Haoran Zhang
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Regularized Calibration with Successive Rounding for Post-Training Quantization
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) deliver robust performance across diverse applications, yet their deployment often faces challenges due to the memory and latency costs of storing and accessing billions of parameters. Post-training quantization (PTQ) enables efficient inference by mapping pretrained weights to low-bit formats without retraining, but its effectiveness depends critically on both the quantization objective and the rounding procedure used to obtain low-bit weight representations. In this work, we show that interpolating between symmetric and asymmetric calibration acts as a form of regularization that preserves the standard quadratic structure used in PTQ while providing robustness to activation mismatch. Building on this perspective, we derive a simple successive rounding procedure that naturally incorporates asymmetric calibration, as well as a bounded-search extension that allows for an explicit trade-off between quantization quality and the compute cost. Experiments across multiple LLM families, quantization bit-widths, and benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed bounded search based on a regularized asymmetric calibration objective consistently improves perplexity and accuracy over PTQ baselines, while incurring only modest and controllable additional computational cost.
MetaGen: Self-Evolving Roles and Topologies for Multi-Agent LLM Reasoning
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly deployed as multi-agent systems, where specialized roles communicate and collaborate through structured interactions to solve complex tasks that often exceed the capacity of a single agent. However, most existing systems still rely on a fixed role library and an execution-frozen interaction topology, a rigid design choice that frequently leads to task mismatch, prevents timely adaptation when new evidence emerges during reasoning, and further inflates inference cost. We introduce MetaGen, a training-free framework that adapts both the role space and the collaboration topology at inference time, without updating base model weights. MetaGen generates and rewrites query-conditioned role specifications to maintain a controllable dynamic role pool, then instantiates a constrained execution graph around a minimal backbone. During execution, it iteratively updates role prompts and adjusts structural decisions using lightweight feedback signals. Experiments on code generation and multi-step reasoning benchmarks show that MetaGen improves the accuracy and cost tradeoff over strong multi-agent baselines.
Explainable AI as a Double-Edged Sword in Dermatology: The Impact on Clinicians versus The Public
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly permeating healthcare, from physician assistants to consumer applications. Since AI algorithm's opacity challenges human interaction, explainable AI (XAI) addresses this by providing AI decision-making insight, but evidence suggests XAI can paradoxically induce over-reliance or bias. We present results from two large-scale experiments (623 lay people; 153 primary care physicians, PCPs) combining a fairness-based diagnosis AI model and different XAI explanations to examine how XAI assistance, particularly multimodal large language models (LLMs), influences diagnostic performance. AI assistance balanced across skin tones improved accuracy and reduced diagnostic disparities. However, LLM explanations yielded divergent effects: lay users showed higher automation bias - accuracy boosted when AI was correct, reduced when AI erred - while experienced PCPs remained resilient, benefiting irrespective of AI accuracy. Presenting AI suggestions first also led to worse outcomes when the AI was incorrect for both groups. These findings highlight XAI's varying impact based on expertise and timing, underscoring LLMs as a "double-edged sword" in medical AI and informing future human-AI collaborative system design.
A Vision-Language-Action-Critic Model for Robotic Real-World Reinforcement Learning
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Robotic real-world reinforcement learning (RL) with vision-language-action (VLA) models is bottlenecked by sparse, handcrafted rewards and inefficient exploration. We introduce VLAC, a general process reward model built upon InternVL and trained on large scale heterogeneous datasets. Given pairwise observations and a language goal, it outputs dense progress delta and done signal, eliminating task-specific reward engineering, and supports one-shot in-context transfer to unseen tasks and environments. VLAC is trained on vision-language datasets to strengthen perception, dialogic and reasoning capabilities, together with robot and human trajectories data that ground action generation and progress estimation, and additionally strengthened to reject irrelevant prompts as well as detect regression or stagnation by constructing large numbers of negative and semantically mismatched samples. With prompt control, a single VLAC model alternately generating reward and action tokens, unifying critic and policy. Deployed inside an asynchronous real-world RL loop, we layer a graded human-in-the-loop protocol (offline demonstration replay, return and explore, human guided explore) that accelerates exploration and stabilizes early learning. Across four distinct real-world manipulation tasks, VLAC lifts success rates from about 30\% to about 90\% within 200 real-world interaction episodes; incorporating human-in-the-loop interventions yields a further 50% improvement in sample efficiency and achieves up to 100% final success.
Reasoning over Boundaries: Enhancing Specification Alignment via Test-time Delibration
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied in diverse real-world scenarios, each governed by bespoke behavioral and safety specifications (spec) custom-tailored by users or organizations. These spec, categorized into safety-spec and behavioral-spec, vary across scenarios and evolve with changing preferences and requirements. We formalize this challenge as specification alignment, focusing on LLMs' ability to follow dynamic, scenario-specific spec from both behavioral and safety perspectives. To address this challenge, we propose Align3, a lightweight method that employs Test-Time Deliberation (TTD) with hierarchical reflection and revision to reason over the specification boundaries. We further present SpecBench, a unified benchmark for measuring specification alignment, covering 5 scenarios, 103 spec, and 1,500 prompts. Experiments on 15 reasoning and 18 instruct models with several TTD methods, including Self-Refine, TPO, and MoreThink, yield three key findings: (i) test-time deliberation enhances specification alignment; (ii) Align3 advances the safety-helpfulness trade-off frontier with minimal overhead; (iii) SpecBench effectively reveals alignment gaps. These results highlight the potential of test-time deliberation as an effective strategy for reasoning over the real-world specification boundaries.
Synthesizing Sheet Music Problems for Evaluation and Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2025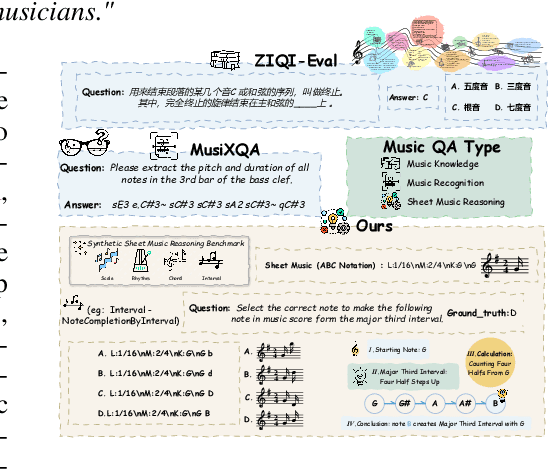

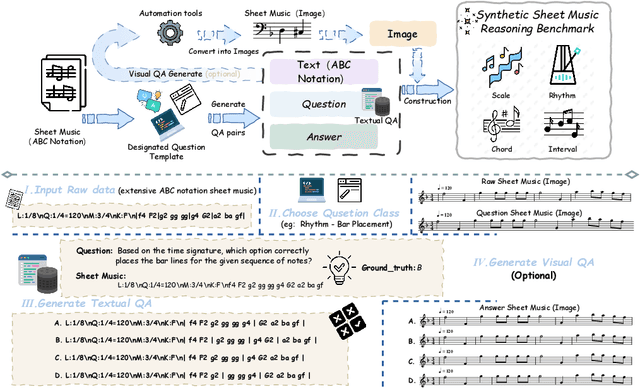
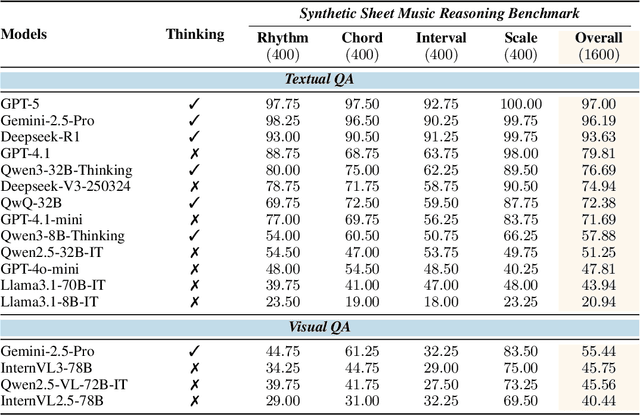
Abstract:Enhancing the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to interpret sheet music is a crucial step toward building AI musicians. However, current research lacks both evaluation benchmarks and training data for sheet music reasoning. To address this, we propose the idea of synthesizing sheet music problems grounded in music theory, which can serve both as evaluation benchmarks and as training data for reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR). We introduce a data synthesis framework that generates verifiable sheet music questions in both textual and visual modalities, leading to the Synthetic Sheet Music Reasoning Benchmark (SSMR-Bench) and a complementary training set. Evaluation results on SSMR-Bench show the importance of models' reasoning abilities in interpreting sheet music. At the same time, the poor performance of Gemini 2.5-Pro highlights the challenges that MLLMs still face in interpreting sheet music in a visual format. By leveraging synthetic data for RLVR, Qwen3-8B-Base and Qwen2.5-VL-Instruct achieve improvements on the SSMR-Bench. Besides, the trained Qwen3-8B-Base surpasses GPT-4 in overall performance on MusicTheoryBench and achieves reasoning performance comparable to GPT-4 with the strategies of Role play and Chain-of-Thought. Notably, its performance on math problems also improves relative to the original Qwen3-8B-Base. Furthermore, our results show that the enhanced reasoning ability can also facilitate music composition. In conclusion, we are the first to propose the idea of synthesizing sheet music problems based on music theory rules, and demonstrate its effectiveness not only in advancing model reasoning for sheet music understanding but also in unlocking new possibilities for AI-assisted music creation.
Player-Centric Multimodal Prompt Generation for Large Language Model Based Identity-Aware Basketball Video Captioning
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Existing sports video captioning methods often focus on the action yet overlook player identities, limiting their applicability. Although some methods integrate extra information to generate identity-aware descriptions, the player identities are sometimes incorrect because the extra information is independent of the video content. This paper proposes a player-centric multimodal prompt generation network for identity-aware sports video captioning (LLM-IAVC), which focuses on recognizing player identities from a visual perspective. Specifically, an identity-related information extraction module (IRIEM) is designed to extract player-related multimodal embeddings. IRIEM includes a player identification network (PIN) for extracting visual features and player names, and a bidirectional semantic interaction module (BSIM) to link player features with video content for mutual enhancement. Additionally, a visual context learning module (VCLM) is designed to capture the key video context information. Finally, by integrating the outputs of the above modules as the multimodal prompt for the large language model (LLM), it facilitates the generation of descriptions with player identities. To support this work, we construct a new benchmark called NBA-Identity, a large identity-aware basketball video captioning dataset with 9,726 videos covering 9 major event types. The experimental results on NBA-Identity and VC-NBA-2022 demonstrate that our proposed model achieves advanced performance. Code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/Zeyu1226-mt/LLM-IAVC.
MedPAIR: Measuring Physicians and AI Relevance Alignment in Medical Question Answering
May 29, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on various medical question-answering (QA) benchmarks, including standardized medical exams. However, correct answers alone do not ensure correct logic, and models may reach accurate conclusions through flawed processes. In this study, we introduce the MedPAIR (Medical Dataset Comparing Physicians and AI Relevance Estimation and Question Answering) dataset to evaluate how physician trainees and LLMs prioritize relevant information when answering QA questions. We obtain annotations on 1,300 QA pairs from 36 physician trainees, labeling each sentence within the question components for relevance. We compare these relevance estimates to those for LLMs, and further evaluate the impact of these "relevant" subsets on downstream task performance for both physician trainees and LLMs. We find that LLMs are frequently not aligned with the content relevance estimates of physician trainees. After filtering out physician trainee-labeled irrelevant sentences, accuracy improves for both the trainees and the LLMs. All LLM and physician trainee-labeled data are available at: http://medpair.csail.mit.edu/.
Scaling-up Perceptual Video Quality Assessment
May 28, 2025Abstract:The data scaling law has been shown to significantly enhance the performance of large multi-modal models (LMMs) across various downstream tasks. However, in the domain of perceptual video quality assessment (VQA), the potential of scaling law remains unprecedented due to the scarcity of labeled resources and the insufficient scale of datasets. To address this, we propose \textbf{OmniVQA}, an efficient framework designed to efficiently build high-quality, human-in-the-loop VQA multi-modal instruction databases (MIDBs). We then scale up to create \textbf{OmniVQA-Chat-400K}, the largest MIDB in the VQA field concurrently. Our focus is on the technical and aesthetic quality dimensions, with abundant in-context instruction data to provide fine-grained VQA knowledge. Additionally, we have built the \textbf{OmniVQA-MOS-20K} dataset to enhance the model's quantitative quality rating capabilities. We then introduce a \textbf{complementary} training strategy that effectively leverages the knowledge from datasets for quality understanding and quality rating tasks. Furthermore, we propose the \textbf{OmniVQA-FG (fine-grain)-Benchmark} to evaluate the fine-grained performance of the models. Our results demonstrate that our models achieve state-of-the-art performance in both quality understanding and rating tasks.
Connecting the Dots: A Chain-of-Collaboration Prompting Framework for LLM Agents
May 16, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in executing complex reasoning tasks. Chain-of-thought effectively enhances reasoning capabilities by unlocking the potential of large models, while multi-agent systems provide more comprehensive solutions by integrating collective intelligence of multiple agents. However, both approaches face significant limitations. Single-agent with chain-of-thought, due to the inherent complexity of designing cross-domain prompts, faces collaboration challenges. Meanwhile, multi-agent systems consume substantial tokens and inevitably dilute the primary problem, which is particularly problematic in business workflow tasks. To address these challenges, we propose Cochain, a collaboration prompting framework that effectively solves business workflow collaboration problem by combining knowledge and prompts at a reduced cost. Specifically, we construct an integrated knowledge graph that incorporates knowledge from multiple stages. Furthermore, by maintaining and retrieving a prompts tree, we can obtain prompt information relevant to other stages of the business workflow. We perform extensive evaluations of Cochain across multiple datasets, demonstrating that Cochain outperforms all baselines in both prompt engineering and multi-agent LLMs. Additionally, expert evaluation results indicate that the use of a small model in combination with Cochain outperforms GPT-4.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge