Wenchao Jiang
Efficient and Distortion-less Spectrum Multiplexer via Neural Network-based Filter Banks
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Spectrum multiplexer enables simultaneous transmission of multiple narrow-band IoT signals through gateway devices, thereby enhancing overall spectrum utilization. We propose a novel solution based on filter banks that offer increased efficiency and minimal distortion compared with conventional methods. We follow a model-driven approach to integrate the neural networks into the filter bank design by interpreting the neural network models as filter banks. The proposed NN-based filter banks can leverage advanced learning capabilities to achieve distortionless multiplexing and harness hardware acceleration for high efficiency. Then, we evaluate the performance of the spectrum multiplexer implemented by NN-based filter banks for various types of signals and environmental conditions. The results show that it can achieve a low distortion level down to $-39$dB normalized mean squared error. Furthermore, it achieves up to $35$ times execution efficiency gain and $10$dB SNR gain compared with the conventional methods. The field applications show that it can handle both the heterogeneous and homogeneous IoT networks, resulting in high packet reception ratio at the standard receivers up to $98\%$.
mmSpyVR: Exploiting mmWave Radar for Penetrating Obstacles to Uncover Privacy Vulnerability of Virtual Reality
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:Virtual reality (VR), while enhancing user experiences, introduces significant privacy risks. This paper reveals a novel vulnerability in VR systems that allows attackers to capture VR privacy through obstacles utilizing millimeter-wave (mmWave) signals without physical intrusion and virtual connection with the VR devices. We propose mmSpyVR, a novel attack on VR user's privacy via mmWave radar. The mmSpyVR framework encompasses two main parts: (i) A transfer learning-based feature extraction model to achieve VR feature extraction from mmWave signal. (ii) An attention-based VR privacy spying module to spy VR privacy information from the extracted feature. The mmSpyVR demonstrates the capability to extract critical VR privacy from the mmWave signals that have penetrated through obstacles. We evaluate mmSpyVR through IRB-approved user studies. Across 22 participants engaged in four experimental scenes utilizing VR devices from three different manufacturers, our system achieves an application recognition accuracy of 98.5\% and keystroke recognition accuracy of 92.6\%. This newly discovered vulnerability has implications across various domains, such as cybersecurity, privacy protection, and VR technology development. We also engage with VR manufacturer Meta to discuss and explore potential mitigation strategies. Data and code are publicly available for scrutiny and research at https://github.com/luoyumei1-a/mmSpyVR/
ESP-PCT: Enhanced VR Semantic Performance through Efficient Compression of Temporal and Spatial Redundancies in Point Cloud Transformers
Sep 02, 2024



Abstract:Semantic recognition is pivotal in virtual reality (VR) applications, enabling immersive and interactive experiences. A promising approach is utilizing millimeter-wave (mmWave) signals to generate point clouds. However, the high computational and memory demands of current mmWave point cloud models hinder their efficiency and reliability. To address this limitation, our paper introduces ESP-PCT, a novel Enhanced Semantic Performance Point Cloud Transformer with a two-stage semantic recognition framework tailored for VR applications. ESP-PCT takes advantage of the accuracy of sensory point cloud data and optimizes the semantic recognition process, where the localization and focus stages are trained jointly in an end-to-end manner. We evaluate ESP-PCT on various VR semantic recognition conditions, demonstrating substantial enhancements in recognition efficiency. Notably, ESP-PCT achieves a remarkable accuracy of 93.2% while reducing the computational requirements (FLOPs) by 76.9% and memory usage by 78.2% compared to the existing Point Transformer model simultaneously. These underscore ESP-PCT's potential in VR semantic recognition by achieving high accuracy and reducing redundancy. The code and data of this project are available at \url{https://github.com/lymei-SEU/ESP-PCT}.
Agent-driven Generative Semantic Communication for Remote Surveillance
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:In the era of 6G, featuring compelling visions of intelligent transportation system, digital twins, remote surveillance is poised to become a ubiquitous practice. The substantial data volume and frequent updates present challenges in wireless networks. To address this, we propose a novel agent-driven generative semantic communication (A-GSC) framework based on reinforcement learning. In contrast to the existing research on semantic communication (SemCom), which mainly focuses on semantic compression or semantic sampling, we seamlessly cascade both together by jointly considering the intrinsic attributes of source information and the contextual information regarding the task. Notably, the introduction of the generative artificial intelligence (GAI) enables the independent design of semantic encoders and decoders. In this work, we develop an agent-assisted semantic encoder leveraging the knowledge based soft actor-critic algorithm, which can track the semantic changes, channel condition, and sampling intervals, so as to perform adaptive semantic sampling. Accordingly, we design a semantic decoder with both predictive and generative capabilities, which consists of two tailored modules. Moreover, the effectiveness of the designed models has been verified based on the dataset generated from CDNet2014, and the performance gain of the overall A-GSC framework in both energy saving and reconstruction accuracy have been demonstrated.
NNCTC: Physical Layer Cross-Technology Communication via Neural Networks
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Cross-technology communication(CTC) enables seamless interactions between diverse wireless technologies. Most existing work is based on reversing the transmission path to identify the appropriate payload to generate the waveform that the target devices can recognize. However, this method suffers from many limitations, including dependency on specific technologies and the necessity for intricate algorithms to mitigate distortion. In this work, we present NNCTC, a Neural-Network-based Cross-Technology Communication framework inspired by the adaptability of trainable neural models in wireless communications. By converting signal processing components within the CTC pipeline into neural models, the NNCTC is designed for end-to-end training without requiring labeled data. This enables the NNCTC system to autonomously derive the optimal CTC payload, which significantly eases the development complexity and showcases the scalability potential for various CTC links. Particularly, we construct a CTC system from Wi-Fi to ZigBee. The NNCTC system outperforms the well-recognized WEBee and WIDE design in error performance, achieving an average packet reception rate(PRR) of 92.3% and an average symbol error rate(SER) as low as 1.3%.
NN-Defined Modulator: Reconfigurable and Portable Software Modulator on IoT Gateways
Mar 14, 2024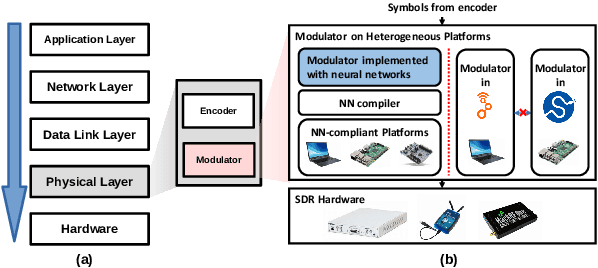
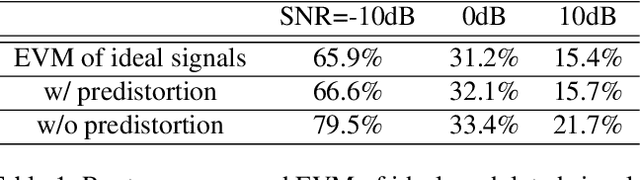
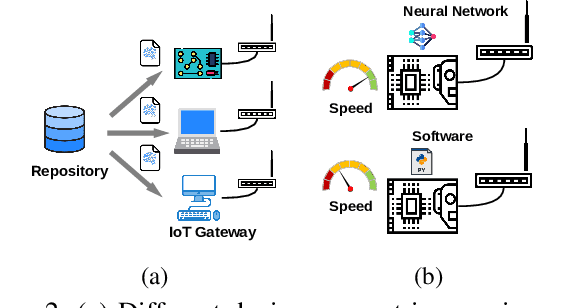

Abstract:A physical-layer modulator is a vital component for an IoT gateway to map the symbols to signals. However, due to the soldered hardware chipsets on the gateway's motherboards or the diverse toolkits on different platforms for the software radio, the existing solutions either have limited extensibility or are platform-specific. Such limitation is hard to ignore when modulation schemes and hardware platforms have become extremely diverse. This paper presents a new paradigm of using neural networks as an abstraction layer for physical layer modulators in IoT gateway devices, referred to as NN-defined modulators. Our approach addresses the challenges of extensibility and portability for multiple technologies on various hardware platforms. The proposed NN-defined modulator uses a model-driven methodology rooted in solid mathematical foundations while having native support for hardware acceleration and portability to heterogeneous platforms. We conduct the evaluation of NN-defined modulators on different platforms, including Nvidia Jetson Nano and Raspberry Pi. Evaluations demonstrate that our NN-defined modulator effectively operates as conventional modulators and provides significant efficiency gains (up to $4.7\times$ on Nvidia Jetson Nano and $1.1\times$ on Raspberry Pi), indicating high portability. Furthermore, we show the real-world applications using our NN-defined modulators to generate ZigBee and WiFi packets, which are compliant with commodity TI CC2650 (ZigBee) and Intel AX201 (WiFi NIC), respectively.
Environment-independent mmWave Fall Detection with Interacting Multiple Model
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:The ageing society brings attention to daily elderly care through sensing technologies. The future smart home is expected to enable in-home daily monitoring, such as fall detection, for seniors in a non-invasive, non-cooperative, and non-contact manner. The mmWave radar is a promising candidate technology for its privacy-preserving and non-contact manner. However, existing solutions suffer from low accuracy and robustness due to environment dependent features. In this paper, we present FADE (\underline{FA}ll \underline{DE}tection), a practical fall detection radar system with enhanced accuracy and robustness in real-world scenarios. The key enabler underlying FADE is an interacting multiple model (IMM) state estimator that can extract environment-independent features for highly accurate and instantaneous fall detection. Furthermore, we proposed a robust multiple-user tracking system to deal with noises from the environment and other human bodies. We deployed our algorithm on low computing power and low power consumption system-on-chip (SoC) composed of data front end, DSP, and ARM processor, and tested its performance in real-world. The experiment shows that the accuracy of fall detection is up to 95\%.
Cross Vision-RF Gait Re-identification with Low-cost RGB-D Cameras and mmWave Radars
Jul 16, 2022
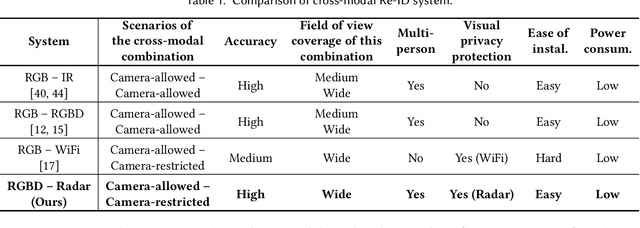
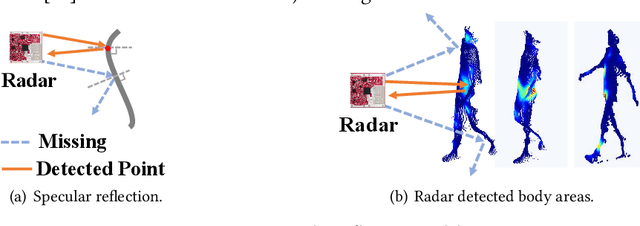
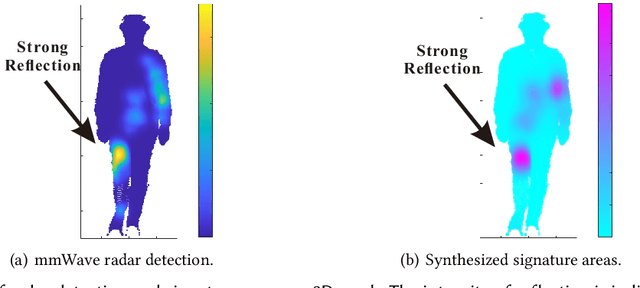
Abstract:Human identification is a key requirement for many applications in everyday life, such as personalized services, automatic surveillance, continuous authentication, and contact tracing during pandemics, etc. This work studies the problem of cross-modal human re-identification (ReID), in response to the regular human movements across camera-allowed regions (e.g., streets) and camera-restricted regions (e.g., offices) deployed with heterogeneous sensors. By leveraging the emerging low-cost RGB-D cameras and mmWave radars, we propose the first-of-its-kind vision-RF system for cross-modal multi-person ReID at the same time. Firstly, to address the fundamental inter-modality discrepancy, we propose a novel signature synthesis algorithm based on the observed specular reflection model of a human body. Secondly, an effective cross-modal deep metric learning model is introduced to deal with interference caused by unsynchronized data across radars and cameras. Through extensive experiments in both indoor and outdoor environments, we demonstrate that our proposed system is able to achieve ~92.5% top-1 accuracy and ~97.5% top-5 accuracy out of 56 volunteers. We also show that our proposed system is able to robustly reidentify subjects even when multiple subjects are present in the sensors' field of view.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge