Jiachi Chen
AlignCoder: Aligning Retrieval with Target Intent for Repository-Level Code Completion
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Repository-level code completion remains a challenging task for existing code large language models (code LLMs) due to their limited understanding of repository-specific context and domain knowledge. While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approaches have shown promise by retrieving relevant code snippets as cross-file context, they suffer from two fundamental problems: misalignment between the query and the target code in the retrieval process, and the inability of existing retrieval methods to effectively utilize the inference information. To address these challenges, we propose AlignCoder, a repository-level code completion framework that introduces a query enhancement mechanism and a reinforcement learning based retriever training method. Our approach generates multiple candidate completions to construct an enhanced query that bridges the semantic gap between the initial query and the target code. Additionally, we employ reinforcement learning to train an AlignRetriever that learns to leverage inference information in the enhanced query for more accurate retrieval. We evaluate AlignCoder on two widely-used benchmarks (CrossCodeEval and RepoEval) across five backbone code LLMs, demonstrating an 18.1% improvement in EM score compared to baselines on the CrossCodeEval benchmark. The results show that our framework achieves superior performance and exhibits high generalizability across various code LLMs and programming languages.
Advances and Frontiers of LLM-based Issue Resolution in Software Engineering: A Comprehensive Survey
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Issue resolution, a complex Software Engineering (SWE) task integral to real-world development, has emerged as a compelling challenge for artificial intelligence. The establishment of benchmarks like SWE-bench revealed this task as profoundly difficult for large language models, thereby significantly accelerating the evolution of autonomous coding agents. This paper presents a systematic survey of this emerging domain. We begin by examining data construction pipelines, covering automated collection and synthesis approaches. We then provide a comprehensive analysis of methodologies, spanning training-free frameworks with their modular components to training-based techniques, including supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. Subsequently, we discuss critical analyses of data quality and agent behavior, alongside practical applications. Finally, we identify key challenges and outline promising directions for future research. An open-source repository is maintained at https://github.com/DeepSoftwareAnalytics/Awesome-Issue-Resolution to serve as a dynamic resource in this field.
ShortCoder: Knowledge-Augmented Syntax Optimization for Token-Efficient Code Generation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Code generation tasks aim to automate the conversion of user requirements into executable code, significantly reducing manual development efforts and enhancing software productivity. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has significantly advanced code generation, though their efficiency is still impacted by certain inherent architectural constraints. Each token generation necessitates a complete inference pass, requiring persistent retention of contextual information in memory and escalating resource consumption. While existing research prioritizes inference-phase optimizations such as prompt compression and model quantization, the generation phase remains underexplored. To tackle these challenges, we propose a knowledge-infused framework named ShortCoder, which optimizes code generation efficiency while preserving semantic equivalence and readability. In particular, we introduce: (1) ten syntax-level simplification rules for Python, derived from AST-preserving transformations, achieving 18.1% token reduction without functional compromise; (2) a hybrid data synthesis pipeline integrating rule-based rewriting with LLM-guided refinement, producing ShorterCodeBench, a corpus of validated tuples of original code and simplified code with semantic consistency; (3) a fine-tuning strategy that injects conciseness awareness into the base LLMs. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that ShortCoder consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on HumanEval, achieving an improvement of 18.1%-37.8% in generation efficiency over previous methods while ensuring the performance of code generation.
SWE-Factory: Your Automated Factory for Issue Resolution Training Data and Evaluation Benchmarks
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Constructing large-scale datasets for the GitHub issue resolution task is crucial for both training and evaluating the software engineering capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the traditional process for creating such benchmarks is notoriously challenging and labor-intensive, particularly in the stages of setting up evaluation environments, grading test outcomes, and validating task instances. In this paper, we propose SWE-Factory, an automated pipeline designed to address these challenges. To tackle these issues, our pipeline integrates three core automated components. First, we introduce SWE-Builder, a multi-agent system that automates evaluation environment construction, which employs four specialized agents that work in a collaborative, iterative loop and leverages an environment memory pool to enhance efficiency. Second, we introduce a standardized, exit-code-based grading method that eliminates the need for manually writing custom parsers. Finally, we automate the fail2pass validation process using these reliable exit code signals. Experiments on 671 issues across four programming languages show that our pipeline can effectively construct valid task instances; for example, with GPT-4.1-mini, our SWE-Builder constructs 269 valid instances at $0.045 per instance, while with Gemini-2.5-flash, it achieves comparable performance at the lowest cost of $0.024 per instance. We also demonstrate that our exit-code-based grading achieves 100% accuracy compared to manual inspection, and our automated fail2pass validation reaches a precision of 0.92 and a recall of 1.00. We hope our automated pipeline will accelerate the collection of large-scale, high-quality GitHub issue resolution datasets for both training and evaluation. Our code and datasets are released at https://github.com/DeepSoftwareAnalytics/swe-factory.
Towards an Understanding of Context Utilization in Code Intelligence
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Code intelligence is an emerging domain in software engineering, aiming to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of various code-related tasks. Recent research suggests that incorporating contextual information beyond the basic original task inputs (i.e., source code) can substantially enhance model performance. Such contextual signals may be obtained directly or indirectly from sources such as API documentation or intermediate representations like abstract syntax trees can significantly improve the effectiveness of code intelligence. Despite growing academic interest, there is a lack of systematic analysis of context in code intelligence. To address this gap, we conduct an extensive literature review of 146 relevant studies published between September 2007 and August 2024. Our investigation yields four main contributions. (1) A quantitative analysis of the research landscape, including publication trends, venues, and the explored domains; (2) A novel taxonomy of context types used in code intelligence; (3) A task-oriented analysis investigating context integration strategies across diverse code intelligence tasks; (4) A critical evaluation of evaluation methodologies for context-aware methods. Based on these findings, we identify fundamental challenges in context utilization in current code intelligence systems and propose a research roadmap that outlines key opportunities for future research.
RepoTransBench: A Real-World Benchmark for Repository-Level Code Translation
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Repository-level code translation refers to translating an entire code repository from one programming language to another while preserving the functionality of the source repository. Many benchmarks have been proposed to evaluate the performance of such code translators. However, previous benchmarks mostly provide fine-grained samples, focusing at either code snippet, function, or file-level code translation. Such benchmarks do not accurately reflect real-world demands, where entire repositories often need to be translated, involving longer code length and more complex functionalities. To address this gap, we propose a new benchmark, named RepoTransBench, which is a real-world repository-level code translation benchmark with an automatically executable test suite. We conduct experiments on RepoTransBench to evaluate the translation performance of 11 advanced LLMs. We find that the Success@1 score (test success in one attempt) of the best-performing LLM is only 7.33%. To further explore the potential of LLMs for repository-level code translation, we provide LLMs with error-related feedback to perform iterative debugging and observe an average 7.09% improvement on Success@1. However, even with this improvement, the Success@1 score of the best-performing LLM is only 21%, which may not meet the need for reliable automatic repository-level code translation. Finally, we conduct a detailed error analysis and highlight current LLMs' deficiencies in repository-level code translation, which could provide a reference for further improvements.
LLM Hallucinations in Practical Code Generation: Phenomena, Mechanism, and Mitigation
Sep 30, 2024
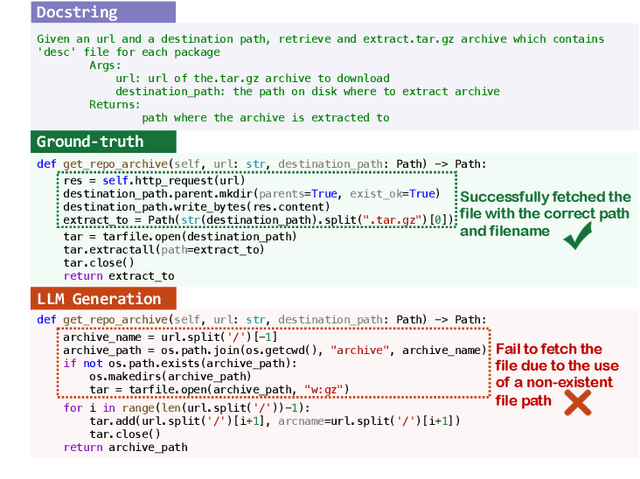
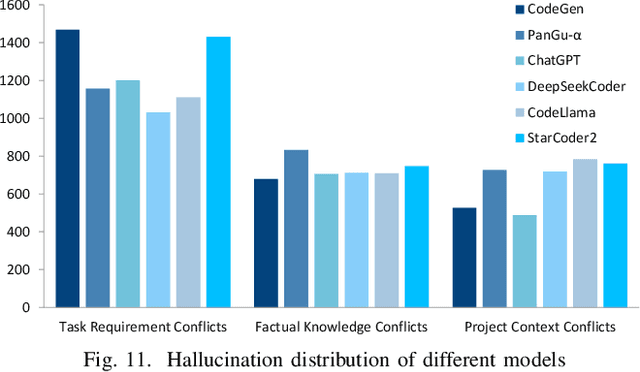
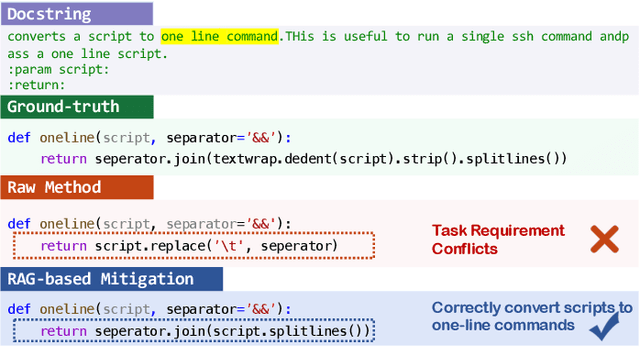
Abstract:Code generation aims to automatically generate code from input requirements, significantly enhancing development efficiency. Recent large language models (LLMs) based approaches have shown promising results and revolutionized code generation task. Despite the promising performance, LLMs often generate contents with hallucinations, especially for the code generation scenario requiring the handling of complex contextual dependencies in practical development process. Although previous study has analyzed hallucinations in LLM-powered code generation, the study is limited to standalone function generation. In this paper, we conduct an empirical study to study the phenomena, mechanism, and mitigation of LLM hallucinations within more practical and complex development contexts in repository-level generation scenario. First, we manually examine the code generation results from six mainstream LLMs to establish a hallucination taxonomy of LLM-generated code. Next, we elaborate on the phenomenon of hallucinations, analyze their distribution across different models. We then analyze causes of hallucinations and identify four potential factors contributing to hallucinations. Finally, we propose an RAG-based mitigation method, which demonstrates consistent effectiveness in all studied LLMs. The replication package including code, data, and experimental results is available at https://github.com/DeepSoftwareAnalytics/LLMCodingHallucination
Agents in Software Engineering: Survey, Landscape, and Vision
Sep 13, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success and have been widely used in various downstream tasks, especially in the tasks of the software engineering (SE) field. We find that many studies combining LLMs with SE have employed the concept of agents either explicitly or implicitly. However, there is a lack of an in-depth survey to sort out the development context of existing works, analyze how existing works combine the LLM-based agent technologies to optimize various tasks, and clarify the framework of LLM-based agents in SE. In this paper, we conduct the first survey of the studies on combining LLM-based agents with SE and present a framework of LLM-based agents in SE which includes three key modules: perception, memory, and action. We also summarize the current challenges in combining the two fields and propose future opportunities in response to existing challenges. We maintain a GitHub repository of the related papers at: https://github.com/DeepSoftwareAnalytics/Awesome-Agent4SE.
Beyond Functional Correctness: Investigating Coding Style Inconsistencies in Large Language Models
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have brought a paradigm shift to the field of code generation, offering the potential to enhance the software development process. However, previous research mainly focuses on the accuracy of code generation, while coding style differences between LLMs and human developers remain under-explored. In this paper, we empirically analyze the differences in coding style between the code generated by mainstream Code LLMs and the code written by human developers, and summarize coding style inconsistency taxonomy. Specifically, we first summarize the types of coding style inconsistencies by manually analyzing a large number of generation results. We then compare the code generated by Code LLMs with the code written by human programmers in terms of readability, conciseness, and robustness. The results reveal that LLMs and developers have different coding styles. Additionally, we study the possible causes of these inconsistencies and provide some solutions to alleviate the problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge