Ke Lei
T2A-Feedback: Improving Basic Capabilities of Text-to-Audio Generation via Fine-grained AI Feedback
May 15, 2025

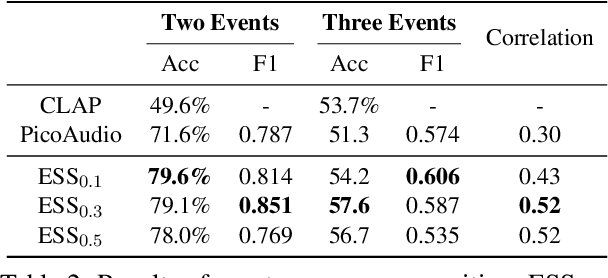

Abstract:Text-to-audio (T2A) generation has achieved remarkable progress in generating a variety of audio outputs from language prompts. However, current state-of-the-art T2A models still struggle to satisfy human preferences for prompt-following and acoustic quality when generating complex multi-event audio. To improve the performance of the model in these high-level applications, we propose to enhance the basic capabilities of the model with AI feedback learning. First, we introduce fine-grained AI audio scoring pipelines to: 1) verify whether each event in the text prompt is present in the audio (Event Occurrence Score), 2) detect deviations in event sequences from the language description (Event Sequence Score), and 3) assess the overall acoustic and harmonic quality of the generated audio (Acoustic&Harmonic Quality). We evaluate these three automatic scoring pipelines and find that they correlate significantly better with human preferences than other evaluation metrics. This highlights their value as both feedback signals and evaluation metrics. Utilizing our robust scoring pipelines, we construct a large audio preference dataset, T2A-FeedBack, which contains 41k prompts and 249k audios, each accompanied by detailed scores. Moreover, we introduce T2A-EpicBench, a benchmark that focuses on long captions, multi-events, and story-telling scenarios, aiming to evaluate the advanced capabilities of T2A models. Finally, we demonstrate how T2A-FeedBack can enhance current state-of-the-art audio model. With simple preference tuning, the audio generation model exhibits significant improvements in both simple (AudioCaps test set) and complex (T2A-EpicBench) scenarios.
Automated MRI Field of View Prescription from Region of Interest Prediction by Intra-stack Attention Neural Network
Nov 09, 2022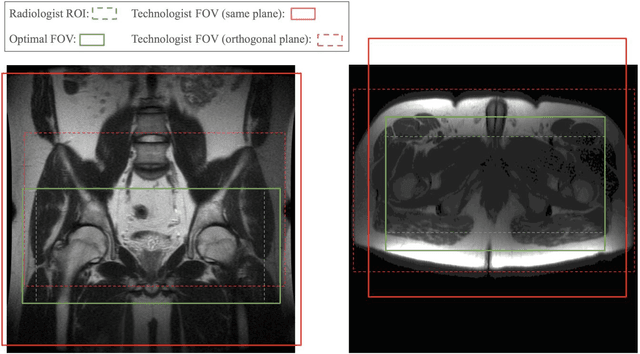
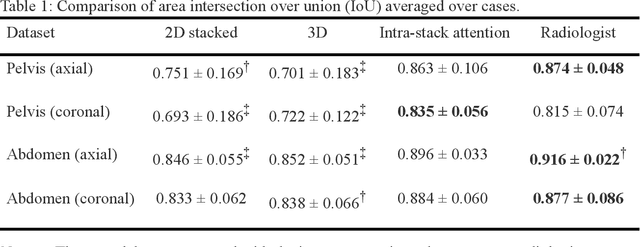
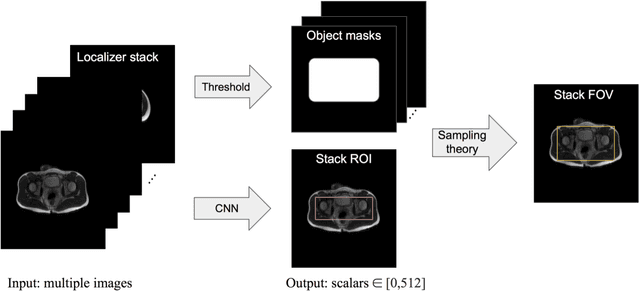
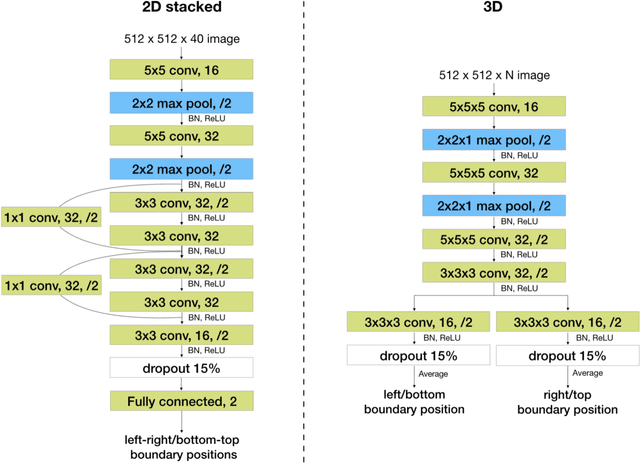
Abstract:Manual prescription of the field of view (FOV) by MRI technologists is variable and prolongs the scanning process. Often, the FOV is too large or crops critical anatomy. We propose a deep-learning framework, trained by radiologists' supervision, for automating FOV prescription. An intra-stack shared feature extraction network and an attention network are used to process a stack of 2D image inputs to generate output scalars defining the location of a rectangular region of interest (ROI). The attention mechanism is used to make the model focus on the small number of informative slices in a stack. Then the smallest FOV that makes the neural network predicted ROI free of aliasing is calculated by an algebraic operation derived from MR sampling theory. We retrospectively collected 595 cases between February 2018 and February 2022. The framework's performance is examined quantitatively with intersection over union (IoU) and pixel error on position, and qualitatively with a reader study. We use the t-test for comparing quantitative results from all models and a radiologist. The proposed model achieves an average IoU of 0.867 and average ROI position error of 9.06 out of 512 pixels on 80 test cases, significantly better (P<0.05) than two baseline models and not significantly different from a radiologist (P>0.12). Finally, the FOV given by the proposed framework achieves an acceptance rate of 92% from an experienced radiologist.
Artifact- and content-specific quality assessment for MRI with image rulers
Nov 06, 2021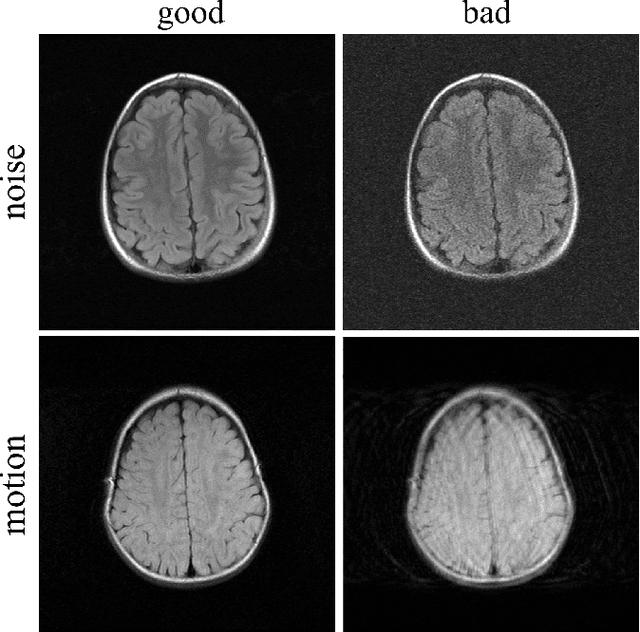
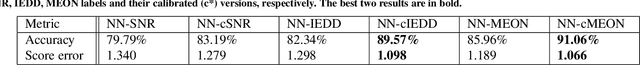
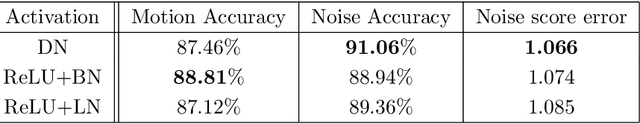
Abstract:In clinical practice MR images are often first seen by radiologists long after the scan. If image quality is inadequate either patients have to return for an additional scan, or a suboptimal interpretation is rendered. An automatic image quality assessment (IQA) would enable real-time remediation. Existing IQA works for MRI give only a general quality score, agnostic to the cause of and solution to low-quality scans. Furthermore, radiologists' image quality requirements vary with the scan type and diagnostic task. Therefore, the same score may have different implications for different scans. We propose a framework with multi-task CNN model trained with calibrated labels and inferenced with image rulers. Labels calibrated by human inputs follow a well-defined and efficient labeling task. Image rulers address varying quality standards and provide a concrete way of interpreting raw scores from the CNN. The model supports assessments of two of the most common artifacts in MRI: noise and motion. It achieves accuracies of around 90%, 6% better than the best previous method examined, and 3% better than human experts on noise assessment. Our experiments show that label calibration, image rulers, and multi-task training improve the model's performance and generalizability.
Wasserstein GANs for MR Imaging: from Paired to Unpaired Training
Oct 15, 2019
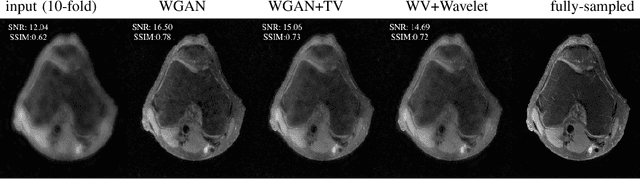
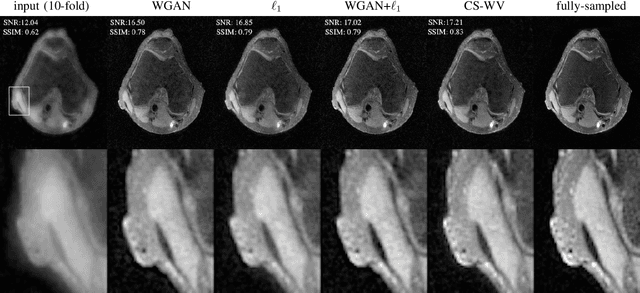
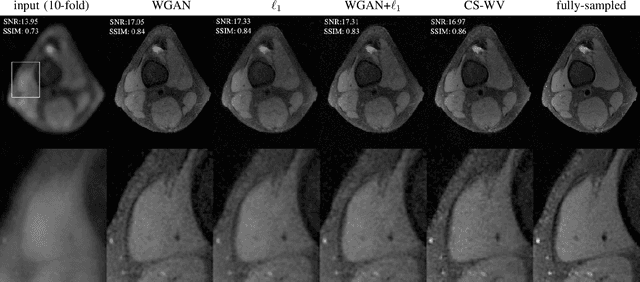
Abstract:Lack of ground-truth MR images (labels) impedes the common supervised training of deep networks for image reconstruction. To cope with this challenge, this paper leverages WGANs for unpaired training of reconstruction networks, where the inputs are the undersampled naively reconstructed images from one dataset, and the outputs are high-quality images from another dataset. The generator network is an unrolled neural network with a cascade of residual blocks and data consistency modules. The discriminator is also a multilayer CNN that plays the role of a critic scoring the quality of reconstructed images. Our extensive experiments with knee MRI datasets demonstrate unpaired WGAN training with minimal supervision is a viable option when there exists insufficient or no fully-sampled training label images that match the input images. Also, supervised paired training with additional WGAN loss achieves better and faster reconstruction compared to wavelet-based compressed sensing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge