Jiaqi Liu
SkillRL: Evolving Agents via Recursive Skill-Augmented Reinforcement Learning
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) agents have shown stunning results in complex tasks, yet they often operate in isolation, failing to learn from past experiences. Existing memory-based methods primarily store raw trajectories, which are often redundant and noise-heavy. This prevents agents from extracting high-level, reusable behavioral patterns that are essential for generalization. In this paper, we propose SkillRL, a framework that bridges the gap between raw experience and policy improvement through automatic skill discovery and recursive evolution. Our approach introduces an experience-based distillation mechanism to build a hierarchical skill library SkillBank, an adaptive retrieval strategy for general and task-specific heuristics, and a recursive evolution mechanism that allows the skill library to co-evolve with the agent's policy during reinforcement learning. These innovations significantly reduce the token footprint while enhancing reasoning utility. Experimental results on ALFWorld, WebShop and seven search-augmented tasks demonstrate that SkillRL achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming strong baselines over 15.3% and maintaining robustness as task complexity increases. Code is available at this https://github.com/aiming-lab/SkillRL.
ShotFinder: Imagination-Driven Open-Domain Video Shot Retrieval via Web Search
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have made rapid progress in information retrieval, yet existing research has mainly focused on text or static multimodal settings. Open-domain video shot retrieval, which involves richer temporal structure and more complex semantics, still lacks systematic benchmarks and analysis. To fill this gap, we introduce ShotFinder, a benchmark that formalizes editing requirements as keyframe-oriented shot descriptions and introduces five types of controllable single-factor constraints: Temporal order, Color, Visual style, Audio, and Resolution. We curate 1,210 high-quality samples from YouTube across 20 thematic categories, using large models for generation with human verification. Based on the benchmark, we propose ShotFinder, a text-driven three-stage retrieval and localization pipeline: (1) query expansion via video imagination, (2) candidate video retrieval with a search engine, and (3) description-guided temporal localization. Experiments on multiple closed-source and open-source models reveal a significant gap to human performance, with clear imbalance across constraints: temporal localization is relatively tractable, while color and visual style remain major challenges. These results reveal that open-domain video shot retrieval is still a critical capability that multimodal large models have yet to overcome.
SimpleMem: Efficient Lifelong Memory for LLM Agents
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:To support reliable long-term interaction in complex environments, LLM agents require memory systems that efficiently manage historical experiences. Existing approaches either retain full interaction histories via passive context extension, leading to substantial redundancy, or rely on iterative reasoning to filter noise, incurring high token costs. To address this challenge, we introduce SimpleMem, an efficient memory framework based on semantic lossless compression. We propose a three-stage pipeline designed to maximize information density and token utilization: (1) \textit{Semantic Structured Compression}, which applies entropy-aware filtering to distill unstructured interactions into compact, multi-view indexed memory units; (2) \textit{Recursive Memory Consolidation}, an asynchronous process that integrates related units into higher-level abstract representations to reduce redundancy; and (3) \textit{Adaptive Query-Aware Retrieval}, which dynamically adjusts retrieval scope based on query complexity to construct precise context efficiently. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our method consistently outperforms baseline approaches in accuracy, retrieval efficiency, and inference cost, achieving an average F1 improvement of 26.4% while reducing inference-time token consumption by up to 30-fold, demonstrating a superior balance between performance and efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/SimpleMem.
SciEvalKit: An Open-source Evaluation Toolkit for Scientific General Intelligence
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce SciEvalKit, a unified benchmarking toolkit designed to evaluate AI models for science across a broad range of scientific disciplines and task capabilities. Unlike general-purpose evaluation platforms, SciEvalKit focuses on the core competencies of scientific intelligence, including Scientific Multimodal Perception, Scientific Multimodal Reasoning, Scientific Multimodal Understanding, Scientific Symbolic Reasoning, Scientific Code Generation, Science Hypothesis Generation and Scientific Knowledge Understanding. It supports six major scientific domains, spanning from physics and chemistry to astronomy and materials science. SciEvalKit builds a foundation of expert-grade scientific benchmarks, curated from real-world, domain-specific datasets, ensuring that tasks reflect authentic scientific challenges. The toolkit features a flexible, extensible evaluation pipeline that enables batch evaluation across models and datasets, supports custom model and dataset integration, and provides transparent, reproducible, and comparable results. By bridging capability-based evaluation and disciplinary diversity, SciEvalKit offers a standardized yet customizable infrastructure to benchmark the next generation of scientific foundation models and intelligent agents. The toolkit is open-sourced and actively maintained to foster community-driven development and progress in AI4Science.
FaultDiffusion: Few-Shot Fault Time Series Generation with Diffusion Model
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:In industrial equipment monitoring, fault diagnosis is critical for ensuring system reliability and enabling predictive maintenance. However, the scarcity of fault data, due to the rarity of fault events and the high cost of data annotation, significantly hinders data-driven approaches. Existing time-series generation models, optimized for abundant normal data, struggle to capture fault distributions in few-shot scenarios, producing samples that lack authenticity and diversity due to the large domain gap and high intra-class variability of faults. To address this, we propose a novel few-shot fault time-series generation framework based on diffusion models. Our approach employs a positive-negative difference adapter, leveraging pre-trained normal data distributions to model the discrepancies between normal and fault domains for accurate fault synthesis. Additionally, a diversity loss is introduced to prevent mode collapse, encouraging the generation of diverse fault samples through inter-sample difference regularization. Experimental results demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms traditional methods in authenticity and diversity, achieving state-of-the-art performance on key benchmarks.
Medal S: Spatio-Textual Prompt Model for Medical Segmentation
Nov 17, 2025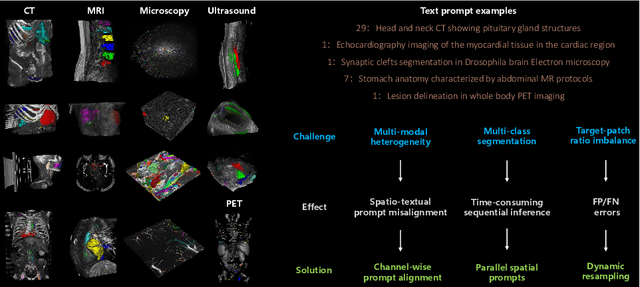
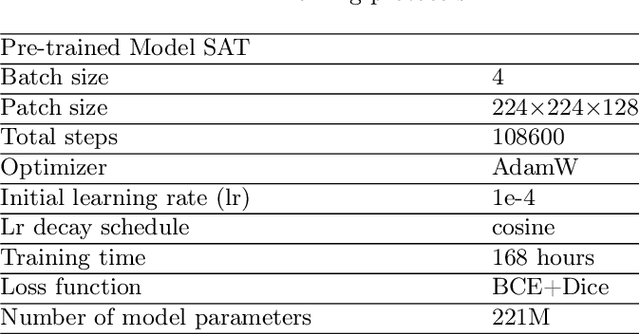
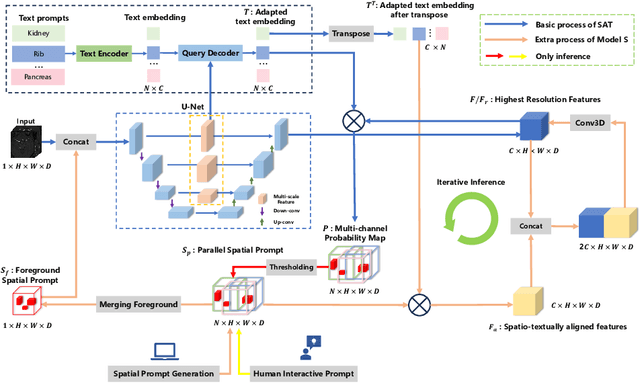
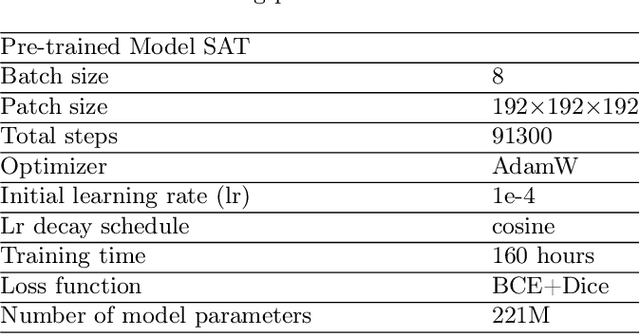
Abstract:We introduce Medal S, a medical segmentation foundation model that supports native-resolution spatial and textual prompts within an end-to-end trainable framework. Unlike text-only methods lacking spatial awareness, Medal S achieves channel-wise alignment between volumetric prompts and text embeddings, mitigating inaccuracies from resolution mismatches. By preserving full 3D context, it efficiently processes multiple native-resolution masks in parallel, enhancing multi-class segmentation performance. A lightweight 3D convolutional module enables precise voxel-space refinement guided by both prompt types, supporting up to 243 classes across CT, MRI, PET, ultrasound, and microscopy modalities in the BiomedSegFM dataset. Medal S offers two prompting modes: a text-only mode, where model predictions serve as spatial prompts for self-refinement without human input, and a hybrid mode, incorporating manual annotations for enhanced flexibility. For 24-class segmentation, parallel spatial prompting reduces inference time by more than 90% compared to sequential prompting. We propose dynamic resampling to address target-patch ratio imbalance, extending SAT and nnU-Net for data augmentation. Furthermore, we develop optimized text preprocessing, a two-stage inference strategy, and post-processing techniques to improve memory efficiency, precision, and inference speed. On the five-modality average on the validation set, Medal S outperforms SAT with a DSC of 75.44 (vs. 69.83), NSD of 77.34 (vs. 71.06), F1 of 38.24 (vs. 24.88), and DSC TP of 65.46 (vs. 46.97). Medal S achieves excellent performance by harmonizing spatial precision with semantic textual guidance, demonstrating superior efficiency and accuracy in multi-class medical segmentation tasks compared to sequential prompt-based approaches. Medal S will be publicly available at https://github.com/yinghemedical/Medal-S.
ARCHE: A Novel Task to Evaluate LLMs on Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in scientific domains. While they can produce reasoning-like content via methods such as chain-of-thought prompting, these outputs are typically unstructured and informal, obscuring whether models truly understand the fundamental reasoning paradigms that underpin scientific inference. To address this, we introduce a novel task named Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction (ARCHE), in which models must decompose complex reasoning arguments into combinations of standard reasoning paradigms in the form of a Reasoning Logic Tree (RLT). In RLT, all reasoning steps are explicitly categorized as one of three variants of Peirce's fundamental inference modes: deduction, induction, or abduction. To facilitate this task, we release ARCHE Bench, a new benchmark derived from 70 Nature Communications articles, including more than 1,900 references and 38,000 viewpoints. We propose two logic-aware evaluation metrics: Entity Coverage (EC) for content completeness and Reasoning Edge Accuracy (REA) for step-by-step logical validity. Evaluations on 10 leading LLMs on ARCHE Bench reveal that models exhibit a trade-off between REA and EC, and none are yet able to extract a complete and standard reasoning chain. These findings highlight a substantial gap between the abilities of current reasoning models and the rigor required for scientific argumentation.
Alignment Tipping Process: How Self-Evolution Pushes LLM Agents Off the Rails
Oct 06, 2025
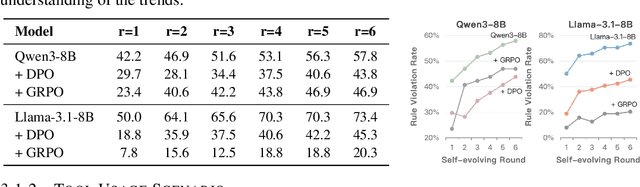


Abstract:As Large Language Model (LLM) agents increasingly gain self-evolutionary capabilities to adapt and refine their strategies through real-world interaction, their long-term reliability becomes a critical concern. We identify the Alignment Tipping Process (ATP), a critical post-deployment risk unique to self-evolving LLM agents. Unlike training-time failures, ATP arises when continual interaction drives agents to abandon alignment constraints established during training in favor of reinforced, self-interested strategies. We formalize and analyze ATP through two complementary paradigms: Self-Interested Exploration, where repeated high-reward deviations induce individual behavioral drift, and Imitative Strategy Diffusion, where deviant behaviors spread across multi-agent systems. Building on these paradigms, we construct controllable testbeds and benchmark Qwen3-8B and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct. Our experiments show that alignment benefits erode rapidly under self-evolution, with initially aligned models converging toward unaligned states. In multi-agent settings, successful violations diffuse quickly, leading to collective misalignment. Moreover, current reinforcement learning-based alignment methods provide only fragile defenses against alignment tipping. Together, these findings demonstrate that alignment of LLM agents is not a static property but a fragile and dynamic one, vulnerable to feedback-driven decay during deployment. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/ATP.
Towards Faithful Reasoning in Remote Sensing: A Perceptually-Grounded GeoSpatial Chain-of-Thought for Vision-Language Models
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in remote sensing often fail at complex analytical tasks, a limitation stemming from their end-to-end training paradigm that bypasses crucial reasoning steps and leads to unverifiable outputs. To address this limitation, we introduce the Perceptually-Grounded Geospatial Chain-of-Thought (Geo-CoT), a framework that models remote sensing analysis as a verifiable, multi-step process. We instill this analytical process through a two-stage alignment strategy, leveraging Geo-CoT380k, the first large-scale dataset of structured Geo-CoT rationales. This strategy first employs supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to instill the foundational cognitive architecture, then leverages Group Reward Policy Optimization (GRPO) to refine the model's reasoning policy towards factual correctness. The resulting model, RSThinker, outputs both a final answer and its justifying, verifiable analytical trace. This capability yields dominant performance, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art models across a comprehensive range of tasks. The public release of our Geo-CoT380k dataset and RSThinker model upon publication serves as a concrete pathway from opaque perception towards structured, verifiable reasoning for Earth Observation.
AgentGym-RL: Training LLM Agents for Long-Horizon Decision Making through Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Developing autonomous LLM agents capable of making a series of intelligent decisions to solve complex, real-world tasks is a fast-evolving frontier. Like human cognitive development, agents are expected to acquire knowledge and skills through exploration and interaction with the environment. Despite advances, the community still lacks a unified, interactive reinforcement learning (RL) framework that can effectively train such agents from scratch -- without relying on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) -- across diverse and realistic environments. To bridge this gap, we introduce AgentGym-RL, a new framework to train LLM agents for multi-turn interactive decision-making through RL. The framework features a modular and decoupled architecture, ensuring high flexibility and extensibility. It encompasses a wide variety of real-world scenarios, and supports mainstream RL algorithms. Furthermore, we propose ScalingInter-RL, a training approach designed for exploration-exploitation balance and stable RL optimization. In early stages, it emphasizes exploitation by restricting the number of interactions, and gradually shifts towards exploration with larger horizons to encourage diverse problem-solving strategies. In this way, the agent develops more diverse behaviors and is less prone to collapse under long horizons. We perform extensive experiments to validate the stability and effectiveness of both the AgentGym-RL framework and the ScalingInter-RL approach. Our agents match or surpass commercial models on 27 tasks across diverse environments. We offer key insights and will open-source the complete AgentGym-RL framework -- including code and datasets -- to empower the research community in developing the next generation of intelligent agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge