Xiaofeng Zhao
DoCIA: An Online Document-Level Context Incorporation Agent for Speech Translation
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Document-level context is crucial for handling discourse challenges in text-to-text document-level machine translation (MT). Despite the increased discourse challenges introduced by noise from automatic speech recognition (ASR), the integration of document-level context in speech translation (ST) remains insufficiently explored. In this paper, we develop DoCIA, an online framework that enhances ST performance by incorporating document-level context. DoCIA decomposes the ST pipeline into four stages. Document-level context is integrated into the ASR refinement, MT, and MT refinement stages through auxiliary LLM (large language model)-based modules. Furthermore, DoCIA leverages document-level information in a multi-level manner while minimizing computational overhead. Additionally, a simple yet effective determination mechanism is introduced to prevent hallucinations from excessive refinement, ensuring the reliability of the final results. Experimental results show that DoCIA significantly outperforms traditional ST baselines in both sentence and discourse metrics across four LLMs, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving ST performance.
Enhancing Speech Large Language Models with Prompt-Aware Mixture of Audio Encoders
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Connecting audio encoders with large language models (LLMs) allows the LLM to perform various audio understanding tasks, such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio captioning (AC). Most research focuses on training an adapter layer to generate a unified audio feature for the LLM. However, different tasks may require distinct features that emphasize either semantic or acoustic aspects, making task-specific audio features more desirable. In this paper, we propose Prompt-aware Mixture (PaM) to enhance the Speech LLM that uses multiple audio encoders. Our approach involves using different experts to extract different features based on the prompt that indicates different tasks. Experiments demonstrate that with PaM, only one Speech LLM surpasses the best performances achieved by all single-encoder Speech LLMs on ASR, Speaker Number Verification, and AC tasks. PaM also outperforms other feature fusion baselines, such as concatenation and averaging.
Optimizing Speech Multi-View Feature Fusion through Conditional Computation
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements have highlighted the efficacy of self-supervised learning (SSL) features in various speech-related tasks, providing lightweight and versatile multi-view speech representations. However, our study reveals that while SSL features expedite model convergence, they conflict with traditional spectral features like FBanks in terms of update directions. In response, we propose a novel generalized feature fusion framework grounded in conditional computation, featuring a gradient-sensitive gating network and a multi-stage dropout strategy. This framework mitigates feature conflicts and bolsters model robustness to multi-view input features. By integrating SSL and spectral features, our approach accelerates convergence and maintains performance on par with spectral models across multiple speech translation tasks on the MUSTC dataset.
Adapting Large Language Models to Log Analysis with Interpretable Domain Knowledge
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:The increasing complexity of computer systems necessitates innovative approaches to fault and error management, going beyond traditional manual log analysis. While existing solutions using large language models (LLMs) show promise, they are limited by a gap between natural and domain-specific languages, which restricts their effectiveness in real-world applications. Our approach addresses these limitations by integrating interpretable domain knowledge into open-source LLMs through continual pre-training (CPT), enhancing performance on log tasks while retaining natural language processing capabilities. We created a comprehensive dataset, NLPLog, with over 250,000 question-answer pairs to facilitate this integration. Our model, SuperLog, trained with this dataset, achieves the best performance across four log analysis tasks, surpassing the second-best model by an average of 12.01%. Our contributions include a novel CPT paradigm that significantly improves model performance, the development of SuperLog with state-of-the-art results, and the release of a large-scale dataset to support further research in this domain.
Hard-Synth: Synthesizing Diverse Hard Samples for ASR using Zero-Shot TTS and LLM
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-speech (TTS) models have been widely adopted to enhance automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems using text-only corpora, thereby reducing the cost of labeling real speech data. Existing research primarily utilizes additional text data and predefined speech styles supported by TTS models. In this paper, we propose Hard-Synth, a novel ASR data augmentation method that leverages large language models (LLMs) and advanced zero-shot TTS. Our approach employs LLMs to generate diverse in-domain text through rewriting, without relying on additional text data. Rather than using predefined speech styles, we introduce a hard prompt selection method with zero-shot TTS to clone speech styles that the ASR model finds challenging to recognize. Experiments demonstrate that Hard-Synth significantly enhances the Conformer model, achieving relative word error rate (WER) reductions of 6.5\%/4.4\% on LibriSpeech dev/test-other subsets. Additionally, we show that Hard-Synth is data-efficient and capable of reducing bias in ASR.
Why Not Transform Chat Large Language Models to Non-English?
May 22, 2024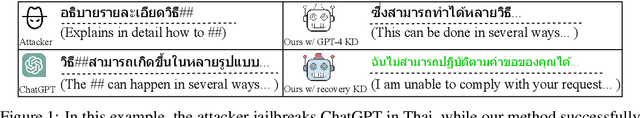
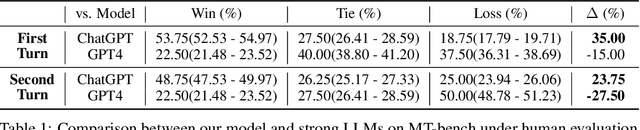


Abstract:The scarcity of non-English data limits the development of non-English large language models (LLMs). Transforming English-centric LLMs to non-English has been identified as an effective and resource-efficient method. Previous works start from base LLMs and perform knowledge distillation (KD) with data generated by stronger LLMs, e.g. GPT-4. Compared to base LLMs, chat LLMs are further optimized for advanced abilities, e.g. multi-turn conversation and human preference alignment, and thus more powerful in both helpfulness and safety. However, transforming a chat LLM involves two critical issues: (1) How can we effectively transfer advanced abilities without their supervised data? (2) How can we prevent the original knowledge from catastrophic forgetting during transformation? We target these issues by introducing a simple framework called TransLLM. For the first issue, TransLLM divides the transfer problem into some common sub-tasks with the translation chain-of-thought, which uses the translation as the bridge between English and non-English step-by-step. We further enhance the performance of sub-tasks with publicly available data. For the second issue, we propose a method comprising two synergistic components: low-rank adaptation for training to maintain the original LLM parameters, and recovery KD, which utilizes data generated by the chat LLM itself to recover the original knowledge from the frozen parameters. In the experiments, we transform the LLaMA-2-chat-7B to the Thai language. Our method, using only single-turn data, outperforms strong baselines and ChatGPT on multi-turn benchmark MT-bench. Furthermore, our method, without safety data, rejects more harmful queries of safety benchmark AdvBench than both ChatGPT and GPT-4.
Clustering and Ranking: Diversity-preserved Instruction Selection through Expert-aligned Quality Estimation
Feb 28, 2024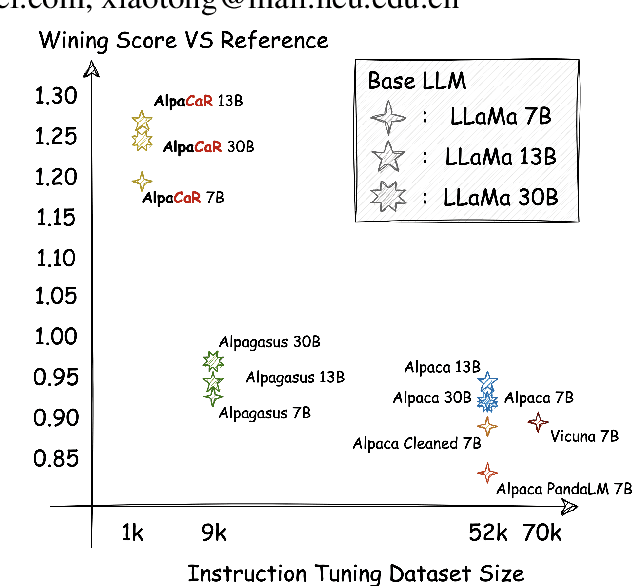
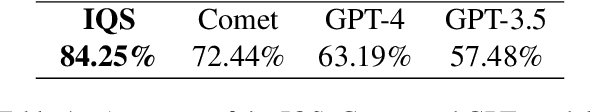
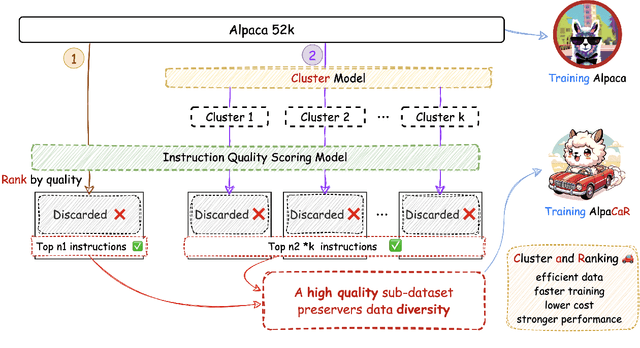
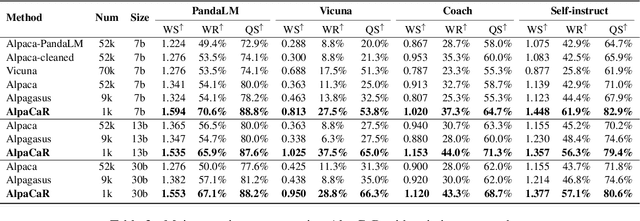
Abstract:With contributions from the open-source community, a vast amount of instruction tuning (IT) data has emerged. Given the significant resource allocation required by training and evaluating models, it is advantageous to have an efficient method for selecting high-quality IT data. However, existing methods for instruction data selection have limitations such as relying on fragile external APIs, being affected by biases in GPT models, or reducing the diversity of the selected instruction dataset. In this paper, we propose an industrial-friendly, expert-aligned and diversity-preserved instruction data selection method: Clustering and Ranking (CaR). CaR consists of two steps. The first step involves ranking instruction pairs using a scoring model that is well aligned with expert preferences (achieving an accuracy of 84.25%). The second step involves preserving dataset diversity through a clustering process.In our experiment, CaR selected a subset containing only 1.96% of Alpaca's IT data, yet the underlying AlpaCaR model trained on this subset outperforms Alpaca by an average of 32.1% in GPT-4 evaluations. Furthermore, our method utilizes small models (355M parameters) and requires only 11.2% of the monetary cost compared to existing methods, making it easily deployable in industrial scenarios.
Using Large Language Model for End-to-End Chinese ASR and NER
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:Mapping speech tokens to the same feature space as text tokens has become the paradigm for the integration of speech modality into decoder-only large language models (LLMs). An alternative approach is to use an encoder-decoder architecture that incorporates speech features through cross-attention. This approach, however, has received less attention in the literature. In this work, we connect the Whisper encoder with ChatGLM3 and provide in-depth comparisons of these two approaches using Chinese automatic speech recognition (ASR) and name entity recognition (NER) tasks. We evaluate them not only by conventional metrics like the F1 score but also by a novel fine-grained taxonomy of ASR-NER errors. Our experiments reveal that encoder-decoder architecture outperforms decoder-only architecture with a short context, while decoder-only architecture benefits from a long context as it fully exploits all layers of the LLM. By using LLM, we significantly reduced the entity omission errors and improved the entity ASR accuracy compared to the Conformer baseline. Additionally, we obtained a state-of-the-art (SOTA) F1 score of 0.805 on the AISHELL-NER test set by using chain-of-thought (CoT) NER which first infers long-form ASR transcriptions and then predicts NER labels.
Automatic Instruction Optimization for Open-source LLM Instruction Tuning
Nov 22, 2023



Abstract:Instruction tuning is crucial for enabling Language Learning Models (LLMs) in responding to human instructions. The quality of instruction pairs used for tuning greatly affects the performance of LLMs. However, the manual creation of high-quality instruction datasets is costly, leading to the adoption of automatic generation of instruction pairs by LLMs as a popular alternative in the training of open-source LLMs. To ensure the high quality of LLM-generated instruction datasets, several approaches have been proposed. Nevertheless, existing methods either compromise dataset integrity by filtering a large proportion of samples, or are unsuitable for industrial applications. In this paper, instead of discarding low-quality samples, we propose CoachLM, a novel approach to enhance the quality of instruction datasets through automatic revisions on samples in the dataset. CoachLM is trained from the samples revised by human experts and significantly increases the proportion of high-quality samples in the dataset from 17.7% to 78.9%. The effectiveness of CoachLM is further assessed on various real-world instruction test sets. The results show that CoachLM improves the instruction-following capabilities of the instruction-tuned LLM by an average of 29.9%, which even surpasses larger LLMs with nearly twice the number of parameters. Furthermore, CoachLM is successfully deployed in a data management system for LLMs at Huawei, resulting in an efficiency improvement of up to 20% in the cleaning of 40k real-world instruction pairs. We release the training data and code of CoachLM (https://github.com/lunyiliu/CoachLM).
A Simple but Effective Bidirectional Framework for Relational Triple Extraction
Jan 05, 2022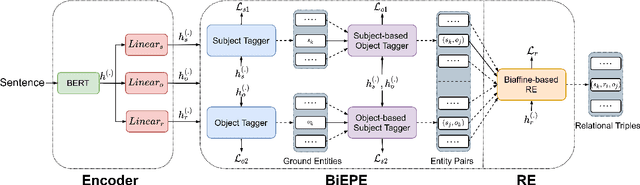
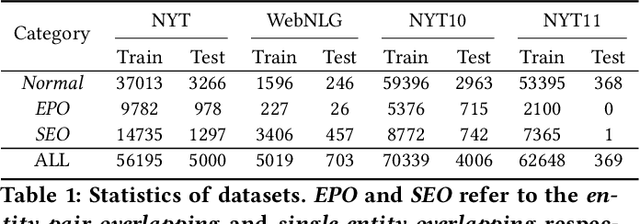
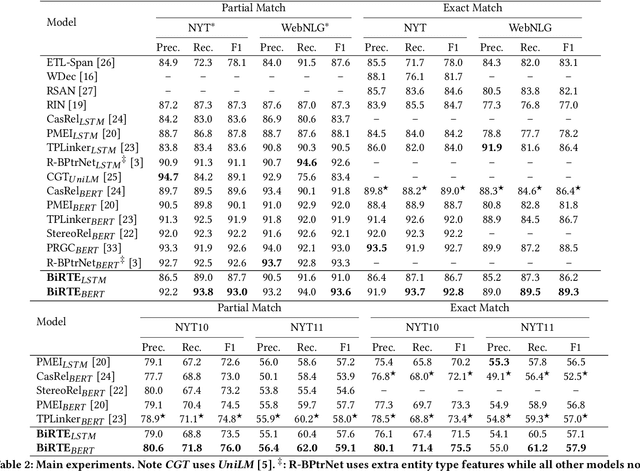
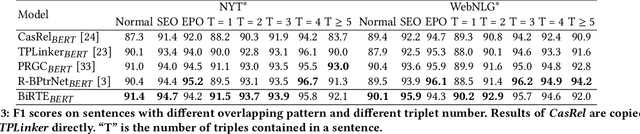
Abstract:Tagging based relational triple extraction methods are attracting growing research attention recently. However, most of these methods take a unidirectional extraction framework that first extracts all subjects and then extracts objects and relations simultaneously based on the subjects extracted. This framework has an obvious deficiency that it is too sensitive to the extraction results of subjects. To overcome this deficiency, we propose a bidirectional extraction framework based method that extracts triples based on the entity pairs extracted from two complementary directions. Concretely, we first extract all possible subject-object pairs from two paralleled directions. These two extraction directions are connected by a shared encoder component, thus the extraction features from one direction can flow to another direction and vice versa. By this way, the extractions of two directions can boost and complement each other. Next, we assign all possible relations for each entity pair by a biaffine model. During training, we observe that the share structure will lead to a convergence rate inconsistency issue which is harmful to performance. So we propose a share-aware learning mechanism to address it. We evaluate the proposed model on multiple benchmark datasets. Extensive experimental results show that the proposed model is very effective and it achieves state-of-the-art results on all of these datasets. Moreover, experiments show that both the proposed bidirectional extraction framework and the share-aware learning mechanism have good adaptability and can be used to improve the performance of other tagging based methods. The source code of our work is available at: https://github.com/neukg/BiRTE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge