Boyu Diao
Teacher-Guided Student Self-Knowledge Distillation Using Diffusion Model
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Existing Knowledge Distillation (KD) methods often align feature information between teacher and student by exploring meaningful feature processing and loss functions. However, due to the difference in feature distributions between the teacher and student, the student model may learn incompatible information from the teacher. To address this problem, we propose teacher-guided student Diffusion Self-KD, dubbed as DSKD. Instead of the direct teacher-student alignment, we leverage the teacher classifier to guide the sampling process of denoising student features through a light-weight diffusion model. We then propose a novel locality-sensitive hashing (LSH)-guided feature distillation method between the original and denoised student features. The denoised student features encapsulate teacher knowledge and could be regarded as a teacher role. In this way, our DSKD method could eliminate discrepancies in mapping manners and feature distributions between the teacher and student, while learning meaningful knowledge from the teacher. Experiments on visual recognition tasks demonstrate that DSKD significantly outperforms existing KD methods across various models and datasets. Our code is attached in supplementary material.
Dynamical Adapter Fusion: Constructing A Global Adapter for Pre-Trained Model-based Class-Incremental Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) requires models to continuously acquire new classes without forgetting previously learned ones. A dominant paradigm involves freezing a pre-trained model and training lightweight, task-specific adapters. However, maintaining task-specific parameters hinders knowledge transfer and incurs high retrieval costs, while naive parameter fusion often leads to destructive interference and catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose Dynamical Adapter Fusion (DAF) to construct a single robust global adapter. Grounded in the PAC-Bayes theorem, we derive a fusion mechanism that explicitly integrates three components: the optimized task-specific adapter parameters, the previous global adapter parameters, and the initialization parameters. We utilize the Taylor expansion of the loss function to derive the optimal fusion coefficients, dynamically achieving the best balance between stability and plasticity. Furthermore, we propose a Robust Initialization strategy to effectively capture global knowledge patterns. Experiments on multiple CIL benchmarks demonstrate that DAF achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance.
Semantic-Guided Dynamic Sparsification for Pre-Trained Model-based Class-Incremental Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) requires a model to continually learn new classes without forgetting old ones. A common and efficient solution freezes a pre-trained model and employs lightweight adapters, whose parameters are often forced to be orthogonal to prevent inter-task interference. However, we argue that this parameter-constraining method is detrimental to plasticity. To this end, we propose Semantic-Guided Dynamic Sparsification (SGDS), a novel method that proactively guides the activation space by governing the orientation and rank of its subspaces through targeted sparsification. Specifically, SGDS promotes knowledge transfer by encouraging similar classes to share a compact activation subspace, while simultaneously preventing interference by assigning non-overlapping activation subspaces to dissimilar classes. By sculpting class-specific sparse subspaces in the activation space, SGDS effectively mitigates interference without imposing rigid constraints on the parameter space. Extensive experiments on various benchmark datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of SGDS.
Overcoming Prompts Pool Confusion via Parameterized Prompt for Incremental Object Detection
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated that incorporating trainable prompts into pretrained models enables effective incremental learning. However, the application of prompts in incremental object detection (IOD) remains underexplored. Existing prompts pool based approaches assume disjoint class sets across incremental tasks, which are unsuitable for IOD as they overlook the inherent co-occurrence phenomenon in detection images. In co-occurring scenarios, unlabeled objects from previous tasks may appear in current task images, leading to confusion in prompts pool. In this paper, we hold that prompt structures should exhibit adaptive consolidation properties across tasks, with constrained updates to prevent catastrophic forgetting. Motivated by this, we introduce Parameterized Prompts for Incremental Object Detection (P$^2$IOD). Leveraging neural networks global evolution properties, P$^2$IOD employs networks as the parameterized prompts to adaptively consolidate knowledge across tasks. To constrain prompts structure updates, P$^2$IOD further engages a parameterized prompts fusion strategy. Extensive experiments on PASCAL VOC2007 and MS COCO datasets demonstrate that P$^2$IOD's effectiveness in IOD and achieves the state-of-the-art performance among existing baselines.
CBPNet: A Continual Backpropagation Prompt Network for Alleviating Plasticity Loss on Edge Devices
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:To meet the demands of applications like robotics and autonomous driving that require real-time responses to dynamic environments, efficient continual learning methods suitable for edge devices have attracted increasing attention. In this transition, using frozen pretrained models with prompts has become a mainstream strategy to combat catastrophic forgetting. However, this approach introduces a new critical bottleneck: plasticity loss, where the model's ability to learn new knowledge diminishes due to the frozen backbone and the limited capacity of prompt parameters. We argue that the reduction in plasticity stems from a lack of update vitality in underutilized parameters during the training process. To this end, we propose the Continual Backpropagation Prompt Network (CBPNet), an effective and parameter efficient framework designed to restore the model's learning vitality. We innovatively integrate an Efficient CBP Block that counteracts plasticity decay by adaptively reinitializing these underutilized parameters. Experimental results on edge devices demonstrate CBPNet's effectiveness across multiple benchmarks. On Split CIFAR-100, it improves average accuracy by over 1% against a strong baseline, and on the more challenging Split ImageNet-R, it achieves a state of the art accuracy of 69.41%. This is accomplished by training additional parameters that constitute less than 0.2% of the backbone's size, validating our approach.
Q-VDiT: Towards Accurate Quantization and Distillation of Video-Generation Diffusion Transformers
May 28, 2025Abstract:Diffusion transformers (DiT) have demonstrated exceptional performance in video generation. However, their large number of parameters and high computational complexity limit their deployment on edge devices. Quantization can reduce storage requirements and accelerate inference by lowering the bit-width of model parameters. Yet, existing quantization methods for image generation models do not generalize well to video generation tasks. We identify two primary challenges: the loss of information during quantization and the misalignment between optimization objectives and the unique requirements of video generation. To address these challenges, we present Q-VDiT, a quantization framework specifically designed for video DiT models. From the quantization perspective, we propose the Token-aware Quantization Estimator (TQE), which compensates for quantization errors in both the token and feature dimensions. From the optimization perspective, we introduce Temporal Maintenance Distillation (TMD), which preserves the spatiotemporal correlations between frames and enables the optimization of each frame with respect to the overall video context. Our W3A6 Q-VDiT achieves a scene consistency of 23.40, setting a new benchmark and outperforming current state-of-the-art quantization methods by 1.9$\times$. Code will be available at https://github.com/cantbebetter2/Q-VDiT.
BLAST: Balanced Sampling Time Series Corpus for Universal Forecasting Models
May 23, 2025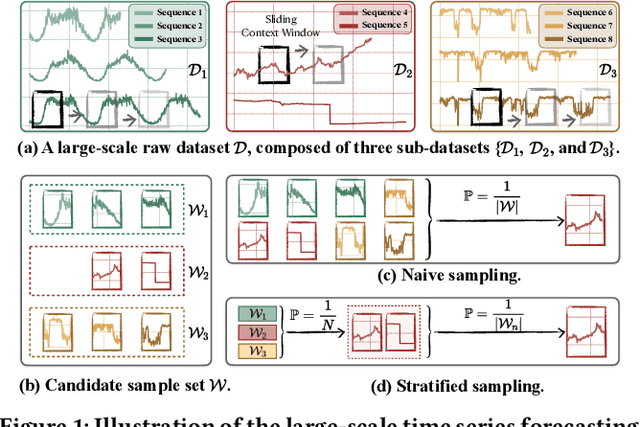
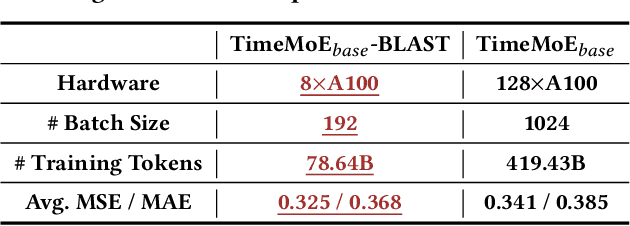
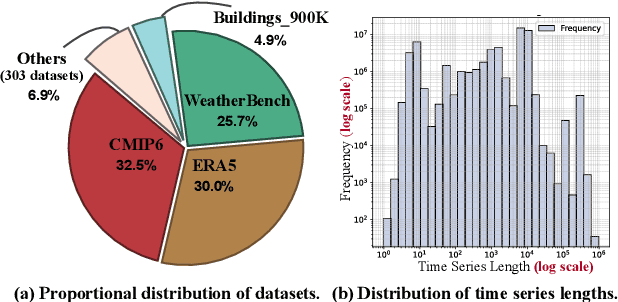
Abstract:The advent of universal time series forecasting models has revolutionized zero-shot forecasting across diverse domains, yet the critical role of data diversity in training these models remains underexplored. Existing large-scale time series datasets often suffer from inherent biases and imbalanced distributions, leading to suboptimal model performance and generalization. To address this gap, we introduce BLAST, a novel pre-training corpus designed to enhance data diversity through a balanced sampling strategy. First, BLAST incorporates 321 billion observations from publicly available datasets and employs a comprehensive suite of statistical metrics to characterize time series patterns. Then, to facilitate pattern-oriented sampling, the data is implicitly clustered using grid-based partitioning. Furthermore, by integrating grid sampling and grid mixup techniques, BLAST ensures a balanced and representative coverage of diverse patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that models pre-trained on BLAST achieve state-of-the-art performance with a fraction of the computational resources and training tokens required by existing methods. Our findings highlight the pivotal role of data diversity in improving both training efficiency and model performance for the universal forecasting task.
PrePrompt: Predictive prompting for class incremental learning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Class Incremental Learning (CIL) based on pre-trained models offers a promising direction for open-world continual learning. Existing methods typically rely on correlation-based strategies, where an image's classification feature is used as a query to retrieve the most related key prompts and select the corresponding value prompts for training. However, these approaches face an inherent limitation: fitting the entire feature space of all tasks with only a few trainable prompts is fundamentally challenging. We propose Predictive Prompting (PrePrompt), a novel CIL framework that circumvents correlation-based limitations by leveraging pre-trained models' natural classification ability to predict task-specific prompts. Specifically, PrePrompt decomposes CIL into a two-stage prediction framework: task-specific prompt prediction followed by label prediction. While theoretically appealing, this framework risks bias toward recent classes due to missing historical data for older classifier calibration. PrePrompt then mitigates this by incorporating feature translation, dynamically balancing stability and plasticity. Experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate PrePrompt's superiority over state-of-the-art prompt-based CIL methods. The code will be released upon acceptance.
A Sensitivity-Driven Expert Allocation Method in LoRA-MoE for Efficient Fine-Tuning
May 06, 2025Abstract:As deep learning models expand, the pre-training-fine-tuning paradigm has become the standard approach for handling various downstream tasks. However, shared parameters can lead to diminished performance when dealing with complex datasets involving multiple tasks. While introducing Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) methods has alleviated this issue to some extent, it also significantly increases the number of parameters required for fine-tuning and training time, introducing greater parameter redundancy. To address these challenges, we propose a method for allocating expert numbers based on parameter sensitivity LoRA-SMoE (A Sensitivity-Driven Expert Allocation Method in LoRA-MoE for Efficient Fine-Tuning). This method rapidly assesses the sensitivity of different tasks to parameters by sampling a small amount of data and using gradient information. It then adaptively allocates expert numbers within a given budget. The process maintains comparable memory consumption to LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) while ensuring an efficient and resource-friendly fine-tuning procedure. Experimental results demonstrate that compared to SOTA fine-tuning methods, our LoRA-SMoE approach can enhance model performance while reducing the number of trainable parameters. This significantly improves model performance in resource-constrained environments. Additionally, due to its efficient parameter sensitivity evaluation mechanism, LoRA-SMoE requires minimal computational overhead to optimize expert allocation, making it particularly suitable for scenarios with limited computational resources. All the code in this study will be made publicly available following the acceptance of the paper for publication. Source code is at https://github.com/EMLS-ICTCAS/LoRA-SMoE
A Nonlinear Hash-based Optimization Method for SpMV on GPUs
Apr 11, 2025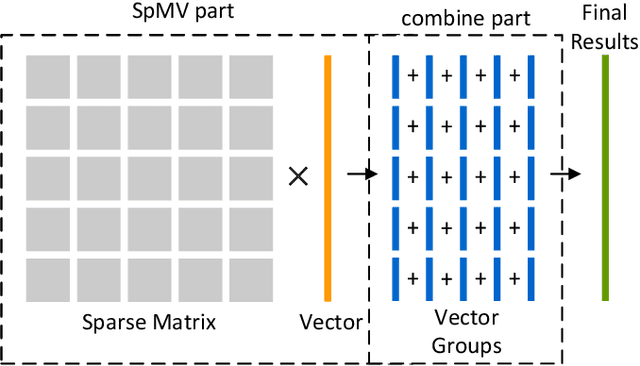
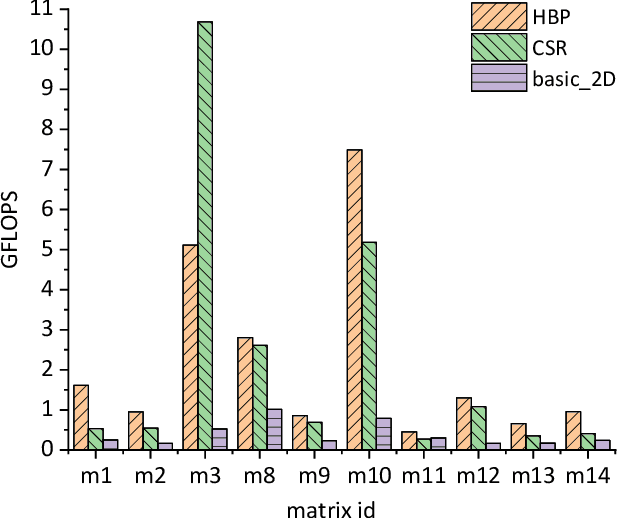
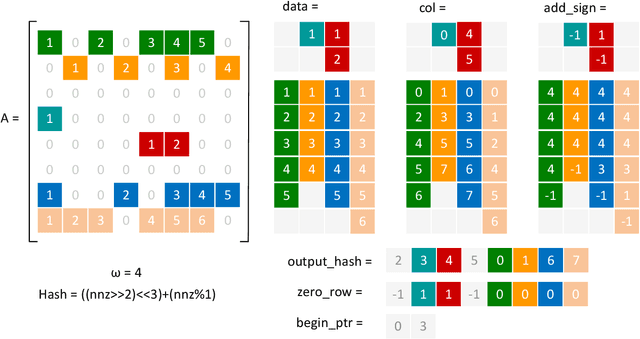

Abstract:Sparse matrix-vector multiplication (SpMV) is a fundamental operation with a wide range of applications in scientific computing and artificial intelligence. However, the large scale and sparsity of sparse matrix often make it a performance bottleneck. In this paper, we highlight the effectiveness of hash-based techniques in optimizing sparse matrix reordering, introducing the Hash-based Partition (HBP) format, a lightweight SpMV approach. HBP retains the performance benefits of the 2D-partitioning method while leveraging the hash transformation's ability to group similar elements, thereby accelerating the pre-processing phase of sparse matrix reordering. Additionally, we achieve parallel load balancing across matrix blocks through a competitive method. Our experiments, conducted on both Nvidia Jetson AGX Orin and Nvidia RTX 4090, show that in the pre-processing step, our method offers an average speedup of 3.53 times compared to the sorting approach and 3.67 times compared to the dynamic programming method employed in Regu2D. Furthermore, in SpMV, our method achieves a maximum speedup of 3.32 times on Orin and 3.01 times on RTX4090 against the CSR format in sparse matrices from the University of Florida Sparse Matrix Collection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge