Lu Qi
SAMTok: Representing Any Mask with Two Words
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Pixel-wise capabilities are essential for building interactive intelligent systems. However, pixel-wise multi-modal LLMs (MLLMs) remain difficult to scale due to complex region-level encoders, specialized segmentation decoders, and incompatible training objectives. To address these challenges, we present SAMTok, a discrete mask tokenizer that converts any region mask into two special tokens and reconstructs the mask using these tokens with high fidelity. By treating masks as new language tokens, SAMTok enables base MLLMs (such as the QwenVL series) to learn pixel-wise capabilities through standard next-token prediction and simple reinforcement learning, without architectural modifications and specialized loss design. SAMTok builds on SAM2 and is trained on 209M diverse masks using a mask encoder and residual vector quantizer to produce discrete, compact, and information-rich tokens. With 5M SAMTok-formatted mask understanding and generation data samples, QwenVL-SAMTok attains state-of-the-art or comparable results on region captioning, region VQA, grounded conversation, referring segmentation, scene graph parsing, and multi-round interactive segmentation. We further introduce a textual answer-matching reward that enables efficient reinforcement learning for mask generation, delivering substantial improvements on GRES and GCG benchmarks. Our results demonstrate a scalable and straightforward paradigm for equipping MLLMs with strong pixel-wise capabilities. Our code and models are available.
Depth Any Panoramas: A Foundation Model for Panoramic Depth Estimation
Dec 18, 2025
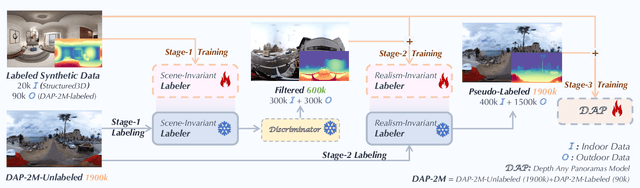

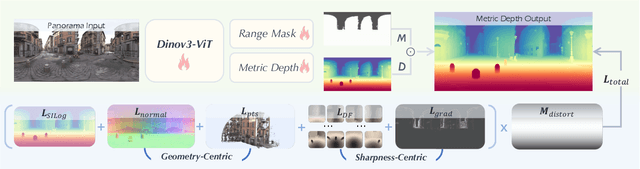
Abstract:In this work, we present a panoramic metric depth foundation model that generalizes across diverse scene distances. We explore a data-in-the-loop paradigm from the view of both data construction and framework design. We collect a large-scale dataset by combining public datasets, high-quality synthetic data from our UE5 simulator and text-to-image models, and real panoramic images from the web. To reduce domain gaps between indoor/outdoor and synthetic/real data, we introduce a three-stage pseudo-label curation pipeline to generate reliable ground truth for unlabeled images. For the model, we adopt DINOv3-Large as the backbone for its strong pre-trained generalization, and introduce a plug-and-play range mask head, sharpness-centric optimization, and geometry-centric optimization to improve robustness to varying distances and enforce geometric consistency across views. Experiments on multiple benchmarks (e.g., Stanford2D3D, Matterport3D, and Deep360) demonstrate strong performance and zero-shot generalization, with particularly robust and stable metric predictions in diverse real-world scenes. The project page can be found at: \href{https://insta360-research-team.github.io/DAP_website/} {https://insta360-research-team.github.io/DAP\_website/}
Seg-VAR: Image Segmentation with Visual Autoregressive Modeling
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:While visual autoregressive modeling (VAR) strategies have shed light on image generation with the autoregressive models, their potential for segmentation, a task that requires precise low-level spatial perception, remains unexplored. Inspired by the multi-scale modeling of classic Mask2Former-based models, we propose Seg-VAR, a novel framework that rethinks segmentation as a conditional autoregressive mask generation problem. This is achieved by replacing the discriminative learning with the latent learning process. Specifically, our method incorporates three core components: (1) an image encoder generating latent priors from input images, (2) a spatial-aware seglat (a latent expression of segmentation mask) encoder that maps segmentation masks into discrete latent tokens using a location-sensitive color mapping to distinguish instances, and (3) a decoder reconstructing masks from these latents. A multi-stage training strategy is introduced: first learning seglat representations via image-seglat joint training, then refining latent transformations, and finally aligning image-encoder-derived latents with seglat distributions. Experiments show Seg-VAR outperforms previous discriminative and generative methods on various segmentation tasks and validation benchmarks. By framing segmentation as a sequential hierarchical prediction task, Seg-VAR opens new avenues for integrating autoregressive reasoning into spatial-aware vision systems. Code will be available at https://github.com/rkzheng99/Seg-VAR.
PANORAMA: The Rise of Omnidirectional Vision in the Embodied AI Era
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Omnidirectional vision, using 360-degree vision to understand the environment, has become increasingly critical across domains like robotics, industrial inspection, and environmental monitoring. Compared to traditional pinhole vision, omnidirectional vision provides holistic environmental awareness, significantly enhancing the completeness of scene perception and the reliability of decision-making. However, foundational research in this area has historically lagged behind traditional pinhole vision. This talk presents an emerging trend in the embodied AI era: the rapid development of omnidirectional vision, driven by growing industrial demand and academic interest. We highlight recent breakthroughs in omnidirectional generation, omnidirectional perception, omnidirectional understanding, and related datasets. Drawing on insights from both academia and industry, we propose an ideal panoramic system architecture in the embodied AI era, PANORAMA, which consists of four key subsystems. Moreover, we offer in-depth opinions related to emerging trends and cross-community impacts at the intersection of panoramic vision and embodied AI, along with the future roadmap and open challenges. This overview synthesizes state-of-the-art advancements and outlines challenges and opportunities for future research in building robust, general-purpose omnidirectional AI systems in the embodied AI era.
One Flight Over the Gap: A Survey from Perspective to Panoramic Vision
Sep 04, 2025



Abstract:Driven by the demand for spatial intelligence and holistic scene perception, omnidirectional images (ODIs), which provide a complete 360\textdegree{} field of view, are receiving growing attention across diverse applications such as virtual reality, autonomous driving, and embodied robotics. Despite their unique characteristics, ODIs exhibit remarkable differences from perspective images in geometric projection, spatial distribution, and boundary continuity, making it challenging for direct domain adaption from perspective methods. This survey reviews recent panoramic vision techniques with a particular emphasis on the perspective-to-panorama adaptation. We first revisit the panoramic imaging pipeline and projection methods to build the prior knowledge required for analyzing the structural disparities. Then, we summarize three challenges of domain adaptation: severe geometric distortions near the poles, non-uniform sampling in Equirectangular Projection (ERP), and periodic boundary continuity. Building on this, we cover 20+ representative tasks drawn from more than 300 research papers in two dimensions. On one hand, we present a cross-method analysis of representative strategies for addressing panoramic specific challenges across different tasks. On the other hand, we conduct a cross-task comparison and classify panoramic vision into four major categories: visual quality enhancement and assessment, visual understanding, multimodal understanding, and visual generation. In addition, we discuss open challenges and future directions in data, models, and applications that will drive the advancement of panoramic vision research. We hope that our work can provide new insight and forward looking perspectives to advance the development of panoramic vision technologies. Our project page is https://insta360-research-team.github.io/Survey-of-Panorama
On the Generalization of SFT: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective with Reward Rectification
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We present a simple yet theoretically motivated improvement to Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) for the Large Language Model (LLM), addressing its limited generalization compared to reinforcement learning (RL). Through mathematical analysis, we reveal that standard SFT gradients implicitly encode a problematic reward structure that may severely restrict the generalization capabilities of model. To rectify this, we propose Dynamic Fine-Tuning (DFT), stabilizing gradient updates for each token by dynamically rescaling the objective function with the probability of this token. Remarkably, this single-line code change significantly outperforms standard SFT across multiple challenging benchmarks and base models, demonstrating greatly improved generalization. Additionally, our approach shows competitive results in offline RL settings, offering an effective yet simpler alternative. This work bridges theoretical insight and practical solutions, substantially advancing SFT performance. The code will be available at https://github.com/yongliang-wu/DFT.
Learning Deblurring Texture Prior from Unpaired Data with Diffusion Model
Jul 18, 2025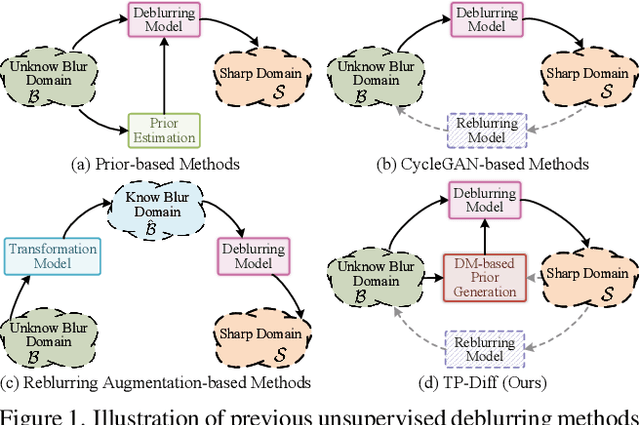
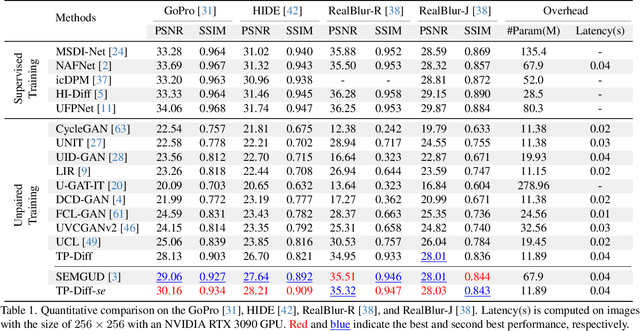
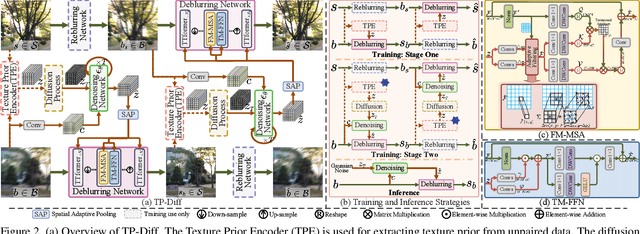
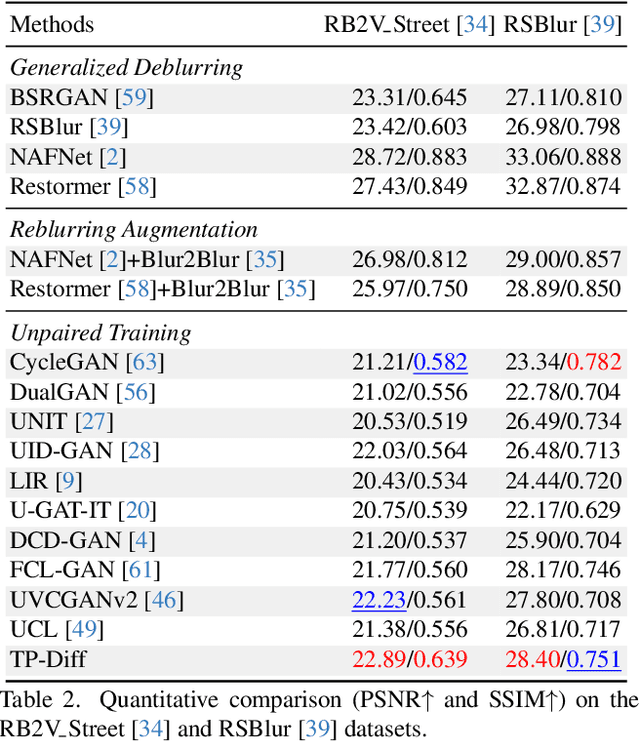
Abstract:Since acquiring large amounts of realistic blurry-sharp image pairs is difficult and expensive, learning blind image deblurring from unpaired data is a more practical and promising solution. Unfortunately, dominant approaches rely heavily on adversarial learning to bridge the gap from blurry domains to sharp domains, ignoring the complex and unpredictable nature of real-world blur patterns. In this paper, we propose a novel diffusion model (DM)-based framework, dubbed \ours, for image deblurring by learning spatially varying texture prior from unpaired data. In particular, \ours performs DM to generate the prior knowledge that aids in recovering the textures of blurry images. To implement this, we propose a Texture Prior Encoder (TPE) that introduces a memory mechanism to represent the image textures and provides supervision for DM training. To fully exploit the generated texture priors, we present the Texture Transfer Transformer layer (TTformer), in which a novel Filter-Modulated Multi-head Self-Attention (FM-MSA) efficiently removes spatially varying blurring through adaptive filtering. Furthermore, we implement a wavelet-based adversarial loss to preserve high-frequency texture details. Extensive evaluations show that \ours provides a promising unsupervised deblurring solution and outperforms SOTA methods in widely-used benchmarks.
Frequency Domain-Based Diffusion Model for Unpaired Image Dehazing
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Unpaired image dehazing has attracted increasing attention due to its flexible data requirements during model training. Dominant methods based on contrastive learning not only introduce haze-unrelated content information, but also ignore haze-specific properties in the frequency domain (\ie,~haze-related degradation is mainly manifested in the amplitude spectrum). To address these issues, we propose a novel frequency domain-based diffusion model, named \ours, for fully exploiting the beneficial knowledge in unpaired clear data. In particular, inspired by the strong generative ability shown by Diffusion Models (DMs), we tackle the dehazing task from the perspective of frequency domain reconstruction and perform the DMs to yield the amplitude spectrum consistent with the distribution of clear images. To implement it, we propose an Amplitude Residual Encoder (ARE) to extract the amplitude residuals, which effectively compensates for the amplitude gap from the hazy to clear domains, as well as provide supervision for the DMs training. In addition, we propose a Phase Correction Module (PCM) to eliminate artifacts by further refining the phase spectrum during dehazing with a simple attention mechanism. Experimental results demonstrate that our \ours outperforms other state-of-the-art methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
CoCo4D: Comprehensive and Complex 4D Scene Generation
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Existing 4D synthesis methods primarily focus on object-level generation or dynamic scene synthesis with limited novel views, restricting their ability to generate multi-view consistent and immersive dynamic 4D scenes. To address these constraints, we propose a framework (dubbed as CoCo4D) for generating detailed dynamic 4D scenes from text prompts, with the option to include images. Our method leverages the crucial observation that articulated motion typically characterizes foreground objects, whereas background alterations are less pronounced. Consequently, CoCo4D divides 4D scene synthesis into two responsibilities: modeling the dynamic foreground and creating the evolving background, both directed by a reference motion sequence. Given a text prompt and an optional reference image, CoCo4D first generates an initial motion sequence utilizing video diffusion models. This motion sequence then guides the synthesis of both the dynamic foreground object and the background using a novel progressive outpainting scheme. To ensure seamless integration of the moving foreground object within the dynamic background, CoCo4D optimizes a parametric trajectory for the foreground, resulting in realistic and coherent blending. Extensive experiments show that CoCo4D achieves comparable or superior performance in 4D scene generation compared to existing methods, demonstrating its effectiveness and efficiency. More results are presented on our website https://colezwhy.github.io/coco4d/.
HoliGS: Holistic Gaussian Splatting for Embodied View Synthesis
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:We propose HoliGS, a novel deformable Gaussian splatting framework that addresses embodied view synthesis from long monocular RGB videos. Unlike prior 4D Gaussian splatting and dynamic NeRF pipelines, which struggle with training overhead in minute-long captures, our method leverages invertible Gaussian Splatting deformation networks to reconstruct large-scale, dynamic environments accurately. Specifically, we decompose each scene into a static background plus time-varying objects, each represented by learned Gaussian primitives undergoing global rigid transformations, skeleton-driven articulation, and subtle non-rigid deformations via an invertible neural flow. This hierarchical warping strategy enables robust free-viewpoint novel-view rendering from various embodied camera trajectories by attaching Gaussians to a complete canonical foreground shape (\eg, egocentric or third-person follow), which may involve substantial viewpoint changes and interactions between multiple actors. Our experiments demonstrate that \ourmethod~ achieves superior reconstruction quality on challenging datasets while significantly reducing both training and rendering time compared to state-of-the-art monocular deformable NeRFs. These results highlight a practical and scalable solution for EVS in real-world scenarios. The source code will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge