Bin Hu
Clarify Before You Draw: Proactive Agents for Robust Text-to-CAD Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language models have recently enabled text-to-CAD systems that synthesize parametric CAD programs (e.g., CadQuery) from natural language prompts. In practice, however, geometric descriptions can be under-specified or internally inconsistent: critical dimensions may be missing and constraints may conflict. Existing fine-tuned models tend to reactively follow user instructions and hallucinate dimensions when the text is ambiguous. To address this, we propose a proactive agentic framework for text-to-CadQuery generation, named ProCAD, that resolves specification issues before code synthesis. Our framework pairs a proactive clarifying agent, which audits the prompt and asks targeted clarification questions only when necessary to produce a self-consistent specification, with a CAD coding agent that translates the specification into an executable CadQuery program. We fine-tune the coding agent on a curated high-quality text-to-CadQuery dataset and train the clarifying agent via agentic SFT on clarification trajectories. Experiments show that proactive clarification significantly improves robustness to ambiguous prompts while keeping interaction overhead low. ProCAD outperforms frontier closed-source models, including Claude Sonnet 4.5, reducing the mean Chamfer distance by 79.9 percent and lowering the invalidity ratio from 4.8 percent to 0.9 percent. Our code and datasets will be made publicly available.
The Art of Socratic Inquiry: A Framework for Proactive Template-Guided Therapeutic Conversation Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Proactive questioning, where therapists deliberately initiate structured, cognition-guiding inquiries, is a cornerstone of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Yet, current psychological large language models (LLMs) remain overwhelmingly reactive, defaulting to empathetic but superficial responses that fail to surface latent beliefs or guide behavioral change. To bridge this gap, we propose the \textbf{Socratic Inquiry Framework (SIF)}, a lightweight, plug-and-play therapeutic intent planner that transforms LLMs from passive listeners into active cognitive guides. SIF decouples \textbf{when to ask} (via Strategy Anchoring) from \textbf{what to ask} (via Template Retrieval), enabling context-aware, theory-grounded questioning without end-to-end retraining. Complementing SIF, we introduce \textbf{Socratic-QA}, a high-quality dataset of strategy-aligned Socratic sequences that provides explicit supervision for proactive reasoning. Experiments show that SIF significantly enhances proactive questioning frequency, conversational depth, and therapeutic alignment, marking a clear shift from reactive comfort to proactive exploration. Our work establishes a new paradigm for psychologically informed LLMs: not just to respond, but to guide.
TSRBench: A Comprehensive Multi-task Multi-modal Time Series Reasoning Benchmark for Generalist Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Time series data is ubiquitous in real-world scenarios and crucial for critical applications ranging from energy management to traffic control. Consequently, the ability to reason over time series is a fundamental skill for generalist models to solve practical problems. However, this dimension is notably absent from existing benchmarks of generalist models. To bridge this gap, we introduce TSRBench, a comprehensive multi-modal benchmark designed to stress-test the full spectrum of time series reasoning capabilities. TSRBench features: i) a diverse set of 4125 problems from 14 domains, and is categorized into 4 major dimensions: Perception, Reasoning, Prediction, and Decision-Making. ii) 15 tasks from the 4 dimensions evaluating essential reasoning capabilities (e.g., numerical reasoning). Through extensive experiments, we evaluated over 30 leading proprietary and open-source LLMs, VLMs, and TSLLMs within TSRBench. Our findings reveal that: i) scaling laws hold for perception and reasoning but break down for prediction; ii) strong reasoning does not guarantee accurate context-aware forecasting, indicating a decoupling between semantic understanding and numerical prediction; and iii) despite the complementary nature of textual and visual represenations of time series as inputs, current multimodal models fail to effectively fuse them for reciprocal performance gains. TSRBench provides a standardized evaluation platform that not only highlights existing challenges but also offers valuable insights to advance generalist models. Our code and dataset are available at https://tsrbench.github.io/.
ReLE: A Scalable System and Structured Benchmark for Diagnosing Capability Anisotropy in Chinese LLMs
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved rapid progress in Chinese language understanding, yet accurately evaluating their capabilities remains challenged by benchmark saturation and prohibitive computational costs. While static leaderboards provide snapshot rankings, they often mask the structural trade-offs between capabilities. In this work, we present ReLE (Robust Efficient Live Evaluation), a scalable system designed to diagnose Capability Anisotropy, the non-uniformity of model performance across domains. Using ReLE, we evaluate 304 models (189 commercial, 115 open-source) across a Domain $\times$ Capability orthogonal matrix comprising 207,843 samples. We introduce two methodological contributions to address current evaluation pitfalls: (1) A Symbolic-Grounded Hybrid Scoring Mechanism that eliminates embedding-based false positives in reasoning tasks; (2) A Dynamic Variance-Aware Scheduler based on Neyman allocation with noise correction, which reduces compute costs by 70\% compared to full-pass evaluations while maintaining a ranking correlation of $ρ=0.96$. Our analysis reveals that aggregate rankings are highly sensitive to weighting schemes: models exhibit a Rank Stability Amplitude (RSA) of 11.4 in ReLE versus $\sim$5.0 in traditional benchmarks, confirming that modern models are highly specialized rather than generally superior. We position ReLE not as a replacement for comprehensive static benchmarks, but as a high-frequency diagnostic monitor for the evolving model landscape.
TrashDet: Iterative Neural Architecture Search for Efficient Waste Detection
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses trash detection on the TACO dataset under strict TinyML constraints using an iterative hardware-aware neural architecture search framework targeting edge and IoT devices. The proposed method constructs a Once-for-All-style ResDets supernet and performs iterative evolutionary search that alternates between backbone and neck/head optimization, supported by a population passthrough mechanism and an accuracy predictor to reduce search cost and improve stability. This framework yields a family of deployment-ready detectors, termed TrashDets. On a five-class TACO subset (paper, plastic, bottle, can, cigarette), the strongest variant, TrashDet-l, achieves 19.5 mAP50 with 30.5M parameters, improving accuracy by up to 3.6 mAP50 over prior detectors while using substantially fewer parameters. The TrashDet family spans 1.2M to 30.5M parameters with mAP50 values between 11.4 and 19.5, providing scalable detector options for diverse TinyML deployment budgets on resource-constrained hardware. On the MAX78002 microcontroller with the TrashNet dataset, two specialized variants, TrashDet-ResNet and TrashDet-MBNet, jointly dominate the ai87-fpndetector baseline, with TrashDet-ResNet achieving 7525~$μ$J energy per inference at 26.7 ms latency and 37.45 FPS, and TrashDet-MBNet improving mAP50 by 10.2%; together they reduce energy consumption by up to 88%, latency by up to 78%, and average power by up to 53% compared to existing TinyML detectors.
Design and Experimental Validation of Closed-Form CBF-Based Safe Control for Stewart Platform Under Multiple Constraints
Dec 11, 2025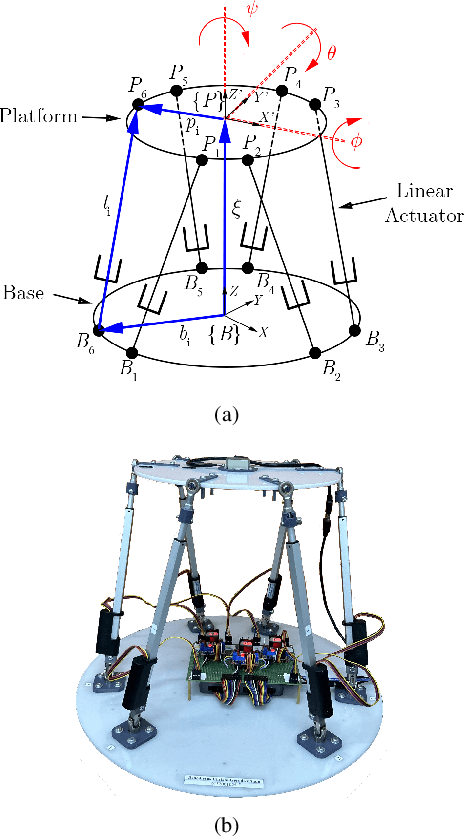
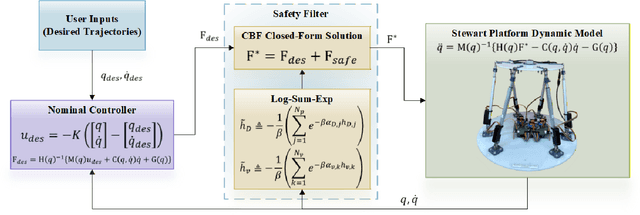
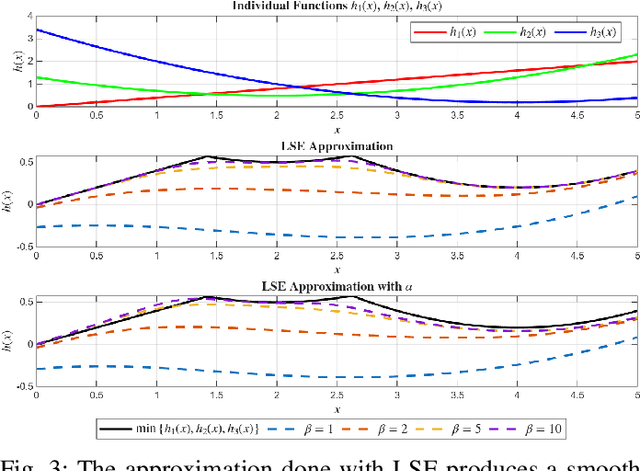
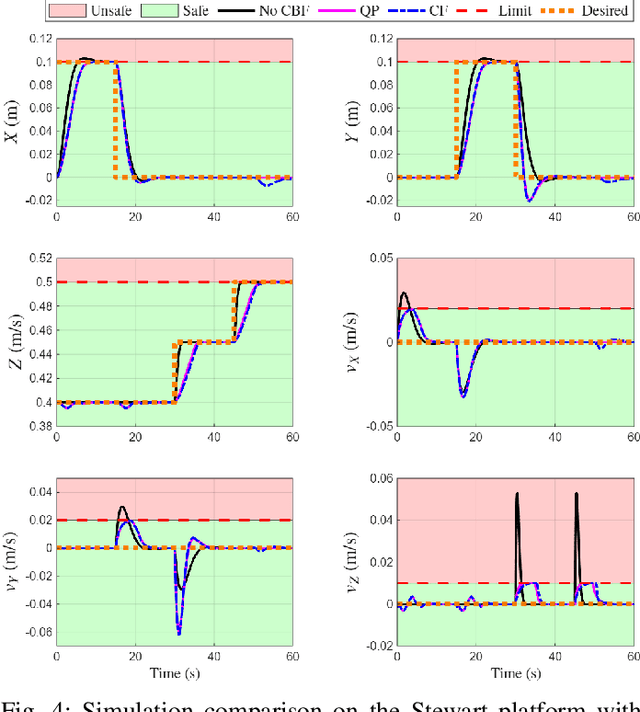
Abstract:This letter presents a closed-form solution of Control Barrier Function (CBF) framework for enforcing safety constraints on a Stewart robotic platform. The proposed method simultaneously handles multiple position and velocity constraints through an explicit closed-form control law, eliminating the need to solve a Quadratic Program (QP) at every control step and enabling efficient real-time implementation. This letter derives necessary and sufficient conditions under which the closed-form expression remains non-singular, thereby ensuring well-posedness of the CBF solution to multi-constraint problem. The controller is validated in both simulation and hardware experiments on a custom-built Stewart platform prototype, demonstrating safetyguaranteed performance that is comparable to the QP-based formulation, while reducing computation time by more than an order of magnitude. The results confirm that the proposed approach provides a reliable and computationally lightweight framework for real-time safe control of parallel robotic systems. The experimental videos are available on the project website. (https://nail-uh.github.io/StewartPlatformSafeControl.github.io/)
End-to-End Design and Validation of a Low-Cost Stewart Platform with Nonlinear Estimation and Control
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the complete design, control, and experimental validation of a low-cost Stewart platform prototype developed as an affordable yet capable robotic testbed for research and education. The platform combines off the shelf components with 3D printed and custom fabricated parts to deliver full six degrees of freedom motions using six linear actuators connecting a moving platform to a fixed base. The system software integrates dynamic modeling, data acquisition, and real time control within a unified framework. A robust trajectory tracking controller based on feedback linearization, augmented with an LQR scheme, compensates for the platform's nonlinear dynamics to achieve precise motion control. In parallel, an Extended Kalman Filter fuses IMU and actuator encoder feedback to provide accurate and reliable state estimation under sensor noise and external disturbances. Unlike prior efforts that emphasize only isolated aspects such as modeling or control, this work delivers a complete hardware-software platform validated through both simulation and experiments on static and dynamic trajectories. Results demonstrate effective trajectory tracking and real-time state estimation, highlighting the platform's potential as a cost effective and versatile tool for advanced research and educational applications.
Every Step Evolves: Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Trillion-Scale Thinking Model
Oct 21, 2025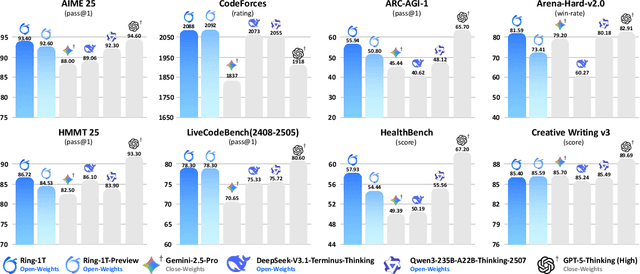
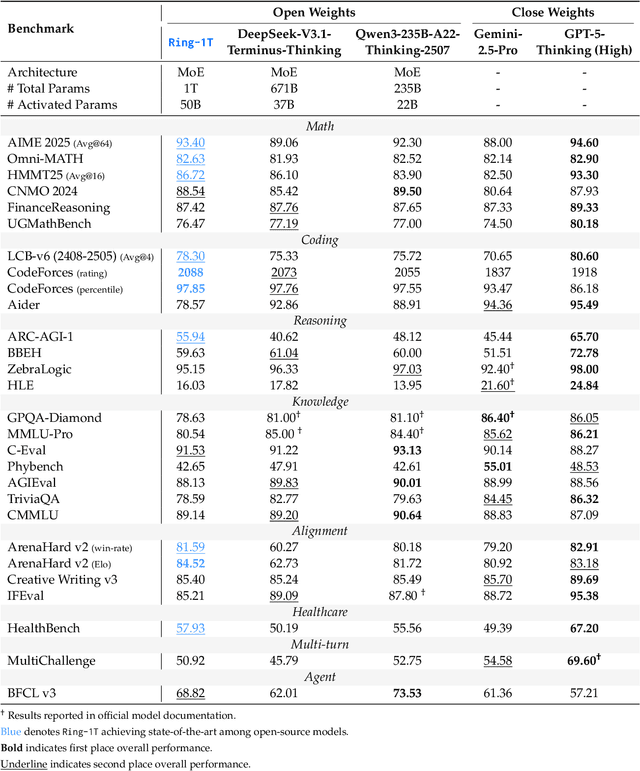
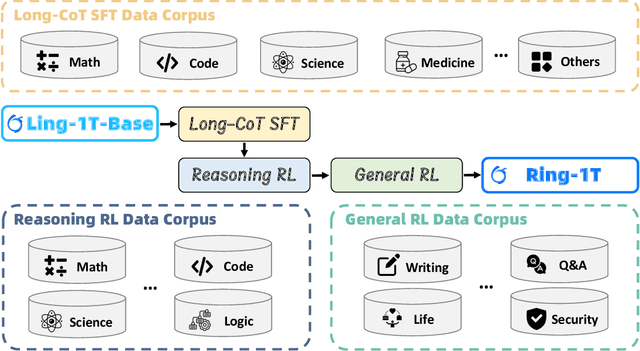
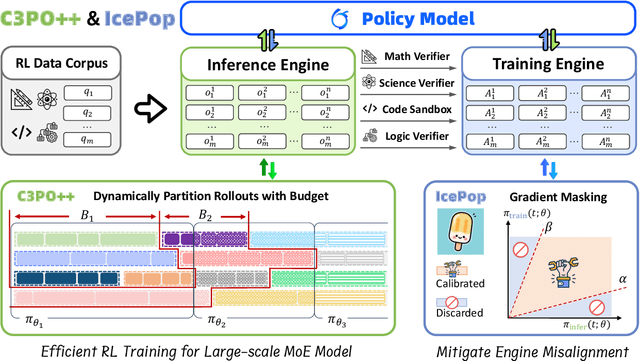
Abstract:We present Ring-1T, the first open-source, state-of-the-art thinking model with a trillion-scale parameter. It features 1 trillion total parameters and activates approximately 50 billion per token. Training such models at a trillion-parameter scale introduces unprecedented challenges, including train-inference misalignment, inefficiencies in rollout processing, and bottlenecks in the RL system. To address these, we pioneer three interconnected innovations: (1) IcePop stabilizes RL training via token-level discrepancy masking and clipping, resolving instability from training-inference mismatches; (2) C3PO++ improves resource utilization for long rollouts under a token budget by dynamically partitioning them, thereby obtaining high time efficiency; and (3) ASystem, a high-performance RL framework designed to overcome the systemic bottlenecks that impede trillion-parameter model training. Ring-1T delivers breakthrough results across critical benchmarks: 93.4 on AIME-2025, 86.72 on HMMT-2025, 2088 on CodeForces, and 55.94 on ARC-AGI-v1. Notably, it attains a silver medal-level result on the IMO-2025, underscoring its exceptional reasoning capabilities. By releasing the complete 1T parameter MoE model to the community, we provide the research community with direct access to cutting-edge reasoning capabilities. This contribution marks a significant milestone in democratizing large-scale reasoning intelligence and establishes a new baseline for open-source model performance.
Beyond Seeing: Evaluating Multimodal LLMs on Tool-Enabled Image Perception, Transformation, and Reasoning
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are increasingly applied in real-world scenarios where user-provided images are often imperfect, requiring active image manipulations such as cropping, editing, or enhancement to uncover salient visual cues. Beyond static visual perception, MLLMs must also think with images: dynamically transforming visual content and integrating it with other tools to solve complex tasks. However, this shift from treating vision as passive context to a manipulable cognitive workspace remains underexplored. Most existing benchmarks still follow a think about images paradigm, where images are regarded as static inputs. To address this gap, we introduce IRIS, an Interactive Reasoning with Images and Systems that evaluates MLLMs' ability to perceive, transform, and reason across complex visual-textual tasks under the think with images paradigm. IRIS comprises 1,204 challenging, open-ended vision tasks (603 single-turn, 601 multi-turn) spanning across five diverse domains, each paired with detailed rubrics to enable systematic evaluation. Our evaluation shows that current MLLMs struggle with tasks requiring effective integration of vision and general-purpose tools. Even the strongest model (GPT-5-think) reaches only 18.68% pass rate. We further observe divergent tool-use behaviors, with OpenAI models benefiting from diverse image manipulations while Gemini-2.5-pro shows no improvement. By introducing the first benchmark centered on think with images, IRIS offers critical insights for advancing visual intelligence in MLLMs.
Large Foundation Model for Ads Recommendation
Aug 20, 2025


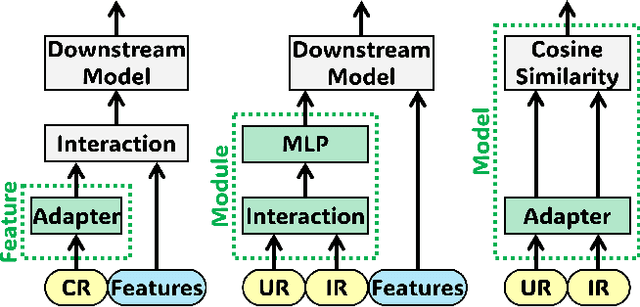
Abstract:Online advertising relies on accurate recommendation models, with recent advances using pre-trained large-scale foundation models (LFMs) to capture users' general interests across multiple scenarios and tasks. However, existing methods have critical limitations: they extract and transfer only user representations (URs), ignoring valuable item representations (IRs) and user-item cross representations (CRs); and they simply use a UR as a feature in downstream applications, which fails to bridge upstream-downstream gaps and overlooks more transfer granularities. In this paper, we propose LFM4Ads, an All-Representation Multi-Granularity transfer framework for ads recommendation. It first comprehensively transfers URs, IRs, and CRs, i.e., all available representations in the pre-trained foundation model. To effectively utilize the CRs, it identifies the optimal extraction layer and aggregates them into transferable coarse-grained forms. Furthermore, we enhance the transferability via multi-granularity mechanisms: non-linear adapters for feature-level transfer, an Isomorphic Interaction Module for module-level transfer, and Standalone Retrieval for model-level transfer. LFM4Ads has been successfully deployed in Tencent's industrial-scale advertising platform, processing tens of billions of daily samples while maintaining terabyte-scale model parameters with billions of sparse embedding keys across approximately two thousand features. Since its production deployment in Q4 2024, LFM4Ads has achieved 10+ successful production launches across various advertising scenarios, including primary ones like Weixin Moments and Channels. These launches achieve an overall GMV lift of 2.45% across the entire platform, translating to estimated annual revenue increases in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge