Chuxin Wang
Chat-Driven Text Generation and Interaction for Person Retrieval
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Text-based person search (TBPS) enables the retrieval of person images from large-scale databases using natural language descriptions, offering critical value in surveillance applications. However, a major challenge lies in the labor-intensive process of obtaining high-quality textual annotations, which limits scalability and practical deployment. To address this, we introduce two complementary modules: Multi-Turn Text Generation (MTG) and Multi-Turn Text Interaction (MTI). MTG generates rich pseudo-labels through simulated dialogues with MLLMs, producing fine-grained and diverse visual descriptions without manual supervision. MTI refines user queries at inference time through dynamic, dialogue-based reasoning, enabling the system to interpret and resolve vague, incomplete, or ambiguous descriptions - characteristics often seen in real-world search scenarios. Together, MTG and MTI form a unified and annotation-free framework that significantly improves retrieval accuracy, robustness, and usability. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our method achieves competitive or superior results while eliminating the need for manual captions, paving the way for scalable and practical deployment of TBPS systems.
Gaussian Variation Field Diffusion for High-fidelity Video-to-4D Synthesis
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel framework for video-to-4D generation that creates high-quality dynamic 3D content from single video inputs. Direct 4D diffusion modeling is extremely challenging due to costly data construction and the high-dimensional nature of jointly representing 3D shape, appearance, and motion. We address these challenges by introducing a Direct 4DMesh-to-GS Variation Field VAE that directly encodes canonical Gaussian Splats (GS) and their temporal variations from 3D animation data without per-instance fitting, and compresses high-dimensional animations into a compact latent space. Building upon this efficient representation, we train a Gaussian Variation Field diffusion model with temporal-aware Diffusion Transformer conditioned on input videos and canonical GS. Trained on carefully-curated animatable 3D objects from the Objaverse dataset, our model demonstrates superior generation quality compared to existing methods. It also exhibits remarkable generalization to in-the-wild video inputs despite being trained exclusively on synthetic data, paving the way for generating high-quality animated 3D content. Project page: https://gvfdiffusion.github.io/.
StruMamba3D: Exploring Structural Mamba for Self-supervised Point Cloud Representation Learning
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Recently, Mamba-based methods have demonstrated impressive performance in point cloud representation learning by leveraging State Space Model (SSM) with the efficient context modeling ability and linear complexity. However, these methods still face two key issues that limit the potential of SSM: Destroying the adjacency of 3D points during SSM processing and failing to retain long-sequence memory as the input length increases in downstream tasks. To address these issues, we propose StruMamba3D, a novel paradigm for self-supervised point cloud representation learning. It enjoys several merits. First, we design spatial states and use them as proxies to preserve spatial dependencies among points. Second, we enhance the SSM with a state-wise update strategy and incorporate a lightweight convolution to facilitate interactions between spatial states for efficient structure modeling. Third, our method reduces the sensitivity of pre-trained Mamba-based models to varying input lengths by introducing a sequence length-adaptive strategy. Experimental results across four downstream tasks showcase the superior performance of our method. In addition, our method attains the SOTA 95.1% accuracy on ModelNet40 and 92.75% accuracy on the most challenging split of ScanObjectNN without voting strategy.
State Space Model Meets Transformer: A New Paradigm for 3D Object Detection
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:DETR-based methods, which use multi-layer transformer decoders to refine object queries iteratively, have shown promising performance in 3D indoor object detection. However, the scene point features in the transformer decoder remain fixed, leading to minimal contributions from later decoder layers, thereby limiting performance improvement. Recently, State Space Models (SSM) have shown efficient context modeling ability with linear complexity through iterative interactions between system states and inputs. Inspired by SSMs, we propose a new 3D object DEtection paradigm with an interactive STate space model (DEST). In the interactive SSM, we design a novel state-dependent SSM parameterization method that enables system states to effectively serve as queries in 3D indoor detection tasks. In addition, we introduce four key designs tailored to the characteristics of point cloud and SSM: The serialization and bidirectional scanning strategies enable bidirectional feature interaction among scene points within the SSM. The inter-state attention mechanism models the relationships between state points, while the gated feed-forward network enhances inter-channel correlations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first method to model queries as system states and scene points as system inputs, which can simultaneously update scene point features and query features with linear complexity. Extensive experiments on two challenging datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our DEST-based method. Our method improves the GroupFree baseline in terms of AP50 on ScanNet V2 (+5.3) and SUN RGB-D (+3.2) datasets. Based on the VDETR baseline, Our method sets a new SOTA on the ScanNetV2 and SUN RGB-D datasets.
TCSinger: Zero-Shot Singing Voice Synthesis with Style Transfer and Multi-Level Style Control
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Zero-shot singing voice synthesis (SVS) with style transfer and style control aims to generate high-quality singing voices with unseen timbres and styles (including singing method, emotion, rhythm, technique, and pronunciation) from audio and text prompts. However, the multifaceted nature of singing styles poses a significant challenge for effective modeling, transfer, and control. Furthermore, current SVS models often fail to generate singing voices rich in stylistic nuances for unseen singers. To address these challenges, we introduce TCSinger, the first zero-shot SVS model for style transfer across cross-lingual speech and singing styles, along with multi-level style control. Specifically, TCSinger proposes three primary modules: 1) the clustering style encoder employs a clustering vector quantization model to stably condense style information into a compact latent space; 2) the Style and Duration Language Model (S\&D-LM) concurrently predicts style information and phoneme duration, which benefits both; 3) the style adaptive decoder uses a novel mel-style adaptive normalization method to generate singing voices with enhanced details. Experimental results show that TCSinger outperforms all baseline models in synthesis quality, singer similarity, and style controllability across various tasks, including zero-shot style transfer, multi-level style control, cross-lingual style transfer, and speech-to-singing style transfer. Singing voice samples can be accessed at https://tcsinger.github.io/.
GTSinger: A Global Multi-Technique Singing Corpus with Realistic Music Scores for All Singing Tasks
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:The scarcity of high-quality and multi-task singing datasets significantly hinders the development of diverse controllable and personalized singing tasks, as existing singing datasets suffer from low quality, limited diversity of languages and singers, absence of multi-technique information and realistic music scores, and poor task suitability. To tackle these problems, we present GTSinger, a large global, multi-technique, free-to-use, high-quality singing corpus with realistic music scores, designed for all singing tasks, along with its benchmarks. Particularly, (1) we collect 80.59 hours of high-quality singing voices, forming the largest recorded singing dataset; (2) 20 professional singers across nine widely spoken languages offer diverse timbres and styles; (3) we provide controlled comparison and phoneme-level annotations of six commonly used singing techniques, helping technique modeling and control; (4) GTSinger offers realistic music scores, assisting real-world musical composition; (5) singing voices are accompanied by manual phoneme-to-audio alignments, global style labels, and 16.16 hours of paired speech for various singing tasks. Moreover, to facilitate the use of GTSinger, we conduct four benchmark experiments: technique-controllable singing voice synthesis, technique recognition, style transfer, and speech-to-singing conversion. The corpus and demos can be found at http://gtsinger.github.io. We provide the dataset and the code for processing data and conducting benchmarks at https://huggingface.co/datasets/GTSinger/GTSinger and https://github.com/GTSinger/GTSinger.
ScaleDepth: Decomposing Metric Depth Estimation into Scale Prediction and Relative Depth Estimation
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:Estimating depth from a single image is a challenging visual task. Compared to relative depth estimation, metric depth estimation attracts more attention due to its practical physical significance and critical applications in real-life scenarios. However, existing metric depth estimation methods are typically trained on specific datasets with similar scenes, facing challenges in generalizing across scenes with significant scale variations. To address this challenge, we propose a novel monocular depth estimation method called ScaleDepth. Our method decomposes metric depth into scene scale and relative depth, and predicts them through a semantic-aware scale prediction (SASP) module and an adaptive relative depth estimation (ARDE) module, respectively. The proposed ScaleDepth enjoys several merits. First, the SASP module can implicitly combine structural and semantic features of the images to predict precise scene scales. Second, the ARDE module can adaptively estimate the relative depth distribution of each image within a normalized depth space. Third, our method achieves metric depth estimation for both indoor and outdoor scenes in a unified framework, without the need for setting the depth range or fine-tuning model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method attains state-of-the-art performance across indoor, outdoor, unconstrained, and unseen scenes. Project page: https://ruijiezhu94.github.io/ScaleDepth
EC-Depth: Exploring the consistency of self-supervised monocular depth estimation under challenging scenes
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised monocular depth estimation holds significant importance in the fields of autonomous driving and robotics. However, existing methods are typically designed to train and test on clear and pristine datasets, overlooking the impact of various adverse conditions prevalent in real-world scenarios. As a result, it is commonly observed that most self-supervised monocular depth estimation methods struggle to perform adequately under challenging conditions. To address this issue, we present EC-Depth, a novel self-supervised two-stage training framework to achieve a robust depth estimation, starting from the foundation of depth prediction consistency under different perturbations. Leveraging the proposed perturbation-invariant depth consistency constraint module and the consistency-based pseudo-label selection module, our model attains accurate and consistent depth predictions in both standard and challenging scenarios. Extensive experiments substantiate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Moreover, our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods on KITTI, KITTI-C and DrivingStereo benchmarks, demonstrating its potential for enhancing the reliability of self-supervised monocular depth estimation models in real-world applications.
SE-ORNet: Self-Ensembling Orientation-aware Network for Unsupervised Point Cloud Shape Correspondence
Apr 10, 2023



Abstract:Unsupervised point cloud shape correspondence aims to obtain dense point-to-point correspondences between point clouds without manually annotated pairs. However, humans and some animals have bilateral symmetry and various orientations, which lead to severe mispredictions of symmetrical parts. Besides, point cloud noise disrupts consistent representations for point cloud and thus degrades the shape correspondence accuracy. To address the above issues, we propose a Self-Ensembling ORientation-aware Network termed SE-ORNet. The key of our approach is to exploit an orientation estimation module with a domain adaptive discriminator to align the orientations of point cloud pairs, which significantly alleviates the mispredictions of symmetrical parts. Additionally, we design a selfensembling framework for unsupervised point cloud shape correspondence. In this framework, the disturbances of point cloud noise are overcome by perturbing the inputs of the student and teacher networks with different data augmentations and constraining the consistency of predictions. Extensive experiments on both human and animal datasets show that our SE-ORNet can surpass state-of-the-art unsupervised point cloud shape correspondence methods.
Style-based Point Generator with Adversarial Rendering for Point Cloud Completion
Mar 26, 2021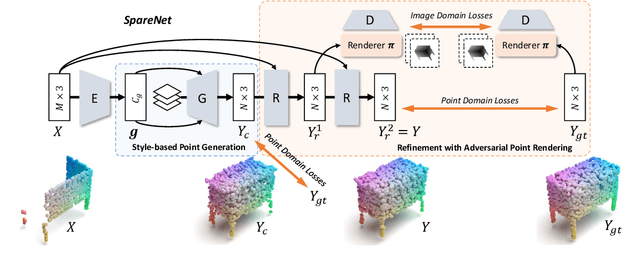
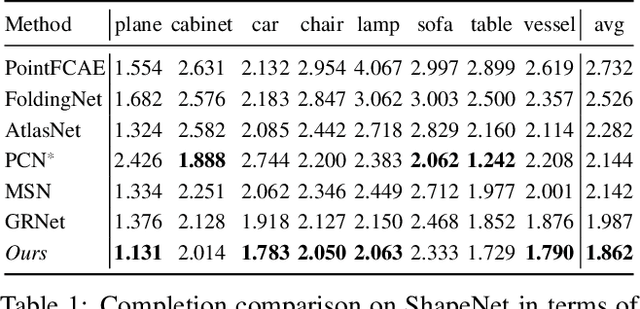
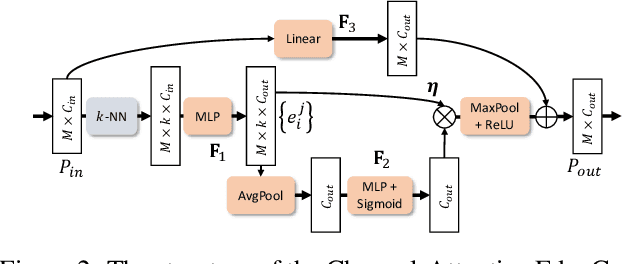
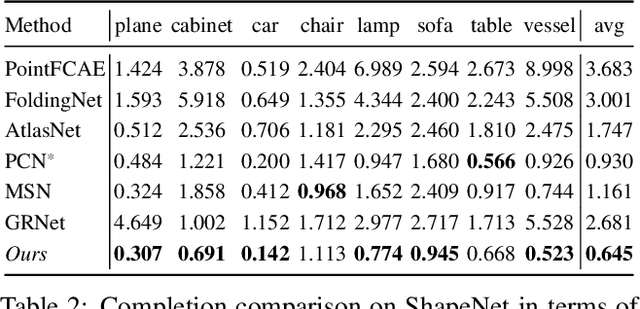
Abstract:In this paper, we proposed a novel Style-based Point Generator with Adversarial Rendering (SpareNet) for point cloud completion. Firstly, we present the channel-attentive EdgeConv to fully exploit the local structures as well as the global shape in point features. Secondly, we observe that the concatenation manner used by vanilla foldings limits its potential of generating a complex and faithful shape. Enlightened by the success of StyleGAN, we regard the shape feature as style code that modulates the normalization layers during the folding, which considerably enhances its capability. Thirdly, we realize that existing point supervisions, e.g., Chamfer Distance or Earth Mover's Distance, cannot faithfully reflect the perceptual quality of the reconstructed points. To address this, we propose to project the completed points to depth maps with a differentiable renderer and apply adversarial training to advocate the perceptual realism under different viewpoints. Comprehensive experiments on ShapeNet and KITTI prove the effectiveness of our method, which achieves state-of-the-art quantitative performance while offering superior visual quality. Code is available at https://github.com/microsoft/SpareNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge