Tong Xiao
Jack
CoMeT: Collaborative Memory Transformer for Efficient Long Context Modeling
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The quadratic complexity and indefinitely growing key-value (KV) cache of standard Transformers pose a major barrier to long-context processing. To overcome this, we introduce the Collaborative Memory Transformer (CoMeT), a novel architecture that enables LLMs to handle arbitrarily long sequences with constant memory usage and linear time complexity. Designed as an efficient, plug-in module, CoMeT can be integrated into pre-trained models with only minimal fine-tuning. It operates on sequential data chunks, using a dual-memory system to manage context: a temporary memory on a FIFO queue for recent events, and a global memory with a gated update rule for long-range dependencies. These memories then act as a dynamic soft prompt for the next chunk. To enable efficient fine-tuning on extremely long contexts, we introduce a novel layer-level pipeline parallelism strategy. The effectiveness of our approach is remarkable: a model equipped with CoMeT and fine-tuned on 32k contexts can accurately retrieve a passkey from any position within a 1M token sequence. On the SCROLLS benchmark, CoMeT surpasses other efficient methods and achieves performance comparable to a full-attention baseline on summarization tasks. Its practical effectiveness is further validated on real-world agent and user behavior QA tasks. The code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/comet-B00B/
APR: Penalizing Structural Redundancy in Large Reasoning Models via Anchor-based Process Rewards
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Test-Time Scaling (TTS) has significantly enhanced the capabilities of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) but introduces a critical side-effect known as Overthinking. We conduct a preliminary study to rethink this phenomenon from a fine-grained perspective. We observe that LRMs frequently conduct repetitive self-verification without revision even after obtaining the final answer during the reasoning process. We formally define this specific position where the answer first stabilizes as the Reasoning Anchor. By analyzing pre- and post-anchor reasoning behaviors, we uncover the structural redundancy fixed in LRMs: the meaningless repetitive verification after deriving the first complete answer, which we term the Answer-Stable Tail (AST). Motivated by this observation, we propose Anchor-based Process Reward (APR), a structure-aware reward shaping method that localizes the reasoning anchor and penalizes exclusively the post-anchor AST. Leveraging the policy optimization algorithm suitable for length penalties, our APR models achieved the performance-efficiency Pareto frontier at 1.5B and 7B scales averaged across five mathematical reasoning datasets while requiring significantly fewer computational resources for RL training.
SpanNorm: Reconciling Training Stability and Performance in Deep Transformers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The success of Large Language Models (LLMs) hinges on the stable training of deep Transformer architectures. A critical design choice is the placement of normalization layers, leading to a fundamental trade-off: the ``PreNorm'' architecture ensures training stability at the cost of potential performance degradation in deep models, while the ``PostNorm'' architecture offers strong performance but suffers from severe training instability. In this work, we propose SpanNorm, a novel technique designed to resolve this dilemma by integrating the strengths of both paradigms. Structurally, SpanNorm establishes a clean residual connection that spans the entire transformer block to stabilize signal propagation, while employing a PostNorm-style computation that normalizes the aggregated output to enhance model performance. We provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating that SpanNorm, combined with a principled scaling strategy, maintains bounded signal variance throughout the network, preventing the gradient issues that plague PostNorm models, and also alleviating the representation collapse of PreNorm. Empirically, SpanNorm consistently outperforms standard normalization schemes in both dense and Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) scenarios, paving the way for more powerful and stable Transformer architectures.
Causal Autoregressive Diffusion Language Model
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In this work, we propose Causal Autoregressive Diffusion (CARD), a novel framework that unifies the training efficiency of ARMs with the high-throughput inference of diffusion models. CARD reformulates the diffusion process within a strictly causal attention mask, enabling dense, per-token supervision in a single forward pass. To address the optimization instability of causal diffusion, we introduce a soft-tailed masking schema to preserve local context and a context-aware reweighting mechanism derived from signal-to-noise principles. This design enables dynamic parallel decoding, where the model leverages KV-caching to adaptively generate variable-length token sequences based on confidence. Empirically, CARD outperforms existing discrete diffusion baselines while reducing training latency by 3 $\times$ compared to block diffusion methods. Our results demonstrate that CARD achieves ARM-level data efficiency while unlocking the latency benefits of parallel generation, establishing a robust paradigm for next-generation efficient LLMs.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
SERM: Self-Evolving Relevance Model with Agent-Driven Learning from Massive Query Streams
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Due to the dynamically evolving nature of real-world query streams, relevance models struggle to generalize to practical search scenarios. A sophisticated solution is self-evolution techniques. However, in large-scale industrial settings with massive query streams, this technique faces two challenges: (1) informative samples are often sparse and difficult to identify, and (2) pseudo-labels generated by the current model could be unreliable. To address these challenges, in this work, we propose a Self-Evolving Relevance Model approach (SERM), which comprises two complementary multi-agent modules: a multi-agent sample miner, designed to detect distributional shifts and identify informative training samples, and a multi-agent relevance annotator, which provides reliable labels through a two-level agreement framework. We evaluate SERM in a large-scale industrial setting, which serves billions of user requests daily. Experimental results demonstrate that SERM can achieve significant performance gains through iterative self-evolution, as validated by extensive offline multilingual evaluations and online testing.
REFA: Real-time Egocentric Facial Animations for Virtual Reality
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:We present a novel system for real-time tracking of facial expressions using egocentric views captured from a set of infrared cameras embedded in a virtual reality (VR) headset. Our technology facilitates any user to accurately drive the facial expressions of virtual characters in a non-intrusive manner and without the need of a lengthy calibration step. At the core of our system is a distillation based approach to train a machine learning model on heterogeneous data and labels coming form multiple sources, \eg synthetic and real images. As part of our dataset, we collected 18k diverse subjects using a lightweight capture setup consisting of a mobile phone and a custom VR headset with extra cameras. To process this data, we developed a robust differentiable rendering pipeline enabling us to automatically extract facial expression labels. Our system opens up new avenues for communication and expression in virtual environments, with applications in video conferencing, gaming, entertainment, and remote collaboration.
Probing Preference Representations: A Multi-Dimensional Evaluation and Analysis Method for Reward Models
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Previous methods evaluate reward models by testing them on a fixed pairwise ranking test set, but they typically do not provide performance information on each preference dimension. In this work, we address the evaluation challenge of reward models by probing preference representations. To confirm the effectiveness of this evaluation method, we construct a Multi-dimensional Reward Model Benchmark (MRMBench), a collection of six probing tasks for different preference dimensions. We design it to favor and encourage reward models that better capture preferences across different dimensions. Furthermore, we introduce an analysis method, inference-time probing, which identifies the dimensions used during the reward prediction and enhances its interpretability. Through extensive experiments, we find that MRMBench strongly correlates with the alignment performance of large language models (LLMs), making it a reliable reference for developing advanced reward models. Our analysis of MRMBench evaluation results reveals that reward models often struggle to capture preferences across multiple dimensions, highlighting the potential of multi-objective optimization in reward modeling. Additionally, our findings show that the proposed inference-time probing method offers a reliable metric for assessing the confidence of reward predictions, which ultimately improves the alignment of LLMs.
Beyond English: Toward Inclusive and Scalable Multilingual Machine Translation with LLMs
Nov 10, 2025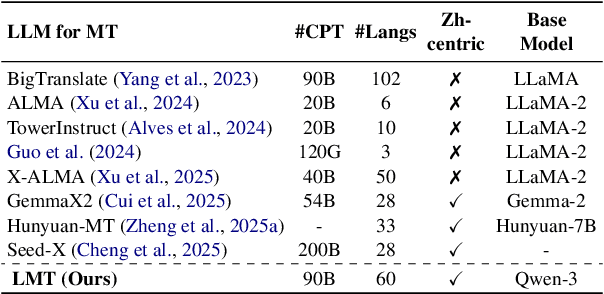
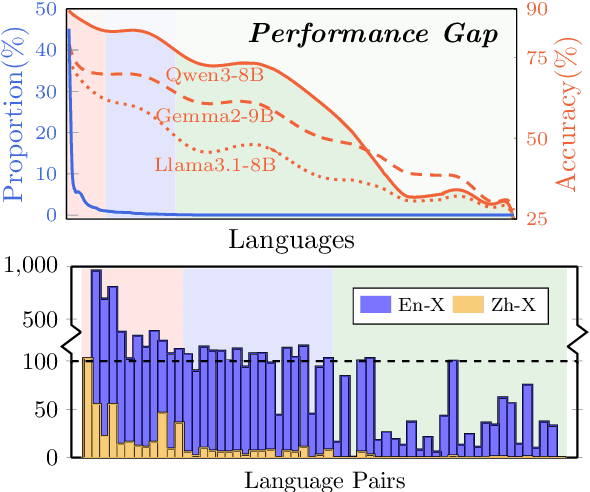
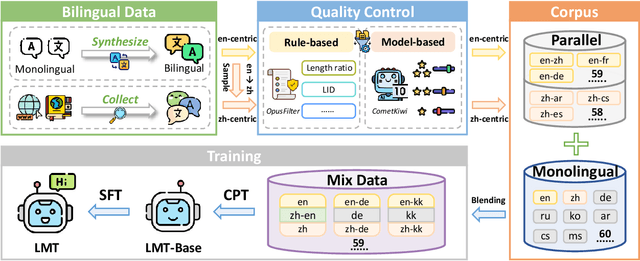
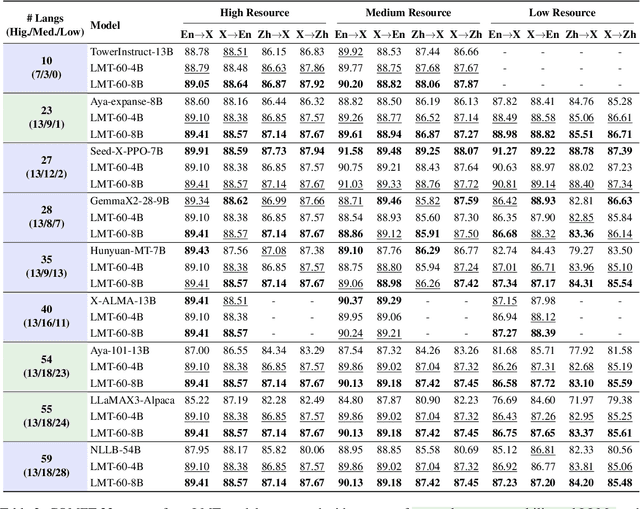
Abstract:Large language models have significantly advanced Multilingual Machine Translation (MMT), yet the broad language coverage, consistent translation quality, and English-centric bias remain open challenges. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{LMT}, a suite of \textbf{L}arge-scale \textbf{M}ultilingual \textbf{T}ranslation models centered on both Chinese and English, covering 60 languages and 234 translation directions. During development, we identify a previously overlooked phenomenon of \textbf{directional degeneration}, where symmetric multi-way fine-tuning data overemphasize reverse directions (X $\to$ En/Zh), leading to excessive many-to-one mappings and degraded translation quality. We propose \textbf{Strategic Downsampling}, a simple yet effective method to mitigate this degeneration. In addition, we design \textbf{Parallel Multilingual Prompting (PMP)}, which leverages typologically related auxiliary languages to enhance cross-lingual transfer. Through rigorous data curation and refined adaptation strategies, LMT achieves SOTA performance among models of comparable language coverage, with our 4B model (LMT-60-4B) surpassing the much larger Aya-101-13B and NLLB-54B models by a substantial margin. We release LMT in four sizes (0.6B/1.7B/4B/8B) to catalyze future research and provide strong baselines for inclusive, scalable, and high-quality MMT \footnote{\href{https://github.com/NiuTrans/LMT}{https://github.com/NiuTrans/LMT}}.
TimeSense:Making Large Language Models Proficient in Time-Series Analysis
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:In the time-series domain, an increasing number of works combine text with temporal data to leverage the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for various downstream time-series understanding tasks. This enables a single model to flexibly perform tasks that previously required specialized models for each domain. However, these methods typically rely on text labels for supervision during training, biasing the model toward textual cues while potentially neglecting the full temporal features. Such a bias can lead to outputs that contradict the underlying time-series context. To address this issue, we construct the EvalTS benchmark, comprising 10 tasks across three difficulty levels, from fundamental temporal pattern recognition to complex real-world reasoning, to evaluate models under more challenging and realistic scenarios. We also propose TimeSense, a multimodal framework that makes LLMs proficient in time-series analysis by balancing textual reasoning with a preserved temporal sense. TimeSense incorporates a Temporal Sense module that reconstructs the input time-series within the model's context, ensuring that textual reasoning is grounded in the time-series dynamics. Moreover, to enhance spatial understanding of time-series data, we explicitly incorporate coordinate-based positional embeddings, which provide each time point with spatial context and enable the model to capture structural dependencies more effectively. Experimental results demonstrate that TimeSense achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple tasks, and it particularly outperforms existing methods on complex multi-dimensional time-series reasoning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge