Wenbo Zhu
HUAWEI
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
On the Generalization of SFT: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective with Reward Rectification
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We present a simple yet theoretically motivated improvement to Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) for the Large Language Model (LLM), addressing its limited generalization compared to reinforcement learning (RL). Through mathematical analysis, we reveal that standard SFT gradients implicitly encode a problematic reward structure that may severely restrict the generalization capabilities of model. To rectify this, we propose Dynamic Fine-Tuning (DFT), stabilizing gradient updates for each token by dynamically rescaling the objective function with the probability of this token. Remarkably, this single-line code change significantly outperforms standard SFT across multiple challenging benchmarks and base models, demonstrating greatly improved generalization. Additionally, our approach shows competitive results in offline RL settings, offering an effective yet simpler alternative. This work bridges theoretical insight and practical solutions, substantially advancing SFT performance. The code will be available at https://github.com/yongliang-wu/DFT.
KRIS-Bench: Benchmarking Next-Level Intelligent Image Editing Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in multi-modal generative models have enabled significant progress in instruction-based image editing. However, while these models produce visually plausible outputs, their capacity for knowledge-based reasoning editing tasks remains under-explored. In this paper, we introduce KRIS-Bench (Knowledge-based Reasoning in Image-editing Systems Benchmark), a diagnostic benchmark designed to assess models through a cognitively informed lens. Drawing from educational theory, KRIS-Bench categorizes editing tasks across three foundational knowledge types: Factual, Conceptual, and Procedural. Based on this taxonomy, we design 22 representative tasks spanning 7 reasoning dimensions and release 1,267 high-quality annotated editing instances. To support fine-grained evaluation, we propose a comprehensive protocol that incorporates a novel Knowledge Plausibility metric, enhanced by knowledge hints and calibrated through human studies. Empirical results on 10 state-of-the-art models reveal significant gaps in reasoning performance, highlighting the need for knowledge-centric benchmarks to advance the development of intelligent image editing systems.
VEU-Bench: Towards Comprehensive Understanding of Video Editing
Apr 24, 2025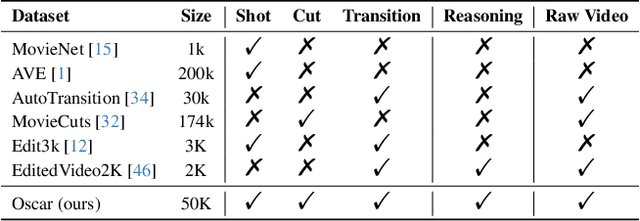
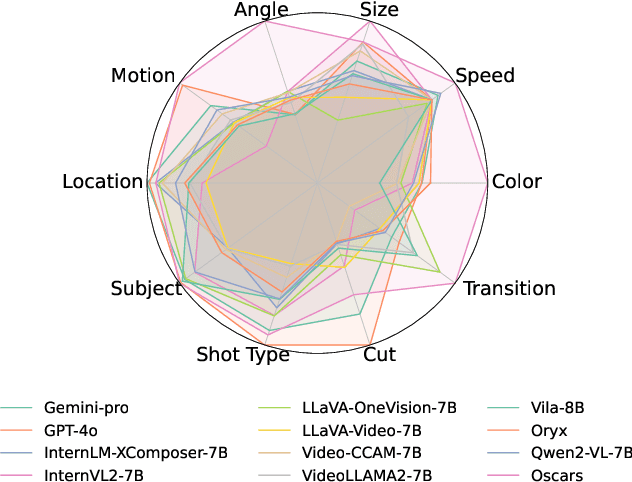
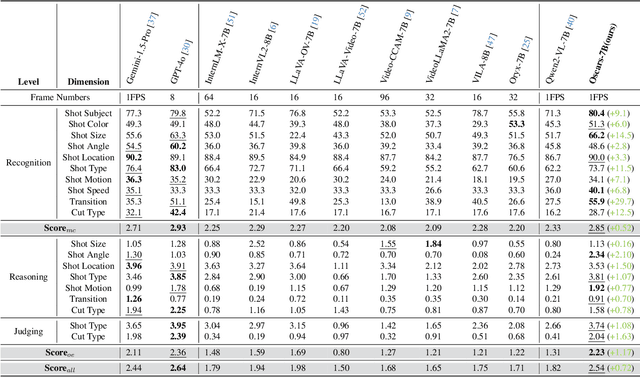
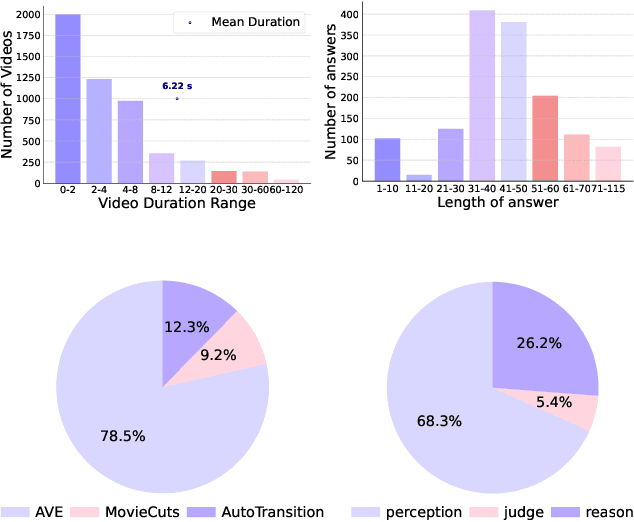
Abstract:Widely shared videos on the internet are often edited. Recently, although Video Large Language Models (Vid-LLMs) have made great progress in general video understanding tasks, their capabilities in video editing understanding (VEU) tasks remain unexplored. To address this gap, in this paper, we introduce VEU-Bench (Video Editing Understanding Benchmark), a comprehensive benchmark that categorizes video editing components across various dimensions, from intra-frame features like shot size to inter-shot attributes such as cut types and transitions. Unlike previous video editing understanding benchmarks that focus mainly on editing element classification, VEU-Bench encompasses 19 fine-grained tasks across three stages: recognition, reasoning, and judging. To enhance the annotation of VEU automatically, we built an annotation pipeline integrated with an ontology-based knowledge base. Through extensive experiments with 11 state-of-the-art Vid-LLMs, our findings reveal that current Vid-LLMs face significant challenges in VEU tasks, with some performing worse than random choice. To alleviate this issue, we develop Oscars, a VEU expert model fine-tuned on the curated VEU-Bench dataset. It outperforms existing open-source Vid-LLMs on VEU-Bench by over 28.3% in accuracy and achieves performance comparable to commercial models like GPT-4o. We also demonstrate that incorporating VEU data significantly enhances the performance of Vid-LLMs on general video understanding benchmarks, with an average improvement of 8.3% across nine reasoning tasks.
Automatically Planning Optimal Parallel Strategy for Large Language Models
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:The number of parameters in large-scale language models based on transformers is gradually increasing, and the scale of computing clusters is also growing. The technology of quickly mobilizing large amounts of computing resources for parallel computing is becoming increasingly important. In this paper, we propose an automatic parallel algorithm that automatically plans the parallel strategy with maximum throughput based on model and hardware information. By decoupling the training time into computation, communication, and overlap, we established a training duration simulation model. Based on this simulation model, we prune the parallel solution space to shorten the search time required. The multi-node experiment results show that the algorithm can estimate the parallel training duration in real time with an average accuracy of 96%. In our test, the recommendation strategy provided by the algorithm is always globally optimal.
Video Repurposing from User Generated Content: A Large-scale Dataset and Benchmark
Dec 12, 2024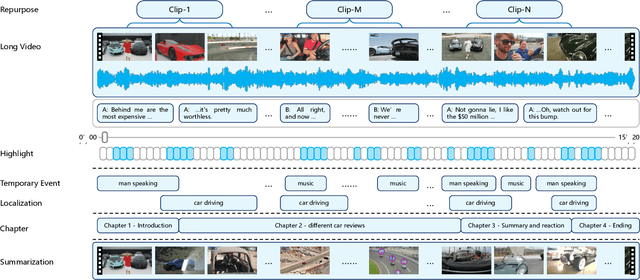
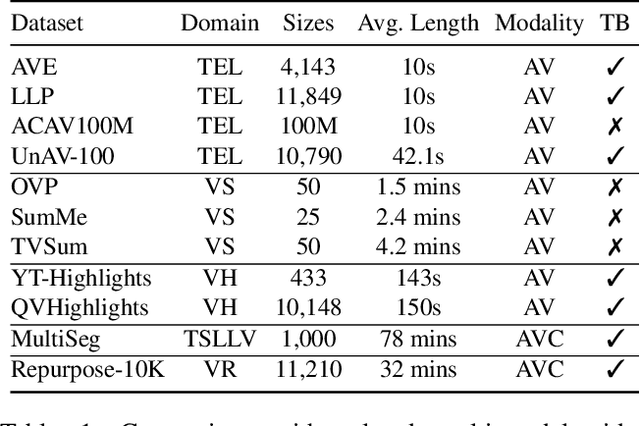
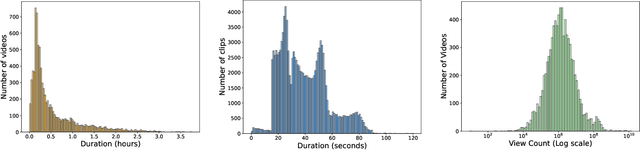
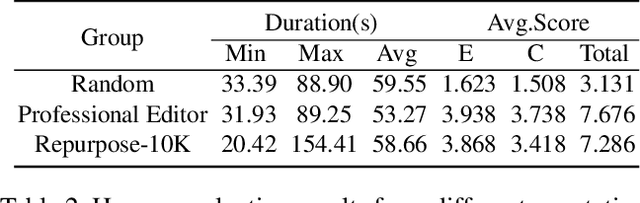
Abstract:The demand for producing short-form videos for sharing on social media platforms has experienced significant growth in recent times. Despite notable advancements in the fields of video summarization and highlight detection, which can create partially usable short films from raw videos, these approaches are often domain-specific and require an in-depth understanding of real-world video content. To tackle this predicament, we propose Repurpose-10K, an extensive dataset comprising over 10,000 videos with more than 120,000 annotated clips aimed at resolving the video long-to-short task. Recognizing the inherent constraints posed by untrained human annotators, which can result in inaccurate annotations for repurposed videos, we propose a two-stage solution to obtain annotations from real-world user-generated content. Furthermore, we offer a baseline model to address this challenging task by integrating audio, visual, and caption aspects through a cross-modal fusion and alignment framework. We aspire for our work to ignite groundbreaking research in the lesser-explored realms of video repurposing. The code and data will be available at https://github.com/yongliang-wu/Repurpose.
Number it: Temporal Grounding Videos like Flipping Manga
Nov 15, 2024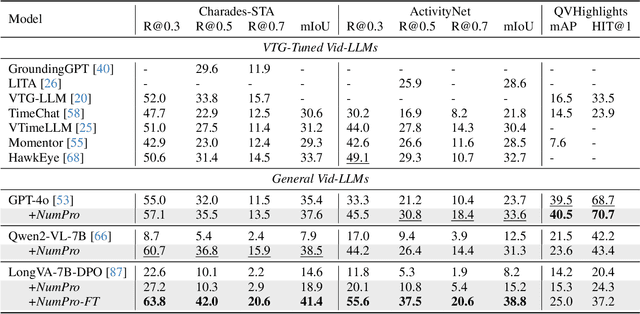

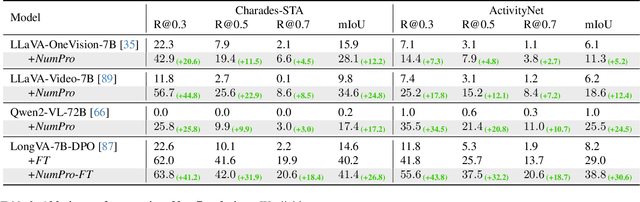
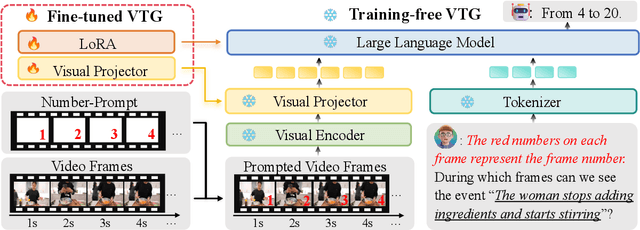
Abstract:Video Large Language Models (Vid-LLMs) have made remarkable advancements in comprehending video content for QA dialogue. However, they struggle to extend this visual understanding to tasks requiring precise temporal localization, known as Video Temporal Grounding (VTG). To address this gap, we introduce Number-Prompt (NumPro), a novel method that empowers Vid-LLMs to bridge visual comprehension with temporal grounding by adding unique numerical identifiers to each video frame. Treating a video as a sequence of numbered frame images, NumPro transforms VTG into an intuitive process: flipping through manga panels in sequence. This allows Vid-LLMs to "read" event timelines, accurately linking visual content with corresponding temporal information. Our experiments demonstrate that NumPro significantly boosts VTG performance of top-tier Vid-LLMs without additional computational cost. Furthermore, fine-tuning on a NumPro-enhanced dataset defines a new state-of-the-art for VTG, surpassing previous top-performing methods by up to 6.9\% in mIoU for moment retrieval and 8.5\% in mAP for highlight detection. The code will be available at https://github.com/yongliang-wu/NumPro.
Zero-Shot Long-Form Video Understanding through Screenplay
Jun 25, 2024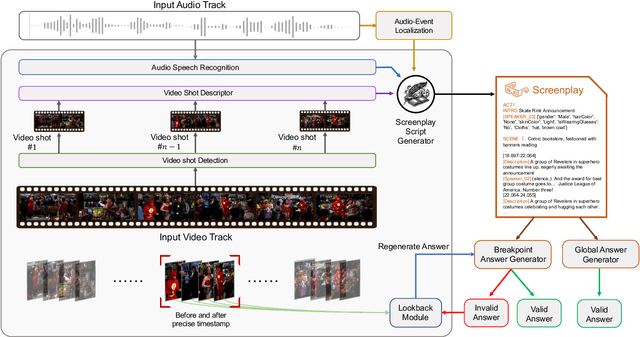
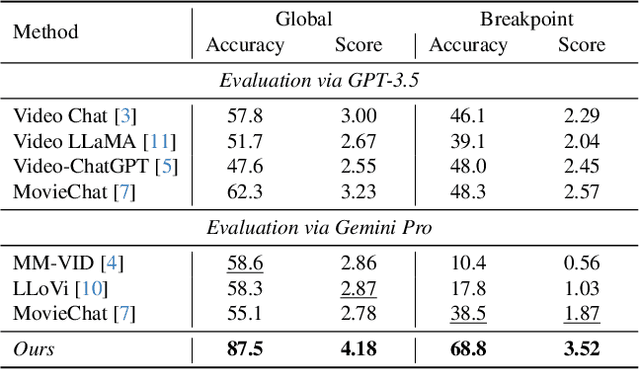
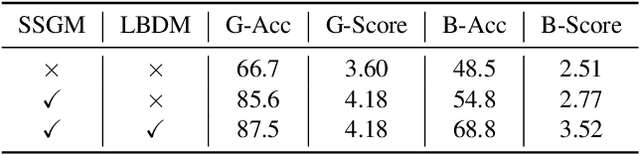

Abstract:The Long-form Video Question-Answering task requires the comprehension and analysis of extended video content to respond accurately to questions by utilizing both temporal and contextual information. In this paper, we present MM-Screenplayer, an advanced video understanding system with multi-modal perception capabilities that can convert any video into textual screenplay representations. Unlike previous storytelling methods, we organize video content into scenes as the basic unit, rather than just visually continuous shots. Additionally, we developed a ``Look Back'' strategy to reassess and validate uncertain information, particularly targeting breakpoint mode. MM-Screenplayer achieved highest score in the CVPR'2024 LOng-form VidEo Understanding (LOVEU) Track 1 Challenge, with a global accuracy of 87.5% and a breakpoint accuracy of 68.8%.
Unlearning Concepts in Diffusion Model via Concept Domain Correction and Concept Preserving Gradient
May 24, 2024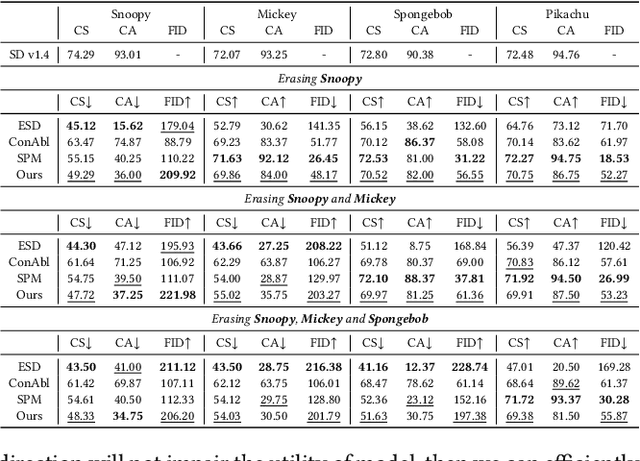
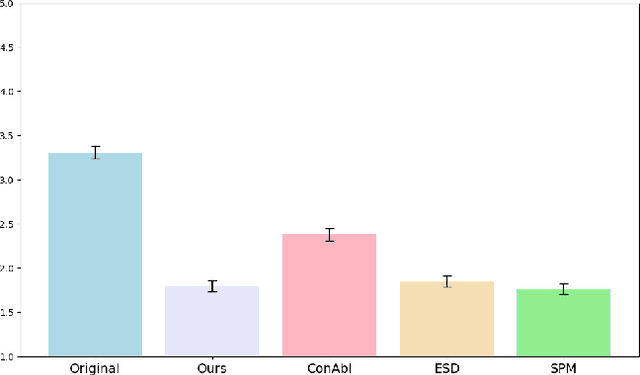

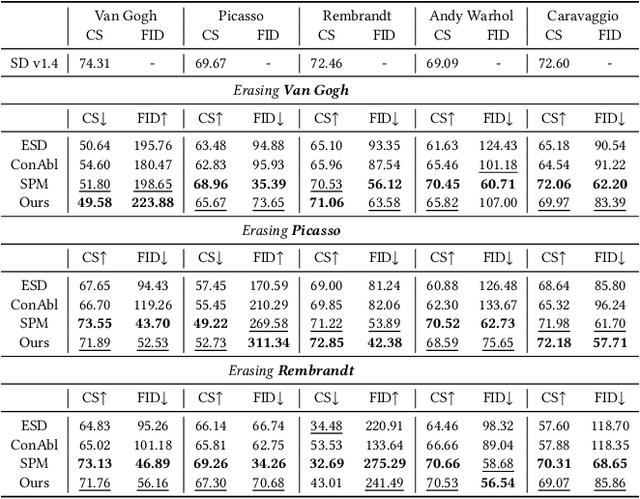
Abstract:Current text-to-image diffusion models have achieved groundbreaking results in image generation tasks. However, the unavoidable inclusion of sensitive information during pre-training introduces significant risks such as copyright infringement and privacy violations in the generated images. Machine Unlearning (MU) provides a effective way to the sensitive concepts captured by the model, has been shown to be a promising approach to addressing these issues. Nonetheless, existing MU methods for concept erasure encounter two primary bottlenecks: 1) generalization issues, where concept erasure is effective only for the data within the unlearn set, and prompts outside the unlearn set often still result in the generation of sensitive concepts; and 2) utility drop, where erasing target concepts significantly degrades the model's performance. To this end, this paper first proposes a concept domain correction framework for unlearning concepts in diffusion models. By aligning the output domains of sensitive concepts and anchor concepts through adversarial training, we enhance the generalizability of the unlearning results. Secondly, we devise a concept-preserving scheme based on gradient surgery. This approach alleviates the parts of the unlearning gradient that contradict the relearning gradient, ensuring that the process of unlearning minimally disrupts the model's performance. Finally, extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our model, demonstrating our method's capability to address the challenges of concept unlearning in diffusion models while preserving model utility.
Reframe Anything: LLM Agent for Open World Video Reframing
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of mobile devices and social media has revolutionized content dissemination, with short-form video becoming increasingly prevalent. This shift has introduced the challenge of video reframing to fit various screen aspect ratios, a process that highlights the most compelling parts of a video. Traditionally, video reframing is a manual, time-consuming task requiring professional expertise, which incurs high production costs. A potential solution is to adopt some machine learning models, such as video salient object detection, to automate the process. However, these methods often lack generalizability due to their reliance on specific training data. The advent of powerful large language models (LLMs) open new avenues for AI capabilities. Building on this, we introduce Reframe Any Video Agent (RAVA), a LLM-based agent that leverages visual foundation models and human instructions to restructure visual content for video reframing. RAVA operates in three stages: perception, where it interprets user instructions and video content; planning, where it determines aspect ratios and reframing strategies; and execution, where it invokes the editing tools to produce the final video. Our experiments validate the effectiveness of RAVA in video salient object detection and real-world reframing tasks, demonstrating its potential as a tool for AI-powered video editing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge