Menglong Xu
TouchASP: Elastic Automatic Speech Perception that Everyone Can Touch
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Large Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models demand a vast number of parameters, copious amounts of data, and significant computational resources during the training process. However, such models can merely be deployed on high-compute cloud platforms and are only capable of performing speech recognition tasks. This leads to high costs and restricted capabilities. In this report, we initially propose the elastic mixture of the expert (eMoE) model. This model can be trained just once and then be elastically scaled in accordance with deployment requirements. Secondly, we devise an unsupervised data creation and validation procedure and gather millions of hours of audio data from diverse domains for training. Using these two techniques, our system achieves elastic deployment capabilities while reducing the Character Error Rate (CER) on the SpeechIO testsets from 4.98\% to 2.45\%. Thirdly, our model is not only competent in Mandarin speech recognition but also proficient in multilingual, multi-dialect, emotion, gender, and sound event perception. We refer to this as Automatic Speech Perception (ASP), and the perception results are presented in the experimental section.
WeKws: A production first small-footprint end-to-end Keyword Spotting Toolkit
Oct 30, 2022



Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) enables speech-based user interaction and gradually becomes an indispensable component of smart devices. Recently, end-to-end (E2E) methods have become the most popular approach for on-device KWS tasks. However, there is still a gap between the research and deployment of E2E KWS methods. In this paper, we introduce WeKws, a production-quality, easy-to-build, and convenient-to-be-applied E2E KWS toolkit. WeKws contains the implementations of several state-of-the-art backbone networks, making it achieve highly competitive results on three publicly available datasets. To make WeKws a pure E2E toolkit, we utilize a refined max-pooling loss to make the model learn the ending position of the keyword by itself, which significantly simplifies the training pipeline and makes WeKws very efficient to be applied in real-world scenarios. The toolkit is publicly available at https://github.com/wenet-e2e/wekws.
Conformer-based End-to-end Speech Recognition With Rotary Position Embedding
Jul 13, 2021



Abstract:Transformer-based end-to-end speech recognition models have received considerable attention in recent years due to their high training speed and ability to model a long-range global context. Position embedding in the transformer architecture is indispensable because it provides supervision for dependency modeling between elements at different positions in the input sequence. To make use of the time order of the input sequence, many works inject some information about the relative or absolute position of the element into the input sequence. In this work, we investigate various position embedding methods in the convolution-augmented transformer (conformer) and adopt a novel implementation named rotary position embedding (RoPE). RoPE encodes absolute positional information into the input sequence by a rotation matrix, and then naturally incorporates explicit relative position information into a self-attention module. To evaluate the effectiveness of the RoPE method, we conducted experiments on AISHELL-1 and LibriSpeech corpora. Results show that the conformer enhanced with RoPE achieves superior performance in the speech recognition task. Specifically, our model achieves a relative word error rate reduction of 8.70% and 7.27% over the conformer on test-clean and test-other sets of the LibriSpeech corpus respectively.
AUC Optimization for Robust Small-footprint Keyword Spotting with Limited Training Data
Jul 13, 2021



Abstract:Deep neural networks provide effective solutions to small-footprint keyword spotting (KWS). However, if training data is limited, it remains challenging to achieve robust and highly accurate KWS in real-world scenarios where unseen sounds that are out of the training data are frequently encountered. Most conventional methods aim to maximize the classification accuracy on the training set, without taking the unseen sounds into account. To enhance the robustness of the deep neural networks based KWS, in this paper, we introduce a new loss function, named the maximization of the area under the receiver-operating-characteristic curve (AUC). The proposed method not only maximizes the classification accuracy of keywords on the closed training set, but also maximizes the AUC score for optimizing the performance of non-keyword segments detection. Experimental results on the Google Speech Commands dataset v1 and v2 show that our method achieves new state-of-the-art performance in terms of most evaluation metrics.
Efficient conformer-based speech recognition with linear attention
Apr 14, 2021



Abstract:Recently, conformer-based end-to-end automatic speech recognition, which outperforms recurrent neural network based ones, has received much attention. Although the parallel computing of conformer is more efficient than recurrent neural networks, the computational complexity of its dot-product self-attention is quadratic with respect to the length of the input feature. To reduce the computational complexity of the self-attention layer, we propose multi-head linear self-attention for the self-attention layer, which reduces its computational complexity to linear order. In addition, we propose to factorize the feed forward module of the conformer by low-rank matrix factorization, which successfully reduces the number of the parameters by approximate 50% with little performance loss. The proposed model, named linear attention based conformer (LAC), can be trained and inferenced jointly with the connectionist temporal classification objective, which further improves the performance of LAC. To evaluate the effectiveness of LAC, we conduct experiments on the AISHELL-1 and LibriSpeech corpora. Results show that the proposed LAC achieves better performance than 7 recently proposed speech recognition models, and is competitive with the state-of-the-art conformer. Meanwhile, the proposed LAC has a number of parameters of only 50% over the conformer with faster training speed than the latter.
Libri-adhoc40: A dataset collected from synchronized ad-hoc microphone arrays
Apr 07, 2021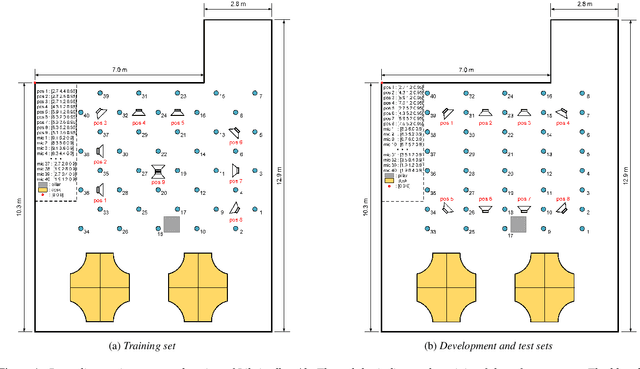
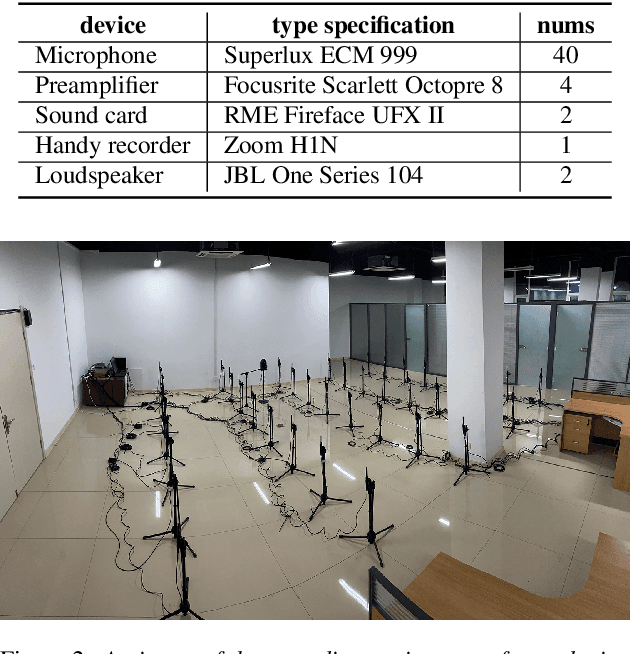
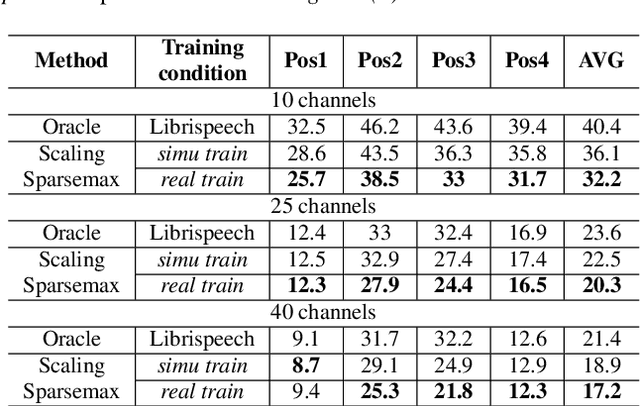

Abstract:Recently, there is a research trend on ad-hoc microphone arrays. However, most research was conducted on simulated data. Although some data sets were collected with a small number of distributed devices, they were not synchronized which hinders the fundamental theoretical research to ad-hoc microphone arrays. To address this issue, this paper presents a synchronized speech corpus, named Libri-adhoc40, which collects the replayed Librispeech data from loudspeakers by ad-hoc microphone arrays of 40 strongly synchronized distributed nodes in a real office environment. Besides, to provide the evaluation target for speech frontend processing and other applications, we also recorded the replayed speech in an anechoic chamber. We trained several multi-device speech recognition systems on both the Libri-adhoc40 dataset and a simulated dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the validness of the proposed corpus which can be used as a benchmark to reflect the trend and difference of the models with different ad-hoc microphone arrays. The dataset is online available at https://github.com/ISmallFish/Libri-adhoc40.
Transformer-based end-to-end speech recognition with residual Gaussian-based self-attention
Apr 02, 2021Abstract:Self-attention (SA), which encodes vector sequences according to their pairwise similarity, is widely used in speech recognition due to its strong context modeling ability. However, when applied to long sequence data, its accuracy is reduced. This is caused by the fact that its weighted average operator may lead to the dispersion of the attention distribution, which results in the relationship between adjacent signals ignored. To address this issue, in this paper, we introduce relative-position-awareness self-attention (RPSA). It not only maintains the global-range dependency modeling ability of self-attention, but also improves the localness modeling ability. Because the local window length of the original RPSA is fixed and sensitive to different test data, here we propose Gaussian-based self-attention (GSA) whose window length is learnable and adaptive to the test data automatically. We further generalize GSA to a new residual Gaussian self-attention (resGSA) for the performance improvement. We apply RPSA, GSA, and resGSA to Transformer-based speech recognition respectively. Experimental results on the AISHELL-1 Mandarin speech recognition corpus demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods. For example, the resGSA-Transformer achieves a character error rate (CER) of 5.86% on the test set, which is relative 7.8% lower than that of the SA-Transformer. Although the performance of the proposed resGSA-Transformer is only slightly better than that of the RPSA-Transformer, it does not have to tune the window length manually.
Transformer-based End-to-End Speech Recognition with Local Dense Synthesizer Attention
Oct 23, 2020



Abstract:Recently, several studies reported that dot-product selfattention (SA) may not be indispensable to the state-of-theart Transformer models. Motivated by the fact that dense synthesizer attention (DSA), which dispenses with dot products and pairwise interactions, achieved competitive results in many language processing tasks, in this paper, we first propose a DSA-based speech recognition, as an alternative to SA. To reduce the computational complexity and improve the performance, we further propose local DSA (LDSA) to restrict the attention scope of DSA to a local range around the current central frame for speech recognition. Finally, we combine LDSA with SA to extract the local and global information simultaneously. Experimental results on the Ai-shell1 Mandarine speech recognition corpus show that the proposed LDSA-Transformer achieves a character error rate (CER) of 6.49%, which is slightly better than that of the SA-Transformer. Meanwhile, the LDSA-Transformer requires less computation than the SATransformer. The proposed combination method not only achieves a CER of 6.18%, which significantly outperforms the SA-Transformer, but also has roughly the same number of parameters and computational complexity as the latter. The implementation of the multi-head LDSA is available at https://github.com/mlxu995/multihead-LDSA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge