Xize Cheng
T2A-Feedback: Improving Basic Capabilities of Text-to-Audio Generation via Fine-grained AI Feedback
May 15, 2025

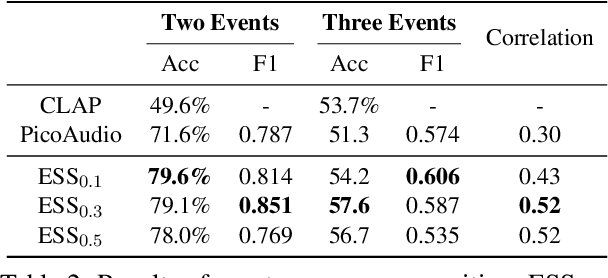

Abstract:Text-to-audio (T2A) generation has achieved remarkable progress in generating a variety of audio outputs from language prompts. However, current state-of-the-art T2A models still struggle to satisfy human preferences for prompt-following and acoustic quality when generating complex multi-event audio. To improve the performance of the model in these high-level applications, we propose to enhance the basic capabilities of the model with AI feedback learning. First, we introduce fine-grained AI audio scoring pipelines to: 1) verify whether each event in the text prompt is present in the audio (Event Occurrence Score), 2) detect deviations in event sequences from the language description (Event Sequence Score), and 3) assess the overall acoustic and harmonic quality of the generated audio (Acoustic&Harmonic Quality). We evaluate these three automatic scoring pipelines and find that they correlate significantly better with human preferences than other evaluation metrics. This highlights their value as both feedback signals and evaluation metrics. Utilizing our robust scoring pipelines, we construct a large audio preference dataset, T2A-FeedBack, which contains 41k prompts and 249k audios, each accompanied by detailed scores. Moreover, we introduce T2A-EpicBench, a benchmark that focuses on long captions, multi-events, and story-telling scenarios, aiming to evaluate the advanced capabilities of T2A models. Finally, we demonstrate how T2A-FeedBack can enhance current state-of-the-art audio model. With simple preference tuning, the audio generation model exhibits significant improvements in both simple (AudioCaps test set) and complex (T2A-EpicBench) scenarios.
WavReward: Spoken Dialogue Models With Generalist Reward Evaluators
May 14, 2025Abstract:End-to-end spoken dialogue models such as GPT-4o-audio have recently garnered significant attention in the speech domain. However, the evaluation of spoken dialogue models' conversational performance has largely been overlooked. This is primarily due to the intelligent chatbots convey a wealth of non-textual information which cannot be easily measured using text-based language models like ChatGPT. To address this gap, we propose WavReward, a reward feedback model based on audio language models that can evaluate both the IQ and EQ of spoken dialogue systems with speech input. Specifically, 1) based on audio language models, WavReward incorporates the deep reasoning process and the nonlinear reward mechanism for post-training. By utilizing multi-sample feedback via the reinforcement learning algorithm, we construct a specialized evaluator tailored to spoken dialogue models. 2) We introduce ChatReward-30K, a preference dataset used to train WavReward. ChatReward-30K includes both comprehension and generation aspects of spoken dialogue models. These scenarios span various tasks, such as text-based chats, nine acoustic attributes of instruction chats, and implicit chats. WavReward outperforms previous state-of-the-art evaluation models across multiple spoken dialogue scenarios, achieving a substantial improvement about Qwen2.5-Omni in objective accuracy from 55.1$\%$ to 91.5$\%$. In subjective A/B testing, WavReward also leads by a margin of 83$\%$. Comprehensive ablation studies confirm the necessity of each component of WavReward. All data and code will be publicly at https://github.com/jishengpeng/WavReward after the paper is accepted.
Unleashing the Power of Natural Audio Featuring Multiple Sound Sources
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Universal sound separation aims to extract clean audio tracks corresponding to distinct events from mixed audio, which is critical for artificial auditory perception. However, current methods heavily rely on artificially mixed audio for training, which limits their ability to generalize to naturally mixed audio collected in real-world environments. To overcome this limitation, we propose ClearSep, an innovative framework that employs a data engine to decompose complex naturally mixed audio into multiple independent tracks, thereby allowing effective sound separation in real-world scenarios. We introduce two remix-based evaluation metrics to quantitatively assess separation quality and use these metrics as thresholds to iteratively apply the data engine alongside model training, progressively optimizing separation performance. In addition, we propose a series of training strategies tailored to these separated independent tracks to make the best use of them. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ClearSep achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple sound separation tasks, highlighting its potential for advancing sound separation in natural audio scenarios. For more examples and detailed results, please visit our demo page at https://clearsep.github.io.
Enhancing Expressive Voice Conversion with Discrete Pitch-Conditioned Flow Matching Model
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces PFlow-VC, a conditional flow matching voice conversion model that leverages fine-grained discrete pitch tokens and target speaker prompt information for expressive voice conversion (VC). Previous VC works primarily focus on speaker conversion, with further exploration needed in enhancing expressiveness (such as prosody and emotion) for timbre conversion. Unlike previous methods, we adopt a simple and efficient approach to enhance the style expressiveness of voice conversion models. Specifically, we pretrain a self-supervised pitch VQVAE model to discretize speaker-irrelevant pitch information and leverage a masked pitch-conditioned flow matching model for Mel-spectrogram synthesis, which provides in-context pitch modeling capabilities for the speaker conversion model, effectively improving the voice style transfer capacity. Additionally, we improve timbre similarity by combining global timbre embeddings with time-varying timbre tokens. Experiments on unseen LibriTTS test-clean and emotional speech dataset ESD show the superiority of the PFlow-VC model in both timbre conversion and style transfer. Audio samples are available on the demo page https://speechai-demo.github.io/PFlow-VC/.
OmniChat: Enhancing Spoken Dialogue Systems with Scalable Synthetic Data for Diverse Scenarios
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of large language models, researchers have created increasingly advanced spoken dialogue systems that can naturally converse with humans. However, these systems still struggle to handle the full complexity of real-world conversations, including audio events, musical contexts, and emotional expressions, mainly because current dialogue datasets are constrained in both scale and scenario diversity. In this paper, we propose leveraging synthetic data to enhance the dialogue models across diverse scenarios. We introduce ShareChatX, the first comprehensive, large-scale dataset for spoken dialogue that spans diverse scenarios. Based on this dataset, we introduce OmniChat, a multi-turn dialogue system with a heterogeneous feature fusion module, designed to optimize feature selection in different dialogue contexts. In addition, we explored critical aspects of training dialogue systems using synthetic data. Through comprehensive experimentation, we determined the ideal balance between synthetic and real data, achieving state-of-the-art results on the real-world dialogue dataset DailyTalk. We also highlight the crucial importance of synthetic data in tackling diverse, complex dialogue scenarios, especially those involving audio and music. For more details, please visit our demo page at \url{https://sharechatx.github.io/}.
A Wander Through the Multimodal Landscape: Efficient Transfer Learning via Low-rank Sequence Multimodal Adapter
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Efficient transfer learning methods such as adapter-based methods have shown great success in unimodal models and vision-language models. However, existing methods have two main challenges in fine-tuning multimodal models. Firstly, they are designed for vision-language tasks and fail to extend to situations where there are more than two modalities. Secondly, they exhibit limited exploitation of interactions between modalities and lack efficiency. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose the loW-rank sequence multimodal adapter (Wander). We first use the outer product to fuse the information from different modalities in an element-wise way effectively. For efficiency, we use CP decomposition to factorize tensors into rank-one components and achieve substantial parameter reduction. Furthermore, we implement a token-level low-rank decomposition to extract more fine-grained features and sequence relationships between modalities. With these designs, Wander enables token-level interactions between sequences of different modalities in a parameter-efficient way. We conduct extensive experiments on datasets with different numbers of modalities, where Wander outperforms state-of-the-art efficient transfer learning methods consistently. The results fully demonstrate the effectiveness, efficiency and universality of Wander.
WavChat: A Survey of Spoken Dialogue Models
Nov 26, 2024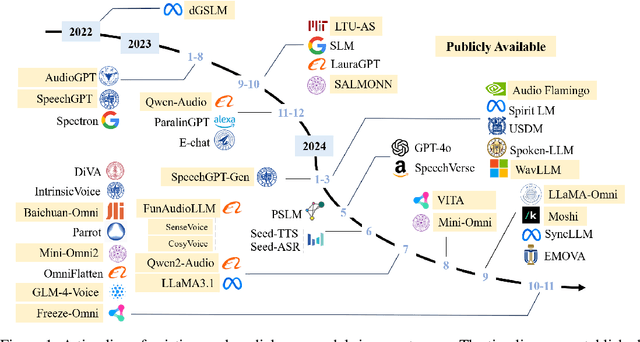

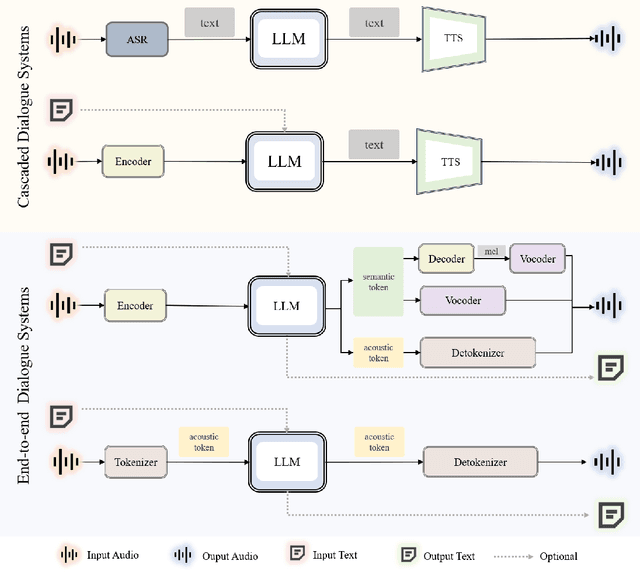
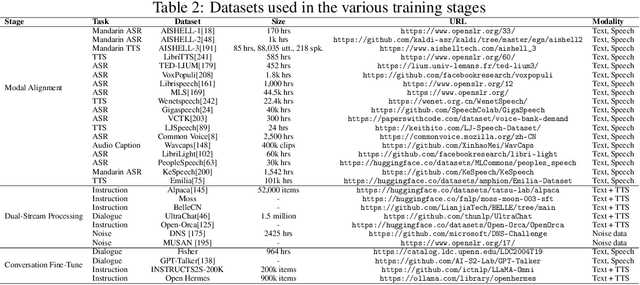
Abstract:Recent advancements in spoken dialogue models, exemplified by systems like GPT-4o, have captured significant attention in the speech domain. Compared to traditional three-tier cascaded spoken dialogue models that comprise speech recognition (ASR), large language models (LLMs), and text-to-speech (TTS), modern spoken dialogue models exhibit greater intelligence. These advanced spoken dialogue models not only comprehend audio, music, and other speech-related features, but also capture stylistic and timbral characteristics in speech. Moreover, they generate high-quality, multi-turn speech responses with low latency, enabling real-time interaction through simultaneous listening and speaking capability. Despite the progress in spoken dialogue systems, there is a lack of comprehensive surveys that systematically organize and analyze these systems and the underlying technologies. To address this, we have first compiled existing spoken dialogue systems in the chronological order and categorized them into the cascaded and end-to-end paradigms. We then provide an in-depth overview of the core technologies in spoken dialogue models, covering aspects such as speech representation, training paradigm, streaming, duplex, and interaction capabilities. Each section discusses the limitations of these technologies and outlines considerations for future research. Additionally, we present a thorough review of relevant datasets, evaluation metrics, and benchmarks from the perspectives of training and evaluating spoken dialogue systems. We hope this survey will contribute to advancing both academic research and industrial applications in the field of spoken dialogue systems. The related material is available at https://github.com/jishengpeng/WavChat.
OmniSep: Unified Omni-Modality Sound Separation with Query-Mixup
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:The scaling up has brought tremendous success in the fields of vision and language in recent years. When it comes to audio, however, researchers encounter a major challenge in scaling up the training data, as most natural audio contains diverse interfering signals. To address this limitation, we introduce Omni-modal Sound Separation (OmniSep), a novel framework capable of isolating clean soundtracks based on omni-modal queries, encompassing both single-modal and multi-modal composed queries. Specifically, we introduce the Query-Mixup strategy, which blends query features from different modalities during training. This enables OmniSep to optimize multiple modalities concurrently, effectively bringing all modalities under a unified framework for sound separation. We further enhance this flexibility by allowing queries to influence sound separation positively or negatively, facilitating the retention or removal of specific sounds as desired. Finally, OmniSep employs a retrieval-augmented approach known as Query-Aug, which enables open-vocabulary sound separation. Experimental evaluations on MUSIC, VGGSOUND-CLEAN+, and MUSIC-CLEAN+ datasets demonstrate effectiveness of OmniSep, achieving state-of-the-art performance in text-, image-, and audio-queried sound separation tasks. For samples and further information, please visit the demo page at \url{https://omnisep.github.io/}.
MuVi: Video-to-Music Generation with Semantic Alignment and Rhythmic Synchronization
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Generating music that aligns with the visual content of a video has been a challenging task, as it requires a deep understanding of visual semantics and involves generating music whose melody, rhythm, and dynamics harmonize with the visual narratives. This paper presents MuVi, a novel framework that effectively addresses these challenges to enhance the cohesion and immersive experience of audio-visual content. MuVi analyzes video content through a specially designed visual adaptor to extract contextually and temporally relevant features. These features are used to generate music that not only matches the video's mood and theme but also its rhythm and pacing. We also introduce a contrastive music-visual pre-training scheme to ensure synchronization, based on the periodicity nature of music phrases. In addition, we demonstrate that our flow-matching-based music generator has in-context learning ability, allowing us to control the style and genre of the generated music. Experimental results show that MuVi demonstrates superior performance in both audio quality and temporal synchronization. The generated music video samples are available at https://muvi-v2m.github.io.
SegTalker: Segmentation-based Talking Face Generation with Mask-guided Local Editing
Sep 05, 2024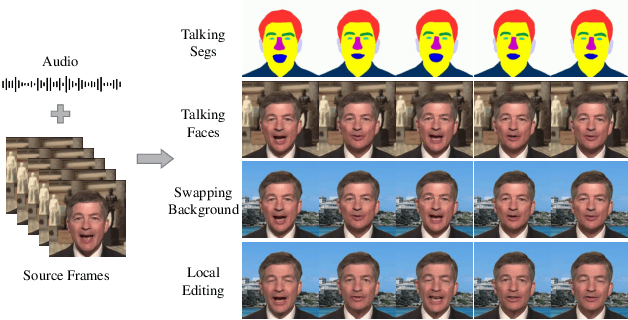
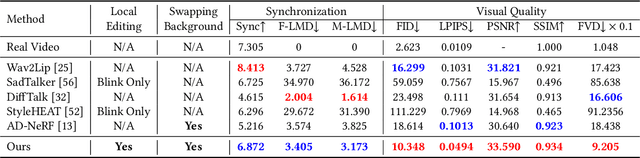
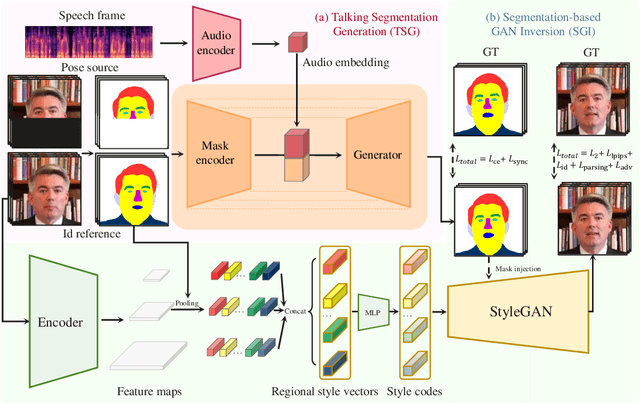
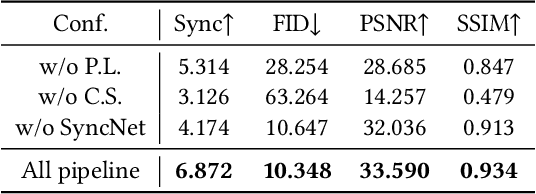
Abstract:Audio-driven talking face generation aims to synthesize video with lip movements synchronized to input audio. However, current generative techniques face challenges in preserving intricate regional textures (skin, teeth). To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose a novel framework called SegTalker to decouple lip movements and image textures by introducing segmentation as intermediate representation. Specifically, given the mask of image employed by a parsing network, we first leverage the speech to drive the mask and generate talking segmentation. Then we disentangle semantic regions of image into style codes using a mask-guided encoder. Ultimately, we inject the previously generated talking segmentation and style codes into a mask-guided StyleGAN to synthesize video frame. In this way, most of textures are fully preserved. Moreover, our approach can inherently achieve background separation and facilitate mask-guided facial local editing. In particular, by editing the mask and swapping the region textures from a given reference image (e.g. hair, lip, eyebrows), our approach enables facial editing seamlessly when generating talking face video. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach can effectively preserve texture details and generate temporally consistent video while remaining competitive in lip synchronization. Quantitative and qualitative results on the HDTF and MEAD datasets illustrate the superior performance of our method over existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge