Derek F. Wong
One Model to Critique Them All: Rewarding Agentic Tool-Use via Efficient Reasoning
Oct 30, 2025

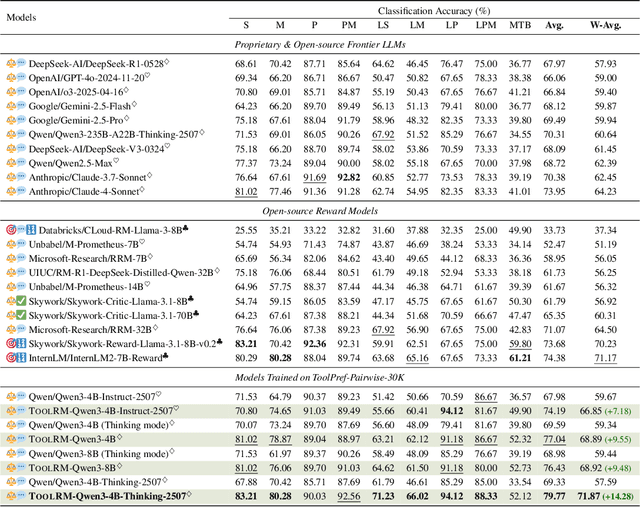

Abstract:Reward models (RMs) play a critical role in aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Yet in the domain of tool learning, the lack of RMs specifically designed for function-calling tasks has limited progress toward more capable agentic AI. We introduce ToolRM, a family of lightweight generative RMs tailored for general tool-use scenarios. To build these models, we propose a novel pipeline that constructs pairwise preference data using rule-based scoring and multidimensional sampling. This yields ToolPref-Pairwise-30K, a diverse, balanced, and challenging dataset of critique tasks that supports reinforcement learning with verifiable feedback. To evaluate tool-use RMs, we also introduce TRBench$_{BFCL}$, a benchmark built on the agentic evaluation suite BFCL. Trained on our constructed data, models from the Qwen3-4B/8B series achieve up to 14.28% higher accuracy, substantially outperforming frontier models such as Claude 4 and OpenAI o3 in pairwise reward judgments. Beyond training objectives, ToolRM generalizes to broader critique tasks, including Best-of-N sampling and self-correction. Experiments on ACEBench highlight its effectiveness and efficiency, enabling inference-time scaling and reducing output token usage by over 66%. We release data and model checkpoints to facilitate future research.
Are Large Reasoning Models Good Translation Evaluators? Analysis and Performance Boost
Oct 23, 2025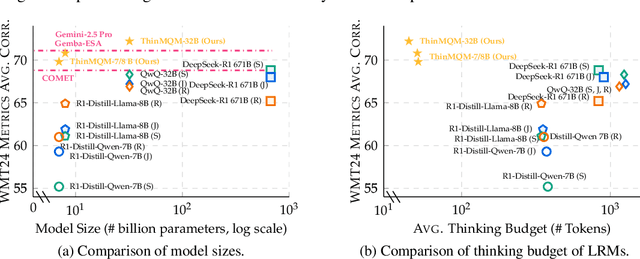
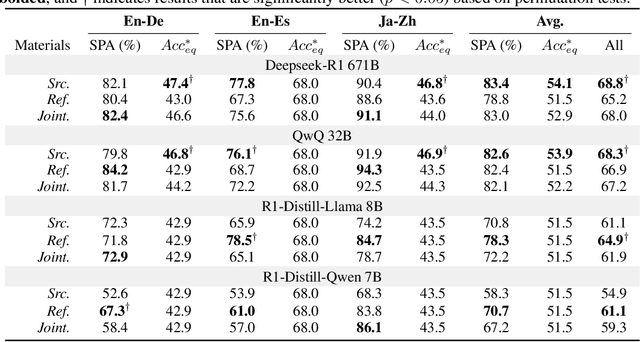
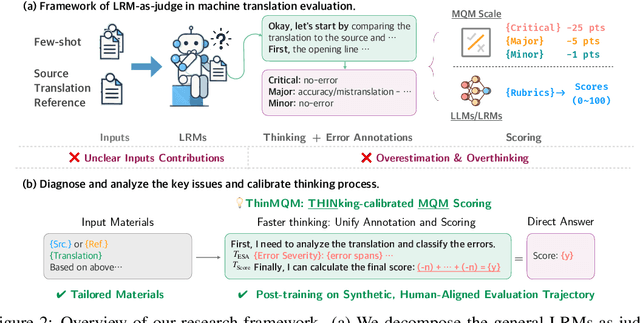
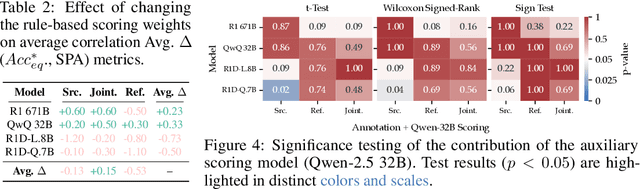
Abstract:Recent advancements in large reasoning models (LRMs) have introduced an intermediate "thinking" process prior to generating final answers, improving their reasoning capabilities on complex downstream tasks. However, the potential of LRMs as evaluators for machine translation (MT) quality remains underexplored. We provides the first systematic analysis of LRM-as-a-judge in MT evaluation. We identify key challenges, revealing LRMs require tailored evaluation materials, tend to "overthink" simpler instances and have issues with scoring mechanisms leading to overestimation. To address these, we propose to calibrate LRM thinking by training them on synthetic, human-like thinking trajectories. Our experiments on WMT24 Metrics benchmarks demonstrate that this approach largely reduces thinking budgets by ~35x while concurrently improving evaluation performance across different LRM scales from 7B to 32B (e.g., R1-Distill-Qwen-7B achieves a +8.7 correlation point improvement). These findings highlight the potential of efficiently calibrated LRMs to advance fine-grained automatic MT evaluation.
ExGRPO: Learning to Reason from Experience
Oct 02, 2025
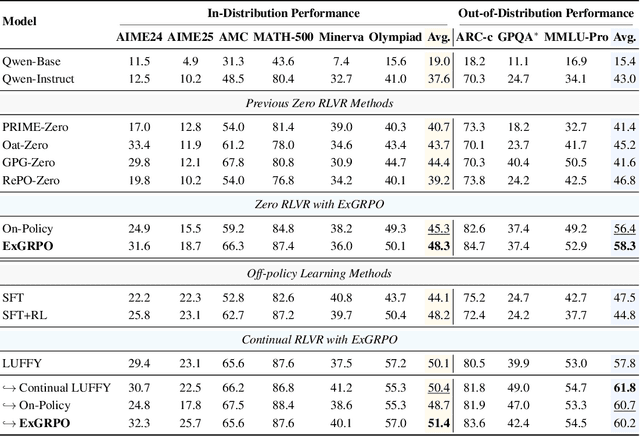
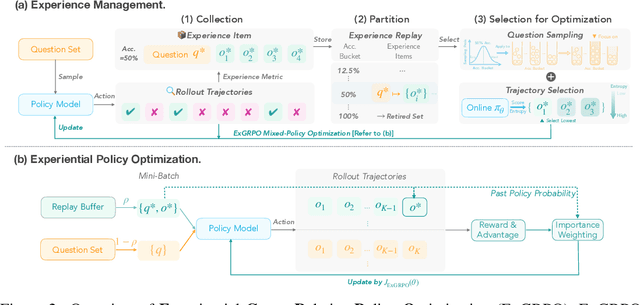
Abstract:Reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) is an emerging paradigm for improving the reasoning ability of large language models. However, standard on-policy training discards rollout experiences after a single update, leading to computational inefficiency and instability. While prior work on RL has highlighted the benefits of reusing past experience, the role of experience characteristics in shaping learning dynamics of large reasoning models remains underexplored. In this paper, we are the first to investigate what makes a reasoning experience valuable and identify rollout correctness and entropy as effective indicators of experience value. Based on these insights, we propose ExGRPO (Experiential Group Relative Policy Optimization), a framework that organizes and prioritizes valuable experiences, and employs a mixed-policy objective to balance exploration with experience exploitation. Experiments on five backbone models (1.5B-8B parameters) show that ExGRPO consistently improves reasoning performance on mathematical/general benchmarks, with an average gain of +3.5/7.6 points over on-policy RLVR. Moreover, ExGRPO stabilizes training on both stronger and weaker models where on-policy methods fail. These results highlight principled experience management as a key ingredient for efficient and scalable RLVR.
Beyond Simple Fusion: Adaptive Gated Fusion for Robust Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Oct 02, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal sentiment analysis (MSA) leverages information fusion from diverse modalities (e.g., text, audio, visual) to enhance sentiment prediction. However, simple fusion techniques often fail to account for variations in modality quality, such as those that are noisy, missing, or semantically conflicting. This oversight leads to suboptimal performance, especially in discerning subtle emotional nuances. To mitigate this limitation, we introduce a simple yet efficient \textbf{A}daptive \textbf{G}ated \textbf{F}usion \textbf{N}etwork that adaptively adjusts feature weights via a dual gate fusion mechanism based on information entropy and modality importance. This mechanism mitigates the influence of noisy modalities and prioritizes informative cues following unimodal encoding and cross-modal interaction. Experiments on CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI show that AGFN significantly outperforms strong baselines in accuracy, effectively discerning subtle emotions with robust performance. Visualization analysis of feature representations demonstrates that AGFN enhances generalization by learning from a broader feature distribution, achieved by reducing the correlation between feature location and prediction error, thereby decreasing reliance on specific locations and creating more robust multimodal feature representations.
Exposing the Cracks: Vulnerabilities of Retrieval-Augmented LLM-based Machine Translation
Oct 01, 2025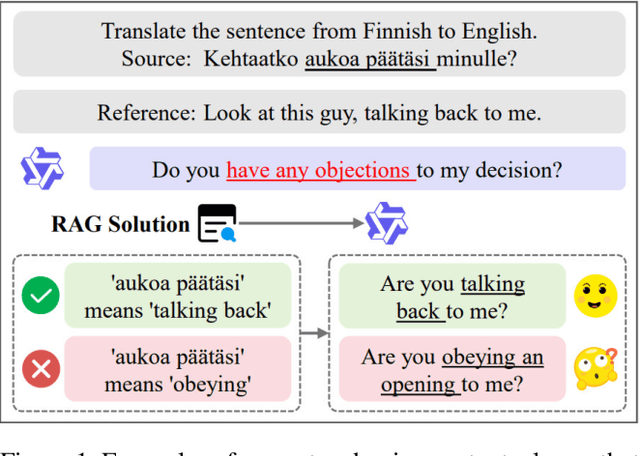

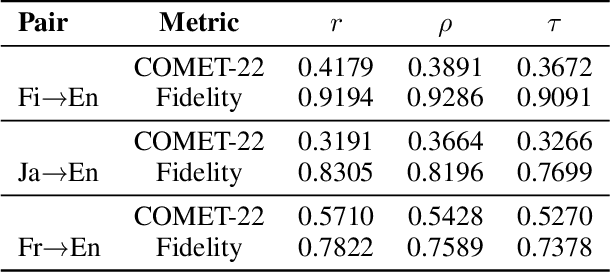
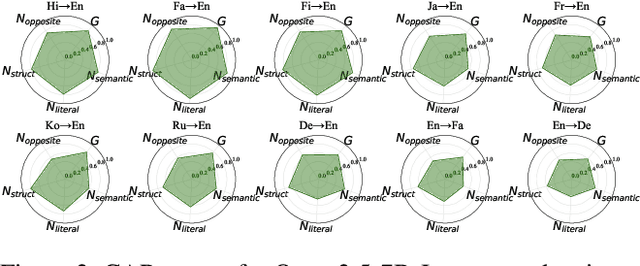
Abstract:\textbf{RE}trieval-\textbf{A}ugmented \textbf{L}LM-based \textbf{M}achine \textbf{T}ranslation (REAL-MT) shows promise for knowledge-intensive tasks like idiomatic translation, but its reliability under noisy retrieval contexts remains poorly understood despite this being a common challenge in real-world deployment. To address this gap, we propose a noise synthesis framework and new metrics to evaluate the robustness of REAL-MT systematically. Using this framework, we instantiate REAL-MT with Qwen-series models, including standard LLMs and large reasoning models (LRMs) with enhanced reasoning, and evaluate their performance on idiomatic translation across high-, medium-, and low-resource language pairs under synthesized noise. Our results show that low-resource language pairs, which rely more heavily on retrieved context, degrade more severely under noise than high-resource ones and often produce nonsensical translations. Although LRMs possess enhanced reasoning capabilities, they show no improvement in error correction and are even more susceptible to noise, tending to rationalize incorrect contexts. We find that this stems from an attention shift away from the source idiom to noisy content, while confidence increases despite declining accuracy, indicating poor calibration. To mitigate these issues, we investigate training-free and fine-tuning strategies, which improve robustness at the cost of performance in clean contexts, revealing a fundamental trade-off. Our findings highlight the limitations of current approaches, underscoring the need for self-verifying integration mechanisms.
Direct Simultaneous Translation Activation for Large Audio-Language Models
Sep 19, 2025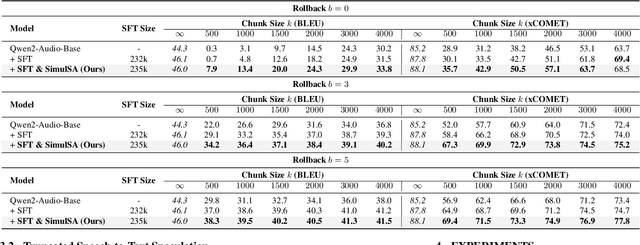
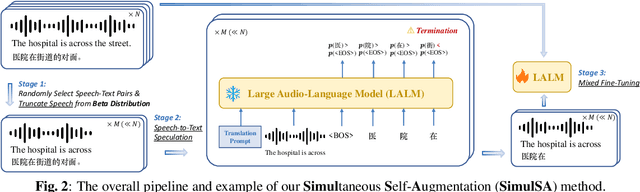

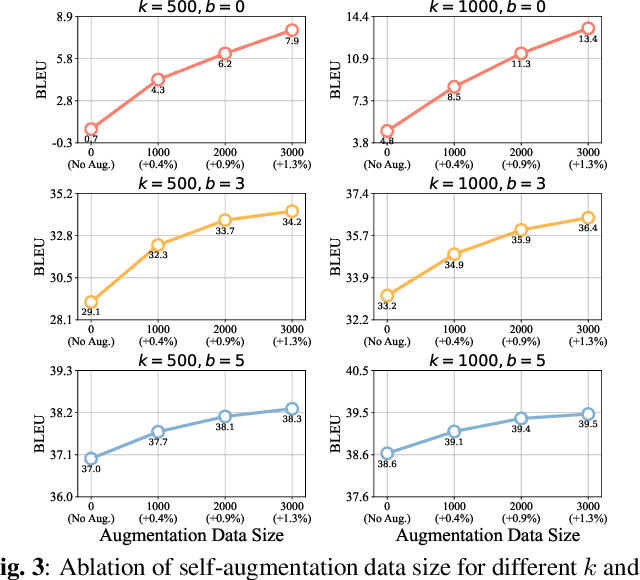
Abstract:Simultaneous speech-to-text translation (Simul-S2TT) aims to translate speech into target text in real time, outputting translations while receiving source speech input, rather than waiting for the entire utterance to be spoken. Simul-S2TT research often modifies model architectures to implement read-write strategies. However, with the rise of large audio-language models (LALMs), a key challenge is how to directly activate Simul-S2TT capabilities in base models without additional architectural changes. In this paper, we introduce {\bf Simul}taneous {\bf S}elf-{\bf A}ugmentation ({\bf SimulSA}), a strategy that utilizes LALMs' inherent capabilities to obtain simultaneous data by randomly truncating speech and constructing partially aligned translation. By incorporating them into offline SFT data, SimulSA effectively bridges the distribution gap between offline translation during pretraining and simultaneous translation during inference. Experimental results demonstrate that augmenting only about {\bf 1\%} of the simultaneous data, compared to the full offline SFT data, can significantly activate LALMs' Simul-S2TT capabilities without modifications to model architecture or decoding strategy.
Synthesizing Sheet Music Problems for Evaluation and Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2025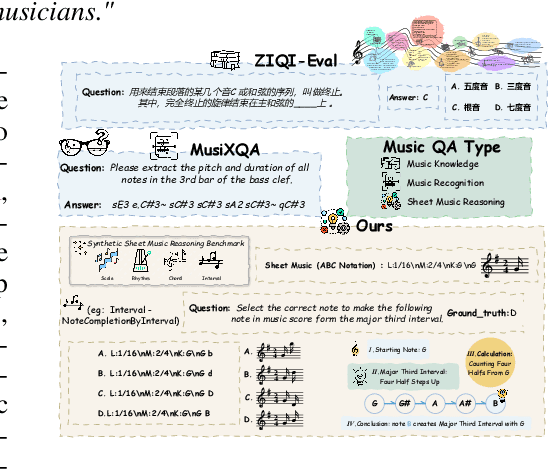

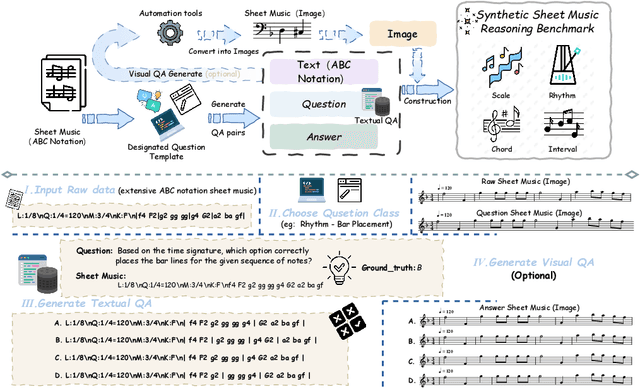
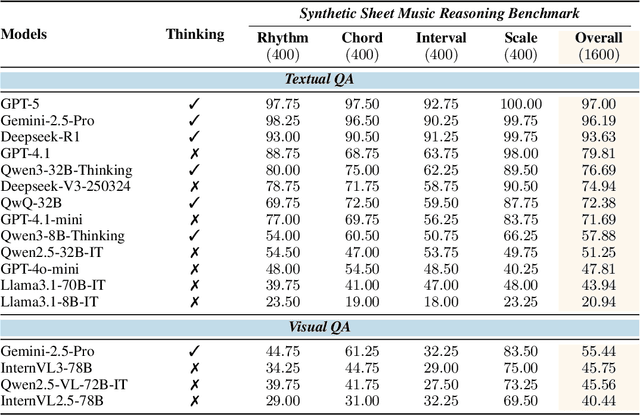
Abstract:Enhancing the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to interpret sheet music is a crucial step toward building AI musicians. However, current research lacks both evaluation benchmarks and training data for sheet music reasoning. To address this, we propose the idea of synthesizing sheet music problems grounded in music theory, which can serve both as evaluation benchmarks and as training data for reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR). We introduce a data synthesis framework that generates verifiable sheet music questions in both textual and visual modalities, leading to the Synthetic Sheet Music Reasoning Benchmark (SSMR-Bench) and a complementary training set. Evaluation results on SSMR-Bench show the importance of models' reasoning abilities in interpreting sheet music. At the same time, the poor performance of Gemini 2.5-Pro highlights the challenges that MLLMs still face in interpreting sheet music in a visual format. By leveraging synthetic data for RLVR, Qwen3-8B-Base and Qwen2.5-VL-Instruct achieve improvements on the SSMR-Bench. Besides, the trained Qwen3-8B-Base surpasses GPT-4 in overall performance on MusicTheoryBench and achieves reasoning performance comparable to GPT-4 with the strategies of Role play and Chain-of-Thought. Notably, its performance on math problems also improves relative to the original Qwen3-8B-Base. Furthermore, our results show that the enhanced reasoning ability can also facilitate music composition. In conclusion, we are the first to propose the idea of synthesizing sheet music problems based on music theory rules, and demonstrate its effectiveness not only in advancing model reasoning for sheet music understanding but also in unlocking new possibilities for AI-assisted music creation.
RepreGuard: Detecting LLM-Generated Text by Revealing Hidden Representation Patterns
Aug 18, 2025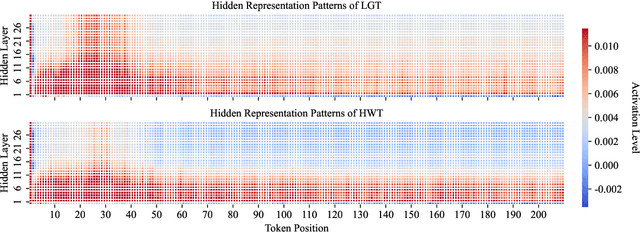

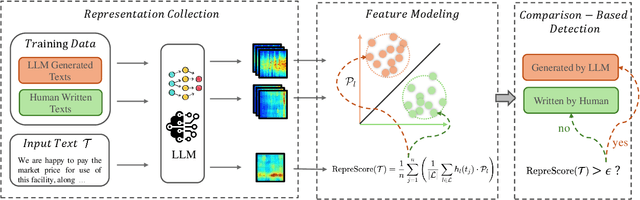

Abstract:Detecting content generated by large language models (LLMs) is crucial for preventing misuse and building trustworthy AI systems. Although existing detection methods perform well, their robustness in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios is still lacking. In this paper, we hypothesize that, compared to features used by existing detection methods, the internal representations of LLMs contain more comprehensive and raw features that can more effectively capture and distinguish the statistical pattern differences between LLM-generated texts (LGT) and human-written texts (HWT). We validated this hypothesis across different LLMs and observed significant differences in neural activation patterns when processing these two types of texts. Based on this, we propose RepreGuard, an efficient statistics-based detection method. Specifically, we first employ a surrogate model to collect representation of LGT and HWT, and extract the distinct activation feature that can better identify LGT. We can classify the text by calculating the projection score of the text representations along this feature direction and comparing with a precomputed threshold. Experimental results show that RepreGuard outperforms all baselines with average 94.92% AUROC on both in-distribution (ID) and OOD scenarios, while also demonstrating robust resilience to various text sizes and mainstream attacks. Data and code are publicly available at: https://github.com/NLP2CT/RepreGuard
Spec-VLA: Speculative Decoding for Vision-Language-Action Models with Relaxed Acceptance
Jul 30, 2025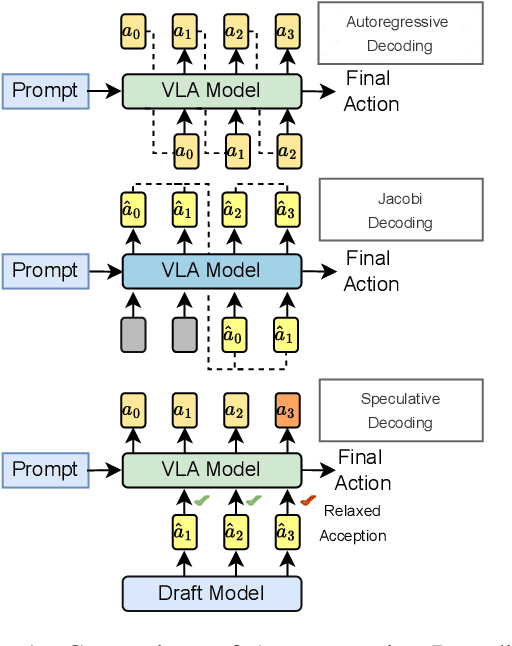
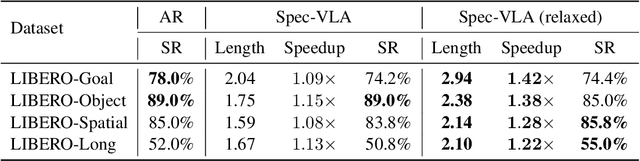
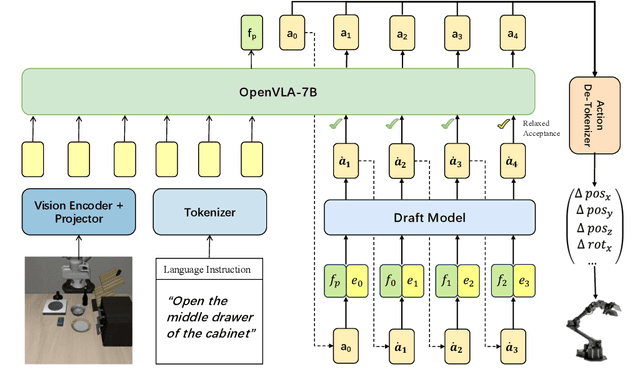
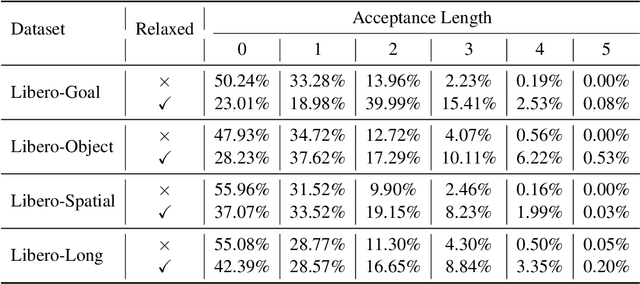
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have made substantial progress by leveraging the robust capabilities of Visual Language Models (VLMs). However, VLMs' significant parameter size and autoregressive (AR) decoding nature impose considerable computational demands on VLA models. While Speculative Decoding (SD) has shown efficacy in accelerating Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating efficient drafting and parallel verification, allowing multiple tokens to be generated in one forward pass, its application to VLA models remains unexplored. This work introduces Spec-VLA, an SD framework designed to accelerate VLA models. Due to the difficulty of the action prediction task and the greedy decoding mechanism of the VLA models, the direct application of the advanced SD framework to the VLA prediction task yields a minor speed improvement. To boost the generation speed, we propose an effective mechanism to relax acceptance utilizing the relative distances represented by the action tokens of the VLA model. Empirical results across diverse test scenarios affirm the effectiveness of the Spec-VLA framework, and further analysis substantiates the impact of our proposed strategies, which enhance the acceptance length by 44%, achieving 1.42 times speedup compared with the OpenVLA baseline, without compromising the success rate. The success of the Spec-VLA framework highlights the potential for broader application of speculative execution in VLA prediction scenarios.
HiMATE: A Hierarchical Multi-Agent Framework for Machine Translation Evaluation
May 22, 2025



Abstract:The advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) enables flexible and interpretable automatic evaluations. In the field of machine translation evaluation, utilizing LLMs with translation error annotations based on Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM) yields more human-aligned judgments. However, current LLM-based evaluation methods still face challenges in accurately identifying error spans and assessing their severity. In this paper, we propose HiMATE, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent Framework for Machine Translation Evaluation. We argue that existing approaches inadequately exploit the fine-grained structural and semantic information within the MQM hierarchy. To address this, we develop a hierarchical multi-agent system grounded in the MQM error typology, enabling granular evaluation of subtype errors. Two key strategies are incorporated to further mitigate systemic hallucinations within the framework: the utilization of the model's self-reflection capability and the facilitation of agent discussion involving asymmetric information. Empirically, HiMATE outperforms competitive baselines across different datasets in conducting human-aligned evaluations. Further analyses underscore its significant advantage in error span detection and severity assessment, achieving an average F1-score improvement of 89% over the best-performing baseline. We make our code and data publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/HiMATE-Anony.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge