Tian He
AddrLLM: Address Rewriting via Large Language Model on Nationwide Logistics Data
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:Textual description of a physical location, commonly known as an address, plays an important role in location-based services(LBS) such as on-demand delivery and navigation. However, the prevalence of abnormal addresses, those containing inaccuracies that fail to pinpoint a location, have led to significant costs. Address rewriting has emerged as a solution to rectify these abnormal addresses. Despite the critical need, existing address rewriting methods are limited, typically tailored to correct specific error types, or frequently require retraining to process new address data effectively. In this study, we introduce AddrLLM, an innovative framework for address rewriting that is built upon a retrieval augmented large language model. AddrLLM overcomes aforementioned limitations through a meticulously designed Supervised Fine-Tuning module, an Address-centric Retrieval Augmented Generation module and a Bias-free Objective Alignment module. To the best of our knowledge, this study pioneers the application of LLM-based address rewriting approach to solve the issue of abnormal addresses. Through comprehensive offline testing with real-world data on a national scale and subsequent online deployment, AddrLLM has demonstrated superior performance in integration with existing logistics system. It has significantly decreased the rate of parcel re-routing by approximately 43\%, underscoring its exceptional efficacy in real-world applications.
mmSpyVR: Exploiting mmWave Radar for Penetrating Obstacles to Uncover Privacy Vulnerability of Virtual Reality
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:Virtual reality (VR), while enhancing user experiences, introduces significant privacy risks. This paper reveals a novel vulnerability in VR systems that allows attackers to capture VR privacy through obstacles utilizing millimeter-wave (mmWave) signals without physical intrusion and virtual connection with the VR devices. We propose mmSpyVR, a novel attack on VR user's privacy via mmWave radar. The mmSpyVR framework encompasses two main parts: (i) A transfer learning-based feature extraction model to achieve VR feature extraction from mmWave signal. (ii) An attention-based VR privacy spying module to spy VR privacy information from the extracted feature. The mmSpyVR demonstrates the capability to extract critical VR privacy from the mmWave signals that have penetrated through obstacles. We evaluate mmSpyVR through IRB-approved user studies. Across 22 participants engaged in four experimental scenes utilizing VR devices from three different manufacturers, our system achieves an application recognition accuracy of 98.5\% and keystroke recognition accuracy of 92.6\%. This newly discovered vulnerability has implications across various domains, such as cybersecurity, privacy protection, and VR technology development. We also engage with VR manufacturer Meta to discuss and explore potential mitigation strategies. Data and code are publicly available for scrutiny and research at https://github.com/luoyumei1-a/mmSpyVR/
Vision-Language Meets the Skeleton: Progressively Distillation with Cross-Modal Knowledge for 3D Action Representation Learning
May 31, 2024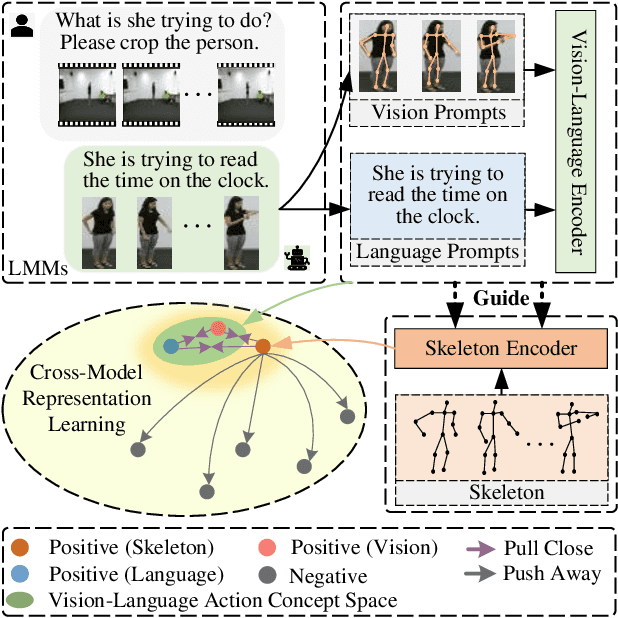



Abstract:Supervised and self-supervised learning are two main training paradigms for skeleton-based human action recognition. However, the former one-hot classification requires labor-intensive predefined action categories annotations, while the latter involves skeleton transformations (e.g., cropping) in the pretext tasks that may impair the skeleton structure. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel skeleton-based training framework (C$^2$VL) based on Cross-modal Contrastive learning that uses the progressive distillation to learn task-agnostic human skeleton action representation from the Vision-Language knowledge prompts. Specifically, we establish the vision-language action concept space through vision-language knowledge prompts generated by pre-trained large multimodal models (LMMs), which enrich the fine-grained details that the skeleton action space lacks. Moreover, we propose the intra-modal self-similarity and inter-modal cross-consistency softened targets in the cross-modal contrastive process to progressively control and guide the degree of pulling vision-language knowledge prompts and corresponding skeletons closer. These soft instance discrimination and self-knowledge distillation strategies contribute to the learning of better skeleton-based action representations from the noisy skeleton-vision-language pairs. During the inference phase, our method requires only the skeleton data as the input for action recognition and no longer for vision-language prompts. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results on NTU RGB+D 60, NTU RGB+D 120, and PKU-MMD datasets. The code will be available in the future.
Fine-Grained Side Information Guided Dual-Prompts for Zero-Shot Skeleton Action Recognition
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Skeleton-based zero-shot action recognition aims to recognize unknown human actions based on the learned priors of the known skeleton-based actions and a semantic descriptor space shared by both known and unknown categories. However, previous works focus on establishing the bridges between the known skeleton representation space and semantic descriptions space at the coarse-grained level for recognizing unknown action categories, ignoring the fine-grained alignment of these two spaces, resulting in suboptimal performance in distinguishing high-similarity action categories. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method via Side information and dual-prompts learning for skeleton-based zero-shot action recognition (STAR) at the fine-grained level. Specifically, 1) we decompose the skeleton into several parts based on its topology structure and introduce the side information concerning multi-part descriptions of human body movements for alignment between the skeleton and the semantic space at the fine-grained level; 2) we design the visual-attribute and semantic-part prompts to improve the intra-class compactness within the skeleton space and inter-class separability within the semantic space, respectively, to distinguish the high-similarity actions. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in ZSL and GZSL settings on NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and PKU-MMD datasets.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Partial Symbol Recovery for Interference Resilience in Low-Power Wide Area Networks
Sep 08, 2021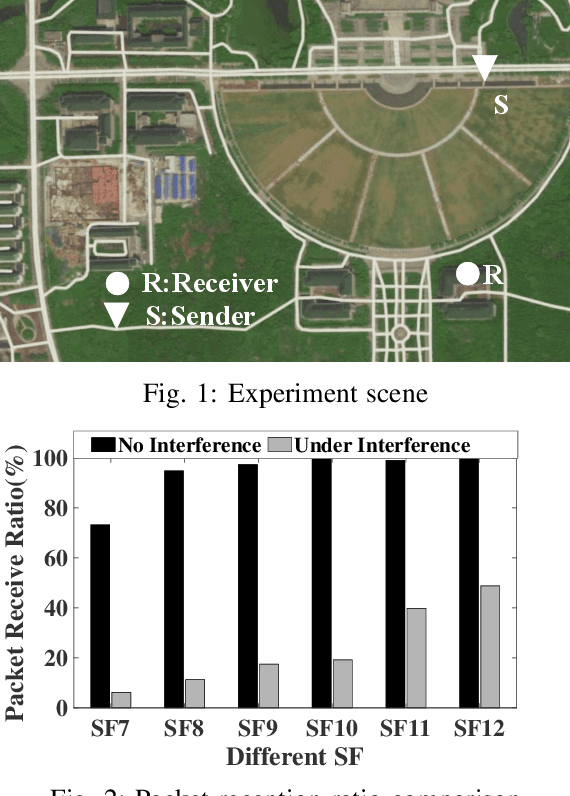
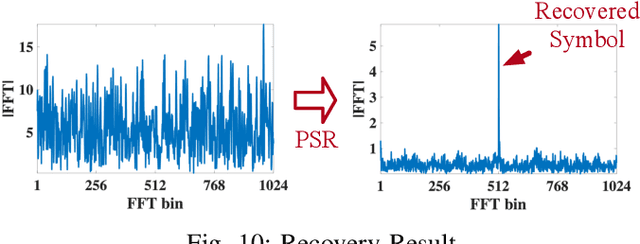
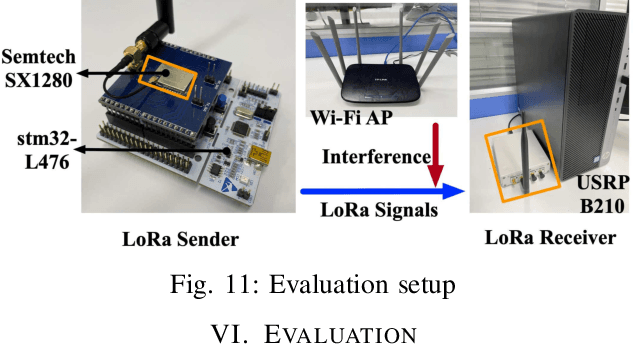
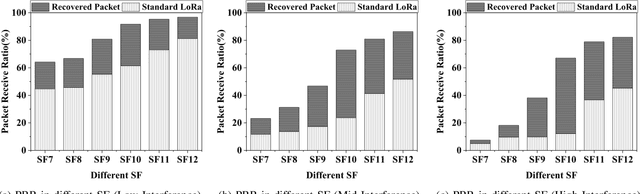
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the proliferation of Low-power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) in the unlicensed band for various Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications. Due to the ultra-low transmission power and long transmission duration, LPWAN devices inevitably suffer from high power Cross Technology Interference (CTI), such as interference from Wi-Fi, coexisting in the same spectrum. To alleviate this issue, this paper introduces the Partial Symbol Recovery (PSR) scheme for improving the CTI resilience of LPWAN. We verify our idea on LoRa, a widely adopted LPWAN technique, as a proof of concept. At the PHY layer, although CTI has much higher power, its duration is relatively shorter compared with LoRa symbols, leaving part of a LoRa symbol uncorrupted. Moreover, due to its high redundancy, LoRa chips within a symbol are highly correlated. This opens the possibility of detecting a LoRa symbol with only part of the chips. By examining the unique frequency patterns in LoRa symbols with time-frequency analysis, our design effectively detects the clean LoRa chips that are free of CTI. This enables PSR to only rely on clean LoRa chips for successfully recovering from communication failures. We evaluate our PSR design with real-world testbeds, including SX1280 LoRa chips and USRP B210, under Wi-Fi interference in various scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our design offers reliable packet recovery performance, successfully boosting the LoRa packet reception ratio from 45.2% to 82.2% with a performance gain of 1.8 times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge