Shreyas S. Vasanawala
On the Foundation Model for Cardiac MRI Reconstruction
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, machine learning (ML) based reconstruction has been widely investigated and employed in cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. ML-based reconstructions can deliver clinically acceptable image quality under substantially accelerated scans. ML-based reconstruction, however, also requires substantial data and computational time to train the neural network, which is often optimized for a fixed acceleration rate or image contrast. In practice, imaging parameters are often tuned to best suit the diagnosis, which may differ from the training data. This can result in degraded image quality, and multiple trained networks are needed to fulfill the clinical demands. In this study, we propose a foundation model that uses adaptive unrolling, channel-shifting, and Pattern and Contrast-Prompt-UNet (PCP-UNet) to tackle the problem. In particular, the undersampled data goes through a different number of unrolled iterations according to its acceleration rate. Channel-shifting improves reconstructed data quality. The PCP-UNet is equipped with an image contrast and sampling pattern prompt. In vivo CMR experiments were performed using mixed combinations of image contrasts, acceleration rates, and (under)sampling patterns. The proposed foundation model has significantly improved image quality for a wide range of CMR protocols and outperforms the conventional ML-based method.
AutoSamp: Autoencoding MRI Sampling via Variational Information Maximization
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:Accelerated MRI protocols routinely involve a predefined sampling pattern that undersamples the k-space. Finding an optimal pattern can enhance the reconstruction quality, however this optimization is a challenging task. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel deep learning framework, AutoSamp, based on variational information maximization that enables joint optimization of sampling pattern and reconstruction of MRI scans. We represent the encoder as a non-uniform Fast Fourier Transform that allows continuous optimization of k-space sample locations on a non-Cartesian plane, and the decoder as a deep reconstruction network. Experiments on public MRI datasets show improved reconstruction quality of the proposed AutoSamp method over the prevailing variable density and variable density Poisson disc sampling. We demonstrate that our data-driven sampling optimization method achieves 4.4dB, 2.0dB, 0.75dB, 0.7dB PSNR improvements over reconstruction with Poisson Disc masks for acceleration factors of R = 5, 10, 15, 25, respectively. Furthermore, we analyze the characteristics of the learned sampling patterns with respect to changes in acceleration factor, measurement noise, underlying anatomy, and coil sensitivities. We show that all these factors contribute to the optimization result by affecting the sampling density, k-space coverage and point spread functions of the learned sampling patterns.
Coil Sketching for computationally-efficient MR iterative reconstruction
May 10, 2023Abstract:Purpose: Parallel imaging and compressed sensing reconstructions of large MRI datasets often have a prohibitive computational cost that bottlenecks clinical deployment, especially for 3D non-Cartesian acquisitions. One common approach is to reduce the number of coil channels actively used during reconstruction as in coil compression. While effective for Cartesian imaging, coil compression inherently loses signal energy, producing shading artifacts that compromise image quality for 3D non-Cartesian imaging. We propose coil sketching, a general and versatile method for computationally-efficient iterative MR image reconstruction. Theory and Methods: We based our method on randomized sketching algorithms, a type of large-scale optimization algorithms well established in the fields of machine learning and big data analysis. We adapt the sketching theory to the MRI reconstruction problem via a structured sketching matrix that, similar to coil compression, reduces the number of coils concurrently used during reconstruction, but unlike coil compression, is able to leverage energy from all coils. Results: First, we performed ablation experiments to validate the sketching matrix design on both Cartesian and non-Cartesian datasets. The resulting design yielded both improved computational efficiency and preserved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as measured by the inverse g-factor. Then, we verified the efficacy of our approach on high-dimensional non-Cartesian 3D cones datasets, where coil sketching yielded up to three-fold faster reconstructions with equivalent image quality. Conclusion: Coil sketching is a general and versatile reconstruction framework for computationally fast and memory-efficient reconstruction.
Automated MRI Field of View Prescription from Region of Interest Prediction by Intra-stack Attention Neural Network
Nov 09, 2022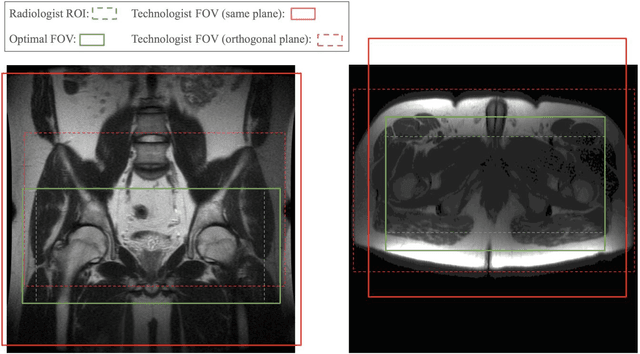
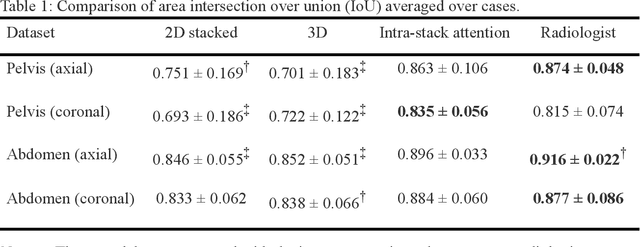
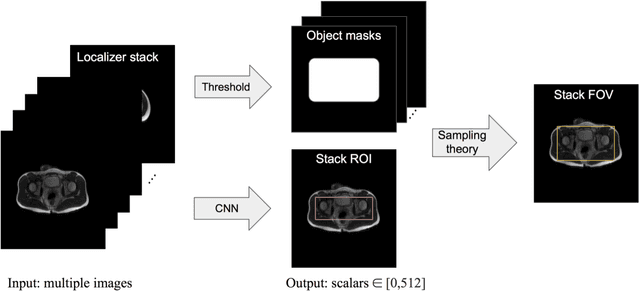
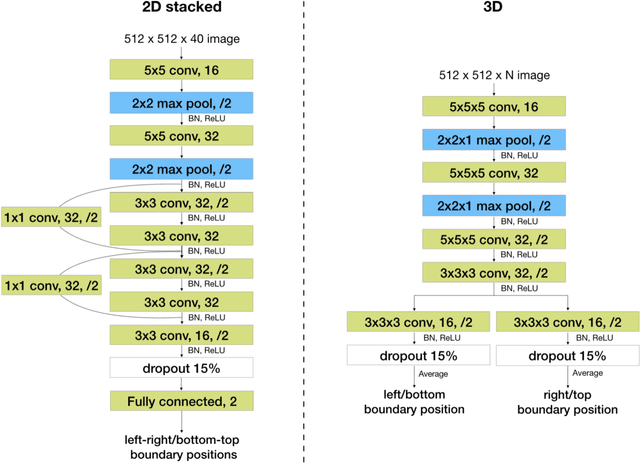
Abstract:Manual prescription of the field of view (FOV) by MRI technologists is variable and prolongs the scanning process. Often, the FOV is too large or crops critical anatomy. We propose a deep-learning framework, trained by radiologists' supervision, for automating FOV prescription. An intra-stack shared feature extraction network and an attention network are used to process a stack of 2D image inputs to generate output scalars defining the location of a rectangular region of interest (ROI). The attention mechanism is used to make the model focus on the small number of informative slices in a stack. Then the smallest FOV that makes the neural network predicted ROI free of aliasing is calculated by an algebraic operation derived from MR sampling theory. We retrospectively collected 595 cases between February 2018 and February 2022. The framework's performance is examined quantitatively with intersection over union (IoU) and pixel error on position, and qualitatively with a reader study. We use the t-test for comparing quantitative results from all models and a radiologist. The proposed model achieves an average IoU of 0.867 and average ROI position error of 9.06 out of 512 pixels on 80 test cases, significantly better (P<0.05) than two baseline models and not significantly different from a radiologist (P>0.12). Finally, the FOV given by the proposed framework achieves an acceptance rate of 92% from an experienced radiologist.
Artifact- and content-specific quality assessment for MRI with image rulers
Nov 06, 2021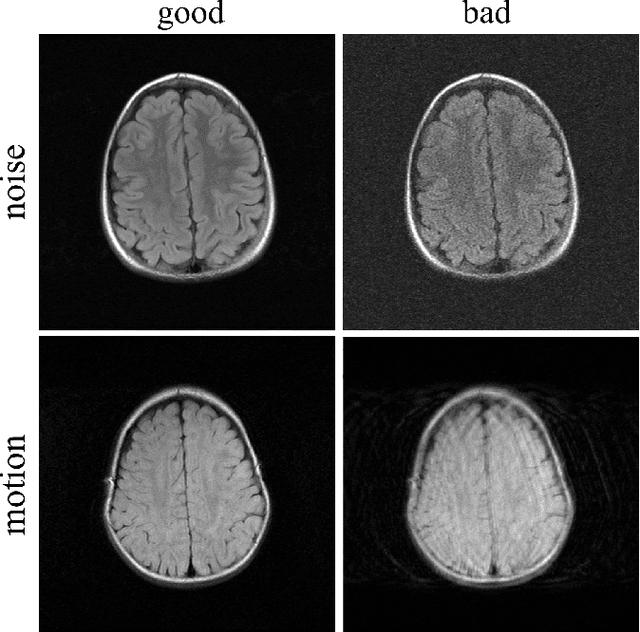
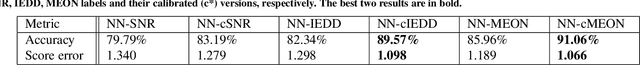
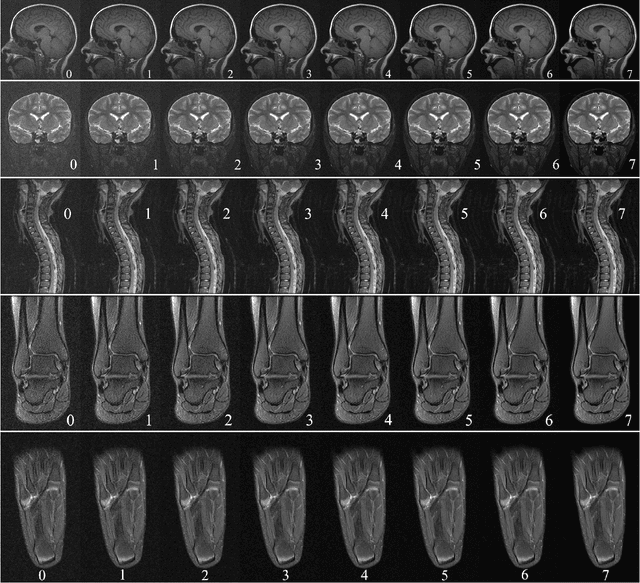
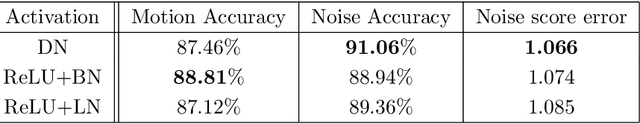
Abstract:In clinical practice MR images are often first seen by radiologists long after the scan. If image quality is inadequate either patients have to return for an additional scan, or a suboptimal interpretation is rendered. An automatic image quality assessment (IQA) would enable real-time remediation. Existing IQA works for MRI give only a general quality score, agnostic to the cause of and solution to low-quality scans. Furthermore, radiologists' image quality requirements vary with the scan type and diagnostic task. Therefore, the same score may have different implications for different scans. We propose a framework with multi-task CNN model trained with calibrated labels and inferenced with image rulers. Labels calibrated by human inputs follow a well-defined and efficient labeling task. Image rulers address varying quality standards and provide a concrete way of interpreting raw scores from the CNN. The model supports assessments of two of the most common artifacts in MRI: noise and motion. It achieves accuracies of around 90%, 6% better than the best previous method examined, and 3% better than human experts on noise assessment. Our experiments show that label calibration, image rulers, and multi-task training improve the model's performance and generalizability.
Memory-efficient Learning for High-Dimensional MRI Reconstruction
Mar 06, 2021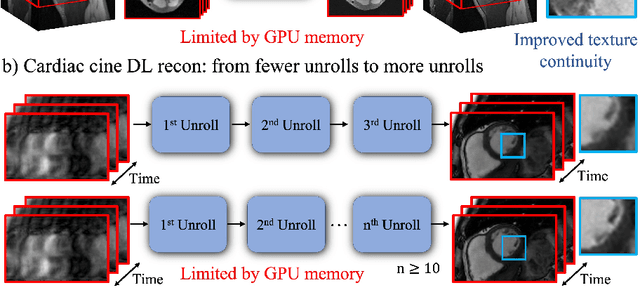



Abstract:Deep learning (DL) based unrolled reconstructions have shown state-of-the-art performance for under-sampled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Similar to compressed sensing, DL can leverage high-dimensional data (e.g. 3D, 2D+time, 3D+time) to further improve performance. However, network size and depth are currently limited by the GPU memory required for backpropagation. Here we use a memory-efficient learning (MEL) framework which favorably trades off storage with a manageable increase in computation during training. Using MEL with multi-dimensional data, we demonstrate improved image reconstruction performance for in-vivo 3D MRI and 2D+time cardiac cine MRI. MEL uses far less GPU memory while marginally increasing the training time, which enables new applications of DL to high-dimensional MRI.
Unsupervised MRI Reconstruction with Generative Adversarial Networks
Aug 29, 2020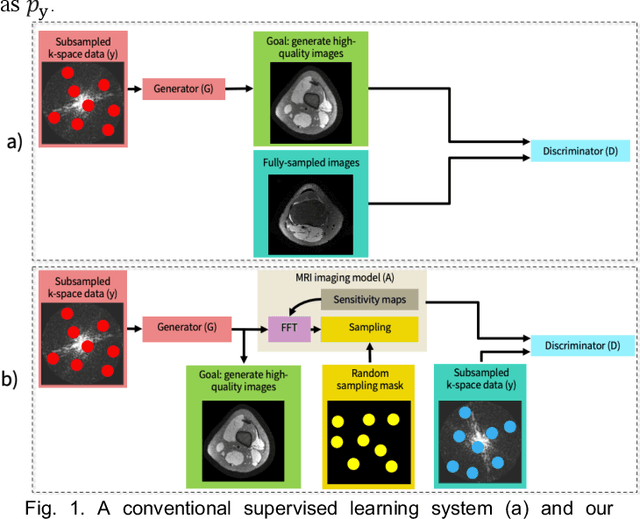
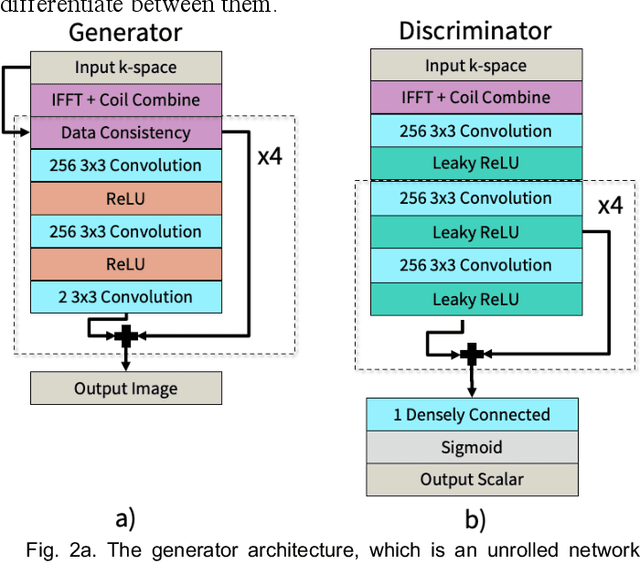
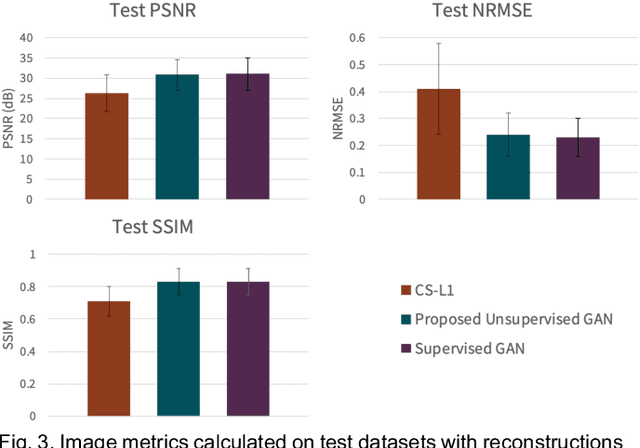
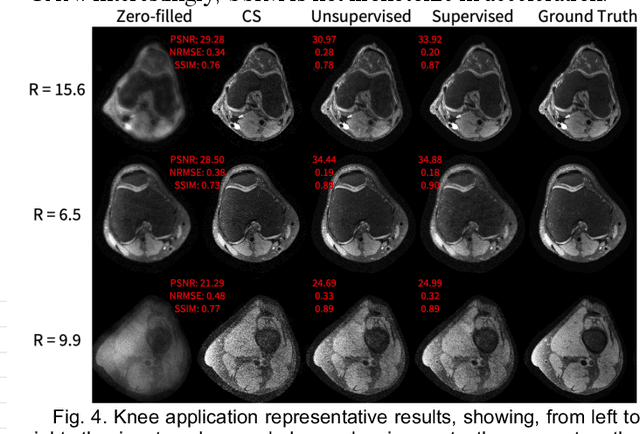
Abstract:Deep learning-based image reconstruction methods have achieved promising results across multiple MRI applications. However, most approaches require large-scale fully-sampled ground truth data for supervised training. Acquiring fully-sampled data is often either difficult or impossible, particularly for dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE), 3D cardiac cine, and 4D flow. We present a deep learning framework for MRI reconstruction without any fully-sampled data using generative adversarial networks. We test the proposed method in two scenarios: retrospectively undersampled fast spin echo knee exams and prospectively undersampled abdominal DCE. The method recovers more anatomical structure compared to conventional methods.
Complex-Valued Convolutional Neural Networks for MRI Reconstruction
Apr 08, 2020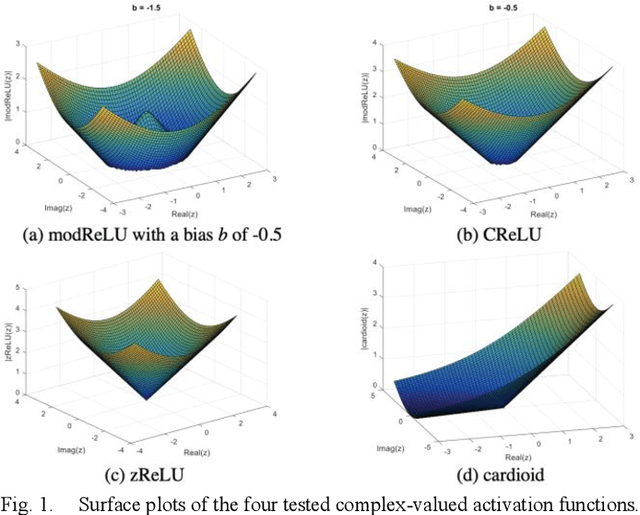
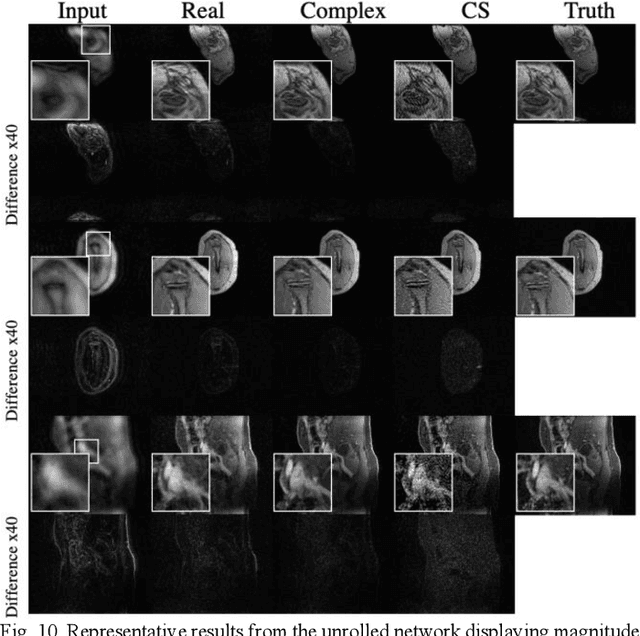
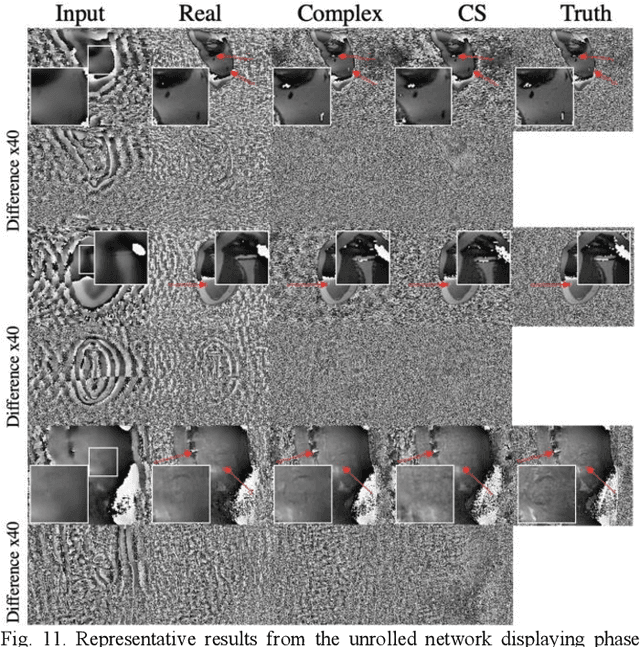
Abstract:Many real-world signal sources are complex-valued, having real and imaginary components. However, the vast majority of existing deep learning platforms and network architectures do not support the use of complex-valued data. MRI data is inherently complex-valued, so existing approaches discard the richer algebraic structure of the complex data. In this work, we investigate end-to-end complex-valued convolutional neural networks - specifically, for image reconstruction in lieu of two-channel real-valued networks. We apply this to magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction for the purpose of accelerating scan times and determine the performance of various promising complex-valued activation functions. We find that complex-valued CNNs with complex-valued convolutions provide superior reconstructions compared to real-valued convolutions with the same number of trainable parameters, over a variety of network architectures and datasets.
Accelerating cardiac cine MRI beyond compressed sensing using DL-ESPIRiT
Nov 13, 2019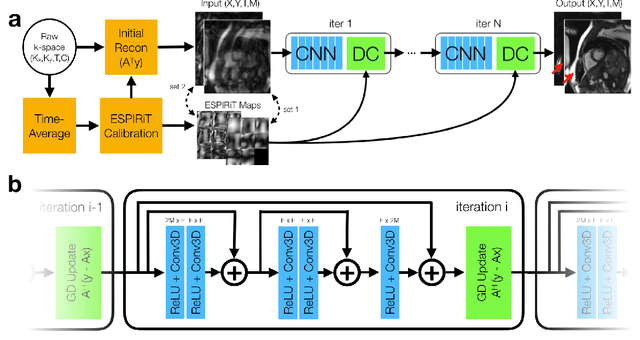
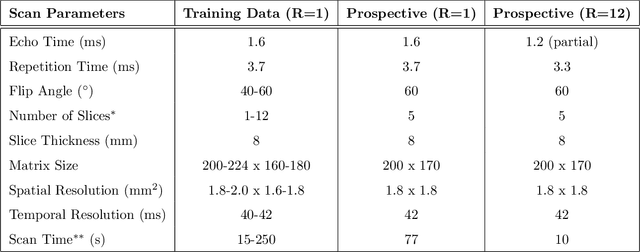
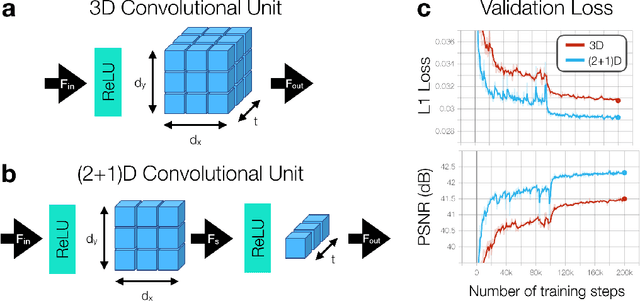
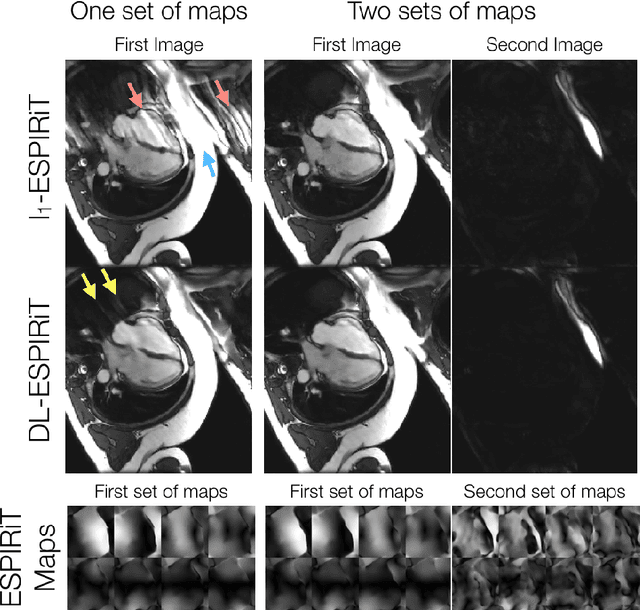
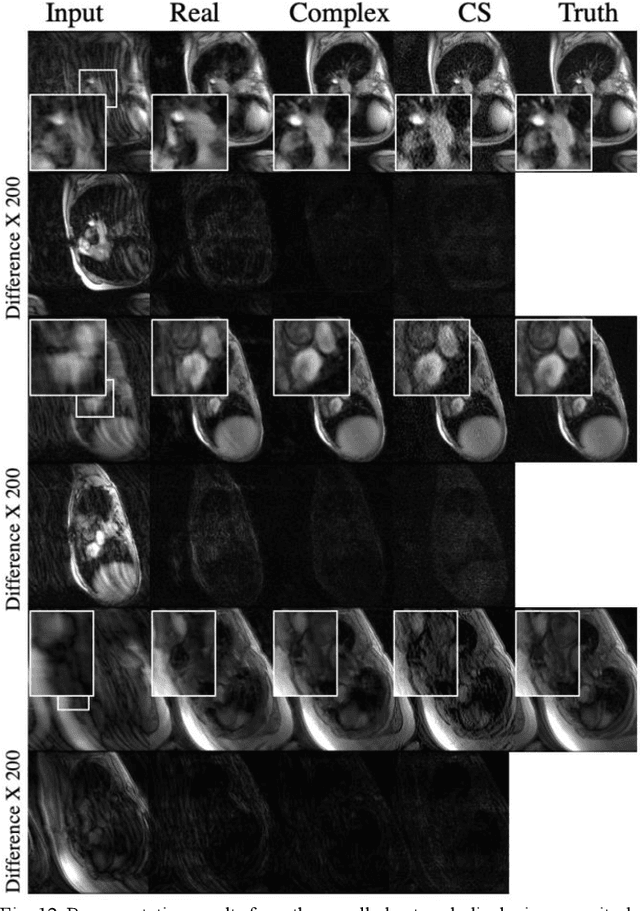
Abstract:A novel neural network architecture, known as DL-ESPIRiT, is proposed to reconstruct rapidly acquired cardiac MRI data without field-of-view limitations which are present in previously proposed deep learning-based reconstruction frameworks. Additionally, a novel convolutional neural network based on separable 3D convolutions is integrated into DL-ESPIRiT to more efficiently learn spatiotemporal priors for dynamic image reconstruction. The network is trained on fully-sampled 2D cardiac cine datasets collected from eleven healthy volunteers with IRB approval. DL-ESPIRiT is compared against a state-of-the-art parallel imaging and compressed sensing method known as $l_1$-ESPIRiT. The reconstruction accuracy of both methods is evaluated on retrospectively undersampled datasets (R=12) with respect to standard image quality metrics as well as automatic deep learning-based segmentations of left ventricular volumes. Feasibility of this approach is demonstrated in reconstructions of prospectively undersampled data which were acquired in a single heartbeat per slice.
Compressed Sensing: From Research to Clinical Practice with Data-Driven Learning
Mar 19, 2019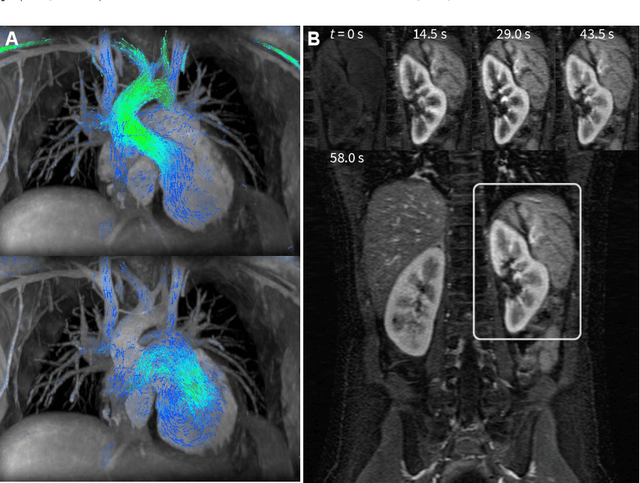

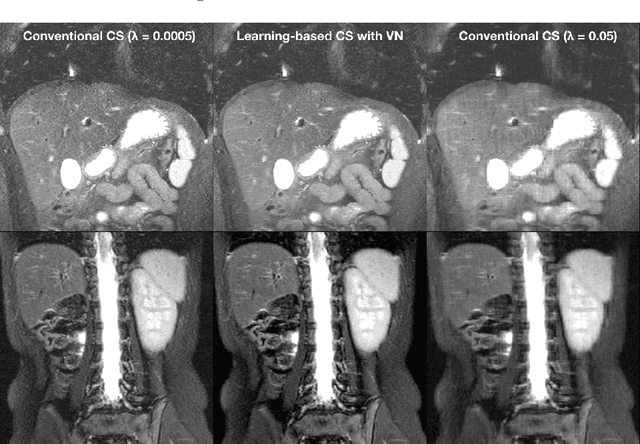
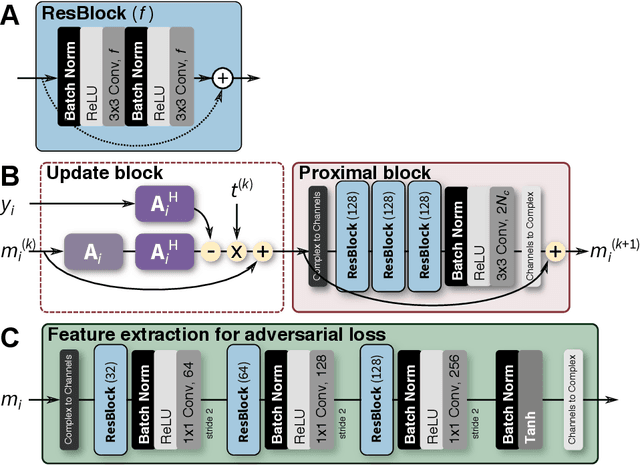
Abstract:Compressed sensing in MRI enables high subsampling factors while maintaining diagnostic image quality. This technique enables shortened scan durations and/or improved image resolution. Further, compressed sensing can increase the diagnostic information and value from each scan performed. Overall, compressed sensing has significant clinical impact in improving the diagnostic quality and patient experience for imaging exams. However, a number of challenges exist when moving compressed sensing from research to the clinic. These challenges include hand-crafted image priors, sensitive tuning parameters, and long reconstruction times. Data-driven learning provides a solution to address these challenges. As a result, compressed sensing can have greater clinical impact. In this tutorial, we will review the compressed sensing formulation and outline steps needed to transform this formulation to a deep learning framework. Supplementary open source code in python will be used to demonstrate this approach with open databases. Further, we will discuss considerations in applying data-driven compressed sensing in the clinical setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge