Yong Guo
LSGQuant: Layer-Sensitivity Guided Quantization for One-Step Diffusion Real-World Video Super-Resolution
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:One-Step Diffusion Models have demonstrated promising capability and fast inference in video super-resolution (VSR) for real-world. Nevertheless, the substantial model size and high computational cost of Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) limit downstream applications. While low-bit quantization is a common approach for model compression, the effectiveness of quantized models is challenged by the high dynamic range of input latent and diverse layer behaviors. To deal with these challenges, we introduce LSGQuant, a layer-sensitivity guided quantizing approach for one-step diffusion-based real-world VSR. Our method incorporates a Dynamic Range Adaptive Quantizer (DRAQ) to fit video token activations. Furthermore, we estimate layer sensitivity and implement a Variance-Oriented Layer Training Strategy (VOLTS) by analyzing layer-wise statistics in calibration. We also introduce Quantization-Aware Optimization (QAO) to jointly refine the quantized branch and a retained high-precision branch. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method has nearly performance to origin model with full-precision and significantly exceeds existing quantization techniques. Code is available at: https://github.com/zhengchen1999/LSGQuant.
Q-DiT4SR: Exploration of Detail-Preserving Diffusion Transformer Quantization for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Recently, Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have emerged in Real-World Image Super-Resolution (Real-ISR) to generate high-quality textures, yet their heavy inference burden hinders real-world deployment. While Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) is a promising solution for acceleration, existing methods in super-resolution mostly focus on U-Net architectures, whereas generic DiT quantization is typically designed for text-to-image tasks. Directly applying these methods to DiT-based super-resolution models leads to severe degradation of local textures. Therefore, we propose Q-DiT4SR, the first PTQ framework specifically tailored for DiT-based Real-ISR. We propose H-SVD, a hierarchical SVD that integrates a global low-rank branch with a local block-wise rank-1 branch under a matched parameter budget. We further propose Variance-aware Spatio-Temporal Mixed Precision: VaSMP allocates cross-layer weight bit-widths in a data-free manner based on rate-distortion theory, while VaTMP schedules intra-layer activation precision across diffusion timesteps via dynamic programming (DP) with minimal calibration. Experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that our Q-DiT4SR achieves SOTA performance under both W4A6 and W4A4 settings. Notably, the W4A4 quantization configuration reduces model size by 5.8$\times$ and computational operations by over 60$\times$. Our code and models will be available at https://github.com/xunzhang1128/Q-DiT4SR.
Towards Any-Quality Image Segmentation via Generative and Adaptive Latent Space Enhancement
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Segment Anything Models (SAMs), known for their exceptional zero-shot segmentation performance, have garnered significant attention in the research community. Nevertheless, their performance drops significantly on severely degraded, low-quality images, limiting their effectiveness in real-world scenarios. To address this, we propose GleSAM++, which utilizes Generative Latent space Enhancement to boost robustness on low-quality images, thus enabling generalization across various image qualities. Additionally, to improve compatibility between the pre-trained diffusion model and the segmentation framework, we introduce two techniques, i.e., Feature Distribution Alignment (FDA) and Channel Replication and Expansion (CRE). However, the above components lack explicit guidance regarding the degree of degradation. The model is forced to implicitly fit a complex noise distribution that spans conditions from mild noise to severe artifacts, which substantially increases the learning burden and leads to suboptimal reconstructions. To address this issue, we further introduce a Degradation-aware Adaptive Enhancement (DAE) mechanism. The key principle of DAE is to decouple the reconstruction process for arbitrary-quality features into two stages: degradation-level prediction and degradation-aware reconstruction. Our method can be applied to pre-trained SAM and SAM2 with only minimal additional learnable parameters, allowing for efficient optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GleSAM++ significantly improves segmentation robustness on complex degradations while maintaining generalization to clear images. Furthermore, GleSAM++ also performs well on unseen degradations, underscoring the versatility of our approach and dataset.
Boosting Segment Anything Model to Generalize Visually Non-Salient Scenarios
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Segment Anything Model (SAM), known for its remarkable zero-shot segmentation capabilities, has garnered significant attention in the community. Nevertheless, its performance is challenged when dealing with what we refer to as visually non-salient scenarios, where there is low contrast between the foreground and background. In these cases, existing methods often cannot capture accurate contours and fail to produce promising segmentation results. In this paper, we propose Visually Non-Salient SAM (VNS-SAM), aiming to enhance SAM's perception of visually non-salient scenarios while preserving its original zero-shot generalizability. We achieve this by effectively exploiting SAM's low-level features through two designs: Mask-Edge Token Interactive decoder and Non-Salient Feature Mining module. These designs help the SAM decoder gain a deeper understanding of non-salient characteristics with only marginal parameter increments and computational requirements. The additional parameters of VNS-SAM can be optimized within 4 hours, demonstrating its feasibility and practicality. In terms of data, we established VNS-SEG, a unified dataset for various VNS scenarios, with more than 35K images, in contrast to previous single-task adaptations. It is designed to make the model learn more robust VNS features and comprehensively benchmark the model's segmentation performance and generalizability on VNS scenarios. Extensive experiments across various VNS segmentation tasks demonstrate the superior performance of VNS-SAM, particularly under zero-shot settings, highlighting its potential for broad real-world applications. Codes and datasets are publicly available at https://guangqian-guo.github.io/VNS-SAM.
RDDM: Practicing RAW Domain Diffusion Model for Real-world Image Restoration
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:We present the RAW domain diffusion model (RDDM), an end-to-end diffusion model that restores photo-realistic images directly from the sensor RAW data. While recent sRGB-domain diffusion methods achieve impressive results, they are caught in a dilemma between high fidelity and realistic generation. As these models process lossy sRGB inputs and neglect the accessibility of the sensor RAW images in many scenarios, e.g., in image and video capturing in edge devices, resulting in sub-optimal performance. RDDM bypasses this limitation by directly restoring images in the RAW domain, replacing the conventional two-stage image signal processing (ISP) + IR pipeline. However, a simple adaptation of pre-trained diffusion models to the RAW domain confronts the out-of-distribution (OOD) issues. To this end, we propose: (1) a RAW-domain VAE (RVAE) learning optimal latent representations, (2) a differentiable Post Tone Processing (PTP) module enabling joint RAW and sRGB space optimization. To compensate for the deficiency in the dataset, we develop a scalable degradation pipeline synthesizing RAW LQ-HQ pairs from existing sRGB datasets for large-scale training. Furthermore, we devise a configurable multi-bayer (CMB) LoRA module handling diverse RAW patterns such as RGGB, BGGR, etc. Extensive experiments demonstrate RDDM's superiority over state-of-the-art sRGB diffusion methods, yielding higher fidelity results with fewer artifacts.
SODiff: Semantic-Oriented Diffusion Model for JPEG Compression Artifacts Removal
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:JPEG, as a widely used image compression standard, often introduces severe visual artifacts when achieving high compression ratios. Although existing deep learning-based restoration methods have made considerable progress, they often struggle to recover complex texture details, resulting in over-smoothed outputs. To overcome these limitations, we propose SODiff, a novel and efficient semantic-oriented one-step diffusion model for JPEG artifacts removal. Our core idea is that effective restoration hinges on providing semantic-oriented guidance to the pre-trained diffusion model, thereby fully leveraging its powerful generative prior. To this end, SODiff incorporates a semantic-aligned image prompt extractor (SAIPE). SAIPE extracts rich features from low-quality (LQ) images and projects them into an embedding space semantically aligned with that of the text encoder. Simultaneously, it preserves crucial information for faithful reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose a quality factor-aware time predictor that implicitly learns the compression quality factor (QF) of the LQ image and adaptively selects the optimal denoising start timestep for the diffusion process. Extensive experimental results show that our SODiff outperforms recent leading methods in both visual quality and quantitative metrics. Code is available at: https://github.com/frakenation/SODiff
QuantVSR: Low-Bit Post-Training Quantization for Real-World Video Super-Resolution
Aug 06, 2025
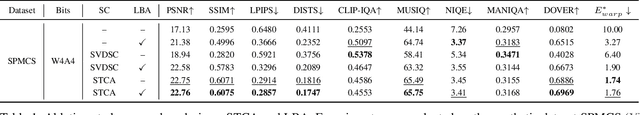
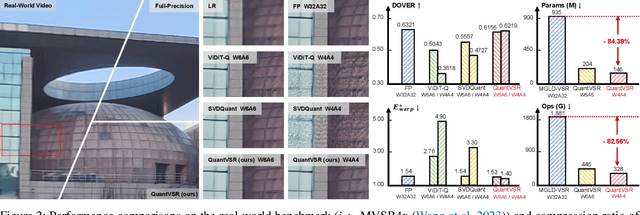
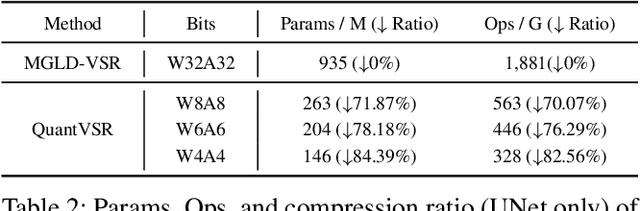
Abstract:Diffusion models have shown superior performance in real-world video super-resolution (VSR). However, the slow processing speeds and heavy resource consumption of diffusion models hinder their practical application and deployment. Quantization offers a potential solution for compressing the VSR model. Nevertheless, quantizing VSR models is challenging due to their temporal characteristics and high fidelity requirements. To address these issues, we propose QuantVSR, a low-bit quantization model for real-world VSR. We propose a spatio-temporal complexity aware (STCA) mechanism, where we first utilize the calibration dataset to measure both spatial and temporal complexities for each layer. Based on these statistics, we allocate layer-specific ranks to the low-rank full-precision (FP) auxiliary branch. Subsequently, we jointly refine the FP and low-bit branches to achieve simultaneous optimization. In addition, we propose a learnable bias alignment (LBA) module to reduce the biased quantization errors. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our method obtains comparable performance with the FP model and significantly outperforms recent leading low-bit quantization methods. Code is available at: https://github.com/bowenchai/QuantVSR.
LoViC: Efficient Long Video Generation with Context Compression
Jul 17, 2025

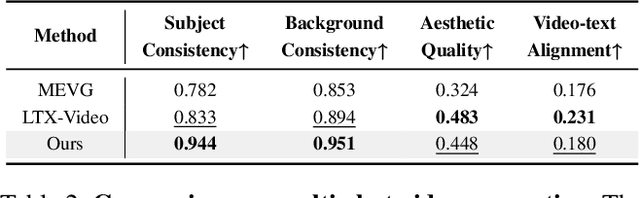

Abstract:Despite recent advances in diffusion transformers (DiTs) for text-to-video generation, scaling to long-duration content remains challenging due to the quadratic complexity of self-attention. While prior efforts -- such as sparse attention and temporally autoregressive models -- offer partial relief, they often compromise temporal coherence or scalability. We introduce LoViC, a DiT-based framework trained on million-scale open-domain videos, designed to produce long, coherent videos through a segment-wise generation process. At the core of our approach is FlexFormer, an expressive autoencoder that jointly compresses video and text into unified latent representations. It supports variable-length inputs with linearly adjustable compression rates, enabled by a single query token design based on the Q-Former architecture. Additionally, by encoding temporal context through position-aware mechanisms, our model seamlessly supports prediction, retradiction, interpolation, and multi-shot generation within a unified paradigm. Extensive experiments across diverse tasks validate the effectiveness and versatility of our approach.
FastFLUX: Pruning FLUX with Block-wise Replacement and Sandwich Training
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-image (T2I) generation have led to the emergence of highly expressive models such as diffusion transformers (DiTs), exemplified by FLUX. However, their massive parameter sizes lead to slow inference, high memory usage, and poor deployability. Existing acceleration methods (e.g., single-step distillation and attention pruning) often suffer from significant performance degradation and incur substantial training costs. To address these limitations, we propose FastFLUX, an architecture-level pruning framework designed to enhance the inference efficiency of FLUX. At its core is the Block-wise Replacement with Linear Layers (BRLL) method, which replaces structurally complex residual branches in ResBlocks with lightweight linear layers while preserving the original shortcut connections for stability. Furthermore, we introduce Sandwich Training (ST), a localized fine-tuning strategy that leverages LoRA to supervise neighboring blocks, mitigating performance drops caused by structural replacement. Experiments show that our FastFLUX maintains high image quality under both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, while significantly improving inference speed, even with 20\% of the hierarchy pruned. Our code will be available soon.
OSCAR: One-Step Diffusion Codec Across Multiple Bit-rates
May 22, 2025Abstract:Pretrained latent diffusion models have shown strong potential for lossy image compression, owing to their powerful generative priors. Most existing diffusion-based methods reconstruct images by iteratively denoising from random noise, guided by compressed latent representations. While these approaches have achieved high reconstruction quality, their multi-step sampling process incurs substantial computational overhead. Moreover, they typically require training separate models for different compression bit-rates, leading to significant training and storage costs. To address these challenges, we propose a one-step diffusion codec across multiple bit-rates. termed OSCAR. Specifically, our method views compressed latents as noisy variants of the original latents, where the level of distortion depends on the bit-rate. This perspective allows them to be modeled as intermediate states along a diffusion trajectory. By establishing a mapping from the compression bit-rate to a pseudo diffusion timestep, we condition a single generative model to support reconstructions at multiple bit-rates. Meanwhile, we argue that the compressed latents retain rich structural information, thereby making one-step denoising feasible. Thus, OSCAR replaces iterative sampling with a single denoising pass, significantly improving inference efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OSCAR achieves superior performance in both quantitative and visual quality metrics. The code and models will be released at https://github.com/jp-guo/OSCAR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge