Minghuan Tan
RxSafeBench: Identifying Medication Safety Issues of Large Language Models in Simulated Consultation
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Numerous medical systems powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in diverse healthcare tasks. However, research on their medication safety remains limited due to the lack of real world datasets, constrained by privacy and accessibility issues. Moreover, evaluation of LLMs in realistic clinical consultation settings, particularly regarding medication safety, is still underexplored. To address these gaps, we propose a framework that simulates and evaluates clinical consultations to systematically assess the medication safety capabilities of LLMs. Within this framework, we generate inquiry diagnosis dialogues with embedded medication risks and construct a dedicated medication safety database, RxRisk DB, containing 6,725 contraindications, 28,781 drug interactions, and 14,906 indication-drug pairs. A two-stage filtering strategy ensures clinical realism and professional quality, resulting in the benchmark RxSafeBench with 2,443 high-quality consultation scenarios. We evaluate leading open-source and proprietary LLMs using structured multiple choice questions that test their ability to recommend safe medications under simulated patient contexts. Results show that current LLMs struggle to integrate contraindication and interaction knowledge, especially when risks are implied rather than explicit. Our findings highlight key challenges in ensuring medication safety in LLM-based systems and provide insights into improving reliability through better prompting and task-specific tuning. RxSafeBench offers the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating medication safety in LLMs, advancing safer and more trustworthy AI-driven clinical decision support.
LongEmotion: Measuring Emotional Intelligence of Large Language Models in Long-Context Interaction
Sep 09, 2025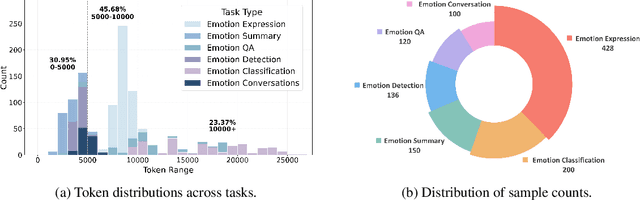
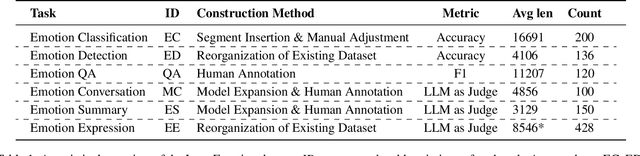
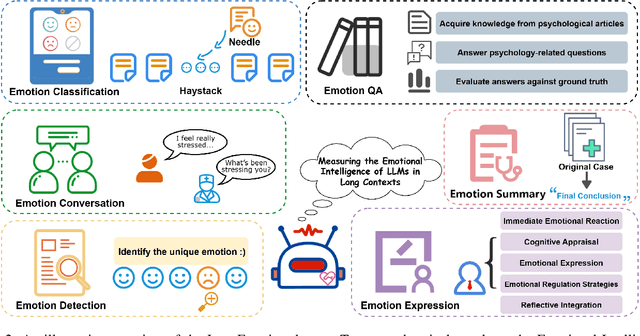
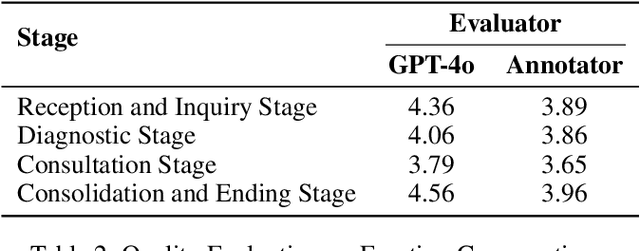
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) make significant progress in Emotional Intelligence (EI) and long-context understanding. However, existing benchmarks tend to overlook certain aspects of EI in long-context scenarios, especially under realistic, practical settings where interactions are lengthy, diverse, and often noisy. To move towards such realistic settings, we present LongEmotion, a benchmark specifically designed for long-context EI tasks. It covers a diverse set of tasks, including Emotion Classification, Emotion Detection, Emotion QA, Emotion Conversation, Emotion Summary, and Emotion Expression. On average, the input length for these tasks reaches 8,777 tokens, with long-form generation required for Emotion Expression. To enhance performance under realistic constraints, we incorporate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Collaborative Emotional Modeling (CoEM), and compare them with standard prompt-based methods. Unlike conventional approaches, our RAG method leverages both the conversation context and the large language model itself as retrieval sources, avoiding reliance on external knowledge bases. The CoEM method further improves performance by decomposing the task into five stages, integrating both retrieval augmentation and limited knowledge injection. Experimental results show that both RAG and CoEM consistently enhance EI-related performance across most long-context tasks, advancing LLMs toward more practical and real-world EI applications. Furthermore, we conducted a comparative case study experiment on the GPT series to demonstrate the differences among various models in terms of EI. Code is available on GitHub at https://github.com/LongEmotion/LongEmotion, and the project page can be found at https://longemotion.github.io/.
AutoCBT: An Autonomous Multi-agent Framework for Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Psychological Counseling
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Traditional in-person psychological counseling remains primarily niche, often chosen by individuals with psychological issues, while online automated counseling offers a potential solution for those hesitant to seek help due to feelings of shame. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an essential and widely used approach in psychological counseling. The advent of large language models (LLMs) and agent technology enables automatic CBT diagnosis and treatment. However, current LLM-based CBT systems use agents with a fixed structure, limiting their self-optimization capabilities, or providing hollow, unhelpful suggestions due to redundant response patterns. In this work, we utilize Quora-like and YiXinLi single-round consultation models to build a general agent framework that generates high-quality responses for single-turn psychological consultation scenarios. We use a bilingual dataset to evaluate the quality of single-response consultations generated by each framework. Then, we incorporate dynamic routing and supervisory mechanisms inspired by real psychological counseling to construct a CBT-oriented autonomous multi-agent framework, demonstrating its general applicability. Experimental results indicate that AutoCBT can provide higher-quality automated psychological counseling services.
DualCoTs: Dual Chain-of-Thoughts Prompting for Sentiment Lexicon Expansion of Idioms
Sep 26, 2024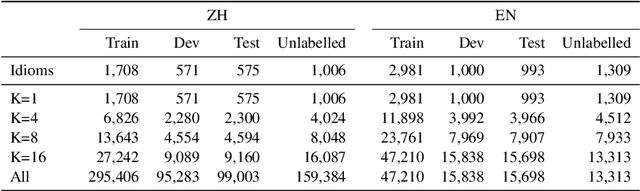
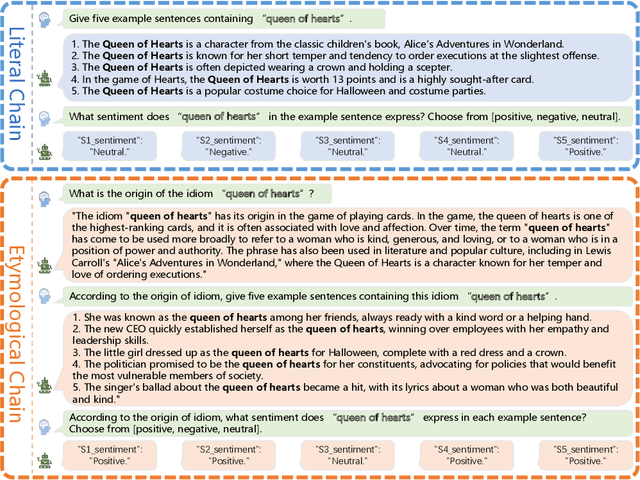
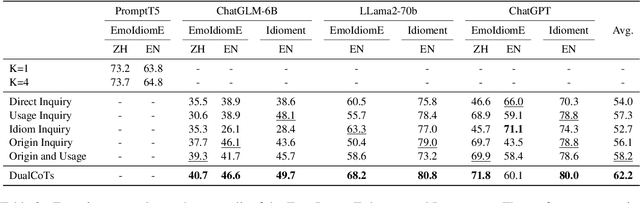
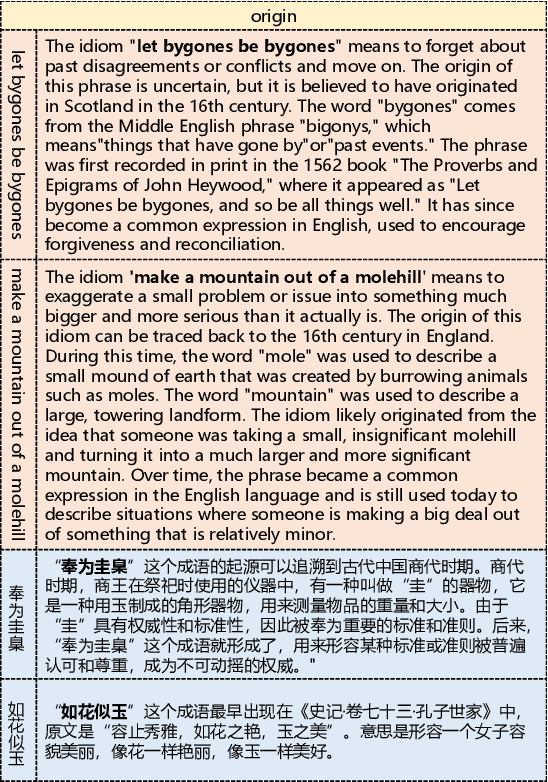
Abstract:Idioms represent a ubiquitous vehicle for conveying sentiments in the realm of everyday discourse, rendering the nuanced analysis of idiom sentiment crucial for a comprehensive understanding of emotional expression within real-world texts. Nevertheless, the existing corpora dedicated to idiom sentiment analysis considerably limit research in text sentiment analysis. In this paper, we propose an innovative approach to automatically expand the sentiment lexicon for idioms, leveraging the capabilities of large language models through the application of Chain-of-Thought prompting. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach, we integrate multiple existing resources and construct an emotional idiom lexicon expansion dataset (called EmoIdiomE), which encompasses a comprehensive repository of Chinese and English idioms. Then we designed the Dual Chain-of-Thoughts (DualCoTs) method, which combines insights from linguistics and psycholinguistics, to demonstrate the effectiveness of using large models to automatically expand the sentiment lexicon for idioms. Experiments show that DualCoTs is effective in idioms sentiment lexicon expansion in both Chinese and English. For reproducibility, we will release the data and code upon acceptance.
CollectiveSFT: Scaling Large Language Models for Chinese Medical Benchmark with Collective Instructions in Healthcare
Jul 29, 2024

Abstract:The rapid progress in Large Language Models (LLMs) has prompted the creation of numerous benchmarks to evaluate their capabilities.This study focuses on the Comprehensive Medical Benchmark in Chinese (CMB), showcasing how dataset diversity and distribution in supervised fine-tuning (SFT) may enhance LLM performance.Remarkably, We successfully trained a smaller base model to achieve scores comparable to larger models, indicating that a diverse and well-distributed dataset can optimize performance regardless of model size.This study suggests that even smaller models may reach high performance levels with carefully curated and varied datasets.By integrating a wide range of instructional content, our approach addresses potential issues such as data quality inconsistencies. Our results imply that a broader spectrum of training data may enhance a model's ability to generalize and perform effectively across different medical scenarios, highlighting the importance of dataset quality and diversity in fine-tuning processes.
APTNESS: Incorporating Appraisal Theory and Emotion Support Strategies for Empathetic Response Generation
Jul 23, 2024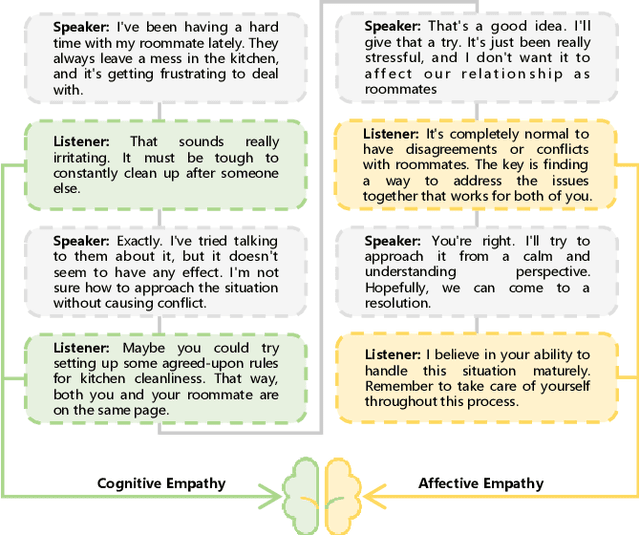
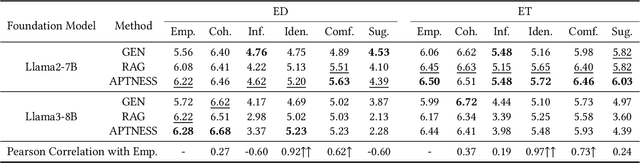
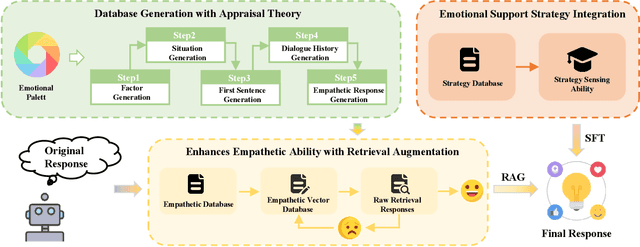

Abstract:Empathetic response generation is designed to comprehend the emotions of others and select the most appropriate strategies to assist them in resolving emotional challenges. Empathy can be categorized into cognitive empathy and affective empathy. The former pertains to the ability to understand and discern the emotional issues and situations of others, while the latter involves the capacity to provide comfort. To enhance one's empathetic abilities, it is essential to develop both these aspects. Therefore, we develop an innovative framework that combines retrieval augmentation and emotional support strategy integration. Our framework starts with the introduction of a comprehensive emotional palette for empathy. We then apply appraisal theory to decompose this palette and create a database of empathetic responses. This database serves as an external resource and enhances the LLM's empathy by integrating semantic retrieval mechanisms. Moreover, our framework places a strong emphasis on the proper articulation of response strategies. By incorporating emotional support strategies, we aim to enrich the model's capabilities in both cognitive and affective empathy, leading to a more nuanced and comprehensive empathetic response. Finally, we extract datasets ED and ET from the empathetic dialogue dataset \textsc{EmpatheticDialogues} and ExTES based on dialogue length. Experiments demonstrate that our framework can enhance the empathy ability of LLMs from both cognitive and affective empathy perspectives. Our code is released at https://github.com/CAS-SIAT-XinHai/APTNESS.
CoEvol: Constructing Better Responses for Instruction Finetuning through Multi-Agent Cooperation
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, instruction fine-tuning (IFT) on large language models (LLMs) has garnered considerable attention to enhance model performance on unseen tasks. Attempts have been made on automatic construction and effective selection for IFT data. However, we posit that previous methods have not fully harnessed the potential of LLMs for enhancing data quality. The responses within IFT data could be further enhanced by leveraging the capabilities of LLMs themselves. In this paper, we propose CoEvol, an LLM-based multi-agent cooperation framework for the improvement of responses to instructions. To effectively refine the responses, we develop an iterative framework following a debate-advise-edit-judge paradigm. A two-stage multi-agent debate strategy is further devised to ensure the diversity and reliability of editing suggestions within the framework. Empirically, models equipped with CoEvol outperform competitive baselines evaluated by MT-Bench and AlpacaEval, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing instruction-following capabilities for LLMs.
NUMCoT: Numerals and Units of Measurement in Chain-of-Thought Reasoning using Large Language Models
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Numeral systems and units of measurement are two conjoined topics in activities of human beings and have mutual effects with the languages expressing them. Currently, the evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) often involves mathematical reasoning, yet little attention is given to how minor changes in numbers or units can drastically alter the complexity of problems and the performance of LLMs. In this paper, we scrutinize existing LLMs on processing of numerals and units of measurement by constructing datasets with perturbations. We first anatomize the reasoning of math word problems to different sub-procedures like numeral conversions from language to numbers and measurement conversions based on units. Then we further annotate math word problems from ancient Chinese arithmetic works which are challenging in numerals and units of measurement. Experiments on perturbed datasets demonstrate that LLMs still encounter difficulties in handling numeral and measurement conversions.
CPsyCoun: A Report-based Multi-turn Dialogue Reconstruction and Evaluation Framework for Chinese Psychological Counseling
May 26, 2024
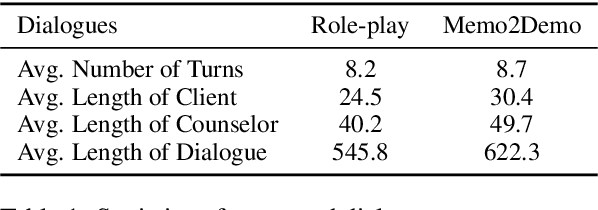

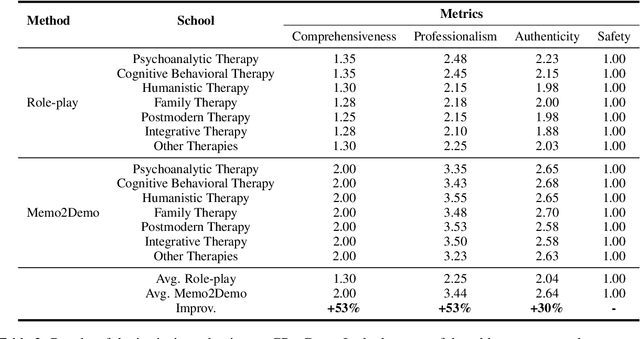
Abstract:Using large language models (LLMs) to assist psychological counseling is a significant but challenging task at present. Attempts have been made on improving empathetic conversations or acting as effective assistants in the treatment with LLMs. However, the existing datasets lack consulting knowledge, resulting in LLMs lacking professional consulting competence. Moreover, how to automatically evaluate multi-turn dialogues within the counseling process remains an understudied area. To bridge the gap, we propose CPsyCoun, a report-based multi-turn dialogue reconstruction and evaluation framework for Chinese psychological counseling. To fully exploit psychological counseling reports, a two-phase approach is devised to construct high-quality dialogues while a comprehensive evaluation benchmark is developed for the effective automatic evaluation of multi-turn psychological consultations. Competitive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework in psychological counseling. We open-source the datasets and model for future research at https://github.com/CAS-SIAT-XinHai/CPsyCoun
CPsyExam: A Chinese Benchmark for Evaluating Psychology using Examinations
May 16, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel psychological benchmark, CPsyExam, constructed from questions sourced from Chinese language examinations. CPsyExam is designed to prioritize psychological knowledge and case analysis separately, recognizing the significance of applying psychological knowledge to real-world scenarios. From the pool of 22k questions, we utilize 4k to create the benchmark that offers balanced coverage of subjects and incorporates a diverse range of case analysis techniques.Furthermore, we evaluate a range of existing large language models~(LLMs), spanning from open-sourced to API-based models. Our experiments and analysis demonstrate that CPsyExam serves as an effective benchmark for enhancing the understanding of psychology within LLMs and enables the comparison of LLMs across various granularities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge