Bei Li
SpanNorm: Reconciling Training Stability and Performance in Deep Transformers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The success of Large Language Models (LLMs) hinges on the stable training of deep Transformer architectures. A critical design choice is the placement of normalization layers, leading to a fundamental trade-off: the ``PreNorm'' architecture ensures training stability at the cost of potential performance degradation in deep models, while the ``PostNorm'' architecture offers strong performance but suffers from severe training instability. In this work, we propose SpanNorm, a novel technique designed to resolve this dilemma by integrating the strengths of both paradigms. Structurally, SpanNorm establishes a clean residual connection that spans the entire transformer block to stabilize signal propagation, while employing a PostNorm-style computation that normalizes the aggregated output to enhance model performance. We provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating that SpanNorm, combined with a principled scaling strategy, maintains bounded signal variance throughout the network, preventing the gradient issues that plague PostNorm models, and also alleviating the representation collapse of PreNorm. Empirically, SpanNorm consistently outperforms standard normalization schemes in both dense and Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) scenarios, paving the way for more powerful and stable Transformer architectures.
Causal Autoregressive Diffusion Language Model
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In this work, we propose Causal Autoregressive Diffusion (CARD), a novel framework that unifies the training efficiency of ARMs with the high-throughput inference of diffusion models. CARD reformulates the diffusion process within a strictly causal attention mask, enabling dense, per-token supervision in a single forward pass. To address the optimization instability of causal diffusion, we introduce a soft-tailed masking schema to preserve local context and a context-aware reweighting mechanism derived from signal-to-noise principles. This design enables dynamic parallel decoding, where the model leverages KV-caching to adaptively generate variable-length token sequences based on confidence. Empirically, CARD outperforms existing discrete diffusion baselines while reducing training latency by 3 $\times$ compared to block diffusion methods. Our results demonstrate that CARD achieves ARM-level data efficiency while unlocking the latency benefits of parallel generation, establishing a robust paradigm for next-generation efficient LLMs.
LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 Technical Report
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We introduce LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601, a 560-billion-parameter open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) reasoning model with superior agentic reasoning capability. LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models on a wide range of agentic benchmarks, including agentic search, agentic tool use, and tool-integrated reasoning. Beyond benchmark performance, the model demonstrates strong generalization to complex tool interactions and robust behavior under noisy real-world environments. Its advanced capability stems from a unified training framework that combines domain-parallel expert training with subsequent fusion, together with an end-to-end co-design of data construction, environments, algorithms, and infrastructure spanning from pre-training to post-training. In particular, the model's strong generalization capability in complex tool-use are driven by our in-depth exploration of environment scaling and principled task construction. To optimize long-tailed, skewed generation and multi-turn agentic interactions, and to enable stable training across over 10,000 environments spanning more than 20 domains, we systematically extend our asynchronous reinforcement learning framework, DORA, for stable and efficient large-scale multi-environment training. Furthermore, recognizing that real-world tasks are inherently noisy, we conduct a systematic analysis and decomposition of real-world noise patterns, and design targeted training procedures to explicitly incorporate such imperfections into the training process, resulting in improved robustness for real-world applications. To further enhance performance on complex reasoning tasks, we introduce a Heavy Thinking mode that enables effective test-time scaling by jointly expanding reasoning depth and width through intensive parallel thinking.
BAPO: Boundary-Aware Policy Optimization for Reliable Agentic Search
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:RL-based agentic search enables LLMs to solve complex questions via dynamic planning and external search. While this approach significantly enhances accuracy with agent policies optimized via large-scale reinforcement learning, we identify a critical gap in reliability: these agents fail to recognize their reasoning boundaries and rarely admit ``I DON'T KNOW'' (IDK) even when evidence is insufficient or reasoning reaches its limit. The lack of reliability often leads to plausible but unreliable answers, introducing significant risks in many real-world scenarios. To this end, we propose Boundary-Aware Policy Optimization (BAPO), a novel RL framework designed to cultivate reliable boundary awareness without compromising accuracy. BAPO introduces two key components: (i) a group-based boundary-aware reward that encourages an IDK response only when the reasoning reaches its limit, and (ii) an adaptive reward modulator that strategically suspends this reward during early exploration, preventing the model from exploiting IDK as a shortcut. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that BAPO substantially enhances the overall reliability of agentic search.
Probing Preference Representations: A Multi-Dimensional Evaluation and Analysis Method for Reward Models
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Previous methods evaluate reward models by testing them on a fixed pairwise ranking test set, but they typically do not provide performance information on each preference dimension. In this work, we address the evaluation challenge of reward models by probing preference representations. To confirm the effectiveness of this evaluation method, we construct a Multi-dimensional Reward Model Benchmark (MRMBench), a collection of six probing tasks for different preference dimensions. We design it to favor and encourage reward models that better capture preferences across different dimensions. Furthermore, we introduce an analysis method, inference-time probing, which identifies the dimensions used during the reward prediction and enhances its interpretability. Through extensive experiments, we find that MRMBench strongly correlates with the alignment performance of large language models (LLMs), making it a reliable reference for developing advanced reward models. Our analysis of MRMBench evaluation results reveals that reward models often struggle to capture preferences across multiple dimensions, highlighting the potential of multi-objective optimization in reward modeling. Additionally, our findings show that the proposed inference-time probing method offers a reliable metric for assessing the confidence of reward predictions, which ultimately improves the alignment of LLMs.
Beyond English: Toward Inclusive and Scalable Multilingual Machine Translation with LLMs
Nov 10, 2025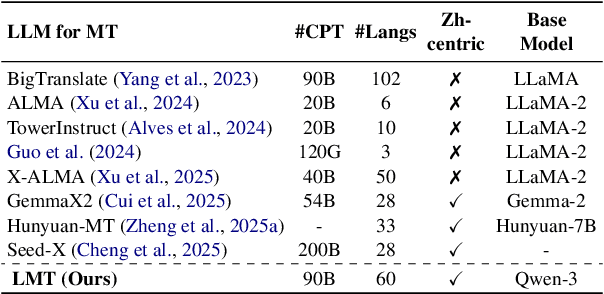
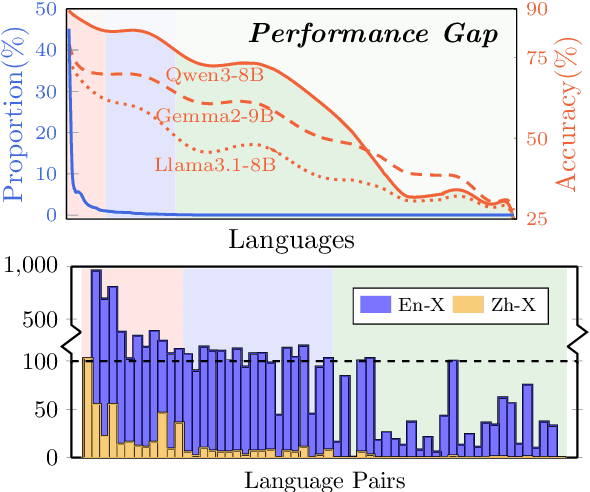
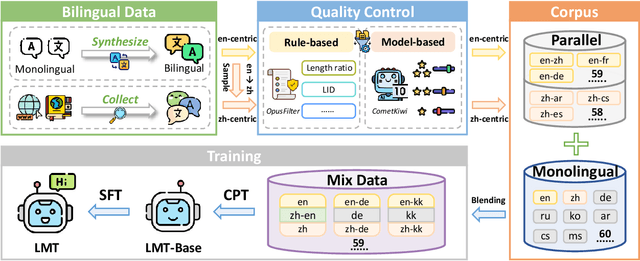
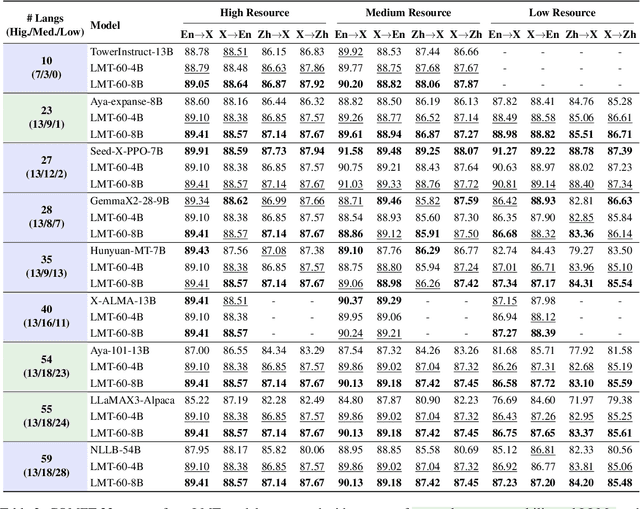
Abstract:Large language models have significantly advanced Multilingual Machine Translation (MMT), yet the broad language coverage, consistent translation quality, and English-centric bias remain open challenges. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{LMT}, a suite of \textbf{L}arge-scale \textbf{M}ultilingual \textbf{T}ranslation models centered on both Chinese and English, covering 60 languages and 234 translation directions. During development, we identify a previously overlooked phenomenon of \textbf{directional degeneration}, where symmetric multi-way fine-tuning data overemphasize reverse directions (X $\to$ En/Zh), leading to excessive many-to-one mappings and degraded translation quality. We propose \textbf{Strategic Downsampling}, a simple yet effective method to mitigate this degeneration. In addition, we design \textbf{Parallel Multilingual Prompting (PMP)}, which leverages typologically related auxiliary languages to enhance cross-lingual transfer. Through rigorous data curation and refined adaptation strategies, LMT achieves SOTA performance among models of comparable language coverage, with our 4B model (LMT-60-4B) surpassing the much larger Aya-101-13B and NLLB-54B models by a substantial margin. We release LMT in four sizes (0.6B/1.7B/4B/8B) to catalyze future research and provide strong baselines for inclusive, scalable, and high-quality MMT \footnote{\href{https://github.com/NiuTrans/LMT}{https://github.com/NiuTrans/LMT}}.
MRO: Enhancing Reasoning in Diffusion Language Models via Multi-Reward Optimization
Oct 24, 2025


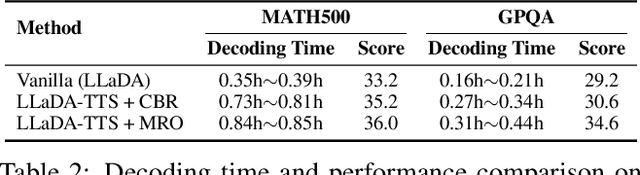
Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion language models (DLMs) have presented a promising alternative to traditional autoregressive large language models (LLMs). However, DLMs still lag behind LLMs in reasoning performance, especially as the number of denoising steps decreases. Our analysis reveals that this shortcoming arises primarily from the independent generation of masked tokens across denoising steps, which fails to capture the token correlation. In this paper, we define two types of token correlation: intra-sequence correlation and inter-sequence correlation, and demonstrate that enhancing these correlations improves reasoning performance. To this end, we propose a Multi-Reward Optimization (MRO) approach, which encourages DLMs to consider the token correlation during the denoising process. More specifically, our MRO approach leverages test-time scaling, reject sampling, and reinforcement learning to directly optimize the token correlation with multiple elaborate rewards. Additionally, we introduce group step and importance sampling strategies to mitigate reward variance and enhance sampling efficiency. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that MRO not only improves reasoning performance but also achieves significant sampling speedups while maintaining high performance on reasoning benchmarks.
IIET: Efficient Numerical Transformer via Implicit Iterative Euler Method
Sep 26, 2025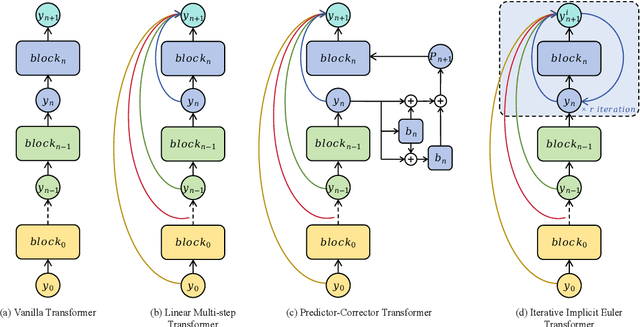
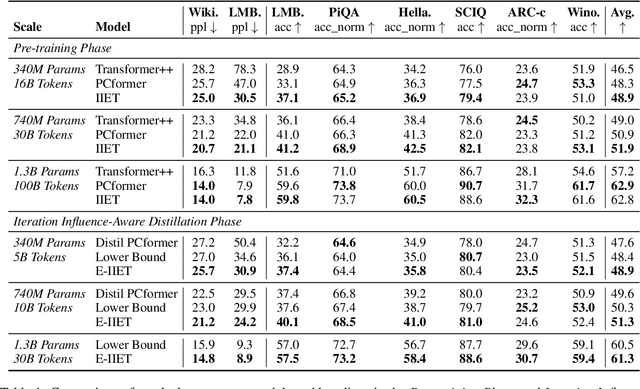
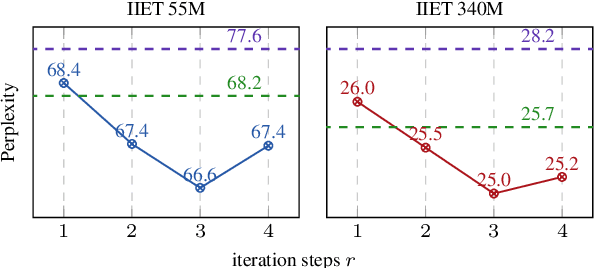
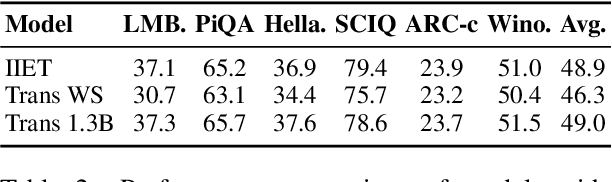
Abstract:High-order numerical methods enhance Transformer performance in tasks like NLP and CV, but introduce a performance-efficiency trade-off due to increased computational overhead. Our analysis reveals that conventional efficiency techniques, such as distillation, can be detrimental to the performance of these models, exemplified by PCformer. To explore more optimizable ODE-based Transformer architectures, we propose the \textbf{I}terative \textbf{I}mplicit \textbf{E}uler \textbf{T}ransformer \textbf{(IIET)}, which simplifies high-order methods using an iterative implicit Euler approach. This simplification not only leads to superior performance but also facilitates model compression compared to PCformer. To enhance inference efficiency, we introduce \textbf{I}teration \textbf{I}nfluence-\textbf{A}ware \textbf{D}istillation \textbf{(IIAD)}. Through a flexible threshold, IIAD allows users to effectively balance the performance-efficiency trade-off. On lm-evaluation-harness, IIET boosts average accuracy by 2.65\% over vanilla Transformers and 0.8\% over PCformer. Its efficient variant, E-IIET, significantly cuts inference overhead by 55\% while retaining 99.4\% of the original task accuracy. Moreover, the most efficient IIET variant achieves an average performance gain exceeding 1.6\% over vanilla Transformer with comparable speed.
TCPO: Thought-Centric Preference Optimization for Effective Embodied Decision-making
Sep 10, 2025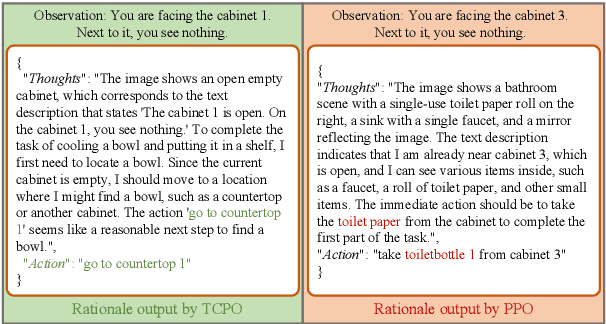
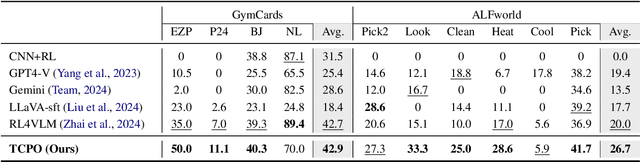
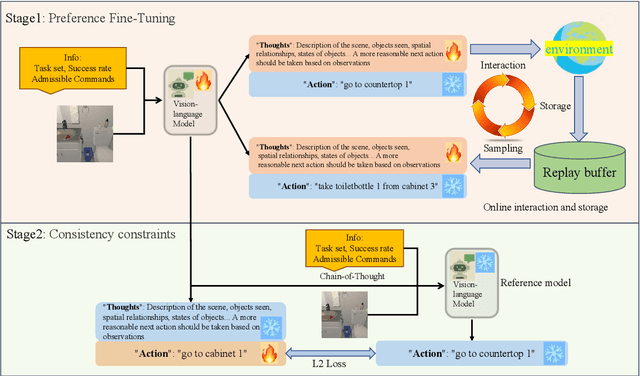

Abstract:Using effective generalization capabilities of vision language models (VLMs) in context-specific dynamic tasks for embodied artificial intelligence remains a significant challenge. Although supervised fine-tuned models can better align with the real physical world, they still exhibit sluggish responses and hallucination issues in dynamically changing environments, necessitating further alignment. Existing post-SFT methods, reliant on reinforcement learning and chain-of-thought (CoT) approaches, are constrained by sparse rewards and action-only optimization, resulting in low sample efficiency, poor consistency, and model degradation. To address these issues, this paper proposes Thought-Centric Preference Optimization (TCPO) for effective embodied decision-making. Specifically, TCPO introduces a stepwise preference-based optimization approach, transforming sparse reward signals into richer step sample pairs. It emphasizes the alignment of the model's intermediate reasoning process, mitigating the problem of model degradation. Moreover, by incorporating Action Policy Consistency Constraint (APC), it further imposes consistency constraints on the model output. Experiments in the ALFWorld environment demonstrate an average success rate of 26.67%, achieving a 6% improvement over RL4VLM and validating the effectiveness of our approach in mitigating model degradation after fine-tuning. These results highlight the potential of integrating preference-based learning techniques with CoT processes to enhance the decision-making capabilities of vision-language models in embodied agents.
SageLM: A Multi-aspect and Explainable Large Language Model for Speech Judgement
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Speech-to-Speech (S2S) Large Language Models (LLMs) are foundational to natural human-computer interaction, enabling end-to-end spoken dialogue systems. However, evaluating these models remains a fundamental challenge. We propose \texttt{SageLM}, an end-to-end, multi-aspect, and explainable speech LLM for comprehensive S2S LLMs evaluation. First, unlike cascaded approaches that disregard acoustic features, SageLM jointly assesses both semantic and acoustic dimensions. Second, it leverages rationale-based supervision to enhance explainability and guide model learning, achieving superior alignment with evaluation outcomes compared to rule-based reinforcement learning methods. Third, we introduce \textit{SpeechFeedback}, a synthetic preference dataset, and employ a two-stage training paradigm to mitigate the scarcity of speech preference data. Trained on both semantic and acoustic dimensions, SageLM achieves an 82.79\% agreement rate with human evaluators, outperforming cascaded and SLM-based baselines by at least 7.42\% and 26.20\%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge