Haotong Qin
MambaVF: State Space Model for Efficient Video Fusion
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Video fusion is a fundamental technique in various video processing tasks. However, existing video fusion methods heavily rely on optical flow estimation and feature warping, resulting in severe computational overhead and limited scalability. This paper presents MambaVF, an efficient video fusion framework based on state space models (SSMs) that performs temporal modeling without explicit motion estimation. First, by reformulating video fusion as a sequential state update process, MambaVF captures long-range temporal dependencies with linear complexity while significantly reducing computation and memory costs. Second, MambaVF proposes a lightweight SSM-based fusion module that replaces conventional flow-guided alignment via a spatio-temporal bidirectional scanning mechanism. This module enables efficient information aggregation across frames. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our MambaVF achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-exposure, multi-focus, infrared-visible, and medical video fusion tasks. We highlight that MambaVF enjoys high efficiency, reducing up to 92.25% of parameters and 88.79% of computational FLOPs and a 2.1x speedup compared to existing methods. Project page: https://mambavf.github.io
Fast-SAM3D: 3Dfy Anything in Images but Faster
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:SAM3D enables scalable, open-world 3D reconstruction from complex scenes, yet its deployment is hindered by prohibitive inference latency. In this work, we conduct the \textbf{first systematic investigation} into its inference dynamics, revealing that generic acceleration strategies are brittle in this context. We demonstrate that these failures stem from neglecting the pipeline's inherent multi-level \textbf{heterogeneity}: the kinematic distinctiveness between shape and layout, the intrinsic sparsity of texture refinement, and the spectral variance across geometries. To address this, we present \textbf{Fast-SAM3D}, a training-free framework that dynamically aligns computation with instantaneous generation complexity. Our approach integrates three heterogeneity-aware mechanisms: (1) \textit{Modality-Aware Step Caching} to decouple structural evolution from sensitive layout updates; (2) \textit{Joint Spatiotemporal Token Carving} to concentrate refinement on high-entropy regions; and (3) \textit{Spectral-Aware Token Aggregation} to adapt decoding resolution. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Fast-SAM3D delivers up to \textbf{2.67$\times$} end-to-end speedup with negligible fidelity loss, establishing a new Pareto frontier for efficient single-view 3D generation. Our code is released in https://github.com/wlfeng0509/Fast-SAM3D.
Q-DiT4SR: Exploration of Detail-Preserving Diffusion Transformer Quantization for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Recently, Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have emerged in Real-World Image Super-Resolution (Real-ISR) to generate high-quality textures, yet their heavy inference burden hinders real-world deployment. While Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) is a promising solution for acceleration, existing methods in super-resolution mostly focus on U-Net architectures, whereas generic DiT quantization is typically designed for text-to-image tasks. Directly applying these methods to DiT-based super-resolution models leads to severe degradation of local textures. Therefore, we propose Q-DiT4SR, the first PTQ framework specifically tailored for DiT-based Real-ISR. We propose H-SVD, a hierarchical SVD that integrates a global low-rank branch with a local block-wise rank-1 branch under a matched parameter budget. We further propose Variance-aware Spatio-Temporal Mixed Precision: VaSMP allocates cross-layer weight bit-widths in a data-free manner based on rate-distortion theory, while VaTMP schedules intra-layer activation precision across diffusion timesteps via dynamic programming (DP) with minimal calibration. Experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that our Q-DiT4SR achieves SOTA performance under both W4A6 and W4A4 settings. Notably, the W4A4 quantization configuration reduces model size by 5.8$\times$ and computational operations by over 60$\times$. Our code and models will be available at https://github.com/xunzhang1128/Q-DiT4SR.
Exploring Semantic-constrained Adversarial Example with Instruction Uncertainty Reduction
Oct 27, 2025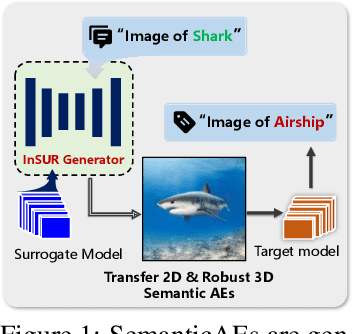
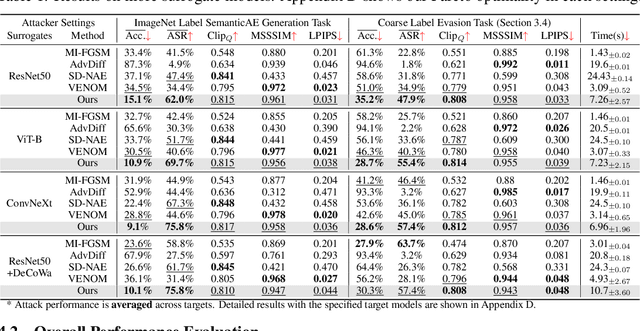
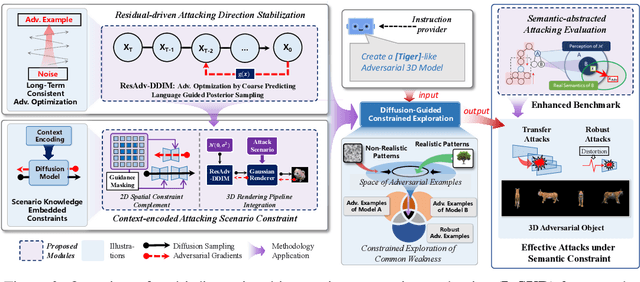
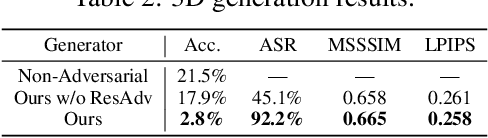
Abstract:Recently, semantically constrained adversarial examples (SemanticAE), which are directly generated from natural language instructions, have become a promising avenue for future research due to their flexible attacking forms. To generate SemanticAEs, current methods fall short of satisfactory attacking ability as the key underlying factors of semantic uncertainty in human instructions, such as referring diversity, descriptive incompleteness, and boundary ambiguity, have not been fully investigated. To tackle the issues, this paper develops a multi-dimensional instruction uncertainty reduction (InSUR) framework to generate more satisfactory SemanticAE, i.e., transferable, adaptive, and effective. Specifically, in the dimension of the sampling method, we propose the residual-driven attacking direction stabilization to alleviate the unstable adversarial optimization caused by the diversity of language references. By coarsely predicting the language-guided sampling process, the optimization process will be stabilized by the designed ResAdv-DDIM sampler, therefore releasing the transferable and robust adversarial capability of multi-step diffusion models. In task modeling, we propose the context-encoded attacking scenario constraint to supplement the missing knowledge from incomplete human instructions. Guidance masking and renderer integration are proposed to regulate the constraints of 2D/3D SemanticAE, activating stronger scenario-adapted attacks. Moreover, in the dimension of generator evaluation, we propose the semantic-abstracted attacking evaluation enhancement by clarifying the evaluation boundary, facilitating the development of more effective SemanticAE generators. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the transfer attack performance of InSUR. Moreover, we realize the reference-free generation of semantically constrained 3D adversarial examples for the first time.
FlashEdit: Decoupling Speed, Structure, and Semantics for Precise Image Editing
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Text-guided image editing with diffusion models has achieved remarkable quality but suffers from prohibitive latency, hindering real-world applications. We introduce FlashEdit, a novel framework designed to enable high-fidelity, real-time image editing. Its efficiency stems from three key innovations: (1) a One-Step Inversion-and-Editing (OSIE) pipeline that bypasses costly iterative processes; (2) a Background Shield (BG-Shield) technique that guarantees background preservation by selectively modifying features only within the edit region; and (3) a Sparsified Spatial Cross-Attention (SSCA) mechanism that ensures precise, localized edits by suppressing semantic leakage to the background. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FlashEdit maintains superior background consistency and structural integrity, while performing edits in under 0.2 seconds, which is an over 150$\times$ speedup compared to prior multi-step methods. Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit.
$\text{S}^2$Q-VDiT: Accurate Quantized Video Diffusion Transformer with Salient Data and Sparse Token Distillation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Diffusion transformers have emerged as the mainstream paradigm for video generation models. However, the use of up to billions of parameters incurs significant computational costs. Quantization offers a promising solution by reducing memory usage and accelerating inference. Nonetheless, we observe that the joint modeling of spatial and temporal information in video diffusion models (V-DMs) leads to extremely long token sequences, which introduces high calibration variance and learning challenges. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{$\text{S}^2$Q-VDiT}, a post-training quantization framework for V-DMs that leverages \textbf{S}alient data and \textbf{S}parse token distillation. During the calibration phase, we identify that quantization performance is highly sensitive to the choice of calibration data. To mitigate this, we introduce \textit{Hessian-aware Salient Data Selection}, which constructs high-quality calibration datasets by considering both diffusion and quantization characteristics unique to V-DMs. To tackle the learning challenges, we further analyze the sparse attention patterns inherent in V-DMs. Based on this observation, we propose \textit{Attention-guided Sparse Token Distillation}, which exploits token-wise attention distributions to emphasize tokens that are more influential to the model's output. Under W4A6 quantization, $\text{S}^2$Q-VDiT achieves lossless performance while delivering $3.9\times$ model compression and $1.3\times$ inference acceleration. Code will be available at \href{https://github.com/wlfeng0509/s2q-vdit}{https://github.com/wlfeng0509/s2q-vdit}.
Pay Less Attention to Deceptive Artifacts: Robust Detection of Compressed Deepfakes on Online Social Networks
Jun 25, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid advancement of deep learning, particularly through generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models (DMs), AI-generated images, or ``deepfakes", have become nearly indistinguishable from real ones. These images are widely shared across Online Social Networks (OSNs), raising concerns about their misuse. Existing deepfake detection methods overlook the ``block effects" introduced by compression in OSNs, which obscure deepfake artifacts, and primarily focus on raw images, rarely encountered in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose PLADA (Pay Less Attention to Deceptive Artifacts), a novel framework designed to tackle the lack of paired data and the ineffective use of compressed images. PLADA consists of two core modules: Block Effect Eraser (B2E), which uses a dual-stage attention mechanism to handle block effects, and Open Data Aggregation (ODA), which processes both paired and unpaired data to improve detection. Extensive experiments across 26 datasets demonstrate that PLADA achieves a remarkable balance in deepfake detection, outperforming SoTA methods in detecting deepfakes on OSNs, even with limited paired data and compression. More importantly, this work introduces the ``block effect" as a critical factor in deepfake detection, providing a robust solution for open-world scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/ManyiLee/PLADA.
PicoSAM2: Low-Latency Segmentation In-Sensor for Edge Vision Applications
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Real-time, on-device segmentation is critical for latency-sensitive and privacy-aware applications like smart glasses and IoT devices. We introduce PicoSAM2, a lightweight (1.3M parameters, 336M MACs) promptable segmentation model optimized for edge and in-sensor execution, including the Sony IMX500. It builds on a depthwise separable U-Net, with knowledge distillation and fixed-point prompt encoding to learn from the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2). On COCO and LVIS, it achieves 51.9% and 44.9% mIoU, respectively. The quantized model (1.22MB) runs at 14.3 ms on the IMX500-achieving 86 MACs/cycle, making it the only model meeting both memory and compute constraints for in-sensor deployment. Distillation boosts LVIS performance by +3.5% mIoU and +5.1% mAP. These results demonstrate that efficient, promptable segmentation is feasible directly on-camera, enabling privacy-preserving vision without cloud or host processing.
Pushing the Limits of Safety: A Technical Report on the ATLAS Challenge 2025
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have enabled transformative advancements across diverse applications but remain susceptible to safety threats, especially jailbreak attacks that induce harmful outputs. To systematically evaluate and improve their safety, we organized the Adversarial Testing & Large-model Alignment Safety Grand Challenge (ATLAS) 2025}. This technical report presents findings from the competition, which involved 86 teams testing MLLM vulnerabilities via adversarial image-text attacks in two phases: white-box and black-box evaluations. The competition results highlight ongoing challenges in securing MLLMs and provide valuable guidance for developing stronger defense mechanisms. The challenge establishes new benchmarks for MLLM safety evaluation and lays groundwork for advancing safer multimodal AI systems. The code and data for this challenge are openly available at https://github.com/NY1024/ATLAS_Challenge_2025.
Post-Training Quantization for Video Matting
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Video matting is crucial for applications such as film production and virtual reality, yet deploying its computationally intensive models on resource-constrained devices presents challenges. Quantization is a key technique for model compression and acceleration. As an efficient approach, Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) is still in its nascent stages for video matting, facing significant hurdles in maintaining accuracy and temporal coherence. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel and general PTQ framework specifically designed for video matting models, marking, to the best of our knowledge, the first systematic attempt in this domain. Our contributions include: (1) A two-stage PTQ strategy that combines block-reconstruction-based optimization for fast, stable initial quantization and local dependency capture, followed by a global calibration of quantization parameters to minimize accuracy loss. (2) A Statistically-Driven Global Affine Calibration (GAC) method that enables the network to compensate for cumulative statistical distortions arising from factors such as neglected BN layer effects, even reducing the error of existing PTQ methods on video matting tasks up to 20%. (3) An Optical Flow Assistance (OFA) component that leverages temporal and semantic priors from frames to guide the PTQ process, enhancing the model's ability to distinguish moving foregrounds in complex scenes and ultimately achieving near full-precision performance even under ultra-low-bit quantization. Comprehensive quantitative and visual results show that our PTQ4VM achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy performance across different bit-widths compared to the existing quantization methods. We highlight that the 4-bit PTQ4VM even achieves performance close to the full-precision counterpart while enjoying 8x FLOP savings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge