Peniel Argaw
CancerGUIDE: Cancer Guideline Understanding via Internal Disagreement Estimation
Sep 09, 2025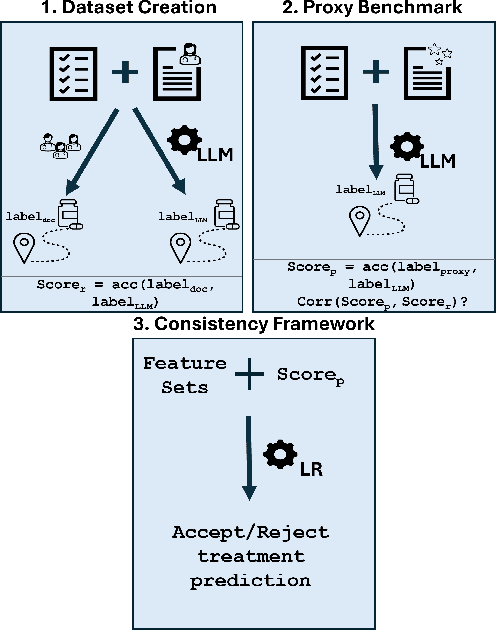
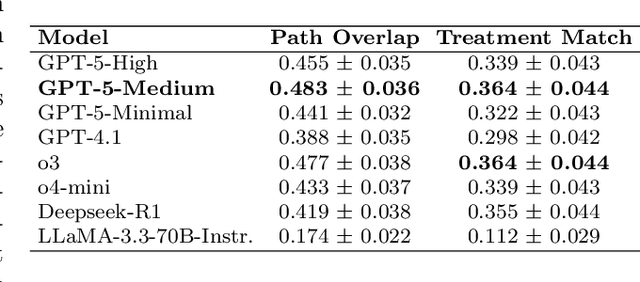
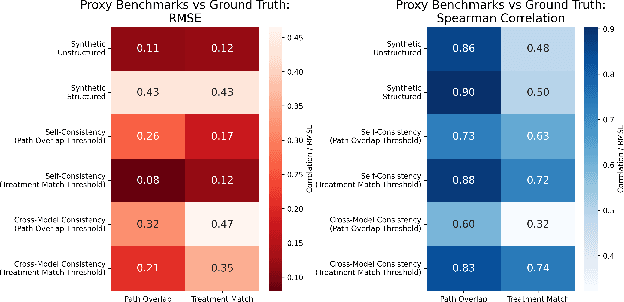
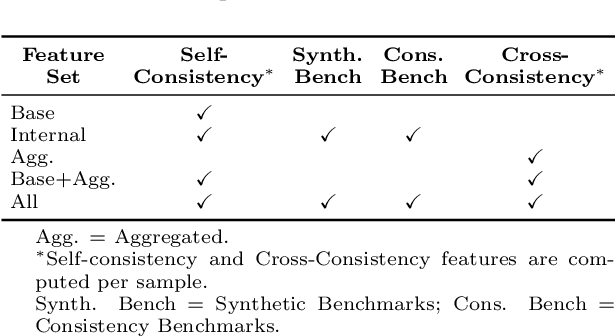
Abstract:The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) provides evidence-based guidelines for cancer treatment. Translating complex patient presentations into guideline-compliant treatment recommendations is time-intensive, requires specialized expertise, and is prone to error. Advances in large language model (LLM) capabilities promise to reduce the time required to generate treatment recommendations and improve accuracy. We present an LLM agent-based approach to automatically generate guideline-concordant treatment trajectories for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Our contributions are threefold. First, we construct a novel longitudinal dataset of 121 cases of NSCLC patients that includes clinical encounters, diagnostic results, and medical histories, each expertly annotated with the corresponding NCCN guideline trajectories by board-certified oncologists. Second, we demonstrate that existing LLMs possess domain-specific knowledge that enables high-quality proxy benchmark generation for both model development and evaluation, achieving strong correlation (Spearman coefficient r=0.88, RMSE = 0.08) with expert-annotated benchmarks. Third, we develop a hybrid approach combining expensive human annotations with model consistency information to create both the agent framework that predicts the relevant guidelines for a patient, as well as a meta-classifier that verifies prediction accuracy with calibrated confidence scores for treatment recommendations (AUROC=0.800), a critical capability for communicating the accuracy of outputs, custom-tailoring tradeoffs in performance, and supporting regulatory compliance. This work establishes a framework for clinically viable LLM-based guideline adherence systems that balance accuracy, interpretability, and regulatory requirements while reducing annotation costs, providing a scalable pathway toward automated clinical decision support.
Machine Learning for Health symposium 2024 -- Findings track
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:A collection of the accepted Findings papers that were presented at the 4th Machine Learning for Health symposium (ML4H 2024), which was held on December 15-16, 2024, in Vancouver, BC, Canada. ML4H 2024 invited high-quality submissions describing innovative research in a variety of health-related disciplines including healthcare, biomedicine, and public health. Works could be submitted to either the archival Proceedings track, or the non-archival Findings track. The Proceedings track targeted mature, cohesive works with technical sophistication and high-impact relevance to health. The Findings track promoted works that would spark new insights, collaborations, and discussions at ML4H. Both tracks were given the opportunity to share their work through the in-person poster session. All the manuscripts submitted to ML4H Symposium underwent a double-blind peer-review process.
Event Stream GPT: A Data Pre-processing and Modeling Library for Generative, Pre-trained Transformers over Continuous-time Sequences of Complex Events
Jun 21, 2023Abstract:Generative, pre-trained transformers (GPTs, a.k.a. "Foundation Models") have reshaped natural language processing (NLP) through their versatility in diverse downstream tasks. However, their potential extends far beyond NLP. This paper provides a software utility to help realize this potential, extending the applicability of GPTs to continuous-time sequences of complex events with internal dependencies, such as medical record datasets. Despite their potential, the adoption of foundation models in these domains has been hampered by the lack of suitable tools for model construction and evaluation. To bridge this gap, we introduce Event Stream GPT (ESGPT), an open-source library designed to streamline the end-to-end process for building GPTs for continuous-time event sequences. ESGPT allows users to (1) build flexible, foundation-model scale input datasets by specifying only a minimal configuration file, (2) leverage a Hugging Face compatible modeling API for GPTs over this modality that incorporates intra-event causal dependency structures and autoregressive generation capabilities, and (3) evaluate models via standardized processes that can assess few and even zero-shot performance of pre-trained models on user-specified fine-tuning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge