Daya Guo
AlignCoder: Aligning Retrieval with Target Intent for Repository-Level Code Completion
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Repository-level code completion remains a challenging task for existing code large language models (code LLMs) due to their limited understanding of repository-specific context and domain knowledge. While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approaches have shown promise by retrieving relevant code snippets as cross-file context, they suffer from two fundamental problems: misalignment between the query and the target code in the retrieval process, and the inability of existing retrieval methods to effectively utilize the inference information. To address these challenges, we propose AlignCoder, a repository-level code completion framework that introduces a query enhancement mechanism and a reinforcement learning based retriever training method. Our approach generates multiple candidate completions to construct an enhanced query that bridges the semantic gap between the initial query and the target code. Additionally, we employ reinforcement learning to train an AlignRetriever that learns to leverage inference information in the enhanced query for more accurate retrieval. We evaluate AlignCoder on two widely-used benchmarks (CrossCodeEval and RepoEval) across five backbone code LLMs, demonstrating an 18.1% improvement in EM score compared to baselines on the CrossCodeEval benchmark. The results show that our framework achieves superior performance and exhibits high generalizability across various code LLMs and programming languages.
Advances and Frontiers of LLM-based Issue Resolution in Software Engineering: A Comprehensive Survey
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Issue resolution, a complex Software Engineering (SWE) task integral to real-world development, has emerged as a compelling challenge for artificial intelligence. The establishment of benchmarks like SWE-bench revealed this task as profoundly difficult for large language models, thereby significantly accelerating the evolution of autonomous coding agents. This paper presents a systematic survey of this emerging domain. We begin by examining data construction pipelines, covering automated collection and synthesis approaches. We then provide a comprehensive analysis of methodologies, spanning training-free frameworks with their modular components to training-based techniques, including supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. Subsequently, we discuss critical analyses of data quality and agent behavior, alongside practical applications. Finally, we identify key challenges and outline promising directions for future research. An open-source repository is maintained at https://github.com/DeepSoftwareAnalytics/Awesome-Issue-Resolution to serve as a dynamic resource in this field.
DeepSeek-Prover-V2: Advancing Formal Mathematical Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning for Subgoal Decomposition
Apr 30, 2025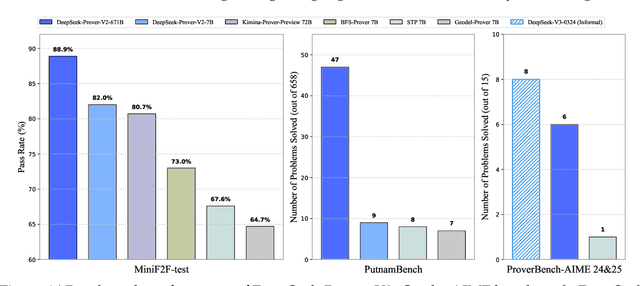
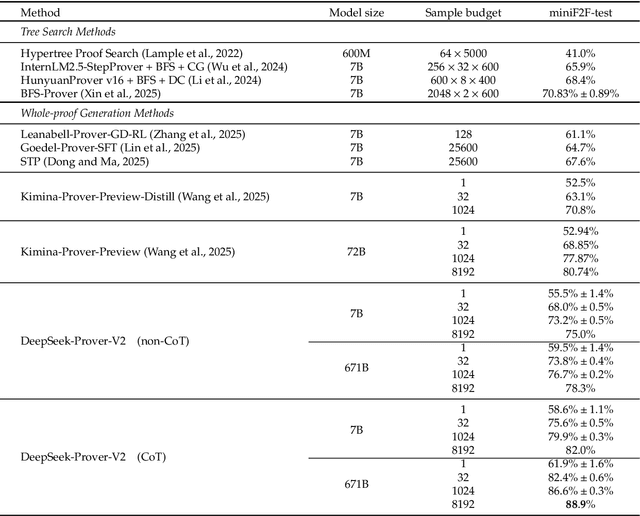

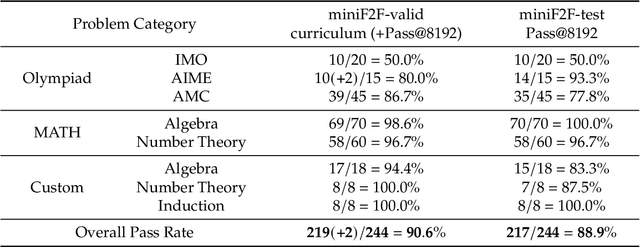
Abstract:We introduce DeepSeek-Prover-V2, an open-source large language model designed for formal theorem proving in Lean 4, with initialization data collected through a recursive theorem proving pipeline powered by DeepSeek-V3. The cold-start training procedure begins by prompting DeepSeek-V3 to decompose complex problems into a series of subgoals. The proofs of resolved subgoals are synthesized into a chain-of-thought process, combined with DeepSeek-V3's step-by-step reasoning, to create an initial cold start for reinforcement learning. This process enables us to integrate both informal and formal mathematical reasoning into a unified model. The resulting model, DeepSeek-Prover-V2-671B, achieves state-of-the-art performance in neural theorem proving, reaching 88.9% pass ratio on the MiniF2F-test and solving 49 out of 658 problems from PutnamBench. In addition to standard benchmarks, we introduce ProverBench, a collection of 325 formalized problems, to enrich our evaluation, including 15 selected problems from the recent AIME competitions (years 24-25). Further evaluation on these 15 AIME problems shows that the model successfully solves 6 of them. In comparison, DeepSeek-V3 solves 8 of these problems using majority voting, highlighting that the gap between formal and informal mathematical reasoning in large language models is substantially narrowing.
CodeI/O: Condensing Reasoning Patterns via Code Input-Output Prediction
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Reasoning is a fundamental capability of Large Language Models. While prior research predominantly focuses on enhancing narrow skills like math or code generation, improving performance on many other reasoning tasks remains challenging due to sparse and fragmented training data. To address this issue, we propose CodeI/O, a novel approach that systematically condenses diverse reasoning patterns inherently embedded in contextually-grounded codes, through transforming the original code into a code input-output prediction format. By training models to predict inputs/outputs given code and test cases entirely in natural language as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationales, we expose them to universal reasoning primitives -- like logic flow planning, state-space searching, decision tree traversal, and modular decomposition -- while decoupling structured reasoning from code-specific syntax and preserving procedural rigor. Experimental results demonstrate CodeI/O leads to consistent improvements across symbolic, scientific, logic, math & numerical, and commonsense reasoning tasks. By matching the existing ground-truth outputs or re-executing the code with predicted inputs, we can verify each prediction and further enhance the CoTs through multi-turn revision, resulting in CodeI/O++ and achieving higher performance. Our data and models are available at https://github.com/hkust-nlp/CodeIO.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
RepoTransBench: A Real-World Benchmark for Repository-Level Code Translation
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Repository-level code translation refers to translating an entire code repository from one programming language to another while preserving the functionality of the source repository. Many benchmarks have been proposed to evaluate the performance of such code translators. However, previous benchmarks mostly provide fine-grained samples, focusing at either code snippet, function, or file-level code translation. Such benchmarks do not accurately reflect real-world demands, where entire repositories often need to be translated, involving longer code length and more complex functionalities. To address this gap, we propose a new benchmark, named RepoTransBench, which is a real-world repository-level code translation benchmark with an automatically executable test suite. We conduct experiments on RepoTransBench to evaluate the translation performance of 11 advanced LLMs. We find that the Success@1 score (test success in one attempt) of the best-performing LLM is only 7.33%. To further explore the potential of LLMs for repository-level code translation, we provide LLMs with error-related feedback to perform iterative debugging and observe an average 7.09% improvement on Success@1. However, even with this improvement, the Success@1 score of the best-performing LLM is only 21%, which may not meet the need for reliable automatic repository-level code translation. Finally, we conduct a detailed error analysis and highlight current LLMs' deficiencies in repository-level code translation, which could provide a reference for further improvements.
DeepSeek-Coder-V2: Breaking the Barrier of Closed-Source Models in Code Intelligence
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-Coder-V2, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) code language model that achieves performance comparable to GPT4-Turbo in code-specific tasks. Specifically, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 is further pre-trained from an intermediate checkpoint of DeepSeek-V2 with additional 6 trillion tokens. Through this continued pre-training, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 substantially enhances the coding and mathematical reasoning capabilities of DeepSeek-V2, while maintaining comparable performance in general language tasks. Compared to DeepSeek-Coder-33B, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 demonstrates significant advancements in various aspects of code-related tasks, as well as reasoning and general capabilities. Additionally, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 expands its support for programming languages from 86 to 338, while extending the context length from 16K to 128K. In standard benchmark evaluations, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 achieves superior performance compared to closed-source models such as GPT4-Turbo, Claude 3 Opus, and Gemini 1.5 Pro in coding and math benchmarks.
DeepSeek-Prover: Advancing Theorem Proving in LLMs through Large-Scale Synthetic Data
May 23, 2024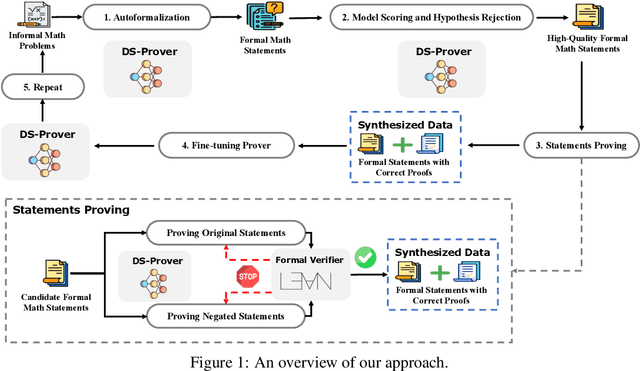



Abstract:Proof assistants like Lean have revolutionized mathematical proof verification, ensuring high accuracy and reliability. Although large language models (LLMs) show promise in mathematical reasoning, their advancement in formal theorem proving is hindered by a lack of training data. To address this issue, we introduce an approach to generate extensive Lean 4 proof data derived from high-school and undergraduate-level mathematical competition problems. This approach involves translating natural language problems into formal statements, filtering out low-quality statements, and generating proofs to create synthetic data. After fine-tuning the DeepSeekMath 7B model on this synthetic dataset, which comprises 8 million formal statements with proofs, our model achieved whole-proof generation accuracies of 46.3% with 64 samples and 52% cumulatively on the Lean 4 miniF2F test, surpassing the baseline GPT-4 at 23.0% with 64 samples and a tree search reinforcement learning method at 41.0%. Additionally, our model successfully proved 5 out of 148 problems in the Lean 4 Formalized International Mathematical Olympiad (FIMO) benchmark, while GPT-4 failed to prove any. These results demonstrate the potential of leveraging large-scale synthetic data to enhance theorem-proving capabilities in LLMs. Both the synthetic dataset and the model will be made available to facilitate further research in this promising field.
DeepSeekMath: Pushing the Limits of Mathematical Reasoning in Open Language Models
Feb 06, 2024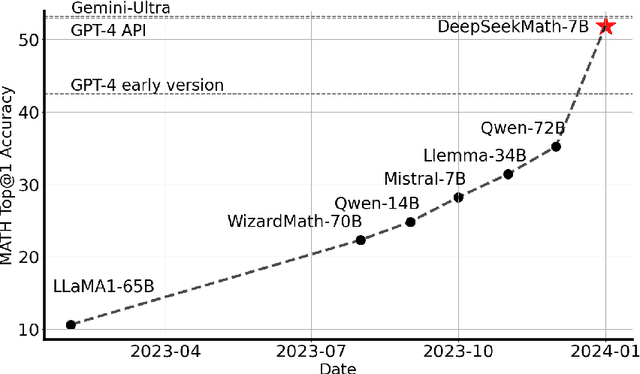
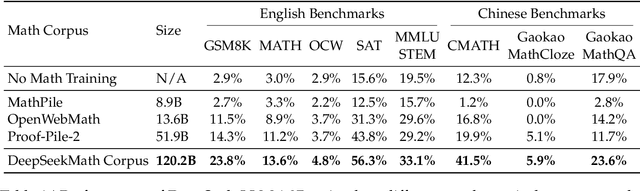
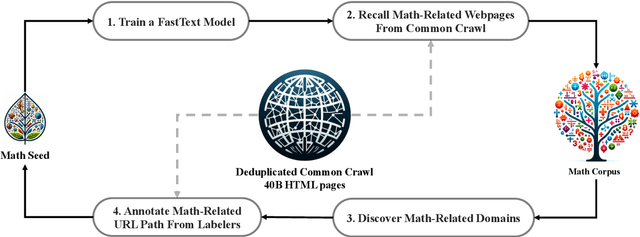
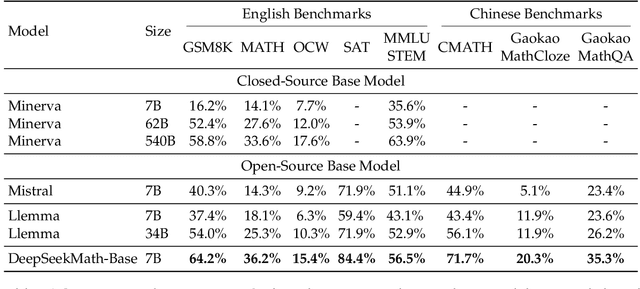
Abstract:Mathematical reasoning poses a significant challenge for language models due to its complex and structured nature. In this paper, we introduce DeepSeekMath 7B, which continues pre-training DeepSeek-Coder-Base-v1.5 7B with 120B math-related tokens sourced from Common Crawl, together with natural language and code data. DeepSeekMath 7B has achieved an impressive score of 51.7% on the competition-level MATH benchmark without relying on external toolkits and voting techniques, approaching the performance level of Gemini-Ultra and GPT-4. Self-consistency over 64 samples from DeepSeekMath 7B achieves 60.9% on MATH. The mathematical reasoning capability of DeepSeekMath is attributed to two key factors: First, we harness the significant potential of publicly available web data through a meticulously engineered data selection pipeline. Second, we introduce Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), a variant of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), that enhances mathematical reasoning abilities while concurrently optimizing the memory usage of PPO.
DeepSeek-Coder: When the Large Language Model Meets Programming -- The Rise of Code Intelligence
Jan 26, 2024



Abstract:The rapid development of large language models has revolutionized code intelligence in software development. However, the predominance of closed-source models has restricted extensive research and development. To address this, we introduce the DeepSeek-Coder series, a range of open-source code models with sizes from 1.3B to 33B, trained from scratch on 2 trillion tokens. These models are pre-trained on a high-quality project-level code corpus and employ a fill-in-the-blank task with a 16K window to enhance code generation and infilling. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate that DeepSeek-Coder not only achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source code models across multiple benchmarks but also surpasses existing closed-source models like Codex and GPT-3.5. Furthermore, DeepSeek-Coder models are under a permissive license that allows for both research and unrestricted commercial use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge