Yafu Li
New Skills or Sharper Primitives? A Probabilistic Perspective on the Emergence of Reasoning in RLVR
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Whether Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) endows Large Language Models (LLMs) with new capabilities or merely elicits latent traces remains a central debate. In this work, we align with the former view, proposing a probabilistic framework where capability is defined by instance-level solvability. We hypothesize that the emergence of complex reasoning can be driven by sharpening atomic step probabilities, which enables models to overcome the exponential decay of success rates inherent in multi-step reasoning chains. Utilizing the Algebrarium framework, we train models exclusively on single-step operations and evaluate their performance on unseen multi-step tasks. Our empirical results confirm that: (1) RLVR incentivizes the exploration of previously inaccessible solution paths by amplifying the model's existing skills; (2) composite performance is strictly governed by the joint probability of atomic steps, evidenced by high Pearson correlation coefficients ($ρ\in [0.69, 0.96]$); and (3) RLVR, acting as a global optimizer, can cause specific skills to be sacrificed to maximize aggregate reward. Our work offers a novel explanation for emergent abilities in RLVR, suggesting that the iterative optimization of solvable problems enables models to develop the capabilities to tackle previously unsolvable scenarios.
Characterizing, Evaluating, and Optimizing Complex Reasoning
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) increasingly rely on reasoning traces with complex internal structures. However, existing work lacks a unified answer to three fundamental questions: (1) what defines high-quality reasoning, (2) how to reliably evaluate long, implicitly structured reasoning traces, and (3) how to use such evaluation signals for reasoning optimization. To address these challenges, we provide a unified perspective. (1) We introduce the ME$^2$ principle to characterize reasoning quality along macro- and micro-level concerning efficiency and effectiveness. (2) Built on this principle, we model reasoning traces as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) and develop a DAG-based pairwise evaluation method, capturing complex reasoning structures. (3) Based on this method, we construct the TRM-Preference dataset and train a Thinking Reward Model (TRM) to evaluate reasoning quality at scale. Experiments show that thinking rewards serve as an effective optimization signal. At test time, selecting better reasoning leads to better outcomes (up to 19.3% gain), and during RL training, thinking rewards enhance reasoning and performance (up to 3.9% gain) across diverse tasks.
LatentMem: Customizing Latent Memory for Multi-Agent Systems
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-powered multi-agent systems (MAS) demonstrate remarkable collective intelligence, wherein multi-agent memory serves as a pivotal mechanism for continual adaptation. However, existing multi-agent memory designs remain constrained by two fundamental bottlenecks: (i) memory homogenization arising from the absence of role-aware customization, and (ii) information overload induced by excessively fine-grained memory entries. To address these limitations, we propose LatentMem, a learnable multi-agent memory framework designed to customize agent-specific memories in a token-efficient manner. Specifically, LatentMem comprises an experience bank that stores raw interaction trajectories in a lightweight form, and a memory composer that synthesizes compact latent memories conditioned on retrieved experience and agent-specific contexts. Further, we introduce Latent Memory Policy Optimization (LMPO), which propagates task-level optimization signals through latent memories to the composer, encouraging it to produce compact and high-utility representations. Extensive experiments across diverse benchmarks and mainstream MAS frameworks show that LatentMem achieves a performance gain of up to $19.36$% over vanilla settings and consistently outperforms existing memory architectures, without requiring any modifications to the underlying frameworks.
Learning to Reason Faithfully through Step-Level Faithfulness Maximization
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has markedly improved the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) on tasks requiring multi-step reasoning. However, most RLVR pipelines rely on sparse outcome-based rewards, providing little supervision over intermediate steps and thus encouraging over-confidence and spurious reasoning, which in turn increases hallucinations. To address this, we propose FaithRL, a general reinforcement learning framework that directly optimizes reasoning faithfulness. We formalize a faithfulness-maximization objective and theoretically show that optimizing it mitigates over-confidence. To instantiate this objective, we introduce a geometric reward design and a faithfulness-aware advantage modulation mechanism that assigns step-level credit by penalizing unsupported steps while preserving valid partial derivations. Across diverse backbones and benchmarks, FaithRL consistently reduces hallucination rates while maintaining (and often improving) answer correctness. Further analysis confirms that FaithRL increases step-wise reasoning faithfulness and generalizes robustly. Our code is available at https://github.com/aintdoin/FaithRL.
DiffThinker: Towards Generative Multimodal Reasoning with Diffusion Models
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:While recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have attained significant strides in multimodal reasoning, their reasoning processes remain predominantly text-centric, leading to suboptimal performance in complex long-horizon, vision-centric tasks. In this paper, we establish a novel Generative Multimodal Reasoning paradigm and introduce DiffThinker, a diffusion-based reasoning framework. Conceptually, DiffThinker reformulates multimodal reasoning as a native generative image-to-image task, achieving superior logical consistency and spatial precision in vision-centric tasks. We perform a systematic comparison between DiffThinker and MLLMs, providing the first in-depth investigation into the intrinsic characteristics of this paradigm, revealing four core properties: efficiency, controllability, native parallelism, and collaboration. Extensive experiments across four domains (sequential planning, combinatorial optimization, constraint satisfaction, and spatial configuration) demonstrate that DiffThinker significantly outperforms leading closed source models including GPT-5 (+314.2\%) and Gemini-3-Flash (+111.6\%), as well as the fine-tuned Qwen3-VL-32B baseline (+39.0\%), highlighting generative multimodal reasoning as a promising approach for vision-centric reasoning.
VideoSSR: Video Self-Supervised Reinforcement Learning
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has substantially advanced the video understanding capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). However, the rapid progress of MLLMs is outpacing the complexity of existing video datasets, while the manual annotation of new, high-quality data remains prohibitively expensive. This work investigates a pivotal question: Can the rich, intrinsic information within videos be harnessed to self-generate high-quality, verifiable training data? To investigate this, we introduce three self-supervised pretext tasks: Anomaly Grounding, Object Counting, and Temporal Jigsaw. We construct the Video Intrinsic Understanding Benchmark (VIUBench) to validate their difficulty, revealing that current state-of-the-art MLLMs struggle significantly on these tasks. Building upon these pretext tasks, we develop the VideoSSR-30K dataset and propose VideoSSR, a novel video self-supervised reinforcement learning framework for RLVR. Extensive experiments across 17 benchmarks, spanning four major video domains (General Video QA, Long Video QA, Temporal Grounding, and Complex Reasoning), demonstrate that VideoSSR consistently enhances model performance, yielding an average improvement of over 5\%. These results establish VideoSSR as a potent foundational framework for developing more advanced video understanding in MLLMs. The code is available at https://github.com/lcqysl/VideoSSR.
ExGRPO: Learning to Reason from Experience
Oct 02, 2025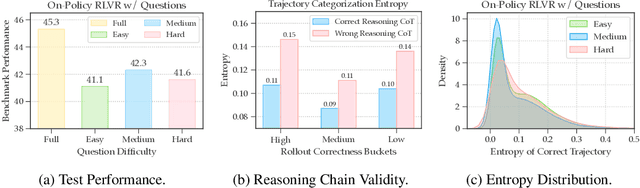
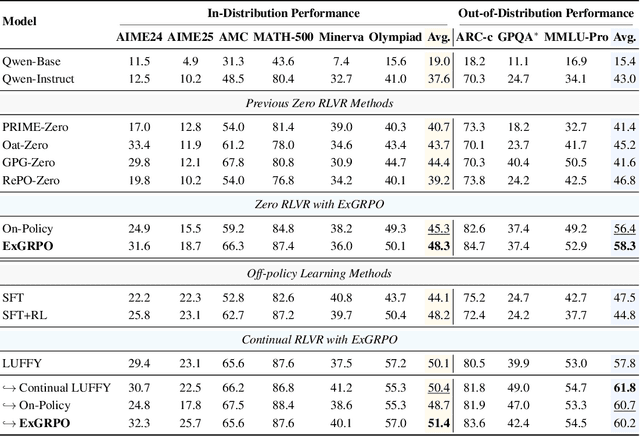
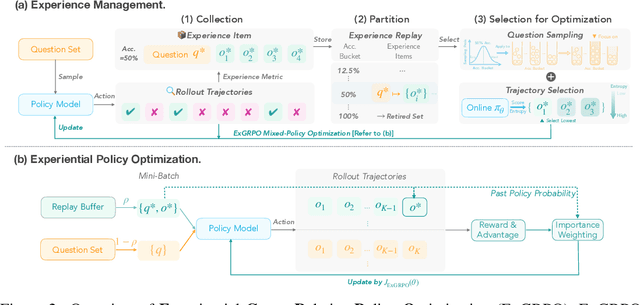
Abstract:Reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) is an emerging paradigm for improving the reasoning ability of large language models. However, standard on-policy training discards rollout experiences after a single update, leading to computational inefficiency and instability. While prior work on RL has highlighted the benefits of reusing past experience, the role of experience characteristics in shaping learning dynamics of large reasoning models remains underexplored. In this paper, we are the first to investigate what makes a reasoning experience valuable and identify rollout correctness and entropy as effective indicators of experience value. Based on these insights, we propose ExGRPO (Experiential Group Relative Policy Optimization), a framework that organizes and prioritizes valuable experiences, and employs a mixed-policy objective to balance exploration with experience exploitation. Experiments on five backbone models (1.5B-8B parameters) show that ExGRPO consistently improves reasoning performance on mathematical/general benchmarks, with an average gain of +3.5/7.6 points over on-policy RLVR. Moreover, ExGRPO stabilizes training on both stronger and weaker models where on-policy methods fail. These results highlight principled experience management as a key ingredient for efficient and scalable RLVR.
Reasoning over Boundaries: Enhancing Specification Alignment via Test-time Delibration
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied in diverse real-world scenarios, each governed by bespoke behavioral and safety specifications (spec) custom-tailored by users or organizations. These spec, categorized into safety-spec and behavioral-spec, vary across scenarios and evolve with changing preferences and requirements. We formalize this challenge as specification alignment, focusing on LLMs' ability to follow dynamic, scenario-specific spec from both behavioral and safety perspectives. To address this challenge, we propose Align3, a lightweight method that employs Test-Time Deliberation (TTD) with hierarchical reflection and revision to reason over the specification boundaries. We further present SpecBench, a unified benchmark for measuring specification alignment, covering 5 scenarios, 103 spec, and 1,500 prompts. Experiments on 15 reasoning and 18 instruct models with several TTD methods, including Self-Refine, TPO, and MoreThink, yield three key findings: (i) test-time deliberation enhances specification alignment; (ii) Align3 advances the safety-helpfulness trade-off frontier with minimal overhead; (iii) SpecBench effectively reveals alignment gaps. These results highlight the potential of test-time deliberation as an effective strategy for reasoning over the real-world specification boundaries.
A Survey of Reinforcement Learning for Large Reasoning Models
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we survey recent advances in Reinforcement Learning (RL) for reasoning with Large Language Models (LLMs). RL has achieved remarkable success in advancing the frontier of LLM capabilities, particularly in addressing complex logical tasks such as mathematics and coding. As a result, RL has emerged as a foundational methodology for transforming LLMs into LRMs. With the rapid progress of the field, further scaling of RL for LRMs now faces foundational challenges not only in computational resources but also in algorithm design, training data, and infrastructure. To this end, it is timely to revisit the development of this domain, reassess its trajectory, and explore strategies to enhance the scalability of RL toward Artificial SuperIntelligence (ASI). In particular, we examine research applying RL to LLMs and LRMs for reasoning abilities, especially since the release of DeepSeek-R1, including foundational components, core problems, training resources, and downstream applications, to identify future opportunities and directions for this rapidly evolving area. We hope this review will promote future research on RL for broader reasoning models. Github: https://github.com/TsinghuaC3I/Awesome-RL-for-LRMs
Synthesizing Sheet Music Problems for Evaluation and Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2025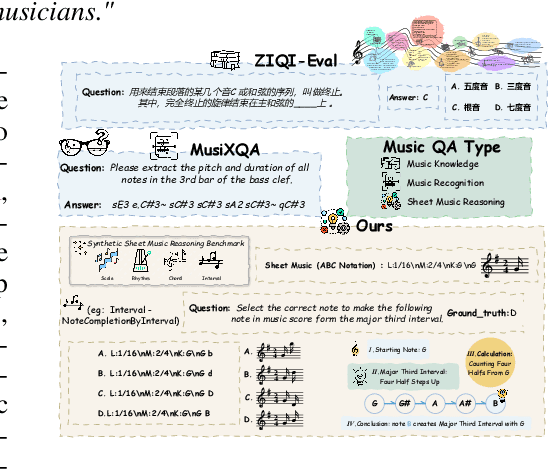

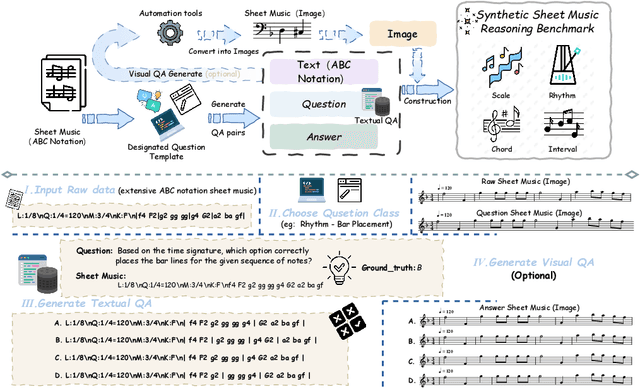
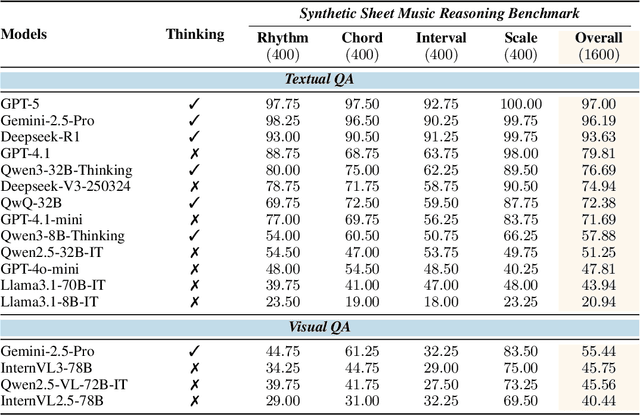
Abstract:Enhancing the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to interpret sheet music is a crucial step toward building AI musicians. However, current research lacks both evaluation benchmarks and training data for sheet music reasoning. To address this, we propose the idea of synthesizing sheet music problems grounded in music theory, which can serve both as evaluation benchmarks and as training data for reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR). We introduce a data synthesis framework that generates verifiable sheet music questions in both textual and visual modalities, leading to the Synthetic Sheet Music Reasoning Benchmark (SSMR-Bench) and a complementary training set. Evaluation results on SSMR-Bench show the importance of models' reasoning abilities in interpreting sheet music. At the same time, the poor performance of Gemini 2.5-Pro highlights the challenges that MLLMs still face in interpreting sheet music in a visual format. By leveraging synthetic data for RLVR, Qwen3-8B-Base and Qwen2.5-VL-Instruct achieve improvements on the SSMR-Bench. Besides, the trained Qwen3-8B-Base surpasses GPT-4 in overall performance on MusicTheoryBench and achieves reasoning performance comparable to GPT-4 with the strategies of Role play and Chain-of-Thought. Notably, its performance on math problems also improves relative to the original Qwen3-8B-Base. Furthermore, our results show that the enhanced reasoning ability can also facilitate music composition. In conclusion, we are the first to propose the idea of synthesizing sheet music problems based on music theory rules, and demonstrate its effectiveness not only in advancing model reasoning for sheet music understanding but also in unlocking new possibilities for AI-assisted music creation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge