Yan Zeng
Rethinking Video Generation Model for the Embodied World
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Video generation models have significantly advanced embodied intelligence, unlocking new possibilities for generating diverse robot data that capture perception, reasoning, and action in the physical world. However, synthesizing high-quality videos that accurately reflect real-world robotic interactions remains challenging, and the lack of a standardized benchmark limits fair comparisons and progress. To address this gap, we introduce a comprehensive robotics benchmark, RBench, designed to evaluate robot-oriented video generation across five task domains and four distinct embodiments. It assesses both task-level correctness and visual fidelity through reproducible sub-metrics, including structural consistency, physical plausibility, and action completeness. Evaluation of 25 representative models highlights significant deficiencies in generating physically realistic robot behaviors. Furthermore, the benchmark achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.96 with human evaluations, validating its effectiveness. While RBench provides the necessary lens to identify these deficiencies, achieving physical realism requires moving beyond evaluation to address the critical shortage of high-quality training data. Driven by these insights, we introduce a refined four-stage data pipeline, resulting in RoVid-X, the largest open-source robotic dataset for video generation with 4 million annotated video clips, covering thousands of tasks and enriched with comprehensive physical property annotations. Collectively, this synergistic ecosystem of evaluation and data establishes a robust foundation for rigorous assessment and scalable training of video models, accelerating the evolution of embodied AI toward general intelligence.
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
RewardDance: Reward Scaling in Visual Generation
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Reward Models (RMs) are critical for improving generation models via Reinforcement Learning (RL), yet the RM scaling paradigm in visual generation remains largely unexplored. It primarily due to fundamental limitations in existing approaches: CLIP-based RMs suffer from architectural and input modality constraints, while prevalent Bradley-Terry losses are fundamentally misaligned with the next-token prediction mechanism of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), hindering effective scaling. More critically, the RLHF optimization process is plagued by Reward Hacking issue, where models exploit flaws in the reward signal without improving true quality. To address these challenges, we introduce RewardDance, a scalable reward modeling framework that overcomes these barriers through a novel generative reward paradigm. By reformulating the reward score as the model's probability of predicting a "yes" token, indicating that the generated image outperforms a reference image according to specific criteria, RewardDance intrinsically aligns reward objectives with VLM architectures. This alignment unlocks scaling across two dimensions: (1) Model Scaling: Systematic scaling of RMs up to 26 billion parameters; (2) Context Scaling: Integration of task-specific instructions, reference examples, and chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RewardDance significantly surpasses state-of-the-art methods in text-to-image, text-to-video, and image-to-video generation. Crucially, we resolve the persistent challenge of "reward hacking": Our large-scale RMs exhibit and maintain high reward variance during RL fine-tuning, proving their resistance to hacking and ability to produce diverse, high-quality outputs. It greatly relieves the mode collapse problem that plagues smaller models.
Confounded Causal Imitation Learning with Instrumental Variables
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning from demonstrations usually suffers from the confounding effects of unmeasured variables (i.e., unmeasured confounders) on the states and actions. If ignoring them, a biased estimation of the policy would be entailed. To break up this confounding gap, in this paper, we take the best of the strong power of instrumental variables (IV) and propose a Confounded Causal Imitation Learning (C2L) model. This model accommodates confounders that influence actions across multiple timesteps, rather than being restricted to immediate temporal dependencies. We develop a two-stage imitation learning framework for valid IV identification and policy optimization. In particular, in the first stage, we construct a testing criterion based on the defined pseudo-variable, with which we achieve identifying a valid IV for the C2L models. Such a criterion entails the sufficient and necessary identifiability conditions for IV validity. In the second stage, with the identified IV, we propose two candidate policy learning approaches: one is based on a simulator, while the other is offline. Extensive experiments verified the effectiveness of identifying the valid IV as well as learning the policy.
Seedance 1.0: Exploring the Boundaries of Video Generation Models
Jun 10, 2025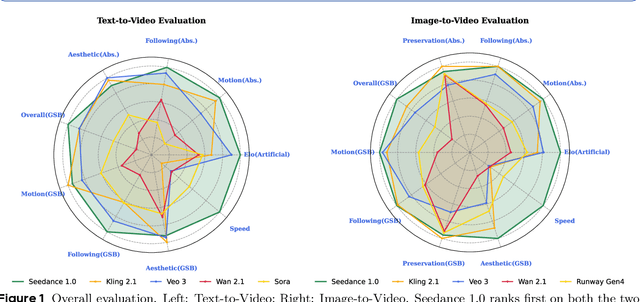
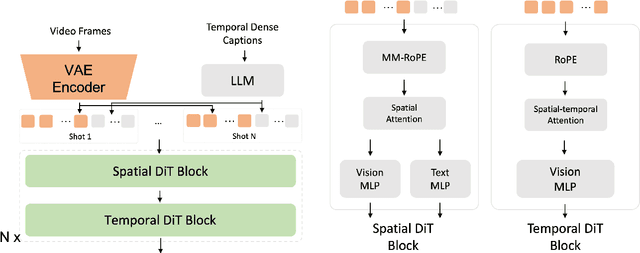
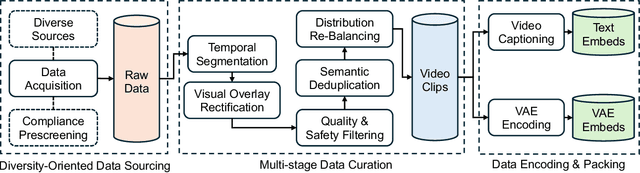
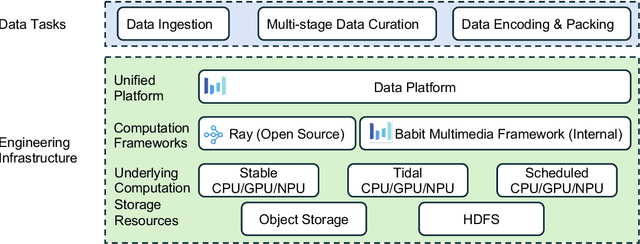
Abstract:Notable breakthroughs in diffusion modeling have propelled rapid improvements in video generation, yet current foundational model still face critical challenges in simultaneously balancing prompt following, motion plausibility, and visual quality. In this report, we introduce Seedance 1.0, a high-performance and inference-efficient video foundation generation model that integrates several core technical improvements: (i) multi-source data curation augmented with precision and meaningful video captioning, enabling comprehensive learning across diverse scenarios; (ii) an efficient architecture design with proposed training paradigm, which allows for natively supporting multi-shot generation and jointly learning of both text-to-video and image-to-video tasks. (iii) carefully-optimized post-training approaches leveraging fine-grained supervised fine-tuning, and video-specific RLHF with multi-dimensional reward mechanisms for comprehensive performance improvements; (iv) excellent model acceleration achieving ~10x inference speedup through multi-stage distillation strategies and system-level optimizations. Seedance 1.0 can generate a 5-second video at 1080p resolution only with 41.4 seconds (NVIDIA-L20). Compared to state-of-the-art video generation models, Seedance 1.0 stands out with high-quality and fast video generation having superior spatiotemporal fluidity with structural stability, precise instruction adherence in complex multi-subject contexts, native multi-shot narrative coherence with consistent subject representation.
PrePrompt: Predictive prompting for class incremental learning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Class Incremental Learning (CIL) based on pre-trained models offers a promising direction for open-world continual learning. Existing methods typically rely on correlation-based strategies, where an image's classification feature is used as a query to retrieve the most related key prompts and select the corresponding value prompts for training. However, these approaches face an inherent limitation: fitting the entire feature space of all tasks with only a few trainable prompts is fundamentally challenging. We propose Predictive Prompting (PrePrompt), a novel CIL framework that circumvents correlation-based limitations by leveraging pre-trained models' natural classification ability to predict task-specific prompts. Specifically, PrePrompt decomposes CIL into a two-stage prediction framework: task-specific prompt prediction followed by label prediction. While theoretically appealing, this framework risks bias toward recent classes due to missing historical data for older classifier calibration. PrePrompt then mitigates this by incorporating feature translation, dynamically balancing stability and plasticity. Experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate PrePrompt's superiority over state-of-the-art prompt-based CIL methods. The code will be released upon acceptance.
CAST: Component-Aligned 3D Scene Reconstruction from an RGB Image
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recovering high-quality 3D scenes from a single RGB image is a challenging task in computer graphics. Current methods often struggle with domain-specific limitations or low-quality object generation. To address these, we propose CAST (Component-Aligned 3D Scene Reconstruction from a Single RGB Image), a novel method for 3D scene reconstruction and recovery. CAST starts by extracting object-level 2D segmentation and relative depth information from the input image, followed by using a GPT-based model to analyze inter-object spatial relationships. This enables the understanding of how objects relate to each other within the scene, ensuring more coherent reconstruction. CAST then employs an occlusion-aware large-scale 3D generation model to independently generate each object's full geometry, using MAE and point cloud conditioning to mitigate the effects of occlusions and partial object information, ensuring accurate alignment with the source image's geometry and texture. To align each object with the scene, the alignment generation model computes the necessary transformations, allowing the generated meshes to be accurately placed and integrated into the scene's point cloud. Finally, CAST incorporates a physics-aware correction step that leverages a fine-grained relation graph to generate a constraint graph. This graph guides the optimization of object poses, ensuring physical consistency and spatial coherence. By utilizing Signed Distance Fields (SDF), the model effectively addresses issues such as occlusions, object penetration, and floating objects, ensuring that the generated scene accurately reflects real-world physical interactions. CAST can be leveraged in robotics, enabling efficient real-to-simulation workflows and providing realistic, scalable simulation environments for robotic systems.
Learning Counterfactual Outcomes Under Rank Preservation
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Counterfactual inference aims to estimate the counterfactual outcome at the individual level given knowledge of an observed treatment and the factual outcome, with broad applications in fields such as epidemiology, econometrics, and management science. Previous methods rely on a known structural causal model (SCM) or assume the homogeneity of the exogenous variable and strict monotonicity between the outcome and exogenous variable. In this paper, we propose a principled approach for identifying and estimating the counterfactual outcome. We first introduce a simple and intuitive rank preservation assumption to identify the counterfactual outcome without relying on a known structural causal model. Building on this, we propose a novel ideal loss for theoretically unbiased learning of the counterfactual outcome and further develop a kernel-based estimator for its empirical estimation. Our theoretical analysis shows that the rank preservation assumption is not stronger than the homogeneity and strict monotonicity assumptions, and shows that the proposed ideal loss is convex, and the proposed estimator is unbiased. Extensive semi-synthetic and real-world experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Accelerating Discovery in Natural Science Laboratories with AI and Robotics: Perspectives and Challenges from the 2024 IEEE ICRA Workshop, Yokohama, Japan
Jan 12, 2025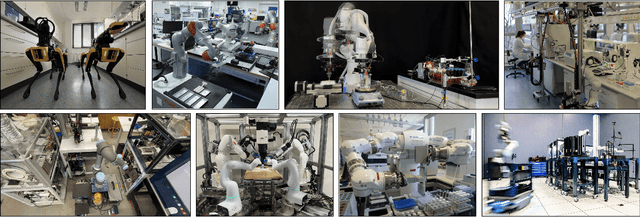
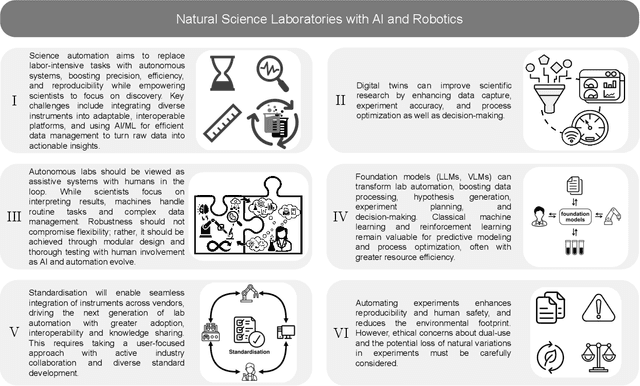
Abstract:Science laboratory automation enables accelerated discovery in life sciences and materials. However, it requires interdisciplinary collaboration to address challenges such as robust and flexible autonomy, reproducibility, throughput, standardization, the role of human scientists, and ethics. This article highlights these issues, reflecting perspectives from leading experts in laboratory automation across different disciplines of the natural sciences.
Leveraging Multimodal Protein Representations to Predict Protein Melting Temperatures
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Accurately predicting protein melting temperature changes (Delta Tm) is fundamental for assessing protein stability and guiding protein engineering. Leveraging multi-modal protein representations has shown great promise in capturing the complex relationships among protein sequences, structures, and functions. In this study, we develop models based on powerful protein language models, including ESM-2, ESM-3, SaProt, and AlphaFold, using various feature extraction methods to enhance prediction accuracy. By utilizing the ESM-3 model, we achieve a new state-of-the-art performance on the s571 test dataset, obtaining a Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) of 0.50. Furthermore, we conduct a fair evaluation to compare the performance of different protein language models in the Delta Tm prediction task. Our results demonstrate that integrating multi-modal protein representations could advance the prediction of protein melting temperatures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge