Artifact- and content-specific quality assessment for MRI with image rulers
Paper and Code
Nov 06, 2021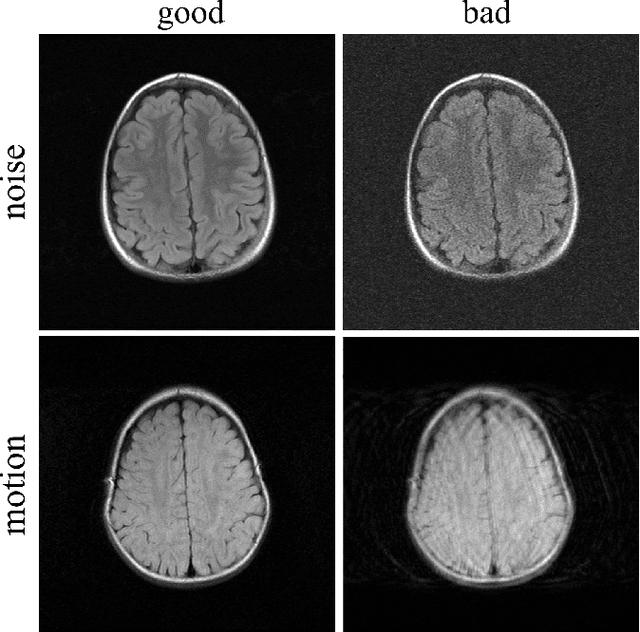
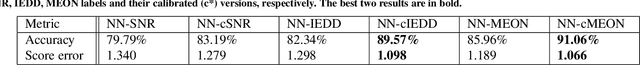
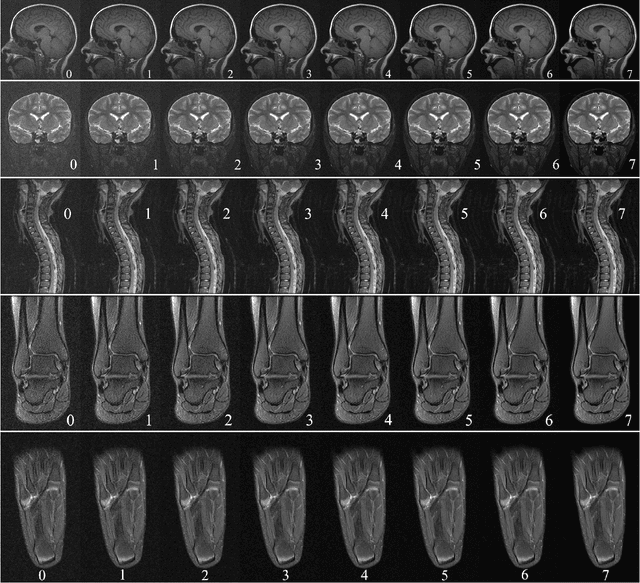
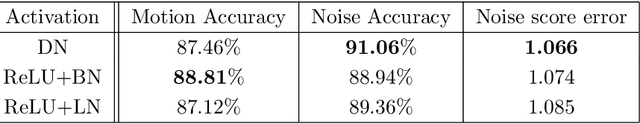
In clinical practice MR images are often first seen by radiologists long after the scan. If image quality is inadequate either patients have to return for an additional scan, or a suboptimal interpretation is rendered. An automatic image quality assessment (IQA) would enable real-time remediation. Existing IQA works for MRI give only a general quality score, agnostic to the cause of and solution to low-quality scans. Furthermore, radiologists' image quality requirements vary with the scan type and diagnostic task. Therefore, the same score may have different implications for different scans. We propose a framework with multi-task CNN model trained with calibrated labels and inferenced with image rulers. Labels calibrated by human inputs follow a well-defined and efficient labeling task. Image rulers address varying quality standards and provide a concrete way of interpreting raw scores from the CNN. The model supports assessments of two of the most common artifacts in MRI: noise and motion. It achieves accuracies of around 90%, 6% better than the best previous method examined, and 3% better than human experts on noise assessment. Our experiments show that label calibration, image rulers, and multi-task training improve the model's performance and generalizability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge