Leyang Cui
LLM-as-a-Supervisor: Mistaken Therapeutic Behaviors Trigger Targeted Supervisory Feedback
Aug 12, 2025



Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) hold significant promise in psychotherapy, their direct application in patient-facing scenarios raises ethical and safety concerns. Therefore, this work shifts towards developing an LLM as a supervisor to train real therapists. In addition to the privacy of clinical therapist training data, a fundamental contradiction complicates the training of therapeutic behaviors: clear feedback standards are necessary to ensure a controlled training system, yet there is no absolute "gold standard" for appropriate therapeutic behaviors in practice. In contrast, many common therapeutic mistakes are universal and identifiable, making them effective triggers for targeted feedback that can serve as clearer evidence. Motivated by this, we create a novel therapist-training paradigm: (1) guidelines for mistaken behaviors and targeted correction strategies are first established as standards; (2) a human-in-the-loop dialogue-feedback dataset is then constructed, where a mistake-prone agent intentionally makes standard mistakes during interviews naturally, and a supervisor agent locates and identifies mistakes and provides targeted feedback; (3) after fine-tuning on this dataset, the final supervisor model is provided for real therapist training. The detailed experimental results of automated, human and downstream assessments demonstrate that models fine-tuned on our dataset MATE, can provide high-quality feedback according to the clinical guideline, showing significant potential for the therapist training scenario.
SeqPE: Transformer with Sequential Position Encoding
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Since self-attention layers in Transformers are permutation invariant by design, positional encodings must be explicitly incorporated to enable spatial understanding. However, fixed-size lookup tables used in traditional learnable position embeddings (PEs) limit extrapolation capabilities beyond pre-trained sequence lengths. Expert-designed methods such as ALiBi and RoPE, mitigate this limitation but demand extensive modifications for adapting to new modalities, underscoring fundamental challenges in adaptability and scalability. In this work, we present SeqPE, a unified and fully learnable position encoding framework that represents each $n$-dimensional position index as a symbolic sequence and employs a lightweight sequential position encoder to learn their embeddings in an end-to-end manner. To regularize SeqPE's embedding space, we introduce two complementary objectives: a contrastive objective that aligns embedding distances with a predefined position-distance function, and a knowledge distillation loss that anchors out-of-distribution position embeddings to in-distribution teacher representations, further enhancing extrapolation performance. Experiments across language modeling, long-context question answering, and 2D image classification demonstrate that SeqPE not only surpasses strong baselines in perplexity, exact match (EM), and accuracy--particularly under context length extrapolation--but also enables seamless generalization to multi-dimensional inputs without requiring manual architectural redesign. We release our code, data, and checkpoints at https://github.com/ghrua/seqpe.
Do Reasoning Models Show Better Verbalized Calibration?
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning by leveraging increased test-time computation and exhibiting behaviors akin to human-like deliberation. Despite these advances, it remains an open question whether LRMs are better calibrated - particularly in their verbalized confidence - compared to instruction-tuned counterparts. In this paper, we investigate the calibration properties of LRMs trained via supervised fine-tuning distillation on long reasoning traces (henceforth SFT reasoning models) and outcome-based reinforcement learning for reasoning (henceforth RL reasoning models) across diverse domains. Our findings reveal that LRMs significantly outperform instruction-tuned models on complex reasoning tasks in both accuracy and confidence calibration. In contrast, we find surprising trends in the domain of factuality in particular. On factuality tasks, while Deepseek-R1 shows strong calibration behavior, smaller QwQ-32B shows no improvement over instruct models; moreover, SFT reasoning models display worse calibration (greater overconfidence) compared to instruct models. Our results provide evidence for a potentially critical role of reasoning-oriented RL training in improving LLMs' capacity for generating trustworthy, self-aware outputs.
Lost in Literalism: How Supervised Training Shapes Translationese in LLMs
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success in machine translation, demonstrating impressive performance across diverse languages. However, translationese, characterized by overly literal and unnatural translations, remains a persistent challenge in LLM-based translation systems. Despite their pre-training on vast corpora of natural utterances, LLMs exhibit translationese errors and generate unexpected unnatural translations, stemming from biases introduced during supervised fine-tuning (SFT). In this work, we systematically evaluate the prevalence of translationese in LLM-generated translations and investigate its roots during supervised training. We introduce methods to mitigate these biases, including polishing golden references and filtering unnatural training instances. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that these approaches significantly reduce translationese while improving translation naturalness, validated by human evaluations and automatic metrics. Our findings highlight the need for training-aware adjustments to optimize LLM translation outputs, paving the way for more fluent and target-language-consistent translations. We release the data and code at https://github.com/yafuly/LLM_Translationese.
ThinkBench: Dynamic Out-of-Distribution Evaluation for Robust LLM Reasoning
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Evaluating large language models (LLMs) poses significant challenges, particularly due to issues of data contamination and the leakage of correct answers. To address these challenges, we introduce ThinkBench, a novel evaluation framework designed to evaluate LLMs' reasoning capability robustly. ThinkBench proposes a dynamic data generation method for constructing out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets and offers an OOD dataset that contains 2,912 samples drawn from reasoning tasks. ThinkBench unifies the evaluation of reasoning models and non-reasoning models. We evaluate 16 LLMs and 4 PRMs under identical experimental conditions and show that most of the LLMs' performance are far from robust and they face a certain level of data leakage. By dynamically generating OOD datasets, ThinkBench effectively provides a reliable evaluation of LLMs and reduces the impact of data contamination.
Selection-p: Self-Supervised Task-Agnostic Prompt Compression for Faithfulness and Transferability
Oct 15, 2024
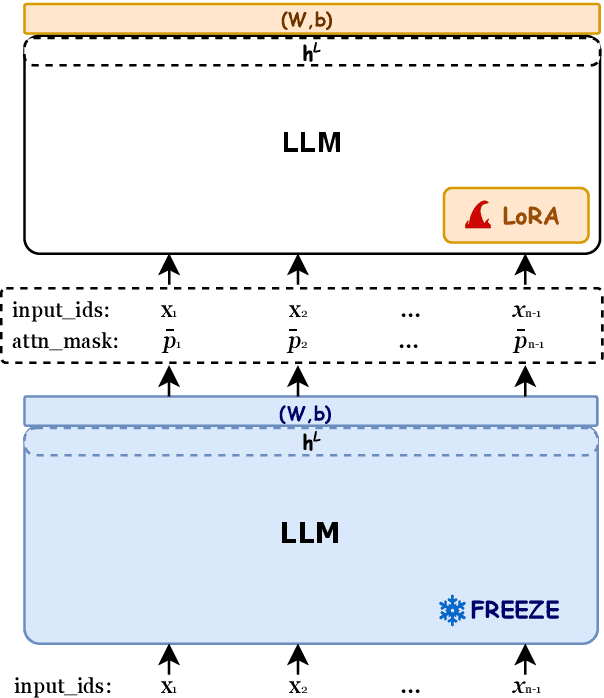


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in a wide range of natural language processing tasks when leveraging in-context learning. To mitigate the additional computational and financial costs associated with in-context learning, several prompt compression methods have been proposed to compress the in-context learning prompts. Despite their success, these methods face challenges with transferability due to model-specific compression, or rely on external training data, such as GPT-4. In this paper, we investigate the ability of LLMs to develop a unified compression method that discretizes uninformative tokens, utilizing a self-supervised pre-training technique. By introducing a small number of parameters during the continual pre-training, the proposed Selection-p produces a probability for each input token, indicating whether to preserve or discard it. Experiments show Selection-p achieves state-of-the-art performance across numerous classification tasks, achieving compression rates of up to 10 times while experiencing only a marginal 0.8% decrease in performance. Moreover, it exhibits superior transferability to different models compared to prior work. Additionally, we further analyze how Selection-p helps maintain performance on in-context learning with long contexts.
Gated Slot Attention for Efficient Linear-Time Sequence Modeling
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Linear attention Transformers and their gated variants, celebrated for enabling parallel training and efficient recurrent inference, still fall short in recall-intensive tasks compared to traditional Transformers and demand significant resources for training from scratch. This paper introduces Gated Slot Attention (GSA), which enhances Attention with Bounded-memory-Control (ABC) by incorporating a gating mechanism inspired by Gated Linear Attention (GLA). Essentially, GSA comprises a two-layer GLA linked via softmax, utilizing context-aware memory reading and adaptive forgetting to improve memory capacity while maintaining compact recurrent state size. This design greatly enhances both training and inference efficiency through GLA's hardware-efficient training algorithm and reduced state size. Additionally, retaining the softmax operation is particularly beneficial in "finetuning pretrained Transformers to RNNs" (T2R) settings, reducing the need for extensive training from scratch. Extensive experiments confirm GSA's superior performance in scenarios requiring in-context recall and in T2R settings.
Not All Preference Pairs Are Created Equal: A Recipe for Annotation-Efficient Iterative Preference Learning
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Iterative preference learning, though yielding superior performances, requires online annotated preference labels. In this work, we study strategies to select worth-annotating response pairs for cost-efficient annotation while achieving competitive or even better performances compared with the random selection baseline for iterative preference learning. Built on assumptions regarding uncertainty and distribution shifts, we propose a comparative view to rank the implicit reward margins as predicted by DPO to select the response pairs that yield more benefits. Through extensive experiments, we show that annotating those response pairs with small margins is generally better than large or random, under both single- and multi-iteration scenarios. Besides, our empirical results suggest allocating more annotation budgets in the earlier iterations rather than later across multiple iterations.
On the Transformations across Reward Model, Parameter Update, and In-Context Prompt
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Despite the general capabilities of pre-trained large language models (LLMs), they still need further adaptation to better serve practical applications. In this paper, we demonstrate the interchangeability of three popular and distinct adaptation tools: parameter updating, reward modeling, and in-context prompting. This interchangeability establishes a triangular framework with six transformation directions, each of which facilitates a variety of applications. Our work offers a holistic view that unifies numerous existing studies and suggests potential research directions. We envision our work as a useful roadmap for future research on LLMs.
Spotting AI's Touch: Identifying LLM-Paraphrased Spans in Text
May 21, 2024



Abstract:AI-generated text detection has attracted increasing attention as powerful language models approach human-level generation. Limited work is devoted to detecting (partially) AI-paraphrased texts. However, AI paraphrasing is commonly employed in various application scenarios for text refinement and diversity. To this end, we propose a novel detection framework, paraphrased text span detection (PTD), aiming to identify paraphrased text spans within a text. Different from text-level detection, PTD takes in the full text and assigns each of the sentences with a score indicating the paraphrasing degree. We construct a dedicated dataset, PASTED, for paraphrased text span detection. Both in-distribution and out-of-distribution results demonstrate the effectiveness of PTD models in identifying AI-paraphrased text spans. Statistical and model analysis explains the crucial role of the surrounding context of the paraphrased text spans. Extensive experiments show that PTD models can generalize to versatile paraphrasing prompts and multiple paraphrased text spans. We release our resources at https://github.com/Linzwcs/PASTED.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge