Yang Cao
Sherman
Beyond Fixed Rounds: Data-Free Early Stopping for Practical Federated Learning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) facilitates decentralized collaborative learning without transmitting raw data. However, reliance on fixed global rounds or validation data for hyperparameter tuning hinders practical deployment by incurring high computational costs and privacy risks. To address this, we propose a data-free early stopping framework that determines the optimal stopping point by monitoring the task vector's growth rate using solely server-side parameters. The numerical results on skin lesion/blood cell classification demonstrate that our approach is comparable to validation-based early stopping across various state-of-the-art FL methods. In particular, the proposed framework spends an average of 47/20 (skin lesion/blood cell) rounds to achieve over 12.5%/10.3% higher performance than early stopping based on validation data. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to propose an early stopping framework for FL methods without using any validation data.
Experimental Performance of Bidirectional Phase Coherent Transmission and Sensing for mmWave Cell-free Massive MIMO Systems with Reciprocity Calibration
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Phase synchronization among distributed transmission reception points (TRPs) is a prerequisite for enabling coherent joint transmission and high-precision sensing in millimeter wave (mmWave) cell-free massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) systems. This paper proposes a bidirectional calibration scheme and a calibration coefficient estimation method for phase synchronization, and presents a calibration coefficient phase tracking method using unilateral uplink/downlink channel state information (CSI). Furthermore, this paper introduces the use of reciprocity calibration to eliminate non-ideal factors in sensing and leverages sensing results to achieve calibration coefficient phase tracking in dynamic scenarios, thus enabling bidirectional empowerment of both communication and sensing. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively implement reciprocal calibration with lower overhead, enabling coherent collaborative transmission, and resolving non-ideal factors to acquire lower sensing error in sensing applications. Experimental results show that, in the mmWave band, over-the-air (OTA) bidirectional calibration enables coherent collaborative transmission for both collaborative TRPs and collaborative user equipments (UEs), achieving beamforming gain and long-time coherent sensing capabilities.
Towards Token-Level Text Anomaly Detection
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Despite significant progress in text anomaly detection for web applications such as spam filtering and fake news detection, existing methods are fundamentally limited to document-level analysis, unable to identify which specific parts of a text are anomalous. We introduce token-level anomaly detection, a novel paradigm that enables fine-grained localization of anomalies within text. We formally define text anomalies at both document and token-levels, and propose a unified detection framework that operates across multiple levels. To facilitate research in this direction, we collect and annotate three benchmark datasets spanning spam, reviews and grammar errors with token-level labels. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework get better performance than other 6 baselines, opening new possibilities for precise anomaly localization in text. All the codes and data are publicly available on https://github.com/charles-cao/TokenCore.
Differentially Private Subspace Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models on downstream tasks is crucial for realizing their cross-domain potential but often relies on sensitive data, raising privacy concerns. Differential privacy (DP) offers rigorous privacy guarantees and has been widely adopted in fine-tuning; however, naively injecting noise across the high-dimensional parameter space creates perturbations with large norms, degrading performance and destabilizing training. To address this issue, we propose DP-SFT, a two-stage subspace fine-tuning method that substantially reduces noise magnitude while preserving formal DP guarantees. Our intuition is that, during fine-tuning, significant parameter updates lie within a low-dimensional, task-specific subspace, while other directions change minimally. Hence, we only inject DP noise into this subspace to protect privacy without perturbing irrelevant parameters. In phase one, we identify the subspace by analyzing principal gradient directions to capture task-specific update signals. In phase two, we project full gradients onto this subspace, add DP noise, and map the perturbed gradients back to the original parameter space for model updates, markedly lowering noise impact. Experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that DP-SFT enhances accuracy and stability under rigorous DP constraints, accelerates convergence, and achieves substantial gains over DP fine-tuning baselines.
IIB-LPO: Latent Policy Optimization via Iterative Information Bottleneck
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) for Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning have been hindered by a persistent challenge: exploration collapse. The semantic homogeneity of random rollouts often traps models in narrow, over-optimized behaviors. While existing methods leverage policy entropy to encourage exploration, they face inherent limitations. Global entropy regularization is susceptible to reward hacking, which can induce meaningless verbosity, whereas local token-selective updates struggle with the strong inductive bias of pre-trained models. To address this, we propose Latent Policy Optimization via Iterative Information Bottleneck (IIB-LPO), a novel approach that shifts exploration from statistical perturbation of token distributions to topological branching of reasoning trajectories. IIB-LPO triggers latent branching at high-entropy states to diversify reasoning paths and employs the Information Bottleneck principle both as a trajectory filter and a self-reward mechanism, ensuring concise and informative exploration. Empirical results across four mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that IIB-LPO achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing prior methods by margins of up to 5.3% in accuracy and 7.4% in diversity metrics.
Stochastic Voronoi Ensembles for Anomaly Detection
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Anomaly detection aims to identify data instances that deviate significantly from majority of data, which has been widely used in fraud detection, network security, and industrial quality control. Existing methods struggle with datasets exhibiting varying local densities: distance-based methods miss local anomalies, while density-based approaches require careful parameter selection and incur quadratic time complexity. We observe that local anomalies, though indistinguishable under global analysis, become conspicuous when the data space is decomposed into restricted regions and each region is examined independently. Leveraging this geometric insight, we propose SVEAD (Stochastic Voronoi Ensembles Anomaly Detector), which constructs ensemble random Voronoi diagrams and scores points by normalized cell-relative distances weighted by local scale. The proposed method achieves linear time complexity and constant space complexity. Experiments on 45 datasets demonstrate that SVEAD outperforms 12 state-of-the-art approaches.
OmniVaT: Single Domain Generalization for Multimodal Visual-Tactile Learning
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Visual-tactile learning (VTL) enables embodied agents to perceive the physical world by integrating visual (VIS) and tactile (TAC) sensors. However, VTL still suffers from modality discrepancies between VIS and TAC images, as well as domain gaps caused by non-standardized tactile sensors and inconsistent data collection procedures. We formulate these challenges as a new task, termed single domain generalization for multimodal VTL (SDG-VTL). In this paper, we propose an OmniVaT framework that, for the first time, successfully addresses this task. On the one hand, OmniVaT integrates a multimodal fractional Fourier adapter (MFFA) to map VIS and TAC embeddings into a unified embedding-frequency space, thereby effectively mitigating the modality gap without multi-domain training data or careful cross-modal fusion strategies. On the other hand, it also incorporates a discrete tree generation (DTG) module that obtains diverse and reliable multimodal fractional representations through a hierarchical tree structure, thereby enhancing its adaptivity to fluctuating domain shifts in unseen domains. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior cross-domain generalization performance of OmniVaT on the SDG-VTL task.
A Stepwise-Enhanced Reasoning Framework for Large Language Models Based on External Subgraph Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved strong performance across a wide range of natural language processing tasks in recent years, including machine translation, text generation, and question answering. As their applications extend to increasingly complex scenarios, however, LLMs continue to face challenges in tasks that require deep reasoning and logical inference. In particular, models trained on large scale textual corpora may incorporate noisy or irrelevant information during generation, which can lead to incorrect predictions or outputs that are inconsistent with factual knowledge. To address this limitation, we propose a stepwise reasoning enhancement framework for LLMs based on external subgraph generation, termed SGR. The proposed framework dynamically constructs query relevant subgraphs from external knowledge bases and leverages their semantic structure to guide the reasoning process. By performing reasoning in a step by step manner over structured subgraphs, SGR reduces the influence of noisy information and improves reasoning accuracy. Specifically, the framework first generates an external subgraph tailored to the input query, then guides the model to conduct multi step reasoning grounded in the subgraph, and finally integrates multiple reasoning paths to produce the final answer. Experimental results on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that SGR consistently outperforms strong baselines, indicating its effectiveness in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
MatE: Material Extraction from Single-Image via Geometric Prior
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:The creation of high-fidelity, physically-based rendering (PBR) materials remains a bottleneck in many graphics pipelines, typically requiring specialized equipment and expert-driven post-processing. To democratize this process, we present MatE, a novel method for generating tileable PBR materials from a single image taken under unconstrained, real-world conditions. Given an image and a user-provided mask, MatE first performs coarse rectification using an estimated depth map as a geometric prior, and then employs a dual-branch diffusion model. Leveraging a learned consistency from rotation-aligned and scale-aligned training data, this model further rectify residual distortions from the coarse result and translate it into a complete set of material maps, including albedo, normal, roughness and height. Our framework achieves invariance to the unknown illumination and perspective of the input image, allowing for the recovery of intrinsic material properties from casual captures. Through comprehensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world data, we demonstrate the efficacy and robustness of our approach, enabling users to create realistic materials from real-world image.
Staggered Batch Scheduling: Co-optimizing Time-to-First-Token and Throughput for High-Efficiency LLM Inference
Dec 18, 2025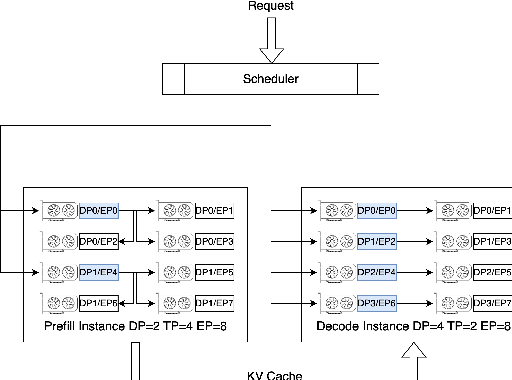
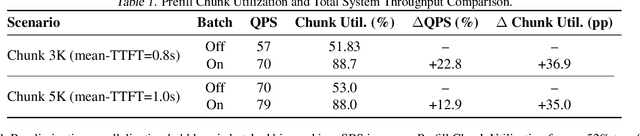
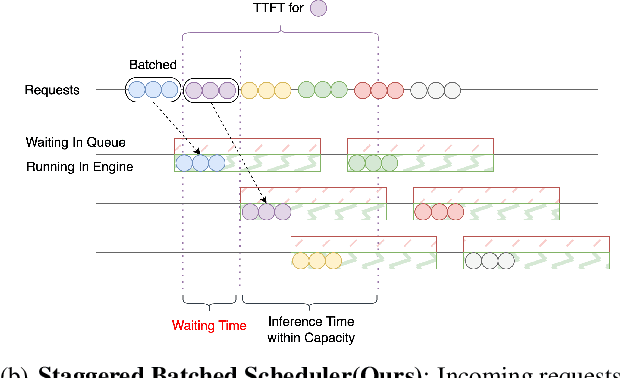
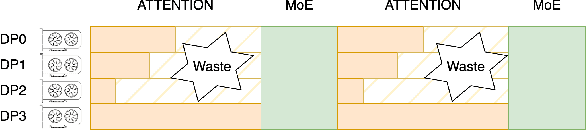
Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Model (LLM) serving towards complex, distributed architectures--specifically the P/D-separated, large-scale DP+EP paradigm--introduces distinct scheduling challenges. Unlike traditional deployments where schedulers can treat instances as black boxes, DP+EP architectures exhibit high internal synchronization costs. We identify that immediate request dispatching in such systems leads to severe in-engine queuing and parallelization bubbles, degrading Time-to-First-Token (TTFT). To address this, we propose Staggered Batch Scheduling (SBS), a mechanism that deliberately buffers requests to form optimal execution batches. This temporal decoupling eliminates internal queuing bubbles without compromising throughput. Furthermore, leveraging the scheduling window created by buffering, we introduce a Load-Aware Global Allocation strategy that balances computational load across DP units for both Prefill and Decode phases. Deployed on a production H800 cluster serving Deepseek-V3, our system reduces TTFT by 30%-40% and improves throughput by 15%-20% compared to state-of-the-art immediate scheduling baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge