Jianfei Zhang
OPE: Overcoming Information Saturation in Parallel Thinking via Outline-Guided Path Exploration
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Parallel thinking has emerged as a new paradigm for large reasoning models (LRMs) in tackling complex problems. Recent methods leverage Reinforcement Learning (RL) to enhance parallel thinking, aiming to address the limitations in computational resources and effectiveness encountered with supervised fine-tuning. However, most existing studies primarily focus on optimizing the aggregation phase, with limited attention to the path exploration stage. In this paper, we theoretically analyze the optimization of parallel thinking under the Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) setting, and identify that the mutual information bottleneck among exploration paths fundamentally restricts overall performance. To address this, we propose Outline-Guided Path Exploration (OPE), which explicitly partitions the solution space by generating diverse reasoning outlines prior to parallel path reasoning, thereby reducing information redundancy and improving the diversity of information captured across exploration paths. We implement OPE with an iterative RL strategy that optimizes outline planning and outline-guided reasoning independently. Extensive experiments across multiple challenging mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that OPE effectively improves reasoning performance in different aggregation strategies, enabling LRMs to more reliably discover correct solutions.
LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 Technical Report
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We introduce LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601, a 560-billion-parameter open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) reasoning model with superior agentic reasoning capability. LongCat-Flash-Thinking-2601 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models on a wide range of agentic benchmarks, including agentic search, agentic tool use, and tool-integrated reasoning. Beyond benchmark performance, the model demonstrates strong generalization to complex tool interactions and robust behavior under noisy real-world environments. Its advanced capability stems from a unified training framework that combines domain-parallel expert training with subsequent fusion, together with an end-to-end co-design of data construction, environments, algorithms, and infrastructure spanning from pre-training to post-training. In particular, the model's strong generalization capability in complex tool-use are driven by our in-depth exploration of environment scaling and principled task construction. To optimize long-tailed, skewed generation and multi-turn agentic interactions, and to enable stable training across over 10,000 environments spanning more than 20 domains, we systematically extend our asynchronous reinforcement learning framework, DORA, for stable and efficient large-scale multi-environment training. Furthermore, recognizing that real-world tasks are inherently noisy, we conduct a systematic analysis and decomposition of real-world noise patterns, and design targeted training procedures to explicitly incorporate such imperfections into the training process, resulting in improved robustness for real-world applications. To further enhance performance on complex reasoning tasks, we introduce a Heavy Thinking mode that enables effective test-time scaling by jointly expanding reasoning depth and width through intensive parallel thinking.
Autoformalizer with Tool Feedback
Oct 08, 2025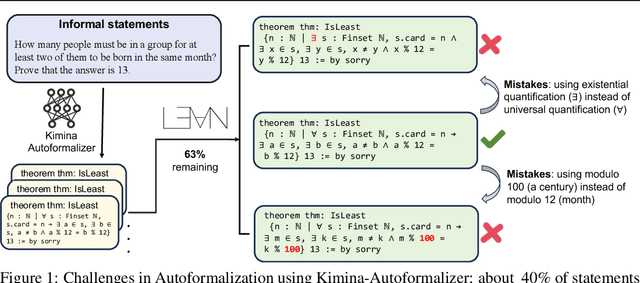
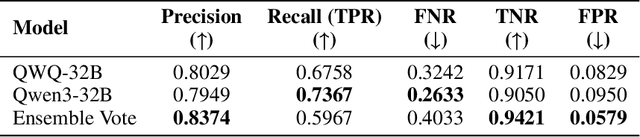
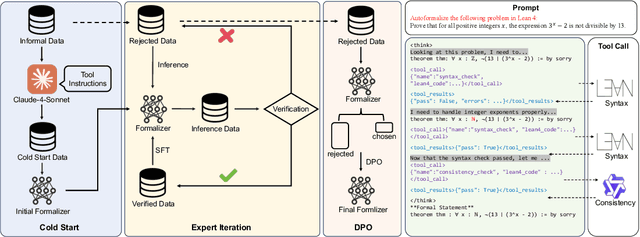
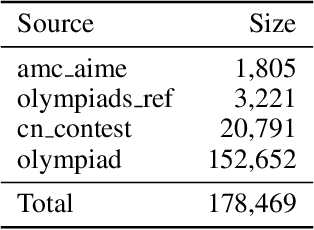
Abstract:Autoformalization addresses the scarcity of data for Automated Theorem Proving (ATP) by translating mathematical problems from natural language into formal statements. Efforts in recent work shift from directly prompting large language models to training an end-to-end formalizer model from scratch, achieving remarkable advancements. However, existing formalizer still struggles to consistently generate valid statements that meet syntactic validity and semantic consistency. To address this issue, we propose the Autoformalizer with Tool Feedback (ATF), a novel approach that incorporates syntactic and consistency information as tools into the formalization process. By integrating Lean 4 compilers for syntax corrections and employing a multi-LLMs-as-judge approach for consistency validation, the model is able to adaptively refine generated statements according to the tool feedback, enhancing both syntactic validity and semantic consistency. The training of ATF involves a cold-start phase on synthetic tool-calling data, an expert iteration phase to improve formalization capabilities, and Direct Preference Optimization to alleviate ineffective revisions. Experimental results show that ATF markedly outperforms a range of baseline formalizer models, with its superior performance further validated by human evaluations. Subsequent analysis reveals that ATF demonstrates excellent inference scaling properties. Moreover, we open-source Numina-ATF, a dataset containing 750K synthetic formal statements to facilitate advancements in autoformalization and ATP research.
Selecting Demonstrations for Many-Shot In-Context Learning via Gradient Matching
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:In-Context Learning (ICL) empowers Large Language Models (LLMs) for rapid task adaptation without Fine-Tuning (FT), but its reliance on demonstration selection remains a critical challenge. While many-shot ICL shows promising performance through scaled demonstrations, the selection method for many-shot demonstrations remains limited to random selection in existing work. Since the conventional instance-level retrieval is not suitable for many-shot scenarios, we hypothesize that the data requirements for in-context learning and fine-tuning are analogous. To this end, we introduce a novel gradient matching approach that selects demonstrations by aligning fine-tuning gradients between the entire training set of the target task and the selected examples, so as to approach the learning effect on the entire training set within the selected examples. Through gradient matching on relatively small models, e.g., Qwen2.5-3B or Llama3-8B, our method consistently outperforms random selection on larger LLMs from 4-shot to 128-shot scenarios across 9 diverse datasets. For instance, it surpasses random selection by 4% on Qwen2.5-72B and Llama3-70B, and by around 2% on 5 closed-source LLMs. This work unlocks more reliable and effective many-shot ICL, paving the way for its broader application.
Survival Analysis with Machine Learning for Predicting Li-ion Battery Remaining Useful Life
Mar 21, 2025



Abstract:The accurate prediction of RUL for lithium-ion batteries is crucial for enhancing the reliability and longevity of energy storage systems. Traditional methods for RUL prediction often struggle with issues such as data sparsity, varying battery chemistries, and the inability to capture complex degradation patterns over time. In this study, we propose a survival analysis-based framework combined with deep learning models to predict the RUL of lithium-ion batteries. Specifically, we utilize five advanced models: the Cox-type models (Cox, CoxPH, and CoxTime) and two machine-learning-based models (DeepHit and MTLR). These models address the challenges of accurate RUL estimation by transforming raw time-series battery data into survival data, including key degradation indicators such as voltage, current, and internal resistance. Advanced feature extraction techniques enhance the model's robustness in diverse real-world scenarios, including varying charging conditions and battery chemistries. Our models are tested using 10-fold cross-validation, ensuring generalizability and minimizing overfitting. Experimental results show that our survival-based framework significantly improves RUL prediction accuracy compared to traditional methods, providing a reliable tool for battery management and maintenance optimization. This study contributes to the advancement of predictive maintenance in battery technology, offering valuable insights for both researchers and industry practitioners aiming to enhance the operational lifespan of lithium-ion batteries.
Cohort-attention Evaluation Metric against Tied Data: Studying Performance of Classification Models in Cancer Detection
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly improved medical screening accuracy, particularly in cancer detection and risk assessment. However, traditional classification metrics often fail to account for imbalanced data, varying performance across cohorts, and patient-level inconsistencies, leading to biased evaluations. We propose the Cohort-Attention Evaluation Metrics (CAT) framework to address these challenges. CAT introduces patient-level assessment, entropy-based distribution weighting, and cohort-weighted sensitivity and specificity. Key metrics like CATSensitivity (CATSen), CATSpecificity (CATSpe), and CATMean ensure balanced and fair evaluation across diverse populations. This approach enhances predictive reliability, fairness, and interpretability, providing a robust evaluation method for AI-driven medical screening models.
3D Gaussian Splatting against Moving Objects for High-Fidelity Street Scene Reconstruction
Mar 15, 2025



Abstract:The accurate reconstruction of dynamic street scenes is critical for applications in autonomous driving, augmented reality, and virtual reality. Traditional methods relying on dense point clouds and triangular meshes struggle with moving objects, occlusions, and real-time processing constraints, limiting their effectiveness in complex urban environments. While multi-view stereo and neural radiance fields have advanced 3D reconstruction, they face challenges in computational efficiency and handling scene dynamics. This paper proposes a novel 3D Gaussian point distribution method for dynamic street scene reconstruction. Our approach introduces an adaptive transparency mechanism that eliminates moving objects while preserving high-fidelity static scene details. Additionally, iterative refinement of Gaussian point distribution enhances geometric accuracy and texture representation. We integrate directional encoding with spatial position optimization to optimize storage and rendering efficiency, reducing redundancy while maintaining scene integrity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves high reconstruction quality, improved rendering performance, and adaptability in large-scale dynamic environments. These contributions establish a robust framework for real-time, high-precision 3D reconstruction, advancing the practicality of dynamic scene modeling across multiple applications. The source code for this work is available to the public at https://github.com/deepcoxcom/3dgs
AAKT: Enhancing Knowledge Tracing with Alternate Autoregressive Modeling
Feb 17, 2025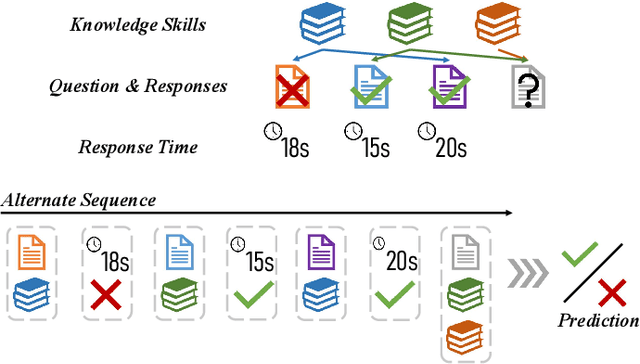
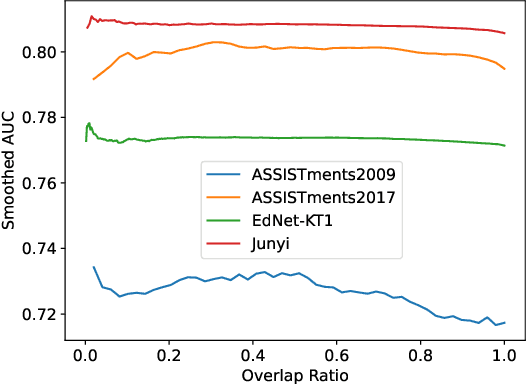
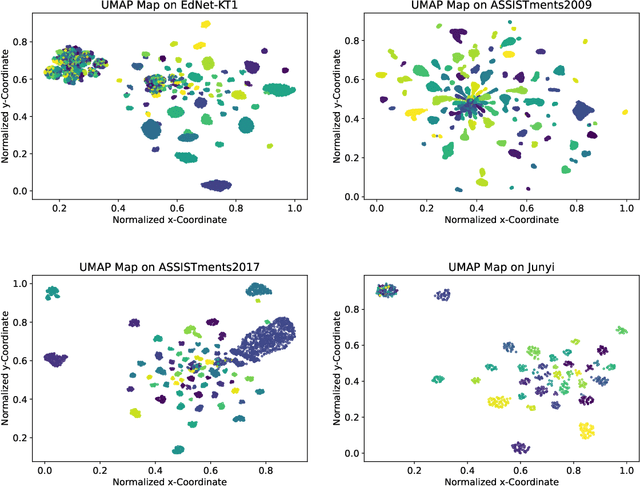
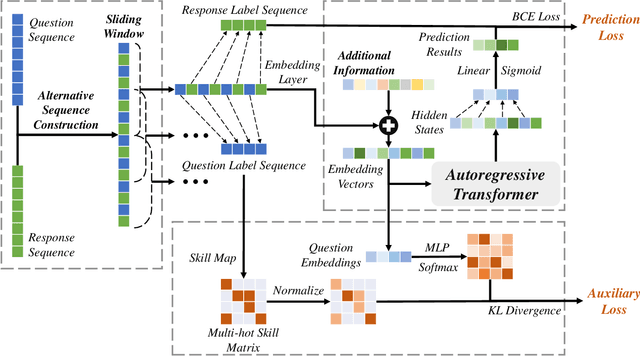
Abstract:Knowledge Tracing (KT) aims to predict students' future performances based on their former exercises and additional information in educational settings. KT has received significant attention since it facilitates personalized experiences in educational situations. Simultaneously, the autoregressive modeling on the sequence of former exercises has been proven effective for this task. One of the primary challenges in autoregressive modeling for Knowledge Tracing is effectively representing the anterior (pre-response) and posterior (post-response) states of learners across exercises. Existing methods often employ complex model architectures to update learner states using question and response records. In this study, we propose a novel perspective on knowledge tracing task by treating it as a generative process, consistent with the principles of autoregressive models. We demonstrate that knowledge states can be directly represented through autoregressive encodings on a question-response alternate sequence, where model generate the most probable representation in hidden state space by analyzing history interactions. This approach underpins our framework, termed Alternate Autoregressive Knowledge Tracing (AAKT). Additionally, we incorporate supplementary educational information, such as question-related skills, into our framework through an auxiliary task, and include extra exercise details, like response time, as additional inputs. Our proposed framework is implemented using advanced autoregressive technologies from Natural Language Generation (NLG) for both training and prediction. Empirical evaluations on four real-world KT datasets indicate that AAKT consistently outperforms all baseline models in terms of AUC, ACC, and RMSE. Furthermore, extensive ablation studies and visualized analysis validate the effectiveness of key components in AAKT.
Disentangling Preference Representation and Text Generation for Efficient Individual Preference Alignment
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:Aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with general human preferences has been proved crucial in improving the interaction quality between LLMs and human. However, human values are inherently diverse among different individuals, making it insufficient to align LLMs solely with general preferences. To address this, personalizing LLMs according to individual feedback emerges as a promising solution. Nonetheless, this approach presents challenges in terms of the efficiency of alignment algorithms. In this work, we introduce a flexible paradigm for individual preference alignment. Our method fundamentally improves efficiency by disentangling preference representation from text generation in LLMs. We validate our approach across multiple text generation tasks and demonstrate that it can produce aligned quality as well as or better than PEFT-based methods, while reducing additional training time for each new individual preference by $80\%$ to $90\%$ in comparison with them.
Leveraging Estimated Transferability Over Human Intuition for Model Selection in Text Ranking
Sep 24, 2024


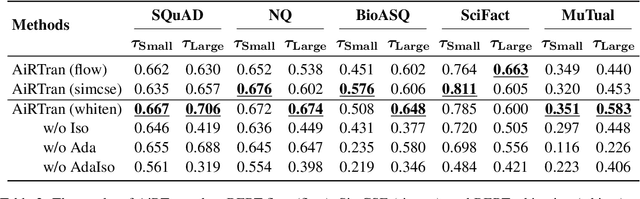
Abstract:Text ranking has witnessed significant advancements, attributed to the utilization of dual-encoder enhanced by Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs). Given the proliferation of available PLMs, selecting the most effective one for a given dataset has become a non-trivial challenge. As a promising alternative to human intuition and brute-force fine-tuning, Transferability Estimation (TE) has emerged as an effective approach to model selection. However, current TE methods are primarily designed for classification tasks, and their estimated transferability may not align well with the objectives of text ranking. To address this challenge, we propose to compute the expected rank as transferability, explicitly reflecting the model's ranking capability. Furthermore, to mitigate anisotropy and incorporate training dynamics, we adaptively scale isotropic sentence embeddings to yield an accurate expected rank score. Our resulting method, Adaptive Ranking Transferability (AiRTran), can effectively capture subtle differences between models. On challenging model selection scenarios across various text ranking datasets, it demonstrates significant improvements over previous classification-oriented TE methods, human intuition, and ChatGPT with minor time consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge