Jiashi Li
mHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Recently, studies exemplified by Hyper-Connections (HC) have extended the ubiquitous residual connection paradigm established over the past decade by expanding the residual stream width and diversifying connectivity patterns. While yielding substantial performance gains, this diversification fundamentally compromises the identity mapping property intrinsic to the residual connection, which causes severe training instability and restricted scalability, and additionally incurs notable memory access overhead. To address these challenges, we propose Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections (mHC), a general framework that projects the residual connection space of HC onto a specific manifold to restore the identity mapping property, while incorporating rigorous infrastructure optimization to ensure efficiency. Empirical experiments demonstrate that mHC is effective for training at scale, offering tangible performance improvements and superior scalability. We anticipate that mHC, as a flexible and practical extension of HC, will contribute to a deeper understanding of topological architecture design and suggest promising directions for the evolution of foundational models.
Seedance 1.0: Exploring the Boundaries of Video Generation Models
Jun 10, 2025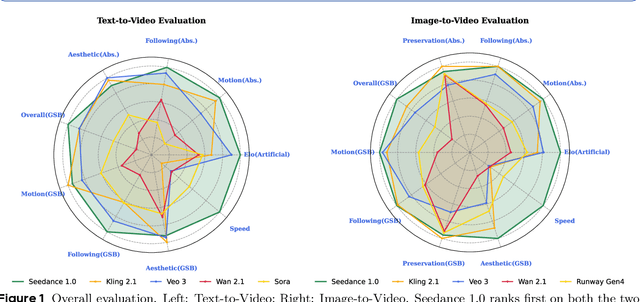
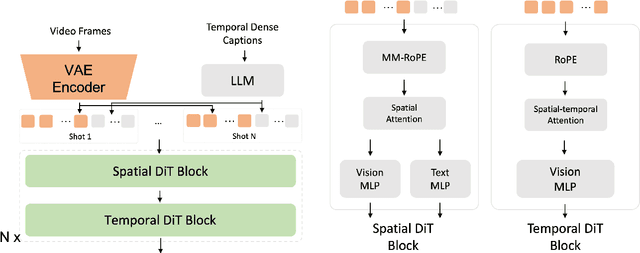
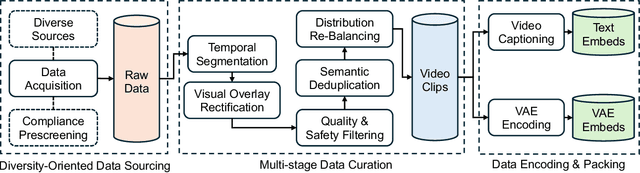
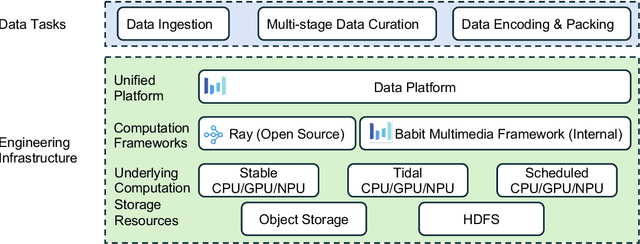
Abstract:Notable breakthroughs in diffusion modeling have propelled rapid improvements in video generation, yet current foundational model still face critical challenges in simultaneously balancing prompt following, motion plausibility, and visual quality. In this report, we introduce Seedance 1.0, a high-performance and inference-efficient video foundation generation model that integrates several core technical improvements: (i) multi-source data curation augmented with precision and meaningful video captioning, enabling comprehensive learning across diverse scenarios; (ii) an efficient architecture design with proposed training paradigm, which allows for natively supporting multi-shot generation and jointly learning of both text-to-video and image-to-video tasks. (iii) carefully-optimized post-training approaches leveraging fine-grained supervised fine-tuning, and video-specific RLHF with multi-dimensional reward mechanisms for comprehensive performance improvements; (iv) excellent model acceleration achieving ~10x inference speedup through multi-stage distillation strategies and system-level optimizations. Seedance 1.0 can generate a 5-second video at 1080p resolution only with 41.4 seconds (NVIDIA-L20). Compared to state-of-the-art video generation models, Seedance 1.0 stands out with high-quality and fast video generation having superior spatiotemporal fluidity with structural stability, precise instruction adherence in complex multi-subject contexts, native multi-shot narrative coherence with consistent subject representation.
Insights into DeepSeek-V3: Scaling Challenges and Reflections on Hardware for AI Architectures
May 14, 2025
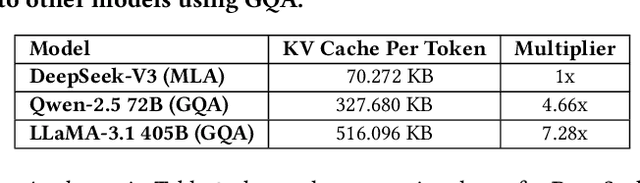
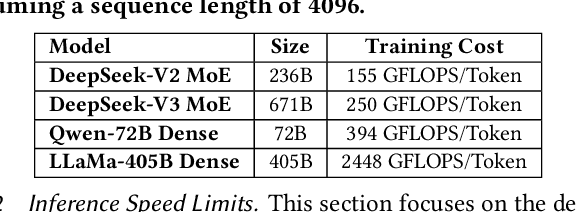
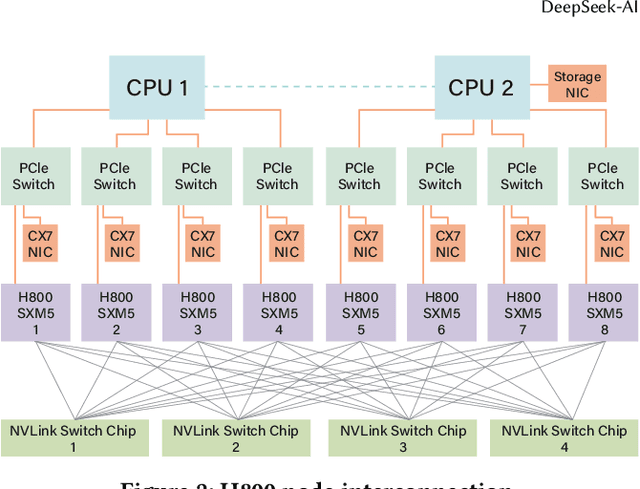
Abstract:The rapid scaling of large language models (LLMs) has unveiled critical limitations in current hardware architectures, including constraints in memory capacity, computational efficiency, and interconnection bandwidth. DeepSeek-V3, trained on 2,048 NVIDIA H800 GPUs, demonstrates how hardware-aware model co-design can effectively address these challenges, enabling cost-efficient training and inference at scale. This paper presents an in-depth analysis of the DeepSeek-V3/R1 model architecture and its AI infrastructure, highlighting key innovations such as Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) for enhanced memory efficiency, Mixture of Experts (MoE) architectures for optimized computation-communication trade-offs, FP8 mixed-precision training to unlock the full potential of hardware capabilities, and a Multi-Plane Network Topology to minimize cluster-level network overhead. Building on the hardware bottlenecks encountered during DeepSeek-V3's development, we engage in a broader discussion with academic and industry peers on potential future hardware directions, including precise low-precision computation units, scale-up and scale-out convergence, and innovations in low-latency communication fabrics. These insights underscore the critical role of hardware and model co-design in meeting the escalating demands of AI workloads, offering a practical blueprint for innovation in next-generation AI systems.
Seaweed-7B: Cost-Effective Training of Video Generation Foundation Model
Apr 11, 2025
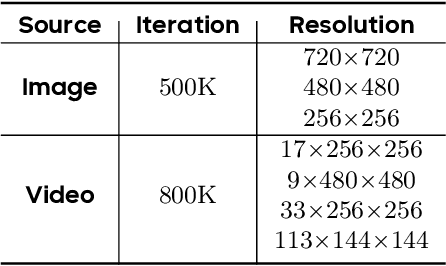

Abstract:This technical report presents a cost-efficient strategy for training a video generation foundation model. We present a mid-sized research model with approximately 7 billion parameters (7B) called Seaweed-7B trained from scratch using 665,000 H100 GPU hours. Despite being trained with moderate computational resources, Seaweed-7B demonstrates highly competitive performance compared to contemporary video generation models of much larger size. Design choices are especially crucial in a resource-constrained setting. This technical report highlights the key design decisions that enhance the performance of the medium-sized diffusion model. Empirically, we make two observations: (1) Seaweed-7B achieves performance comparable to, or even surpasses, larger models trained on substantially greater GPU resources, and (2) our model, which exhibits strong generalization ability, can be effectively adapted across a wide range of downstream applications either by lightweight fine-tuning or continue training. See the project page at https://seaweed.video/
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
Data-Centric and Heterogeneity-Adaptive Sequence Parallelism for Efficient LLM Training
Dec 02, 2024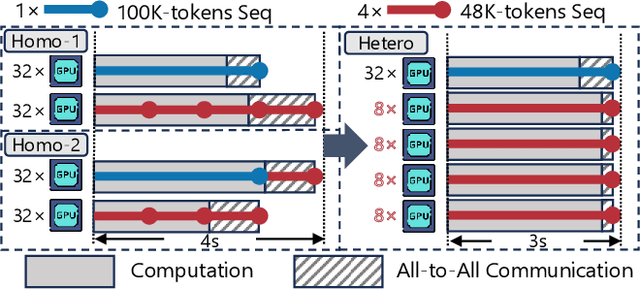
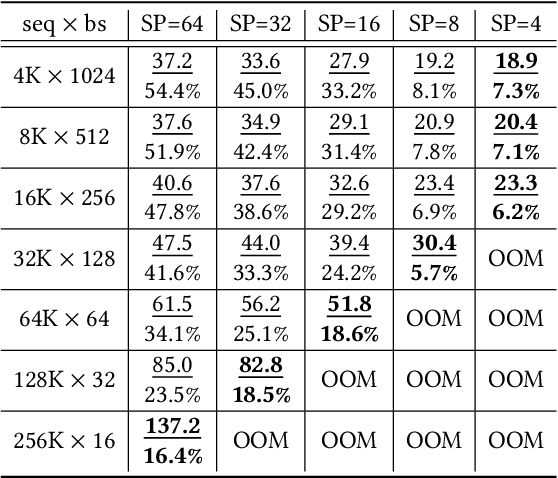
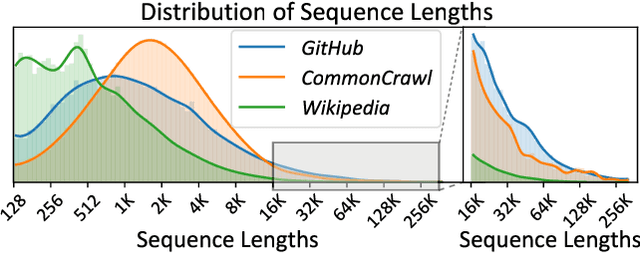
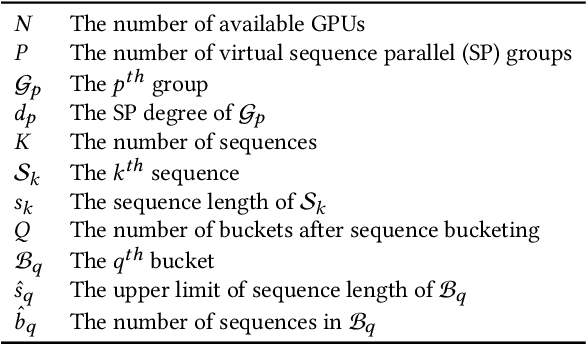
Abstract:Extending the context length (i.e., the maximum supported sequence length) of LLMs is of paramount significance. To facilitate long context training of LLMs, sequence parallelism has emerged as an essential technique, which scatters each input sequence across multiple devices and necessitates communication to process the sequence. In essence, existing sequence parallelism methods assume homogeneous sequence lengths (i.e., all input sequences are equal in length) and therefore leverages a single, static scattering strategy for all input sequences. However, in reality, the sequence lengths in LLM training corpora exhibit substantial variability, often following a long-tail distribution, which leads to workload heterogeneity. In this paper, we show that employing a single, static strategy results in inefficiency and resource under-utilization, highlighting the need for adaptive approaches to handle the heterogeneous workloads across sequences. To address this, we propose a heterogeneity-adaptive sequence parallelism method. For each training step, our approach captures the variability in sequence lengths and assigns the optimal combination of scattering strategies based on workload characteristics. We model this problem as a linear programming optimization and design an efficient and effective solver to find the optimal solution. Furthermore, we implement our method in a high-performance system that supports adaptive parallelization in distributed LLM training. Experimental results demonstrate that our system outperforms state-of-the-art training frameworks by up to 1.98x.
Fire-Flyer AI-HPC: A Cost-Effective Software-Hardware Co-Design for Deep Learning
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:The rapid progress in Deep Learning (DL) and Large Language Models (LLMs) has exponentially increased demands of computational power and bandwidth. This, combined with the high costs of faster computing chips and interconnects, has significantly inflated High Performance Computing (HPC) construction costs. To address these challenges, we introduce the Fire-Flyer AI-HPC architecture, a synergistic hardware-software co-design framework and its best practices. For DL training, we deployed the Fire-Flyer 2 with 10,000 PCIe A100 GPUs, achieved performance approximating the DGX-A100 while reducing costs by half and energy consumption by 40%. We specifically engineered HFReduce to accelerate allreduce communication and implemented numerous measures to keep our Computation-Storage Integrated Network congestion-free. Through our software stack, including HaiScale, 3FS, and HAI-Platform, we achieved substantial scalability by overlapping computation and communication. Our system-oriented experience from DL training provides valuable insights to drive future advancements in AI-HPC.
DeepSeek-Coder-V2: Breaking the Barrier of Closed-Source Models in Code Intelligence
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-Coder-V2, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) code language model that achieves performance comparable to GPT4-Turbo in code-specific tasks. Specifically, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 is further pre-trained from an intermediate checkpoint of DeepSeek-V2 with additional 6 trillion tokens. Through this continued pre-training, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 substantially enhances the coding and mathematical reasoning capabilities of DeepSeek-V2, while maintaining comparable performance in general language tasks. Compared to DeepSeek-Coder-33B, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 demonstrates significant advancements in various aspects of code-related tasks, as well as reasoning and general capabilities. Additionally, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 expands its support for programming languages from 86 to 338, while extending the context length from 16K to 128K. In standard benchmark evaluations, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 achieves superior performance compared to closed-source models such as GPT4-Turbo, Claude 3 Opus, and Gemini 1.5 Pro in coding and math benchmarks.
UniFL: Improve Stable Diffusion via Unified Feedback Learning
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have revolutionized the field of image generation, leading to the proliferation of high-quality models and diverse downstream applications. However, despite these significant advancements, the current competitive solutions still suffer from several limitations, including inferior visual quality, a lack of aesthetic appeal, and inefficient inference, without a comprehensive solution in sight. To address these challenges, we present UniFL, a unified framework that leverages feedback learning to enhance diffusion models comprehensively. UniFL stands out as a universal, effective, and generalizable solution applicable to various diffusion models, such as SD1.5 and SDXL. Notably, UniFL incorporates three key components: perceptual feedback learning, which enhances visual quality; decoupled feedback learning, which improves aesthetic appeal; and adversarial feedback learning, which optimizes inference speed. In-depth experiments and extensive user studies validate the superior performance of our proposed method in enhancing both the quality of generated models and their acceleration. For instance, UniFL surpasses ImageReward by 17% user preference in terms of generation quality and outperforms LCM and SDXL Turbo by 57% and 20% in 4-step inference. Moreover, we have verified the efficacy of our approach in downstream tasks, including Lora, ControlNet, and AnimateDiff.
ResAdapter: Domain Consistent Resolution Adapter for Diffusion Models
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancement in text-to-image models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) and corresponding personalized technologies (e.g., DreamBooth and LoRA) enables individuals to generate high-quality and imaginative images. However, they often suffer from limitations when generating images with resolutions outside of their trained domain. To overcome this limitation, we present the Resolution Adapter (ResAdapter), a domain-consistent adapter designed for diffusion models to generate images with unrestricted resolutions and aspect ratios. Unlike other multi-resolution generation methods that process images of static resolution with complex post-process operations, ResAdapter directly generates images with the dynamical resolution. Especially, after learning a deep understanding of pure resolution priors, ResAdapter trained on the general dataset, generates resolution-free images with personalized diffusion models while preserving their original style domain. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that ResAdapter with only 0.5M can process images with flexible resolutions for arbitrary diffusion models. More extended experiments demonstrate that ResAdapter is compatible with other modules (e.g., ControlNet, IP-Adapter and LCM-LoRA) for image generation across a broad range of resolutions, and can be integrated into other multi-resolution model (e.g., ElasticDiffusion) for efficiently generating higher-resolution images. Project link is https://res-adapter.github.io
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge