in recent years. Although HAR performance has improved considerably in specific scenarios, its generalization capability remains a key barrier to widespread real-world adoption. For example, domain shifts caused by variations in users, sensor positions, or environments can significantly decrease the performance in practice. As a result, in this survey, we explore the rapidly evolving field of IMU-based generalizable HAR, reviewing 229 research papers alongside 25 publicly available datasets to provide a broad and insightful overview. We first present the background and overall framework of IMU-based HAR tasks, as well as the generalization-oriented training settings. Then, we categorize representative methodologies from two perspectives: (i) model-centric approaches, including pre-training method, end-to-end method, and large language model (LLM)-based learning method; and (ii) data-centric approaches, including multi-modal learning and data augmentation techniques. In addition, we summarize widely used datasets in this field, as well as relevant tools and benchmarks. Building on these methodological advances, the broad applicability of IMU-based HAR is also reviewed and discussed. Finally, we discuss persistent challenges (e.g., data scarcity, efficient training, and reliable evaluation) and also outline future directions for HAR, including the adoption of foundation and large language models, physics-informed and context-aware reasoning, generative modeling, and resource-efficient training and inference. The complete list of this survey is available at https://github.com/rh20624/Awesome-IMU-Sensing, which will be updated continuously.
Versatile Framework for Song Generation with Prompt-based Control
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Song generation focuses on producing controllable high-quality songs based on various prompts. However, existing methods struggle to generate vocals and accompaniments with prompt-based control and proper alignment. Additionally, they fall short in supporting various tasks. To address these challenges, we introduce VersBand, a multi-task song generation framework for synthesizing high-quality, aligned songs with prompt-based control. VersBand comprises these primary models: 1) VocalBand, a decoupled model, leverages the flow-matching method for generating singing styles, pitches, and mel-spectrograms, allowing fast, high-quality vocal generation with style control. 2) AccompBand, a flow-based transformer model, incorporates the Band-MOE, selecting suitable experts for enhanced quality, alignment, and control. This model allows for generating controllable, high-quality accompaniments aligned with vocals. 3) Two generation models, LyricBand for lyrics and MelodyBand for melodies, contribute to the comprehensive multi-task song generation system, allowing for extensive control based on multiple prompts. Experimental results demonstrate that VersBand performs better over baseline models across multiple song generation tasks using objective and subjective metrics. Audio samples are available at https://aaronz345.github.io/VersBandDemo.
AddrLLM: Address Rewriting via Large Language Model on Nationwide Logistics Data
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:Textual description of a physical location, commonly known as an address, plays an important role in location-based services(LBS) such as on-demand delivery and navigation. However, the prevalence of abnormal addresses, those containing inaccuracies that fail to pinpoint a location, have led to significant costs. Address rewriting has emerged as a solution to rectify these abnormal addresses. Despite the critical need, existing address rewriting methods are limited, typically tailored to correct specific error types, or frequently require retraining to process new address data effectively. In this study, we introduce AddrLLM, an innovative framework for address rewriting that is built upon a retrieval augmented large language model. AddrLLM overcomes aforementioned limitations through a meticulously designed Supervised Fine-Tuning module, an Address-centric Retrieval Augmented Generation module and a Bias-free Objective Alignment module. To the best of our knowledge, this study pioneers the application of LLM-based address rewriting approach to solve the issue of abnormal addresses. Through comprehensive offline testing with real-world data on a national scale and subsequent online deployment, AddrLLM has demonstrated superior performance in integration with existing logistics system. It has significantly decreased the rate of parcel re-routing by approximately 43\%, underscoring its exceptional efficacy in real-world applications.
Variational Language Concepts for Interpreting Foundation Language Models
Oct 04, 2024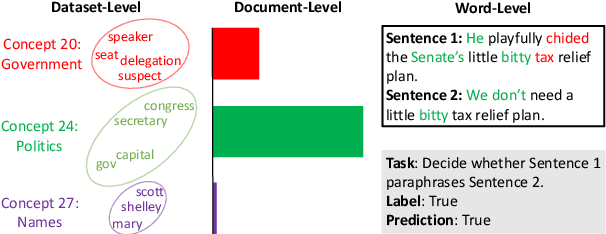
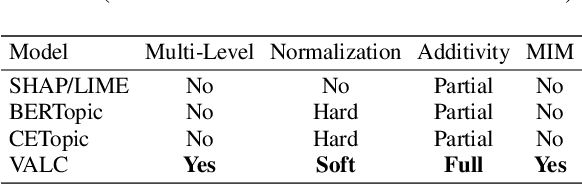
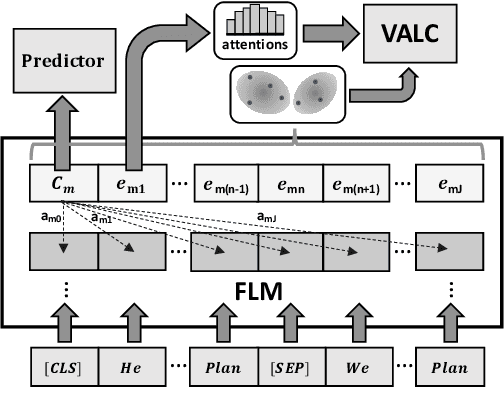
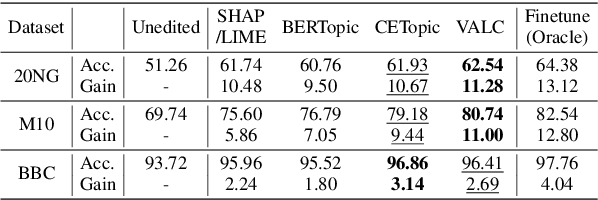
Abstract:Foundation Language Models (FLMs) such as BERT and its variants have achieved remarkable success in natural language processing. To date, the interpretability of FLMs has primarily relied on the attention weights in their self-attention layers. However, these attention weights only provide word-level interpretations, failing to capture higher-level structures, and are therefore lacking in readability and intuitiveness. To address this challenge, we first provide a formal definition of conceptual interpretation and then propose a variational Bayesian framework, dubbed VAriational Language Concept (VALC), to go beyond word-level interpretations and provide concept-level interpretations. Our theoretical analysis shows that our VALC finds the optimal language concepts to interpret FLM predictions. Empirical results on several real-world datasets show that our method can successfully provide conceptual interpretation for FLMs.
GTSinger: A Global Multi-Technique Singing Corpus with Realistic Music Scores for All Singing Tasks
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:The scarcity of high-quality and multi-task singing datasets significantly hinders the development of diverse controllable and personalized singing tasks, as existing singing datasets suffer from low quality, limited diversity of languages and singers, absence of multi-technique information and realistic music scores, and poor task suitability. To tackle these problems, we present GTSinger, a large global, multi-technique, free-to-use, high-quality singing corpus with realistic music scores, designed for all singing tasks, along with its benchmarks. Particularly, (1) we collect 80.59 hours of high-quality singing voices, forming the largest recorded singing dataset; (2) 20 professional singers across nine widely spoken languages offer diverse timbres and styles; (3) we provide controlled comparison and phoneme-level annotations of six commonly used singing techniques, helping technique modeling and control; (4) GTSinger offers realistic music scores, assisting real-world musical composition; (5) singing voices are accompanied by manual phoneme-to-audio alignments, global style labels, and 16.16 hours of paired speech for various singing tasks. Moreover, to facilitate the use of GTSinger, we conduct four benchmark experiments: technique-controllable singing voice synthesis, technique recognition, style transfer, and speech-to-singing conversion. The corpus and demos can be found at http://gtsinger.github.io. We provide the dataset and the code for processing data and conducting benchmarks at https://huggingface.co/datasets/GTSinger/GTSinger and https://github.com/GTSinger/GTSinger.
Accompanied Singing Voice Synthesis with Fully Text-controlled Melody
Jul 02, 2024


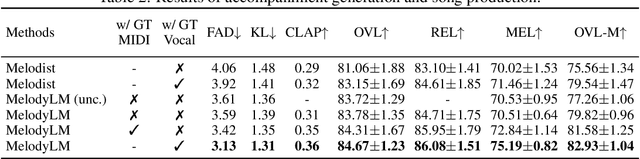
Abstract:Text-to-song (TTSong) is a music generation task that synthesizes accompanied singing voices. Current TTSong methods, inherited from singing voice synthesis (SVS), require melody-related information that can sometimes be impractical, such as music scores or MIDI sequences. We present MelodyLM, the first TTSong model that generates high-quality song pieces with fully text-controlled melodies, achieving minimal user requirements and maximum control flexibility. MelodyLM explicitly models MIDI as the intermediate melody-related feature and sequentially generates vocal tracks in a language model manner, conditioned on textual and vocal prompts. The accompaniment music is subsequently synthesized by a latent diffusion model with hybrid conditioning for temporal alignment. With minimal requirements, users only need to input lyrics and a reference voice to synthesize a song sample. For full control, just input textual prompts or even directly input MIDI. Experimental results indicate that MelodyLM achieves superior performance in terms of both objective and subjective metrics. Audio samples are available at https://melodylm666.github.io.
Self-Supervised Singing Voice Pre-Training towards Speech-to-Singing Conversion
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Speech-to-singing voice conversion (STS) task always suffers from data scarcity, because it requires paired speech and singing data. Compounding this issue are the challenges of content-pitch alignment and the suboptimal quality of generated outputs, presenting significant hurdles in STS research. This paper presents SVPT, an STS approach boosted by a self-supervised singing voice pre-training model. We leverage spoken language model techniques to tackle the rhythm alignment problem and the in-context learning capability to achieve zero-shot conversion. We adopt discrete-unit random resampling and pitch corruption strategies, enabling training with unpaired singing data and thus mitigating the issue of data scarcity. SVPT also serves as an effective backbone for singing voice synthesis (SVS), offering insights into scaling up SVS models. Experimental results indicate that SVPT delivers notable improvements in both STS and SVS endeavors. Audio samples are available at https://speech2sing.github.io.
Robust Singing Voice Transcription Serves Synthesis
May 16, 2024Abstract:Note-level Automatic Singing Voice Transcription (AST) converts singing recordings into note sequences, facilitating the automatic annotation of singing datasets for Singing Voice Synthesis (SVS) applications. Current AST methods, however, struggle with accuracy and robustness when used for practical annotation. This paper presents ROSVOT, the first robust AST model that serves SVS, incorporating a multi-scale framework that effectively captures coarse-grained note information and ensures fine-grained frame-level segmentation, coupled with an attention-based pitch decoder for reliable pitch prediction. We also established a comprehensive annotation-and-training pipeline for SVS to test the model in real-world settings. Experimental findings reveal that ROSVOT achieves state-of-the-art transcription accuracy with either clean or noisy inputs. Moreover, when trained on enlarged, automatically annotated datasets, the SVS model outperforms its baseline, affirming the capability for practical application. Audio samples are available at https://rosvot.github.io.
Text-to-Song: Towards Controllable Music Generation Incorporating Vocals and Accompaniment
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:A song is a combination of singing voice and accompaniment. However, existing works focus on singing voice synthesis and music generation independently. Little attention was paid to explore song synthesis. In this work, we propose a novel task called text-to-song synthesis which incorporating both vocals and accompaniments generation. We develop Melodist, a two-stage text-to-song method that consists of singing voice synthesis (SVS) and vocal-to-accompaniment (V2A) synthesis. Melodist leverages tri-tower contrastive pretraining to learn more effective text representation for controllable V2A synthesis. A Chinese song dataset mined from a music website is built up to alleviate data scarcity for our research. The evaluation results on our dataset demonstrate that Melodist can synthesize songs with comparable quality and style consistency. Audio samples can be found in https://text2songMelodist.github.io/Sample/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge