Shilei Liu
Read As Human: Compressing Context via Parallelizable Close Reading and Skimming
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional capability across diverse tasks. However, their deployment in long-context scenarios is hindered by two challenges: computational inefficiency and redundant information. We propose RAM (Read As HuMan), a context compression framework that adopts an adaptive hybrid reading strategy, to address these challenges. Inspired by human reading behavior (i.e., close reading important content while skimming less relevant content), RAM partitions the context into segments and encodes them with the input query in parallel. High-relevance segments are fully retained (close reading), while low-relevance ones are query-guided compressed into compact summary vectors (skimming). Both explicit textual segments and implicit summary vectors are concatenated and fed into decoder to achieve both superior performance and natural language format interpretability. To refine the decision boundary between close reading and skimming, we further introduce a contrastive learning objective based on positive and negative query-segment pairs. Experiments demonstrate that RAM outperforms existing baselines on multiple question answering and summarization benchmarks across two backbones, while delivering up to a 12x end-to-end speedup on long inputs (average length 16K; maximum length 32K).
COMI: Coarse-to-fine Context Compression via Marginal Information Gain
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities across diverse tasks. However, their deployment in long context scenarios remains hindered by computational inefficiency and information redundancy. Context compression methods address these challenges by significantly reducing input length and eliminating redundancy. We propose COMI, a coarse-to-fine adaptive context compression framework that jointly optimizes for semantic relevance and diversity under high compression rates. We introduce Marginal Information Gain (MIG), a metric defined as the relevance of a unit to the input query minus its semantic redundancy with other units, guiding the compression process to prioritize information that is both relevant and low redundant. The framework operates in two stages: (1) Coarse-Grained Group Reallocation, where the context is partitioned into groups and dynamically assigned compression rates based on inter-group MIG, ensuring compression budgets align with information value distribution; and (2) Fine-Grained Token Merging, where tokens within each group are fused via an intra-group MIG-based weighting mechanism, thereby preserving key semantics while avoiding the accumulation of redundancy. Extensive experiments across question-answering (e.g., NaturalQuestions, 2WikiMQA, HotpotQA and NarrativeQA), summarization (e.g., MultiNews) with various backbones (e.g., LLaMA-2-7B, Qwen2-7B) show that COMI outperforms existing baselines by a large margin, e.g., approximately 25-point Exact Match (EM) improvement under 32x compression constraint with Qwen2-7B on NaturalQuestions.
PretrainRL: Alleviating Factuality Hallucination of Large Language Models at the Beginning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), despite their powerful capabilities, suffer from factual hallucinations where they generate verifiable falsehoods. We identify a root of this issue: the imbalanced data distribution in the pretraining corpus, which leads to a state of "low-probability truth" and "high-probability falsehood". Recent approaches, such as teaching models to say "I don't know" or post-hoc knowledge editing, either evade the problem or face catastrophic forgetting. To address this issue from its root, we propose \textbf{PretrainRL}, a novel framework that integrates reinforcement learning into the pretraining phase to consolidate factual knowledge. The core principle of PretrainRL is "\textbf{debiasing then learning}." It actively reshapes the model's probability distribution by down-weighting high-probability falsehoods, thereby making "room" for low-probability truths to be learned effectively. To enable this, we design an efficient negative sampling strategy to discover these high-probability falsehoods and introduce novel metrics to evaluate the model's probabilistic state concerning factual knowledge. Extensive experiments on three public benchmarks demonstrate that PretrainRL significantly alleviates factual hallucinations and outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Data Distribution Matters: A Data-Centric Perspective on Context Compression for Large Language Model
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in long-context scenarios is hindered by computational inefficiency and significant information redundancy. Although recent advancements have widely adopted context compression to address these challenges, existing research only focus on model-side improvements, the impact of the data distribution itself on context compression remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we are the first to adopt a data-centric perspective to systematically investigate how data distribution impacts compression quality, including two dimensions: input data and intrinsic data (i.e., the model's internal pretrained knowledge). We evaluate the semantic integrity of compressed representations using an autoencoder-based framework to systematically investigate it. Our experimental results reveal that: (1) encoder-measured input entropy negatively correlates with compression quality, while decoder-measured entropy shows no significant relationship under a frozen-decoder setting; and (2) the gap between intrinsic data of the encoder and decoder significantly diminishes compression gains, which is hard to mitigate. Based on these findings, we further present practical guidelines to optimize compression gains.
CoMeT: Collaborative Memory Transformer for Efficient Long Context Modeling
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The quadratic complexity and indefinitely growing key-value (KV) cache of standard Transformers pose a major barrier to long-context processing. To overcome this, we introduce the Collaborative Memory Transformer (CoMeT), a novel architecture that enables LLMs to handle arbitrarily long sequences with constant memory usage and linear time complexity. Designed as an efficient, plug-in module, CoMeT can be integrated into pre-trained models with only minimal fine-tuning. It operates on sequential data chunks, using a dual-memory system to manage context: a temporary memory on a FIFO queue for recent events, and a global memory with a gated update rule for long-range dependencies. These memories then act as a dynamic soft prompt for the next chunk. To enable efficient fine-tuning on extremely long contexts, we introduce a novel layer-level pipeline parallelism strategy. The effectiveness of our approach is remarkable: a model equipped with CoMeT and fine-tuned on 32k contexts can accurately retrieve a passkey from any position within a 1M token sequence. On the SCROLLS benchmark, CoMeT surpasses other efficient methods and achieves performance comparable to a full-attention baseline on summarization tasks. Its practical effectiveness is further validated on real-world agent and user behavior QA tasks. The code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/comet-B00B/
ECKGBench: Benchmarking Large Language Models in E-commerce Leveraging Knowledge Graph
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated their capabilities across various NLP tasks. Their potential in e-commerce is also substantial, evidenced by practical implementations such as platform search, personalized recommendations, and customer service. One primary concern associated with LLMs is their factuality (e.g., hallucination), which is urgent in e-commerce due to its significant impact on user experience and revenue. Despite some methods proposed to evaluate LLMs' factuality, issues such as lack of reliability, high consumption, and lack of domain expertise leave a gap between effective assessment in e-commerce. To bridge the evaluation gap, we propose ECKGBench, a dataset specifically designed to evaluate the capacities of LLMs in e-commerce knowledge. Specifically, we adopt a standardized workflow to automatically generate questions based on a large-scale knowledge graph, guaranteeing sufficient reliability. We employ the simple question-answering paradigm, substantially improving the evaluation efficiency by the least input and output tokens. Furthermore, we inject abundant e-commerce expertise in each evaluation stage, including human annotation, prompt design, negative sampling, and verification. Besides, we explore the LLMs' knowledge boundaries in e-commerce from a novel perspective. Through comprehensive evaluations of several advanced LLMs on ECKGBench, we provide meticulous analysis and insights into leveraging LLMs for e-commerce.
ChineseEcomQA: A Scalable E-commerce Concept Evaluation Benchmark for Large Language Models
Feb 27, 2025
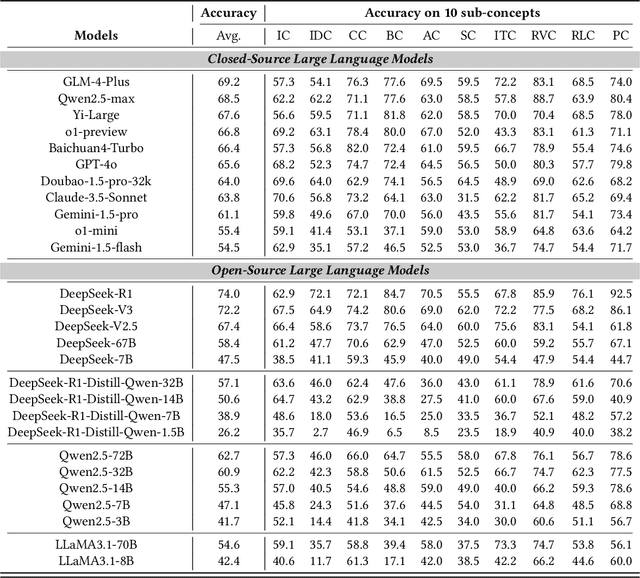
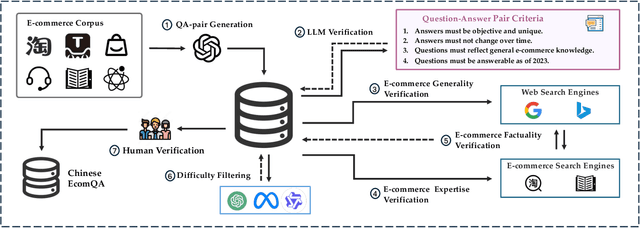
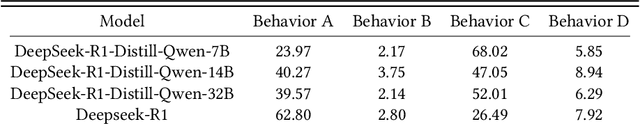
Abstract:With the increasing use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in fields such as e-commerce, domain-specific concept evaluation benchmarks are crucial for assessing their domain capabilities. Existing LLMs may generate factually incorrect information within the complex e-commerce applications. Therefore, it is necessary to build an e-commerce concept benchmark. Existing benchmarks encounter two primary challenges: (1) handle the heterogeneous and diverse nature of tasks, (2) distinguish between generality and specificity within the e-commerce field. To address these problems, we propose \textbf{ChineseEcomQA}, a scalable question-answering benchmark focused on fundamental e-commerce concepts. ChineseEcomQA is built on three core characteristics: \textbf{Focus on Fundamental Concept}, \textbf{E-commerce Generality} and \textbf{E-commerce Expertise}. Fundamental concepts are designed to be applicable across a diverse array of e-commerce tasks, thus addressing the challenge of heterogeneity and diversity. Additionally, by carefully balancing generality and specificity, ChineseEcomQA effectively differentiates between broad e-commerce concepts, allowing for precise validation of domain capabilities. We achieve this through a scalable benchmark construction process that combines LLM validation, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) validation, and rigorous manual annotation. Based on ChineseEcomQA, we conduct extensive evaluations on mainstream LLMs and provide some valuable insights. We hope that ChineseEcomQA could guide future domain-specific evaluations, and facilitate broader LLM adoption in e-commerce applications.
UQABench: Evaluating User Embedding for Prompting LLMs in Personalized Question Answering
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve remarkable success in natural language processing (NLP). In practical scenarios like recommendations, as users increasingly seek personalized experiences, it becomes crucial to incorporate user interaction history into the context of LLMs to enhance personalization. However, from a practical utility perspective, user interactions' extensive length and noise present challenges when used directly as text prompts. A promising solution is to compress and distill interactions into compact embeddings, serving as soft prompts to assist LLMs in generating personalized responses. Although this approach brings efficiency, a critical concern emerges: Can user embeddings adequately capture valuable information and prompt LLMs? To address this concern, we propose \name, a benchmark designed to evaluate the effectiveness of user embeddings in prompting LLMs for personalization. We establish a fair and standardized evaluation process, encompassing pre-training, fine-tuning, and evaluation stages. To thoroughly evaluate user embeddings, we design three dimensions of tasks: sequence understanding, action prediction, and interest perception. These evaluation tasks cover the industry's demands in traditional recommendation tasks, such as improving prediction accuracy, and its aspirations for LLM-based methods, such as accurately understanding user interests and enhancing the user experience. We conduct extensive experiments on various state-of-the-art methods for modeling user embeddings. Additionally, we reveal the scaling laws of leveraging user embeddings to prompt LLMs. The benchmark is available online.
Unlocking Scaling Law in Industrial Recommendation Systems with a Three-step Paradigm based Large User Model
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in autoregressive Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved significant milestones, largely attributed to their scalability, often referred to as the "scaling law". Inspired by these achievements, there has been a growing interest in adapting LLMs for Recommendation Systems (RecSys) by reformulating RecSys tasks into generative problems. However, these End-to-End Generative Recommendation (E2E-GR) methods tend to prioritize idealized goals, often at the expense of the practical advantages offered by traditional Deep Learning based Recommendation Models (DLRMs) in terms of in features, architecture, and practices. This disparity between idealized goals and practical needs introduces several challenges and limitations, locking the scaling law in industrial RecSys. In this paper, we introduce a large user model (LUM) that addresses these limitations through a three-step paradigm, designed to meet the stringent requirements of industrial settings while unlocking the potential for scalable recommendations. Our extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that LUM outperforms both state-of-the-art DLRMs and E2E-GR approaches. Notably, LUM exhibits excellent scalability, with performance improvements observed as the model scales up to 7 billion parameters. Additionally, we have successfully deployed LUM in an industrial application, where it achieved significant gains in an A/B test, further validating its effectiveness and practicality.
Advancements in 3D Lane Detection Using LiDAR Point Clouds: From Data Collection to Model Development
Sep 24, 2023



Abstract:Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) have successfully integrated learning-based techniques into vehicle perception and decision-making. However, their application in 3D lane detection for effective driving environment perception is hindered by the lack of comprehensive LiDAR datasets. The sparse nature of LiDAR point cloud data prevents an efficient manual annotation process. To solve this problem, we present LiSV-3DLane, a large-scale 3D lane dataset that comprises 20k frames of surround-view LiDAR point clouds with enriched semantic annotation. Unlike existing datasets confined to a frontal perspective, LiSV-3DLane provides a full 360-degree spatial panorama around the ego vehicle, capturing complex lane patterns in both urban and highway environments. We leverage the geometric traits of lane lines and the intrinsic spatial attributes of LiDAR data to design a simple yet effective automatic annotation pipeline for generating finer lane labels. To propel future research, we propose a novel LiDAR-based 3D lane detection model, LiLaDet, incorporating the spatial geometry learning of the LiDAR point cloud into Bird's Eye View (BEV) based lane identification. Experimental results indicate that LiLaDet outperforms existing camera- and LiDAR-based approaches in the 3D lane detection task on the K-Lane dataset and our LiSV-3DLane.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge